使用Spring JDBC中的JdbcTemplate对数据进行增删改查操作教程~
jdbcTemplate实现添加数据功能:
spring框架对jdbc框架进行封装,使用jdbcTemplate方便实现对数据库的操作
数据库准备工作:
在已有数据库中创建新的表:
create table t_user (id int,username varchar(20),password varchar(20),age int,gender char(2),email varchar(20));
Spring准备工作:
将连接数据库的部分写在外部的jdbc.poperties文件中:
driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm
name=root
password=root
spring-transaction.xml:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties">context:property-placeholder>
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}">property>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}">property>
<property name="name" value="${jdbc.name}">property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}">property>
bean>
<bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource">property>
bean>
beans>
对数据库进行添加数据:
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)//@RunWith注解表示指定当类的测试环境,此时就可以直接通过注入的方式获取IOC容器中的bean
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:spring-transaction.xml")//设置spring测试环境的配置文件
public class jdbcTemplateTest {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;//通过自动装配的方式为当前属性赋值
@Test
public void TestInsert(){//实现数据的插入功能
String sql="insert into t_user (id,username,password,age,gender,email) values (?,?,?,?,?,?)";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,1,"root","root",23,"女","[email protected]");//这里没有insert方法来实现添加功能,原因是upate方法包含了修改和添加功能
}
}
控制台输出并无任何报错:
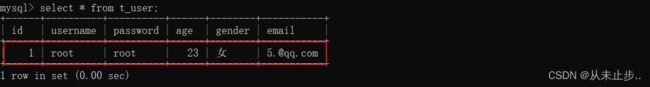
数据库中查询我们创建的表,如下所示:
数据被成功插入
jdbcTemplate实现查询数据功能:
创建实体类:
package pojo;
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String password;
private Integer age;
private String gender;
private String email;
public User() {
}
public User(Integer id,String username,String password,Integer age, String gender,String email) {
this.id = id;
this.username=username;
this.password=password;
this.age=age;
this.gender=gender;
this.email=email;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(String gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", gender='" + gender + '\'' +
", email='" + email + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
查询单条数据:
在测试类中新建TestSelect方法用来查询数据:
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import pojo.User;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)//该注解表示指定当类的测试环境。此时就可以直接通过注入的方式获取IOC容器中的bean
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:spring-transaction.xml")//设置spring测试环境的配置文件
public class jdbcTemplateTest {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;//通过自动装配的方式为当前属性赋值
@Test
public void TestSelect(){
String sql="select * from t_user where id=?";
User user = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql,new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(User.class),1);
System.out.println(user);
}
}
输出如下:
id为1的数据成功被查询
查询多条数据:
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import pojo.User;
import java.util.List;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:spring-transaction.xml")
public class jdbcTemplateTest {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Test
public void TestSelect() {
String sql = "select * from t_user";//查询当前表中的所有数据
List<User> user = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper(User.class));
System.out.println(user);
}
}
输出如下所示:
查询单行/单列数据:
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:spring-transaction.xml")
public class jdbcTemplateTest {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Test
public void TestSelect() {
String sql="select count(*) from t_user";//查询当前表中的记录数
Integer count=jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql,Integer.class);
System.out.println(count);
}
}
显示如下: