Android动画进阶
在Android中,实现动画的方式通常有两种:视图动画和属性动画。然而这两种方式只能实现一些较为简单动画,仅仅通过改变这些控件属性的方式实现一些复杂的动画效果是比较有难度的,那么我们该如何实现复杂的动画。这里介绍两种实现方式:PathMeasure和SVG。
利用PathMeasure实现路径动画
PathMeasure是Android提供给开发者的一个API用于实现一个Path路径点的坐标追踪功能,类似于一个计算器,可以计算出指定路径的一些信息,比如路径总长、指定长度所对应的坐标点等。
常用方法介绍
- 初始化
PathMeasure有两种初始化方式:
PathMeasure pathMeasure = new PathMeasure();
setPath(Path path, boolean forceClosed)。
初始化pathMeasure后,可以通过调用PathMeasure.setPath()函数来将Path和PathMeasure进行绑定。这样就已经初始化完成了,可以调用pathMeasure来返回路径的相关信息。
也可以通过PathMeasure的另一个构造函数直接完成初始化。
PathMeasure(Path path, boolean forceClosed)
在setPath函数和PathMeasure的第二个构造函数中都有一个参数boolean forceClosed,表示Path最终是否需要闭合,如果问true,则不管关联的Path是否是闭合的,都会被闭合。但是forceClosed参数对绑定的Path不会产生任何影响,例如一个折现段的Path,本身没有闭合,当forceClosed设置为true的时候,PathMeasure计算的Path是闭合的,但Path本身绘制出来的是不会闭合的。
- getLength函数
public float getLength();
PathMeasure.getLength()函数的作用就是获取计算的路径长度。如果forceClosed为false,则测量的是当前Path状态的长度;如果forceClosed为true,则不论Path是否闭合,测量的都是Path的闭合长度。
- isClosed函数
public boolean isClosed()
该函数用于判断测量Path时是否计算闭合。所以,如果在关联Path的时候设置forceClosed为true,则这个函数的返回值一定为true。
-
nextContour
Path可以由多条曲线构成,但不论是getLength、getSegment还是其他函数,都只会针对其中第一条线段进行计算。而nextContour就是用于跳转到下一条曲线的函数。如果跳转成功,则返回true;如果跳转失败,则返回false。通过该函数获取得到的曲线的顺序与Path中添加的顺序相同。 -
getSegment
public boolean getSegment(float startD, float stopD, Path dst, boolean startWithMoveTo)
这个API用于截取整个Path中的某个片段,通过参数startD和stopD来控制截取的长度,并将截取后的Path保存到参数dst中。最后一个参数startWithMoveTo表示起始点是否使用moveTo将路径的新起始点移到结果Path的起始点,通常设置为true,以保证每次截取的Path都是正常的、完整的,通常和dst一起使用,因为dst中保存的Path是被不断添加的,而不是每次被覆盖的;如果设置为false,则新增的片段会从上一次Path终点开始计算,这样可以保证截取的Path片段是连续的。
注意:1.如果startD、stopD的数值不在取值范围[0,getLength]内,或者在startD==stopD,则返回值为false,而且不会改变dst中的内容。2.开启硬件加速功能后,绘图会出现问题。因此,在使用getSegment函数时需要禁用硬件加速功能。目前可以在自定义View的构造函数中调用setLayerType(LAYER_TYPE_SOFTWARE,null)函数来禁用硬件加速功能。




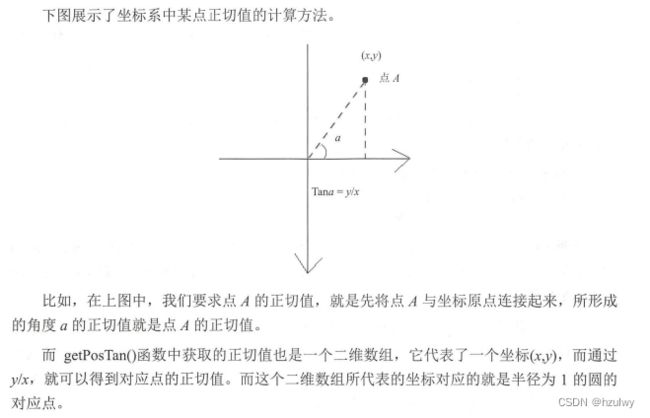
- getPosTan
该函数用于得到路径上某一长度的位置以及该位置的正切值。该函数的声明如下:
public boolean getPosTan(float distance, float pos[], float tan[]) {
if (pos != null && pos.length < 2 ||
tan != null && tan.length < 2) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
return native_getPosTan(native_instance, distance, pos, tan);
}
- distance:距离Path起始点的长度,取值范围为[0,getLength]
- pos:该点的坐标值。当前点在画布上的位置有两个数值,分别为x,y坐标。pos[0]表示x坐标,pos[1]表示y坐标。
- tan:该点的正切值。


- getMatrix
该函数用于得到路径上某一长度的位置以及该位置的正切值的矩阵。
public boolean getMatrix(float distance, Matrix matrix, int flags) {
return native_getMatrix(native_instance, distance, matrix.ni(), flags);
}
- distance:距离Path起始点的长度。
- matrix:根据flags封装好的matrix会根据flags的设置而存入不同的内容。
- flags:用于指定哪些内容会存入matrix中。flags的值有两个:PathMeasure.POSITION_MATRIX_FLAG表示获取位置信息; PathMeasure.TANGENT_MATRIX_FLAG表示获取切边信息,使得图片按Path旋转。可以只指定一个,也可以使用“|”同时指定。
很明显,getMatrix函数只是getPosTan函数的另一种实现而已。getPosTan函数把获取到的位置信息和切边信息分别保存在pos和tan数组中;而getMatrix函数则直接将其保存到matrix数组中。
- 案例如下:
package com.mvp.application;
import android.animation.ValueAnimator;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.BitmapFactory;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.graphics.Matrix;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.graphics.Path;
import android.graphics.PathMeasure;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
import androidx.annotation.Nullable;
public class GetPosTanView extends View {
private Path mCirclePath, mDstPath;
private Paint mPaint;
private PathMeasure mPathMeasure;
private Float mCurAnimValue;
private Bitmap mArrawBmp;
public GetPosTanView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
setLayerType(LAYER_TYPE_SOFTWARE, null);
mArrawBmp = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.arrow_right);//不能时svg类型的图片,拿不到宽高,必须是位图
mPaint = new Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(4);
mPaint.setColor(Color.BLACK);
mDstPath = new Path();
mCirclePath = new Path();
mCirclePath.addCircle(100, 100, 50, Path.Direction.CW);
mPathMeasure = new PathMeasure(mCirclePath, true);
ValueAnimator animator = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(0, 1);
animator.setRepeatCount(ValueAnimator.INFINITE);
animator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
mCurAnimValue = (Float) animation.getAnimatedValue();
invalidate();
}
});
animator.setDuration(2000);
animator.start();
}
private float[] pos = new float[2];
private float[] tan = new float[2];
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
canvas.drawColor(Color.WHITE);
float length = mPathMeasure.getLength();
float stop = length * mCurAnimValue;
float start = (float) (stop - ((0.5 - Math.abs(mCurAnimValue - 0.5)) * length));
mDstPath.reset();
mPathMeasure.getSegment(start, stop, mDstPath, true);
canvas.drawPath(mDstPath, mPaint);
//getPosTan方法实现
//旋转箭头图片,并绘制
mPathMeasure.getPosTan(stop, pos, tan);
float degrees = (float) (Math.atan2(tan[1], tan[0]) * 180.0 / Math.PI);
Matrix matrix = new Matrix();
matrix.postRotate(degrees, mArrawBmp.getWidth() / 2, mArrawBmp.getHeight() / 2);
matrix.postTranslate(pos[0] - mArrawBmp.getWidth() / 2, pos[1] - mArrawBmp.getHeight() / 2);
canvas.drawBitmap(mArrawBmp, matrix, mPaint);
}
}
SVG动画
SVG是矢量图,而且是专门用于网络的矢量图形标准。与矢量图相对应的是位图,Bitmap就是位图,它由一个个像素点组成,当图片放大到一定大小时,就会出现马赛克现象。ps就是常用的位图处理软件。而矢量图则由一个个点组成,经过数学计算利用直线和曲线绘制而成,无论如何放大,都不会出现马赛克现象,Illustrator就是常用的矢量图绘图软件。


vector标签与图像显示
在Android中,SVG矢量图是使用标签定义的,并放在res/drawable目录下。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:height="24dp"
android:width="24dp"
android:viewportWidth="24"
android:viewportHeight="24">
<path
android:fillColor="#000000"
android:pathData="M19.35,10.04 C18.67,6.59,15.64,4,12,4 C9.11,4,6.6,5.64,5.35,8.04
C2.34,8.36,0,10.91,0,14 C0,17.31,2.69,20,6,20 L19,20 C21.76,20,24,17.76,24,15
C24,12.36,21.95,10.22,19.35,10.04 Z M19,18 L6,18 C3.79,18,2,16.21,2,14
S3.79,10,6,10 L6.71,10 C7.37,7.69,9.48,6,12,6 C15.04,6,17.5,8.46,17.5,11.5
L17.5,12 L19,12 C20.66,12,22,13.34,22,15 S20.66,18,19,18 Z" />
<path
android:strokeColor="#000000"
android:strokeWidth="2"
android:pathData="M6.58994,13.1803 C6.58994,13.1803,8.59173,15.8724,12.011,15.8726
C15.2788,15.8728,17.3696,13.2502,17.3696,13.2502" />
</vector>
- width和height属性:表示该SVG图形的具体大小。
- viewportWidth与viewportHeight属性:表示SVG图形划分的比例。具体理解的是,定义了一张SVG图片,它的宽度和高度分别是24dp和24dp。在这里,width和height类似于指定画布的大小,而viewportWidth与viewportHeight则是指将画布的宽、高分为多少个点,而Path中的点坐标都是以viewportWidth与viewportHeight的点数为坐标的,而不是dp值。很明显,vector标签指定的是画布大小,而path标签指定的是路径内容。