Graphql-Java实践-3-graphql-java的请求执行源码浅析
graphql-java的请求执行源码浅析
-
- 1,GraphQL 获取schema信息、解析验证请求
- 2,Execution 构造执行上下文和参数
- 3,ExecutionStrategy 循环字段映射、递归执行层级
- 4, DataLoaderRegistry 控制DataLoader取值逻辑的排队与提交执行
上一篇:Graphql-Java实践-2-graphql-java编码的三层架构
graphql给我们带来了新的编程方式和编程体验。从.graphql文件到Resolver接口,再到Dataloader取值逻辑;及编程中重要的只需给对象的 引子 属性设置值,其他属性的值靠框架自己取到,这些逻辑都是怎样实现的呢,这篇我们一起来探索一下。
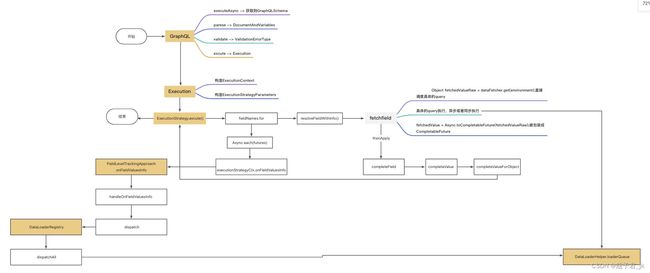
1,GraphQL 获取schema信息、解析验证请求
Graph请求同样是依赖servlet来进行处理的,有对应的GraphQLHttpServlet实现自servlet来处理。
最后发现我们的方法执行到了GraphQL类中的executeAsync()方法,我们以此为起点来切入Graphql-java的处理逻辑

在源码中会看到大量的和instrumentation相关的逻辑,查看类中的注释我们发现,这块内容基本是来做graph请求的监控的,所以我们暂时不关注这一块的代码。
executeAsync()中获取了GraphQLSchema,即定义在graohql文件中的所有信息:
GraphQLSchema graphQLSchema = instrumentation.instrumentSchema(this.graphQLSchema, instrumentationParameters);
接着就是调用parseValidateAndExecute()
CompletableFuture<ExecutionResult> executionResult = parseValidateAndExecute(executionInput, graphQLSchema, instrumentationState);
parse 解析,通过parse()获取到ParseResult,ParseResult中包含的Document信息(即本次请求对应在graphql文件中的信息)和Variables(变量信息)信息
@Internal
public class ParseResult {
private final DocumentAndVariables documentAndVariables;
private final InvalidSyntaxException exception;
Validate验证,Validator对象中定义很多的验证规则
final List<ValidationError> errors = validate(executionInput, document, graphQLSchema, instrumentationState);
if (!errors.isEmpty()) {
logNotSafe.warn("Query failed to validate : '{}'", query);
return new PreparsedDocumentEntry(errors);
}
没有对应的error即验证成功
接下来最重要的excute方法,发现构造了Execution类并在其中执行
Execution execution = new Execution(queryStrategy, mutationStrategy, subscriptionStrategy, instrumentation, valueUnboxer);
ExecutionId executionId = executionInput.getExecutionId();
logNotSafe.debug("Executing '{}'. operation name: '{}'. query: '{}'. variables '{}'", executionId, executionInput.getOperationName(), executionInput.getQuery(), executionInput.getVariables());
CompletableFuture<ExecutionResult> future = execution.execute(document, graphQLSchema, executionId, executionInput, instrumentationState);
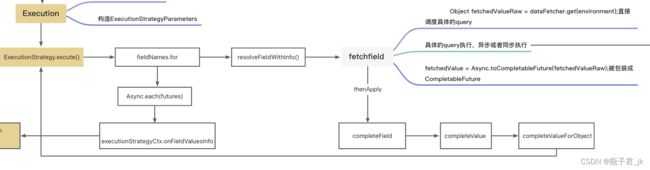
2,Execution 构造执行上下文和参数
Execution类中为后面的执行构造好了执行上下文,和执行参数的封装。
最终的执行调用了ExecutionStrategy类,看类的名字我们也可以知道这是一个具体的执行策略类
ExecutionStrategy executionStrategy;
if (operation == OperationDefinition.Operation.MUTATION) {
executionStrategy = executionContext.getMutationStrategy();
} else if (operation == SUBSCRIPTION) {
executionStrategy = executionContext.getSubscriptionStrategy();
} else {
executionStrategy = executionContext.getQueryStrategy();
}
logNotSafe.debug("Executing '{}' query operation: '{}' using '{}' execution strategy", executionContext.getExecutionId(), operation, executionStrategy.getClass().getName());
result = executionStrategy.execute(executionContext, parameters);
3,ExecutionStrategy 循环字段映射、递归执行层级
最终调用的AsyncExecutionStrategy的excute方法,方法中最显眼的就是对fieldNames的for循环:
for (String fieldName : fieldNames) {
MergedField currentField = fields.getSubField(fieldName);
ExecutionPath fieldPath = parameters.getPath().segment(mkNameForPath(currentField));
ExecutionStrategyParameters newParameters = parameters
.transform(builder -> builder.field(currentField).path(fieldPath).parent(parameters));
resolvedFields.add(fieldName);
CompletableFuture<FieldValueInfo> future;
if (isDeferred(executionContext, newParameters, currentField)) {
executionStrategyCtx.onDeferredField(currentField);
future = resolveFieldWithInfoToNull(executionContext, newParameters);
} else {
future = resolveFieldWithInfo(executionContext, newParameters);
}
futures.add(future);
}
循环取值当前层级的所有值。
resolveFieldWithInfo即去映射对应的值了,里面调用的fetchField方法即会去具体取值

取值的逻辑中如果有需要dataloader取值的,则调度到DataLoaderHelper.loaderQueue,看方法名就知道会去dataloader的队列中等待。
resolveFieldWithInfo()方法中在调用完fetchField后的thenApply中调用了completeField方法
CompletableFuture<FetchedValue> fetchFieldFuture = fetchField(executionContext, parameters);
CompletableFuture<FieldValueInfo> result = fetchFieldFuture.thenApply((fetchedValue) ->
completeField(executionContext, parameters, fetchedValue));
completeField如果该层级就直接是对应的值,即没有下一层的层级了,则直接处理值返回
if (result == null) {
fieldValue = completeValueForNull(parameters);
return FieldValueInfo.newFieldValueInfo(NULL).fieldValue(fieldValue).build();
} else if (isList(fieldType)) {
return completeValueForList(executionContext, parameters, result);
} else if (fieldType instanceof GraphQLScalarType) {
fieldValue = completeValueForScalar(executionContext, parameters, (GraphQLScalarType) fieldType, result);
return FieldValueInfo.newFieldValueInfo(SCALAR).fieldValue(fieldValue).build();
} else if (fieldType instanceof GraphQLEnumType) {
fieldValue = completeValueForEnum(executionContext, parameters, (GraphQLEnumType) fieldType, result);
return FieldValueInfo.newFieldValueInfo(ENUM).fieldValue(fieldValue).build();
}
如果GraphQLObject,则说明有对应的层级,则会调用到completeValueForObject()方法,该方法的最后:
return executionContext.getQueryStrategy().execute(executionContext, newParameters);
回到了executionStrategy的调用中,继续下一层级的逻辑。
4, DataLoaderRegistry 控制DataLoader取值逻辑的排队与提交执行
上一层取值时,有的值被提交到了dataloader的队列,这些队列的取值逻辑什么时候去执行呢

在ExecutionStrategy对fileName的for循环结束后会有阻塞等待执行结果:
Async.each(futures).whenComplete((completeValueInfos, throwable) -> {
BiConsumer<List<ExecutionResult>, Throwable> handleResultsConsumer = handleResults(executionContext, resolvedFields, overallResult);
if (throwable != null) {
handleResultsConsumer.accept(null, throwable.getCause());
return;
}
List<CompletableFuture<ExecutionResult>> executionResultFuture = completeValueInfos.stream().map(FieldValueInfo::getFieldValue).collect(Collectors.toList());
executionStrategyCtx.onFieldValuesInfo(completeValueInfos);
Async.each(executionResultFuture).whenComplete(handleResultsConsumer);
})
executionStrategyCtx.onFieldValuesInfo(completeValueInfos)是实际提交去取值了。
调度到FieldLevelTrackingApproach的onFieldValuesInfo方法:
public void onFieldValuesInfo(List<FieldValueInfo> fieldValueInfoList) {
boolean dispatchNeeded;
synchronized (callStack) {
dispatchNeeded = handleOnFieldValuesInfo(fieldValueInfoList, callStack, curLevel);
}
if (dispatchNeeded) {
dispatch();
}
}
根据handleOnFieldValuesInfo一定的算法逻辑获取到该提交 dispatch了,则执行dispatch:
void dispatch() {
DataLoaderRegistry dataLoaderRegistry = getDataLoaderRegistry();
log.debug("Dispatching data loaders ({})", dataLoaderRegistry.getKeys());
dataLoaderRegistry.dispatchAll();
}
实际执行的DataLoaderRegistry的dispatchAll方法会提交所有dataloader中正在等待执行的值:
public void dispatchAll() {
this.getDataLoaders().forEach(DataLoader::dispatch);
}
取到值返回,整个请求则执行结束。
看源码还是比较有意思的。送大家看源码八字真言:大胆猜测,小心验证!
大胆猜测即看之前想一下大概会怎么执行,往往想的会八九不离十。实际在看源码的时候要多加小心的验证逻辑。