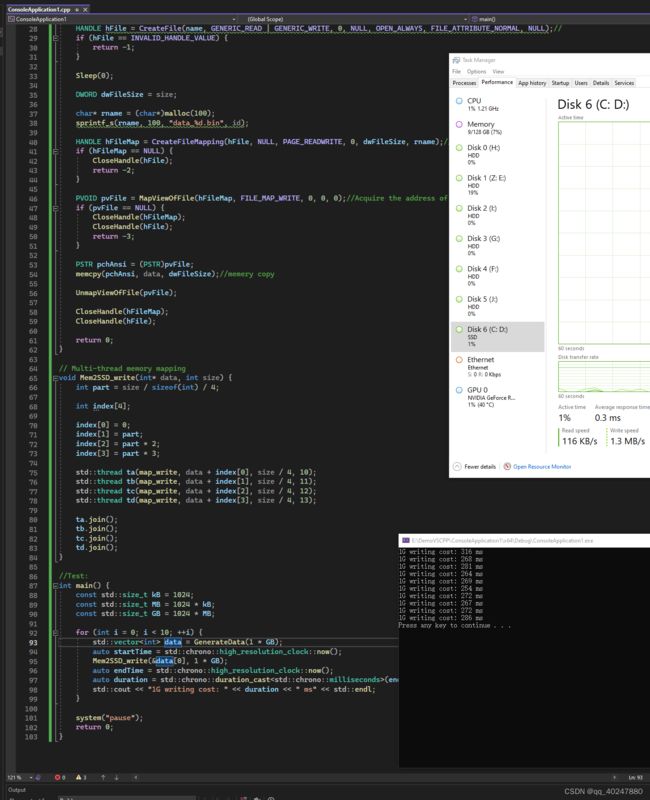
ssd写入速度测试c++
How to write a large buffer into a binary file in C++, fast?
1GBps
// ConsoleApplication1.cpp : This file contains the 'main' function. Program execution begins and ends there.
//
#include #include