JUC源码分析6-locks-AQS-独占模式
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer(下面简称AQS),javadoc说明: Provides a framework for implementing blocking locks and related synchronizers (semaphores, events, etc) that rely on first-in-first-out (FIFO) wait queues。
1.提供一个FIFO等待队列,使用方法伪代码表示就是:
Acquire:
if(!获取到锁){
加入队列
}
Release:
if(释放锁){
unlock等待队列头结点的thread
}
2.内部使用volatile int state来表示一个同步状态,这个字段既可以表示lock的状态,也可以用来表示lock的次数,例如Semaphore使用该字段表示许可次数,ReentrantLock用来表示可重入次数,我们也可以自行定义成状态值来表示线程运行状态。子类继承AQS的时候必须实现Serializable;
3.提供独占和共享2套api,一般使用就是维护一个内部类继承AQS,实现其中一套api,判断是否获取到锁。ReentrantLock使用的是独占api,CountDownLatch使用的共享api。子类实现的protected方法为:
独占api,判断是否获取到锁:
tryAcquire
tryRelease
共享api,判断是否获取到锁:
tryAcquireShared
tryReleaseShared
isHeldExclusively(这个暂时不管)
4.AQS提供了condition用来实现wait/notify功能,入ReentrantLock.newCondition();
5.1.7版本JUC中使用到AQS的有:ReentrantLock/ReentrantReadWriteLock/Semaphore。
AQS继承了AbstractOwnableSynchronizer这个类:
//独占模式下持有锁的线程
private transient Thread exclusiveOwnerThread;
protected final void setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread t) {
exclusiveOwnerThread = t;
}
protected final Thread getExclusiveOwnerThread() {
return exclusiveOwnerThread;
}
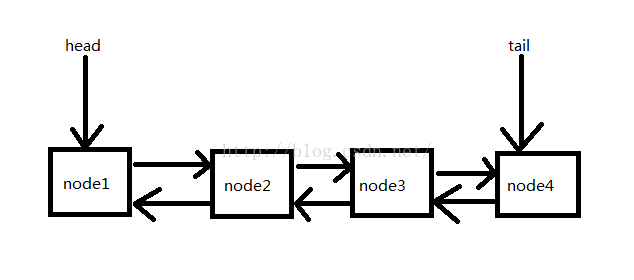
private transient volatile Node head;
private transient volatile Node tail;
private static final Unsafe unsafe = Unsafe.getUnsafe();
private static final long stateOffset;
private static final long headOffset;
private static final long tailOffset;
private static final long waitStatusOffset;
private static final long nextOffset;
static {
try {
stateOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset
(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.class.getDeclaredField("state"));
headOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset
(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.class.getDeclaredField("head"));
tailOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset
(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.class.getDeclaredField("tail"));
waitStatusOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset
(Node.class.getDeclaredField("waitStatus"));
nextOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset
(Node.class.getDeclaredField("next"));
} catch (Exception ex) { throw new Error(ex); }
}
static final class Node {
//标记节点类型是共享还是独占
static final Node SHARED = new Node();
static final Node EXCLUSIVE = null;
//下面4个是节点状态值
static final int CANCELLED = 1;
static final int SIGNAL = -1;
static final int CONDITION = -2;
static final int PROPAGATE = -3;
/**
节点状态,对应上面几个状态值:
0:normal status
1:节点被取消,cancelled状态的节点运行过程会被清理掉
-1:需要唤醒当前节点的下一个节点
-2:用在newCondition的情况下,condition时还为维护另一个条件队列
-3:共享模式下,表示需要将release传递到队列的其他节点
*/
volatile int waitStatus;
volatile Node prev;
//next为null,并不代表改节点是tail节点,因为在加入队列时,是先pre再next的
volatile Node next;
volatile Thread thread;
//独占模式时,指向条件队列的下一个节点,或者共享模式下值为SHARED
Node nextWaiter;
final boolean isShared() {
return nextWaiter == SHARED;
}
final Node predecessor() throws NullPointerException {
Node p = prev;
if (p == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
else
return p;
}
Node() { // Used to establish initial head or SHARED marker
}
Node(Thread thread, Node mode) { // Used by addWaiter
this.nextWaiter = mode;
this.thread = thread;
}
Node(Thread thread, int waitStatus) { // Used by Condition
this.waitStatus = waitStatus;
this.thread = thread;
}
}一.独占模式下acquire和release
Acquire:
不响应中断的acquire
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt(); //挂起后唤醒返回的中断状态是true的话,这里会中断当前线程
} protected boolean tryAcquire(int arg) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}如果没有获取到,则addWaiter加入等待队列,并挂起线程:
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
//初始化一个node节点
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure
Node pred = tail;
//先尝试直接加入到尾节点后面,
//从这里也可以看出,先将node的pre指向尾节点,然后cas设置tail,再将原tail的next指向节点,
//所以可能next为空的情况存在,但是已经加入的节点的pre肯定是存在
if (pred != null) {
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
//失败的话,for循环loop加入
enq(node);
return node;
}看下enq操作:
private Node enq(final Node node) {
//loop操作,tail不存在的情况会初始化一个空节点,并将head和tail都指向空节点,
//然后cas加入node,确保节点一定会加入
for (;;) {
Node t = tail;
if (t == null) { // Must initialize
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
tail = head;
} else {
node.prev = t;
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
t.next = node;
return t;
}
}
}
}在将节点加入等待队列之后,尝试挂起线程:
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
//新加入node的pre节点
final Node p = node.predecessor();
//如果pre节点是头结点,再次重试acquire,如果成功则设置node为头结点
//需要注意的是,头结点代表的是持有锁的节点
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
//如果pre不是头结点或acquire失败,则尝试挂起
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
//如果上面的操作发生异常,需要将node
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
/**
设置头结点
*/
private void setHead(Node node) {
head = node;
node.thread = null;
node.prev = null;
}
/**
检查是否需要挂起
这个方法就是设置新加入节点的pre节点的waitStatus为SIGNAL(肯定成功),
这样在pre节点release的时候判断是不是需要唤醒下个节点
*/
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
int ws = pred.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL)
/*
* This node has already set status asking a release
* to signal it, so it can safely park.
*/
return true;
if (ws > 0) {
/*
* 设置过程中会过滤Cancelled状态的节点,把cancelled状态的节点去掉
*/
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);
pred.next = node;
} else {
/*
* waitStatus must be 0 or PROPAGATE. Indicate that we
* need a signal, but don't park yet. Caller will need to
* retry to make sure it cannot acquire before parking.
*/
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);
}
return false;
}
/**
调用Locksupport.park阻塞线程
*/
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
//挂起线程
LockSupport.park(this);
//当pre节点release的时候检查状态为SIGNAL为会唤醒当前节点,这里会返回线程的中断状态
return Thread.interrupted();
}
/**
acquire和挂起过程中异常,需要取消acquire
*/
private void cancelAcquire(Node node) {
//为null直接返回
if (node == null)
return;
node.thread = null;
// 下面会跳过pre为cancelled的节点,将pre指向队列node前面第一个非取消状态节点
Node pred = node.prev;
while (pred.waitStatus > 0)
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
// predNext是队列node前面第一个非取消状态节点的下一个节点
Node predNext = pred.next;
// Can use unconditional write instead of CAS here.
// After this atomic step, other Nodes can skip past us.
// Before, we are free of interference from other threads.
node.waitStatus = Node.CANCELLED;
// 下面检查node节点的位置,如果是tail节点,直接将pred设置为尾节点,
//然后设置之前的pred的next为null
if (node == tail && compareAndSetTail(node, pred)) {
compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, null);
} else {
// 不是tail节点
int ws;
//这里判断经过上面处理的node的pre是不是head节点
//不是head节点就要cas保证其状态为SIGNAL
if (pred != head &&
((ws = pred.waitStatus) == Node.SIGNAL ||
(ws <= 0 && compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL))) &&
pred.thread != null) {
//node的next不为null且状态不是取消状态就node节点的next关联到pred节点的next节点
Node next = node.next;
if (next != null && next.waitStatus <= 0)
compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, next);
} else {
//如果node的pre是头结点,需要唤醒node的next节点
unparkSuccessor(node);
}
//将next指向自己
node.next = node; // help GC
}
}
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
/*
* If status is negative (i.e., possibly needing signal) try
* to clear in anticipation of signalling. It is OK if this
* fails or if status is changed by waiting thread.
*/
int ws = node.waitStatus;
if (ws < 0)
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
/*
* 之前说过addWaiter的时候是先pre->tail->next,所以存在tail已经改变但是next还没有变化的情况
* 这里就会从tail往前查找不会null,且状态不是取消的节点
*/
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
//找到就unpark,但是unpark后也不一定acquire成功,acquire那边的for就会一直loop
if (s != null)
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}接下来看下响应中断的acquireInterruptibly方法,这里会先判断先线程是否中断,中断的会直接抛出异常,没有中断再尝试请求
public final void acquireInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
if (!tryAcquire(arg))
doAcquireInterruptibly(arg);
}doAcquireInterruptibly方法与之前的区别就是线程中断后直接抛出异常,不是像之前的那样return 中断状态到上一层
private void doAcquireInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE);
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
//区别
throw new InterruptedException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}支持中断和超时时间的
public final boolean tryAcquireNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout)
throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
return tryAcquire(arg) ||
doAcquireNanos(arg, nanosTimeout);
}
private boolean doAcquireNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout)
throws InterruptedException {
//取一次时间
long lastTime = System.nanoTime();
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE);
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return true;
}
//超时时间小于0就直接返回false
if (nanosTimeout <= 0)
return false;
//这里spinForTimeoutThreshold为static final long spinForTimeoutThreshold = 1000L;
//如果超时时间大于spinForTimeoutThreshold,park才有意思,否则直接自旋
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
nanosTimeout > spinForTimeoutThreshold)
//底层调用unsafe.park(false,nanosTimeout)
LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanosTimeout);
//唤醒后重新计算一下时间
long now = System.nanoTime();
nanosTimeout -= now - lastTime;
lastTime = now;
//如果线程中断,直接抛出异常
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}响应中断和响应时间的acquire的其他跟acquire差不多。
Release
public final boolean release(int arg) {
//tryRelease是否可以释放由子类实现判断
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}大致流程为:
参考:
http://brokendreams.iteye.com/blog/2250372
http://www.infoq.com/cn/articles/jdk1.8-abstractqueuedsynchronizer#anch132323