【NLP-运用TF-IDF来判断语句和文档的匹配程度】给出一句话和一个文档,查看此句话与文档中的那些话更加匹配?
效果
给出一句话
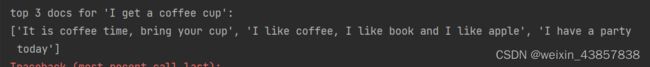
I get a coffee cup
给一个文档
docs = [
“it is a good day, I like to stay here”,
“I am happy to be here”,
“I am bob”,
“it is sunny today”,
“I have a party today”,
“it is a dog and that is a cat”,
“there are dog and cat on the tree”,
“I study hard this morning”,
“today is a good day”,
“tomorrow will be a good day”,
“I like coffee, I like book and I like apple”,
“I do not like it”,
“I am kitty, I like bob”,
“I do not care who like bob, but I like kitty”,
“It is coffee time, bring your cup”, ]
得出最相似的三句话
[‘It is coffee time, bring your cup’,
‘I like coffee, I like book and I like apple’,
‘I have a party today’]
TF-IDF
TF为词频的意思:词语的频率
IDF为逆文本频率指数:词语越常常出现区分力越低(比如:‘我’,这常常出现在所有文档中但并不意味着‘我’是很重要的)词语特定出现区分力更好
TF*IDF 能够表达词语的权重,它综合了词频和区分力
文档预处理
docs_words = [d.replace(",", "").split(" ") for d in docs]
#产生无需不重复的单词集合
vocab = set(itertools.chain(*docs_words))
v2i = {v: i for i, v in enumerate(vocab)}
i2v = {i: v for v, i in v2i.items()}
文档TF函数-计算词频
#三种方式
tf_methods = {
"log": lambda x: np.log(1+x),
"augmented": lambda x: 0.5 + 0.5 * x / np.max(x, axis=1, keepdims=True),
"boolean": lambda x: np.minimum(x, 1),
# "log_avg": lambda x: (1 + safe_log(x)) / (1 + safe_log(np.mean(x, axis=1, keepdims=True))),
}
def get_tf(method="log"):
# term frequency: how frequent a word appears in a doc
_tf = np.zeros((len(vocab), len(docs)), dtype=np.float64) # [n_vocab, n_doc]
for i, d in enumerate(docs_words):
# Counter([7, 7, 8, 9])Counter({7: 2, 8: 1, 9: 1})
counter = Counter(d)
for v in counter.keys():
_tf[v2i[v], i] = counter[v] / counter.most_common(1)[0][1]
weighted_tf = tf_methods.get(method, None)
if weighted_tf is None:
raise ValueError
return weighted_tf(_tf) # [n_vocab, n_doc]
文档IDF-计算区分力
idf_methods = {
"log": lambda x: 1 + np.log(len(docs) / (x+1)),
"prob": lambda x: np.maximum(0, np.log((len(docs) - x) / (x+1))),
"len_norm": lambda x: x / (np.sum(np.square(x))+1),
}
def get_idf(method="log"):
# inverse document frequency: low idf for a word appears in more docs, mean less important
df = np.zeros((len(i2v), 1))
for i in range(len(i2v)):
d_count = 0
for d in docs_words:
d_count += 1 if i2v[i] in d else 0
df[i, 0] = d_count
# print(df)
idf_fn = idf_methods.get(method, None)
if idf_fn is None:
raise ValueError
return idf_fn(df) # [n_vocab, 1]
文档的TF-IDF
tf = get_tf() # [n_vocab, n_doc]
idf = get_idf() # [n_vocab, 1]
tf_idf = tf * idf # [n_vocab, n_doc]
print(tf_idf)
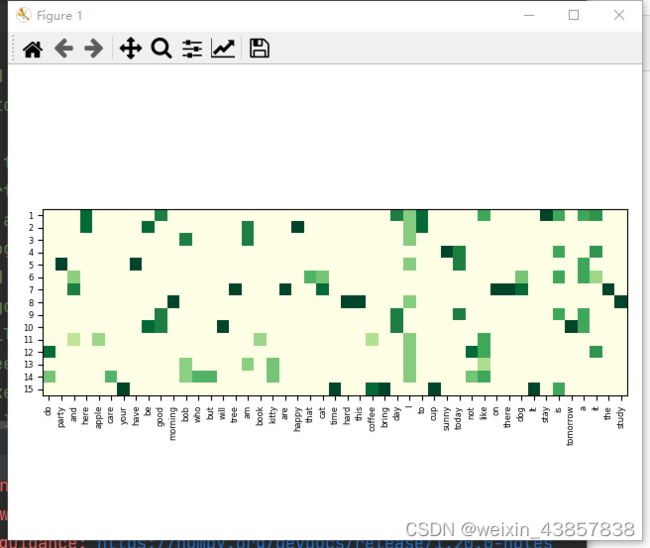
def show_tfidf(tfidf, vocab, filename):
# [n_doc, n_vocab]
plt.imshow(tfidf, cmap="YlGn", vmin=tfidf.min(), vmax=tfidf.max())
plt.xticks(np.arange(tfidf.shape[1]), vocab, fontsize=6, rotation=90)
plt.yticks(np.arange(tfidf.shape[0]), np.arange(1, tfidf.shape[0]+1), fontsize=6)
plt.tight_layout()
# creating the output folder
output_folder = './visual/results/'
os.makedirs(output_folder, exist_ok=True)
plt.savefig(os.path.join(output_folder, '%s.png') % filename, format="png", dpi=500)
plt.show()
测试语句的TF-IDF计算
def docs_score(q, len_norm=False):
q_words = q.replace(",", "").split(" ")
# add unknown words
unknown_v = 0
for v in set(q_words):
if v not in v2i:
v2i[v] = len(v2i)
i2v[len(v2i)-1] = v
unknown_v += 1
if unknown_v > 0:
_idf = np.concatenate((idf, np.zeros((unknown_v, 1), dtype=np.float)), axis=0)
_tf_idf = np.concatenate((tf_idf, np.zeros((unknown_v, tf_idf.shape[1]), dtype=np.float)), axis=0)
else:
_idf, _tf_idf = idf, tf_idf
counter = Counter(q_words)
q_tf = np.zeros((len(_idf), 1), dtype=np.float) # [n_vocab, 1]
for v in counter.keys():
q_tf[v2i[v], 0] = counter[v]
q_vec = q_tf * _idf # [n_vocab, 1]
q_scores = cosine_similarity(q_vec, _tf_idf)
if len_norm:
len_docs = [len(d) for d in docs_words]
q_scores = q_scores / np.array(len_docs)
return q_scores
将测试语句与文档语句相比,选出最匹配的三个
def cosine_similarity(q, _tf_idf):
unit_q = q / np.sqrt(np.sum(np.square(q), axis=0, keepdims=True))
unit_ds = _tf_idf / np.sqrt(np.sum(np.square(_tf_idf), axis=0, keepdims=True))
similarity = unit_ds.T.dot(unit_q).ravel()
return similarity
总体代码
import numpy as np
from collections import Counter
import itertools
docs = [
"it is a good day, I like to stay here",
"I am happy to be here",
"I am bob",
"it is sunny today",
"I have a party today",
"it is a dog and that is a cat",
"there are dog and cat on the tree",
"I study hard this morning",
"today is a good day",
"tomorrow will be a good day",
"I like coffee, I like book and I like apple",
"I do not like it",
"I am kitty, I like bob",
"I do not care who like bob, but I like kitty",
"It is coffee time, bring your cup",
]
docs_words = [d.replace(",", "").split(" ") for d in docs]
#产生无需不重复的单词集合
vocab = set(itertools.chain(*docs_words))
v2i = {v: i for i, v in enumerate(vocab)}
i2v = {i: v for v, i in v2i.items()}
idf_methods = {
"log": lambda x: 1 + np.log(len(docs) / (x+1)),
"prob": lambda x: np.maximum(0, np.log((len(docs) - x) / (x+1))),
"len_norm": lambda x: x / (np.sum(np.square(x))+1),
}
def get_idf(method="log"):
# inverse document frequency: low idf for a word appears in more docs, mean less important
df = np.zeros((len(i2v), 1))
for i in range(len(i2v)):
d_count = 0
for d in docs_words:
d_count += 1 if i2v[i] in d else 0
df[i, 0] = d_count
# print(df)
idf_fn = idf_methods.get(method, None)
if idf_fn is None:
raise ValueError
return idf_fn(df) # [n_vocab, 1]
tf_methods = {
"log": lambda x: np.log(1+x),
"augmented": lambda x: 0.5 + 0.5 * x / np.max(x, axis=1, keepdims=True),
"boolean": lambda x: np.minimum(x, 1),
# "log_avg": lambda x: (1 + safe_log(x)) / (1 + safe_log(np.mean(x, axis=1, keepdims=True))),
}
def get_tf(method="log"):
# term frequency: how frequent a word appears in a doc
_tf = np.zeros((len(vocab), len(docs)), dtype=np.float64) # [n_vocab, n_doc]
for i, d in enumerate(docs_words):
# Counter([7, 7, 8, 9])Counter({7: 2, 8: 1, 9: 1})
counter = Counter(d)
for v in counter.keys():
_tf[v2i[v], i] = counter[v] / counter.most_common(1)[0][1]
weighted_tf = tf_methods.get(method, None)
if weighted_tf is None:
raise ValueError
return weighted_tf(_tf) # [n_vocab, n_doc]
tf = get_tf() # [n_vocab, n_doc]
idf = get_idf() # [n_vocab, 1]
tf_idf = tf * idf # [n_vocab, n_doc]
print(tf_idf)
# print("tf shape(vecb in each docs): ", tf.shape)
# print("\ntf samples:\n", tf[:2])
# print("\nidf shape(vecb in all docs): ", idf.shape)
# print("\nidf samples:\n", idf[:2])
# print("\ntf_idf shape: ", tf_idf.shape)
# print("\ntf_idf sample:\n", tf_idf[:2])
def cosine_similarity(q, _tf_idf):
unit_q = q / np.sqrt(np.sum(np.square(q), axis=0, keepdims=True))
unit_ds = _tf_idf / np.sqrt(np.sum(np.square(_tf_idf), axis=0, keepdims=True))
similarity = unit_ds.T.dot(unit_q).ravel()
return similarity
def docs_score(q, len_norm=False):
q_words = q.replace(",", "").split(" ")
# add unknown words
unknown_v = 0
for v in set(q_words):
if v not in v2i:
v2i[v] = len(v2i)
i2v[len(v2i)-1] = v
unknown_v += 1
if unknown_v > 0:
_idf = np.concatenate((idf, np.zeros((unknown_v, 1), dtype=np.float)), axis=0)
_tf_idf = np.concatenate((tf_idf, np.zeros((unknown_v, tf_idf.shape[1]), dtype=np.float)), axis=0)
else:
_idf, _tf_idf = idf, tf_idf
counter = Counter(q_words)
q_tf = np.zeros((len(_idf), 1), dtype=np.float) # [n_vocab, 1]
for v in counter.keys():
q_tf[v2i[v], 0] = counter[v]
q_vec = q_tf * _idf # [n_vocab, 1]
q_scores = cosine_similarity(q_vec, _tf_idf)
if len_norm:
len_docs = [len(d) for d in docs_words]
q_scores = q_scores / np.array(len_docs)
return q_scores
# def get_keywords(n=2):
# for c in range(3):
# col = tf_idf[:, c]
# idx = np.argsort(col)[-n:]
# print("doc{}, top{} keywords {}".format(c, n, [i2v[i] for i in idx]))
# test
# get_keywords()
q = "I get a coffee cup"
scores = docs_score(q)
d_ids = scores.argsort()[-3:][::-1]
print("\ntop 3 docs for '{}':\n{}".format(q, [docs[i] for i in d_ids]))
show_tfidf(tf_idf.T, [i2v[i] for i in range(tf_idf.shape[0])], "tfidf_matrix")