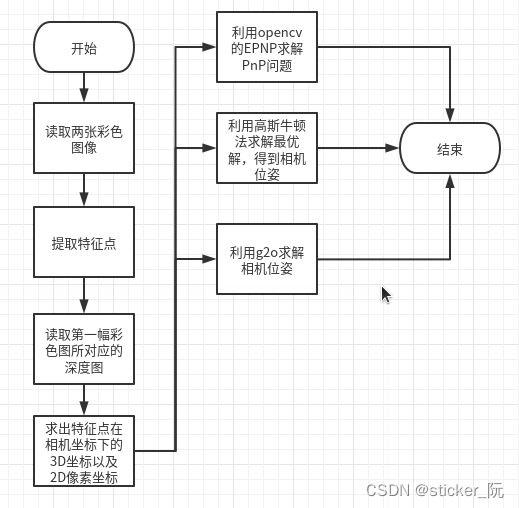
《视觉SLAM十四讲》ch7视觉里程计1学习笔记(4)——实践部分:求解PnP pose_estimation_3D2D
在这篇博客中主要记录了我对《视觉SLAM十四讲》第七讲视觉里程计1中实践部分,求解PnP,3d和2d点求解相机位姿的代码的学习笔记。
0.准备工作:
在运行这个代码时,需要用到g2o库。g2o的下载包可从我的gitcode中下载:
sticker_阮 / g2o下载包 · GitCode
g2o和ceres的下载步骤可参考:
g2o和ceres安装
1.具体操作流程:
(1)首先需要修改原来的CMakeLists.txt文件,否则会报错,修改后的内容如下:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
project(vo1)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Release")
add_definitions("-DENABLE_SSE")
# set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "-std=c++11 -O2 ${SSE_FLAGS} -msse4")
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "-std=c++14 -O2 ${SSE_FLAGS} -msse4")
list(APPEND CMAKE_MODULE_PATH ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/cmake)
find_package(OpenCV 3 REQUIRED)
find_package(G2O REQUIRED)
find_package(Sophus REQUIRED)
include_directories(
${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS}
${G2O_INCLUDE_DIRS}
${Sophus_INCLUDE_DIRS}
"/usr/local/include/eigen3/"
)
add_executable(orb_cv orb_cv.cpp)
target_link_libraries(orb_cv ${OpenCV_LIBS} fmt) #记住fmt前面一定要空格,不然会报错
add_executable(orb_self orb_self.cpp)
target_link_libraries(orb_self ${OpenCV_LIBS} fmt)
# #add_executable( pose_estimation_2d2d pose_estimation_2d2d.cpp extra.cpp ) # use this if in OpenCV2
add_executable(pose_estimation_2d2d pose_estimation_2d2d.cpp)
target_link_libraries(pose_estimation_2d2d ${OpenCV_LIBS} fmt)
# # add_executable( triangulation triangulation.cpp extra.cpp) # use this if in opencv2
add_executable(triangulation triangulation.cpp)
target_link_libraries(triangulation ${OpenCV_LIBS} fmt)
add_executable(pose_estimation_3d2d pose_estimation_3d2d.cpp)
target_link_libraries(pose_estimation_3d2d
g2o_core g2o_stuff
${OpenCV_LIBS} fmt)
add_executable(pose_estimation_3d3d pose_estimation_3d3d.cpp)
target_link_libraries(pose_estimation_3d3d
g2o_core g2o_stuff
${OpenCV_LIBS} fmt)
# add_executable(pose_estimation_3d3d pose_estimation_3d3d.cpp)
# target_link_libraries(pose_estimation_3d3d
# g2o_core g2o_stuff
# ${OpenCV_LIBS})主要是eigen3的地址修改了、c++的标准从c++11换成了c++14、在每个链接库后添加fmt,注意fmt前要加空格,不然,你怎么错的都不知道(心疼我自己一分钟......)
(2)在这个代码中要用到两张彩色图和两张深度图(但实际上只用到两张彩色图和一张深度图),你需要先到build文件夹下查看是否有四张图,因为大部分情况下,这四张图是存放在build的上一个级的文件夹中,然后你在终端输入指令就会显示核心已转储(因为找不到终端输入的图片)。接下来有两种方法:
a.将四张图片放到build文件夹中,如下所示:
随后在终端输入:
./pose_estimation_3d2d 1.png 2.png 1_depth.png 2_depth.png
b. 修改代码内容
在pose_estimation_3d2d代码中,找到argv[1]、argv[2]、argv[3]的位置,将这些改成对应的图片地址,举个栗子:
argv[1]——>/home/rxz/slambook2/ch7/1.png
argv[2]——>/home/rxz/slambook2/ch7/2.png
argv[3]——>/home/rxz/slambook2/ch7/1_depth.png
注:这里的地址都是图片对应所在的位置。
2.代码讲解
2.1 代码流程
源代码(加详细注释):
#include
#include //opencv核心模块
#include //opencv特征点
#include //opencv gui
#include //求解器头文件
#include //eigen核心模块
#include //g2o顶点(Vertex)头文件 视觉slam十四讲p141用顶点表示优化变量,用边表示误差项
#include //g2o边(edge)头文件
#include //稠密矩阵求解
#include //求解器头文件
#include
#include //高斯牛顿算法头文件
#include //线性求解
#include //李群李代数se3
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
void find_feature_matches(
const Mat &img_1, const Mat &img_2,
std::vector &keypoints_1,
std::vector &keypoints_2,
std::vector &matches);
// 像素坐标转相机归一化坐标
Point2d pixel2cam(const Point2d &p, const Mat &K);
// BA by g2o
typedef vector> VecVector2d;
typedef vector> VecVector3d;
void bundleAdjustmentG2O(
const VecVector3d &points_3d,
const VecVector2d &points_2d,
const Mat &K,
Sophus::SE3d &pose
);
// BA by gauss-newton
void bundleAdjustmentGaussNewton(
const VecVector3d &points_3d,
const VecVector2d &points_2d,
const Mat &K,
Sophus::SE3d &pose
);
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
if (argc != 4) {
cout << "usage: pose_estimation_3d2d img1 img2 depth1 depth2" << endl;
return 1;
}
//-- 读取图像
Mat img_1 = imread(argv[1], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR);
Mat img_2 = imread(argv[2], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR);
assert(img_1.data && img_2.data && "Can not load images!");
vector keypoints_1, keypoints_2;
vector matches;
find_feature_matches(img_1, img_2, keypoints_1, keypoints_2, matches);
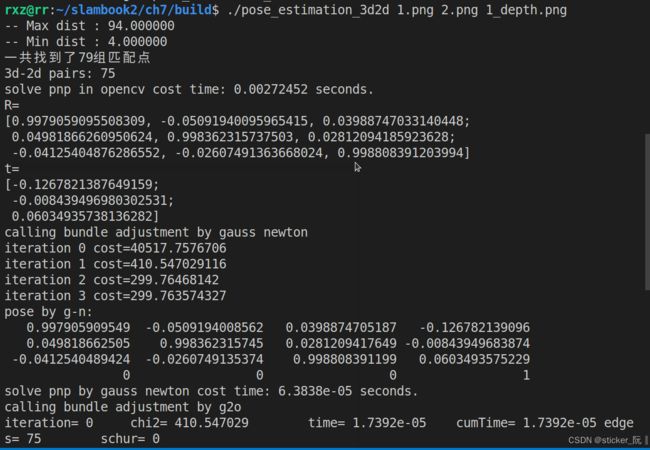
cout << "一共找到了" << matches.size() << "组匹配点" << endl;
// 建立3D点 在第一张图的深度图中寻找它们的深度,并求出空间位置,得到3D点
Mat d1 = imread(argv[3], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_UNCHANGED); // 深度图为16位无符号数,单通道图像
Mat K = (Mat_(3, 3) << 520.9, 0, 325.1, 0, 521.0, 249.7, 0, 0, 1); //相机内参矩阵
vector pts_3d;
vector pts_2d;
for (DMatch m:matches) {
ushort d = d1.ptr(int(keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt.y))[int(keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt.x)];
if (d == 0) // bad depth 排除深度为0的关键点
continue;
float dd = d / 5000.0;
Point2d p1 = pixel2cam(keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt, K); //像素坐标转为相机坐标
pts_3d.push_back(Point3f(p1.x * dd, p1.y * dd, dd)); //得到像素点在相机坐标下的3D信息
pts_2d.push_back(keypoints_2[m.trainIdx].pt); //以第二个图像的特征点位置作为2D点
}
cout << "3d-2d pairs: " << pts_3d.size() << endl;
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
Mat r, t;
//1.PnP求解 opencv求解
solvePnP(pts_3d, pts_2d, K, Mat(), r, t, false); // 调用OpenCV 的 PnP 求解,可选择EPNP,DLS等方法
Mat R;
cv::Rodrigues(r, R); // r为旋转向量形式,用Rodrigues公式转换为矩阵 见书上P53 式(3.15)
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
chrono::duration time_used = chrono::duration_cast>(t2 - t1);
cout << "solve pnp in opencv cost time: " << time_used.count() << " seconds." << endl;
cout << "R=" << endl << R << endl;
cout << "t=" << endl << t << endl;
//2.最小化重投影误差求最优解
VecVector3d pts_3d_eigen;
VecVector2d pts_2d_eigen;
for (size_t i = 0; i < pts_3d.size(); ++i) {
pts_3d_eigen.push_back(Eigen::Vector3d(pts_3d[i].x, pts_3d[i].y, pts_3d[i].z));
pts_2d_eigen.push_back(Eigen::Vector2d(pts_2d[i].x, pts_2d[i].y));
}
//(1)利用高斯牛顿法获取相机位资R和T
cout << "calling bundle adjustment by gauss newton" << endl;
Sophus::SE3d pose_gn;
t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
bundleAdjustmentGaussNewton(pts_3d_eigen, pts_2d_eigen, K, pose_gn);
t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
time_used = chrono::duration_cast>(t2 - t1);
cout << "solve pnp by gauss newton cost time: " << time_used.count() << " seconds." << endl;
//(2)通过g2o图优化算法
cout << "calling bundle adjustment by g2o" << endl;
Sophus::SE3d pose_g2o;
t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
bundleAdjustmentG2O(pts_3d_eigen, pts_2d_eigen, K, pose_g2o);
t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
time_used = chrono::duration_cast>(t2 - t1);
cout << "solve pnp by g2o cost time: " << time_used.count() << " seconds." << endl;
return 0;
}
void find_feature_matches(const Mat &img_1, const Mat &img_2,
std::vector &keypoints_1,
std::vector &keypoints_2,
std::vector &matches) {
//-- 初始化
Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;
// used in OpenCV3
Ptr detector = ORB::create();
Ptr descriptor = ORB::create();
// use this if you are in OpenCV2
// Ptr detector = FeatureDetector::create ( "ORB" );
// Ptr descriptor = DescriptorExtractor::create ( "ORB" );
Ptr matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create("BruteForce-Hamming");
//-- 第一步:检测 Oriented FAST 角点位置
detector->detect(img_1, keypoints_1);
detector->detect(img_2, keypoints_2);
//-- 第二步:根据角点位置计算 BRIEF 描述子
descriptor->compute(img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1);
descriptor->compute(img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2);
//-- 第三步:对两幅图像中的BRIEF描述子进行匹配,使用 Hamming 距离
vector match;
// BFMatcher matcher ( NORM_HAMMING );
matcher->match(descriptors_1, descriptors_2, match);
//-- 第四步:匹配点对筛选
double min_dist = 10000, max_dist = 0;
//找出所有匹配之间的最小距离和最大距离, 即是最相似的和最不相似的两组点之间的距离
for (int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++) {
double dist = match[i].distance;
if (dist < min_dist) min_dist = dist;
if (dist > max_dist) max_dist = dist;
}
printf("-- Max dist : %f \n", max_dist);
printf("-- Min dist : %f \n", min_dist);
//当描述子之间的距离大于两倍的最小距离时,即认为匹配有误.但有时候最小距离会非常小,设置一个经验值30作为下限.
for (int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++) {
if (match[i].distance <= max(2 * min_dist, 30.0)) {
matches.push_back(match[i]);
}
}
}
Point2d pixel2cam(const Point2d &p, const Mat &K) {
return Point2d
(
(p.x - K.at(0, 2)) / K.at(0, 0),
(p.y - K.at(1, 2)) / K.at(1, 1)
);
}
void bundleAdjustmentGaussNewton(
const VecVector3d &points_3d,
const VecVector2d &points_2d,
const Mat &K,
Sophus::SE3d &pose) {
typedef Eigen::Matrix Vector6d;
const int iterations = 10;
double cost = 0, lastCost = 0;
//读取相机内参中的一些参数
double fx = K.at(0, 0);
double fy = K.at(1, 1);
double cx = K.at(0, 2);
double cy = K.at(1, 2);
for (int iter = 0; iter < iterations; iter++) {
Eigen::Matrix H = Eigen::Matrix::Zero();//定义一个6*6的零矩阵
Vector6d b = Vector6d::Zero(); //定义6*1的列向量,元素全为0
cost = 0;
// compute cost
for (int i = 0; i < points_3d.size(); i++) {
Eigen::Vector3d pc = pose * points_3d[i]; //P' = TP =[X',Y',Z'] 视觉slam十四讲p186式7.38
double inv_z = 1.0 / pc[2];//相当于1 / Z'
double inv_z2 = inv_z * inv_z;//相当于( 1 / Z' ) * ( 1 / Z' )
Eigen::Vector2d proj(fx * pc[0] / pc[2] + cx, fy * pc[1] / pc[2] + cy);//转化为像素坐标 u = fx(X' / z') +cx,v = fy(Y' / z') +cy 视觉slam十四讲p186式7.41
Eigen::Vector2d e = points_2d[i] - proj; //比较两个向量,一个是之前利用特征提取得出来的2d像素坐标,一个是现在将3D点投影到2D坐标上
cost += e.squaredNorm(); //squaredNorm()矩阵/向量所有元素的平方和
Eigen::Matrix J;//2*6雅克比矩阵 视觉slam十四讲p186式7.46
//雅克比矩阵表达式见 视觉slam十四讲p186式7.46
//导数矩阵
J << -fx * inv_z, // -fx * inv_z 相当于-fx / Z'
0,//0
fx * pc[0] * inv_z2, //fx * pc[0] * inv_z2相当于fx * X' / ( Z' * Z' )
fx * pc[0] * pc[1] * inv_z2,
-fx - fx * pc[0] * pc[0] * inv_z2,//-fx - fx * pc[0] * pc[0] * inv_z2相当于fx * X' * Y' / ( Z' * Z')
fx * pc[1] * inv_z, //fx * pc[1] * inv_z相当于fx * Y' / Z'
0,//0
-fy * inv_z, //-fy * inv_z相当于-fy / Z'
fy * pc[1] * inv_z2, //fy * pc[1] * inv_z2相当于fy * Y' / (Z' * Z')
fy + fy * pc[1] * pc[1] * inv_z2, //fy + fy * pc[1] * pc[1] * inv_z2相当于fy + fy * Y'*Y' / (Z' * Z')
-fy * pc[0] * pc[1] * inv_z2, //-fy * pc[0] * pc[1] * inv_z2相当于fy * X' * Y' / ( Z' * Z')
-fy * pc[0] * inv_z;//-fy * pc[0] * inv_z相当于-fy * X' / Z'
H += J.transpose() * J;
b += -J.transpose() * e;
}
Vector6d dx;
dx = H.ldlt().solve(b);
if (isnan(dx[0])) {
cout << "result is nan!" << endl;
break;
}
if (iter > 0 && cost >= lastCost) {
// cost increase, update is not good
cout << "cost: " << cost << ", last cost: " << lastCost << endl;
break;
}
// update your estimation
pose = Sophus::SE3d::exp(dx) * pose;
lastCost = cost;
cout << "iteration " << iter << " cost=" << std::setprecision(12) << cost << endl;
if (dx.norm() < 1e-6) {
// converge
break;
}
}
cout << "pose by g-n: \n" << pose.matrix() << endl;
}
/// vertex and edges used in g2o ba
class VertexPose : public g2o::BaseVertex<6, Sophus::SE3d> {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
virtual void setToOriginImpl() override {
_estimate = Sophus::SE3d();
}
/// left multiplication on SE3
virtual void oplusImpl(const double *update) override {
Eigen::Matrix update_eigen;
update_eigen << update[0], update[1], update[2], update[3], update[4], update[5];
_estimate = Sophus::SE3d::exp(update_eigen) * _estimate;
}
virtual bool read(istream &in) override {}
virtual bool write(ostream &out) const override {}
};
class EdgeProjection : public g2o::BaseUnaryEdge<2, Eigen::Vector2d, VertexPose> {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
EdgeProjection(const Eigen::Vector3d &pos, const Eigen::Matrix3d &K) : _pos3d(pos), _K(K) {}
virtual void computeError() override {
const VertexPose *v = static_cast (_vertices[0]);
Sophus::SE3d T = v->estimate();
Eigen::Vector3d pos_pixel = _K * (T * _pos3d);
pos_pixel /= pos_pixel[2];
_error = _measurement - pos_pixel.head<2>();
}
virtual void linearizeOplus() override {
const VertexPose *v = static_cast (_vertices[0]);
Sophus::SE3d T = v->estimate();
Eigen::Vector3d pos_cam = T * _pos3d;
double fx = _K(0, 0);
double fy = _K(1, 1);
double cx = _K(0, 2);
double cy = _K(1, 2);
double X = pos_cam[0];
double Y = pos_cam[1];
double Z = pos_cam[2];
double Z2 = Z * Z;
_jacobianOplusXi
<< -fx / Z, 0, fx * X / Z2, fx * X * Y / Z2, -fx - fx * X * X / Z2, fx * Y / Z,
0, -fy / Z, fy * Y / (Z * Z), fy + fy * Y * Y / Z2, -fy * X * Y / Z2, -fy * X / Z;
}
virtual bool read(istream &in) override {}
virtual bool write(ostream &out) const override {}
private:
Eigen::Vector3d _pos3d;
Eigen::Matrix3d _K;
};
void bundleAdjustmentG2O(
const VecVector3d &points_3d,
const VecVector2d &points_2d,
const Mat &K,
Sophus::SE3d &pose) {
// 构建图优化,先设定g2o
typedef g2o::BlockSolver> BlockSolverType; // pose is 6, landmark is 3
typedef g2o::LinearSolverDense LinearSolverType; // 线性求解器类型
// 梯度下降方法,可以从GN, LM, DogLeg 中选
auto solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmGaussNewton(
g2o::make_unique(g2o::make_unique()));
g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer; // 图模型
optimizer.setAlgorithm(solver); // 设置求解器
optimizer.setVerbose(true); // 打开调试输出
// vertex
VertexPose *vertex_pose = new VertexPose(); // camera vertex_pose
vertex_pose->setId(0);
vertex_pose->setEstimate(Sophus::SE3d());
optimizer.addVertex(vertex_pose);
// K
Eigen::Matrix3d K_eigen;
K_eigen <<
K.at(0, 0), K.at(0, 1), K.at(0, 2),
K.at(1, 0), K.at(1, 1), K.at(1, 2),
K.at(2, 0), K.at(2, 1), K.at(2, 2);
// edges
int index = 1;
for (size_t i = 0; i < points_2d.size(); ++i) {
auto p2d = points_2d[i];
auto p3d = points_3d[i];
EdgeProjection *edge = new EdgeProjection(p3d, K_eigen);
edge->setId(index);
edge->setVertex(0, vertex_pose);
edge->setMeasurement(p2d);
edge->setInformation(Eigen::Matrix2d::Identity());
optimizer.addEdge(edge);
index++;
}
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
optimizer.setVerbose(true);
optimizer.initializeOptimization();
optimizer.optimize(10);
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
chrono::duration time_used = chrono::duration_cast>(t2 - t1);
cout << "optimization costs time: " << time_used.count() << " seconds." << endl;
cout << "pose estimated by g2o =\n" << vertex_pose->estimate().matrix() << endl;
pose = vertex_pose->estimate();
}
2.2函数的讲解
solvePnP(pts_3d, pts_2d, K, Mat(), r, t, false);//求解PNP问题
pts_3d:特征点的世界坐标,坐标值需为float型,不能为double型,可以为mat型,也可以直接输入vector;
pts_2d:特征点在图像中的像素坐标,可以输入mat类型,也可以是vector,但是输入点的顺序要和前面的特征点的世界坐标一致;
K:相机内参矩阵
Mat():相机的畸变参数【mat_()】
r:输出的旋转向量
t:为输出的平移矩阵
2.3运行结果