Tomcat架构【官网翻译】
文章目录
-
- 1.总览
- 2.Tomcat启动过程
-
- 2.1源码解析
-
-
- 序列1:从命令行启动
- 序列2:处理命令行参数
-
- 2.2时序图
- 3.请求处理流程
-
- 3.1请求处理时序图
- 3.2权限认证时序图:
- 4.源码编译
Tomcat架构【官网翻译】–以tomcat9.0.31版本分析
首先,我们看下一个tomcat的server.xml配置【 https://github.com/apache/tomcat/blob/9.0.x/conf/server.xml】
<Server port="8005" shutdown="SHUTDOWN">
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.startup.VersionLoggerListener" />
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.core.AprLifecycleListener" SSLEngine="on" />
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.core.JreMemoryLeakPreventionListener" />
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.mbeans.GlobalResourcesLifecycleListener" />
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.core.ThreadLocalLeakPreventionListener" />
<GlobalNamingResources>
<Resource name="UserDatabase" auth="Container"
type="org.apache.catalina.UserDatabase"
description="User database that can be updated and saved"
factory="org.apache.catalina.users.MemoryUserDatabaseFactory"
pathname="conf/tomcat-users.xml" />
GlobalNamingResources>
<Service name="Catalina">
<Connector port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1"
connectionTimeout="20000"
redirectPort="8443" />
<Engine name="Catalina" defaultHost="localhost">
<Realm className="org.apache.catalina.realm.LockOutRealm">
<Realm className="org.apache.catalina.realm.UserDatabaseRealm"
resourceName="UserDatabase"/>
Realm>
<Host name="localhost" appBase="webapps"
unpackWARs="true" autoDeploy="true">
<Valve className="org.apache.catalina.valves.AccessLogValve" directory="logs"
prefix="localhost_access_log" suffix=".txt"
pattern="%h %l %u %t "%r" %s %b" />
Host>
Engine>
Service>
Server>
1.总览
【https://tomcat.apache.org/tomcat-9.0-doc/architecture/overview.html】
术语
- Server
Server代表整个tomcat容器,tomcat自身提供了一个实现,很少用户会去自定义自己的实现
- Service
Service是位于Server下的一个直接组件,它绑定了一个或者多个Connector到一个Engine。这个接口也很少用户会去自定义
- Engine
Engine代表为特定Service提供服务的管道。Service可能会有多个Connector,Engine接收和处理从这些Connector来的所有请求,然后返回Response给Connector,继而再返回给Client
- Host
通过Host,Tomcat Server可以关联上一个域名,比如www.yourcompany.com。一个Engine可能会包含多个Host,Host可以支持二级域名,比如yourcompany.com和abc.yourcompany.com
- Connector
Connector用于处理与客户端的通讯。Tomcat里面提供了一些Connector。例如Http Connector,当tomcat作为一个标准的服务器时,用于处理http请求。另外,AJP Connector,它实现了AJP协议,用于连接Tomcat到一个web服务器,比如Apache HTTPD server
- Context
一个Context代表一个web应用。一个Host里面可能包含多个Context,每个Context有一个唯一的路劲
2.Tomcat启动过程
2.1源码解析
【https://tomcat.apache.org/tomcat-9.0-doc/architecture/startup/serverStartup.txt】
序列1:从命令行启动
类:org.apache.catalina.startup.Bootstrap
a)设置classloaders
commonLoader (common)-> System Loader
sharedLoader (shared)-> commonLoader -> System Loader
catalinaLoader(server) -> commonLoader -> System Loader
源码如下Bootstrap类:
private void initClassLoaders() {
try {
commonLoader = createClassLoader("common", null);
if (commonLoader == null) {
// no config file, default to this loader - we might be in a 'single' env.
commonLoader = this.getClass().getClassLoader();
}
catalinaLoader = createClassLoader("server", commonLoader);
sharedLoader = createClassLoader("shared", commonLoader);
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleThrowable(t);
log.error("Class loader creation threw exception", t);
System.exit(1);
}
}
b)加载启动类(通过反射)
org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina
setParentClassloader -> sharedLoader
Thread.contextClassloader -> catalinaLoader
源码如下Bootstrap类:
public void init() throws Exception {
initClassLoaders();
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(catalinaLoader);
SecurityClassLoad.securityClassLoad(catalinaLoader);
// Load our startup class and call its process() method
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Loading startup class");
Class<?> startupClass = catalinaLoader.loadClass("org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina");
Object startupInstance = startupClass.getConstructor().newInstance();
// Set the shared extensions class loader
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Setting startup class properties");
String methodName = "setParentClassLoader";
Class<?> paramTypes[] = new Class[1];
paramTypes[0] = Class.forName("java.lang.ClassLoader");
Object paramValues[] = new Object[1];
paramValues[0] = sharedLoader;
Method method =
startupInstance.getClass().getMethod(methodName, paramTypes);
method.invoke(startupInstance, paramValues);
catalinaDaemon = startupInstance;
}
c)Bootstrap.daemon.init()完成
序列2:处理命令行参数
类org.apache.catalina.startup.Bootstrap 这里我们假设命令参数是start
a)Catalina.setAwait(true);
b)Catalina.load()
b1)initDirs()
原文说设置一些属性,如catalina.home,但源码没看到
源码如下Catalina类:
protected void initDirs() {
String temp = System.getProperty("java.io.tmpdir");
if (temp == null || (!(new File(temp)).isDirectory())) {
log.error(sm.getString("embedded.notmp", temp));
}
}
b2)initNaming设置系统属性
b3)createStartDigester()配置digester用于解析server.xml
例如org.apache.catalina.core.StandardServer代表整个tomcat,org.apache.catalina.deploy.NamingResources用于处理JNDI相关,org.apache.catalina.LifecycleListener用于主要组件的start/stop事件监听,org.apache.catalina.core.StandardService,org.apache.catalina.Connector用于处理请求等
源码如下(原方法是在太长,我删减了些)Catalina类:
protected Digester createStartDigester() {
long t1=System.currentTimeMillis();
// Initialize the digester
Digester digester = new Digester();
digester.setValidating(false);
digester.setRulesValidation(true);
Map<Class<?>, List<String>> fakeAttributes = new HashMap<>();
// Ignore className on all elements
List<String> objectAttrs = new ArrayList<>();
objectAttrs.add("className");
fakeAttributes.put(Object.class, objectAttrs);
// Ignore attribute added by Eclipse for its internal tracking
List<String> contextAttrs = new ArrayList<>();
contextAttrs.add("source");
fakeAttributes.put(StandardContext.class, contextAttrs);
// Ignore Connector attribute used internally but set on Server
List<String> connectorAttrs = new ArrayList<>();
connectorAttrs.add("portOffset");
fakeAttributes.put(Connector.class, connectorAttrs);
digester.setFakeAttributes(fakeAttributes);
digester.setUseContextClassLoader(true);
// Configure the actions we will be using
digester.addObjectCreate("Server",
"org.apache.catalina.core.StandardServer",
"className");
digester.addSetProperties("Server");
digester.addSetNext("Server",
"setServer",
"org.apache.catalina.Server");
...
// Add RuleSets for nested elements
digester.addRuleSet(new NamingRuleSet("Server/GlobalNamingResources/"));
digester.addRuleSet(new EngineRuleSet("Server/Service/"));
digester.addRuleSet(new HostRuleSet("Server/Service/Engine/"));
digester.addRuleSet(new ContextRuleSet("Server/Service/Engine/Host/"));
addClusterRuleSet(digester, "Server/Service/Engine/Host/Cluster/");
digester.addRuleSet(new NamingRuleSet("Server/Service/Engine/Host/Context/"));
// When the 'engine' is found, set the parentClassLoader.
digester.addRule("Server/Service/Engine",
new SetParentClassLoaderRule(parentClassLoader));
addClusterRuleSet(digester, "Server/Service/Engine/Cluster/");
long t2=System.currentTimeMillis();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Digester for server.xml created " + ( t2-t1 ));
}
return digester;
}
b4)加载server.xml,并通过上方创建的digester解析,生成对象,但实际还没有start
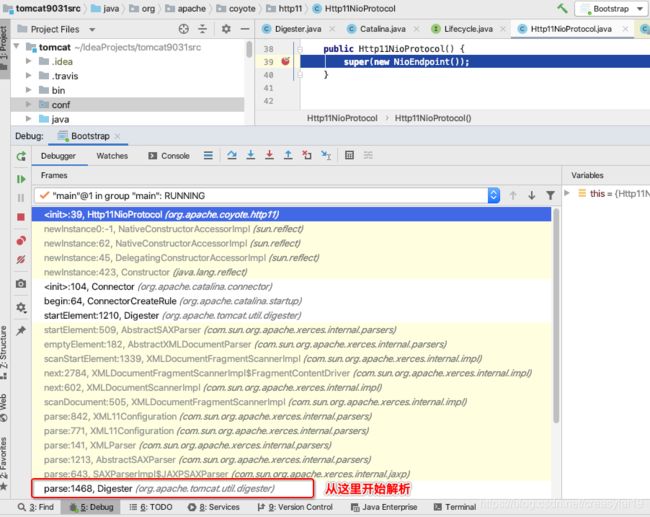
例如Http11NioProtocol的生成,debug截图
源码如下Digester类:
public Object parse(InputSource input) throws IOException, SAXException {
configure();
getXMLReader().parse(input);
return root;
}
b5)设置System.out和System.err到SystemLogHandler类
源码如下Catalina类:
protected void initStreams() {
// Replace System.out and System.err with a custom PrintStream
System.setOut(new SystemLogHandler(System.out));
System.setErr(new SystemLogHandler(System.err));
}
b6)层层调用所有的组件调用初始化方法
例如StandardServer的init
public final synchronized void init() throws LifecycleException {
if (!state.equals(LifecycleState.NEW)) {
invalidTransition(Lifecycle.BEFORE_INIT_EVENT);
}
try {
setStateInternal(LifecycleState.INITIALIZING, null, false);
initInternal();
setStateInternal(LifecycleState.INITIALIZED, null, false);
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleSubClassException(t, "lifecycleBase.initFail", toString());
}
}
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
super.initInternal();
// Initialize utility executor
reconfigureUtilityExecutor(getUtilityThreadsInternal(utilityThreads));
register(utilityExecutor, "type=UtilityExecutor");
// Register global String cache
// Note although the cache is global, if there are multiple Servers
// present in the JVM (may happen when embedding) then the same cache
// will be registered under multiple names
onameStringCache = register(new StringCache(), "type=StringCache");
// Register the MBeanFactory
MBeanFactory factory = new MBeanFactory();
factory.setContainer(this);
onameMBeanFactory = register(factory, "type=MBeanFactory");
// Register the naming resources
globalNamingResources.init();//globalNamingResources的初始化
// Populate the extension validator with JARs from common and shared
// class loaders
if (getCatalina() != null) {
ClassLoader cl = getCatalina().getParentClassLoader();
// Walk the class loader hierarchy. Stop at the system class loader.
// This will add the shared (if present) and common class loaders
while (cl != null && cl != ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader()) {
if (cl instanceof URLClassLoader) {
URL[] urls = ((URLClassLoader) cl).getURLs();
for (URL url : urls) {
if (url.getProtocol().equals("file")) {
try {
File f = new File (url.toURI());
if (f.isFile() &&
f.getName().endsWith(".jar")) {
ExtensionValidator.addSystemResource(f);
}
} catch (URISyntaxException e) {
// Ignore
} catch (IOException e) {
// Ignore
}
}
}
}
cl = cl.getParent();
}
}
// Initialize our defined Services
for (int i = 0; i < services.length; i++) {
services[i].init();//services的初始化
}
}
c)Catalina.start()
c1)启动NamingContext,并绑定所有JNDI
c2)启动services
StandardService -> starts Engine (ContainerBase -> Realm,Cluster etc)
源码如下StandardServer类:
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
fireLifecycleEvent(CONFIGURE_START_EVENT, null);
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
globalNamingResources.start();
// Start our defined Services
synchronized (servicesLock) {
for (int i = 0; i < services.length; i++) {
services[i].start();//Services启动
}
}
if (periodicEventDelay > 0) {
monitorFuture = getUtilityExecutor().scheduleWithFixedDelay(
new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
startPeriodicLifecycleEvent();
}
}, 0, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
c3)StandardHost的启动
作用:
1.配置一个ErrorReportValve根据HTTP的错误码输出对应HTML
2.开启Valves(例如前面这个ErrorReportValve)
3.配置StandardHostValve,用于绑定WebappClassLoader到线程上下文,为request查找session
4.启动HostConfig组件,这个组件会去部署所有的webapps
源码如下HostConfig类:
protected void deployApps() {
File appBase = host.getAppBaseFile();
File configBase = host.getConfigBaseFile();
String[] filteredAppPaths = filterAppPaths(appBase.list());
// Deploy XML descriptors from configBase
deployDescriptors(configBase, configBase.list());
// Deploy WARs
deployWARs(appBase, filteredAppPaths);
// Deploy expanded folders
deployDirectories(appBase, filteredAppPaths);
}
HostConfig之后会创建Digester,Digester会调用ContextConfig.start()用于处理web.xml
c4)在StandardEngine容器的生命周期内,会启动一个后台线程监控context是否有变更。如果context变更了(根据war文件/context.xml文件/web.xml文件的时间戳),热加载将会被触发(stop/remove/deploy/start)
d)Tomcat接收http请求
d1)通过ServerSocket.accept()接收请求,接收是在一个单独的线程中进行的。
其实应该是在Acceptor这个类的run方法中,这个文档可能是很久之前的,还用BIO
源码如下Acceptor类:
@Override
public void run() {
int errorDelay = 0;
// Loop until we receive a shutdown command
while (endpoint.isRunning()) {
// Loop if endpoint is paused
while (endpoint.isPaused() && endpoint.isRunning()) {
state = AcceptorState.PAUSED;
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Ignore
}
}
if (!endpoint.isRunning()) {
break;
}
state = AcceptorState.RUNNING;
try {
...
try {
// Accept the next incoming connection from the server
// socket
socket = endpoint.serverSocketAccept();//接收请求
} catch (Exception ioe) {
...
}
...
} catch (Throwable t) {
...
}
}
state = AcceptorState.ENDED;
}
d2)线程池ThreadPoolExecutor指派TaskThread线程处理
源码如下AbstractEndpoint类:
public boolean processSocket(SocketWrapperBase<S> socketWrapper,
SocketEvent event, boolean dispatch) {
try {
if (socketWrapper == null) {
return false;
}
SocketProcessorBase<S> sc = null;
if (processorCache != null) {
sc = processorCache.pop();
}
if (sc == null) {
sc = createSocketProcessor(socketWrapper, event);
} else {
sc.reset(socketWrapper, event);
}
Executor executor = getExecutor();
if (dispatch && executor != null) {
executor.execute(sc);//提交线程池执行处理
} else {
sc.run();
}
} catch (RejectedExecutionException ree) {
getLog().warn(sm.getString("endpoint.executor.fail", socketWrapper) , ree);
return false;
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
// This means we got an OOM or similar creating a thread, or that
// the pool and its queue are full
getLog().error(sm.getString("endpoint.process.fail"), t);
return false;
}
return true;
}
d3)Http11Processor调用process处理
d4)这个http会使用Http11InputBuffer来解析。解析请求头、请求行等信息,然后把这些信息存储到一个Coyote request(不是HTTP request)中,这个request包含所有HTTP信息,如主机,端口,scheme等
源码如下(原方法太长了,我删了很多代码)Http11InputBuffer类:
boolean parseRequestLine(boolean keptAlive, int connectionTimeout, int keepAliveTimeout)
throws IOException {
...
if ((end - parsingRequestLineStart) > 0) {
request.protocol().setBytes(byteBuffer.array(), parsingRequestLineStart,
end - parsingRequestLineStart);//设置请求的协议,如HTTP/1.1
} else {
request.protocol().setString("");
}
parsingRequestLine = false;
parsingRequestLinePhase = 0;
parsingRequestLineEol = false;
parsingRequestLineStart = 0;
return true;
...
}
d5)Processor有一个Adapter的引用,对于http请求来说,它就是CoyoteAdapter。上方的解析完成之后,Adapter.service()会被调用。在这个service方法中,会创建实现了接口HttpServletRequest的Request对象,和实现了HttpServletResponse接口的Response对象,把cookies和context等关联给到request对象
源码如下(删了部分代码)Mapper类:
private final void internalMap(CharChunk host, CharChunk uri,
String version, MappingData mappingData) throws IOException {
...
mappingData.context = contextVersion.object;
mappingData.contextSlashCount = contextVersion.slashCount;
// Wrapper mapping
if (!contextVersion.isPaused()) {
internalMapWrapper(contextVersion, uri, mappingData);
}
}
d6)CoyoteAdapter调用容器StandardEngine的invoke(request,response)方法
其实这里一句语句connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);直接调用StandardEngineValve的invoke(Request request, Response response)方法了
源码如下CoyoteAdapter类:
public void service(org.apache.coyote.Request req, org.apache.coyote.Response res)
throws Exception {
Request request = (Request) req.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES);
Response response = (Response) res.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES);
if (request == null) {
// Create objects
request = connector.createRequest();//创建request对象
request.setCoyoteRequest(req);
response = connector.createResponse();//创建response对象
response.setCoyoteResponse(res);
// Link objects
request.setResponse(response);
response.setRequest(request);
// Set as notes
req.setNote(ADAPTER_NOTES, request);
res.setNote(ADAPTER_NOTES, response);
// Set query string encoding
req.getParameters().setQueryStringCharset(connector.getURICharset());
}
if (connector.getXpoweredBy()) {
response.addHeader("X-Powered-By", POWERED_BY);
}
boolean async = false;
boolean postParseSuccess = false;
req.getRequestProcessor().setWorkerThreadName(THREAD_NAME.get());
try {
// Parse and set Catalina and configuration specific
// request parameters
postParseSuccess = postParseRequest(req, request, res, response);//传递cookie,context等相关信息到request中
if (postParseSuccess) {
//check valves if we support async
request.setAsyncSupported(
connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().isAsyncSupported());
// Calling the container
connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(
request, response);//调用StandardEngine的invoke方法
}
if (request.isAsync()) {
async = true;
ReadListener readListener = req.getReadListener();
if (readListener != null && request.isFinished()) {
// Possible the all data may have been read during service()
// method so this needs to be checked here
ClassLoader oldCL = null;
try {
oldCL = request.getContext().bind(false, null);
if (req.sendAllDataReadEvent()) {
req.getReadListener().onAllDataRead();
}
} finally {
request.getContext().unbind(false, oldCL);
}
}
Throwable throwable =
(Throwable) request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION);
// If an async request was started, is not going to end once
// this container thread finishes and an error occurred, trigger
// the async error process
if (!request.isAsyncCompleting() && throwable != null) {
request.getAsyncContextInternal().setErrorState(throwable, true);
}
} else {
request.finishRequest();
response.finishResponse();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// Ignore
} finally {
...
}
}
d7)d8)调用StandardEngineValve的invoke(Request request, Response response)方法
d9)StandardHost默认有两个valves,一个StandardHostValve,另一个ErrorReportValve
其实加上server.xml中配置的org.apache.catalina.valves.AccessLogValve,总计有三个,他们都是通过getNext().invoke(request,response);调用下一个处理
源码如下AbstractAccessLogValve类:
public void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException,
ServletException {
if (tlsAttributeRequired) {
// The log pattern uses TLS attributes. Ensure these are populated
// before the request is processed because with NIO2 it is possible
// for the connection to be closed (and the TLS info lost) before
// the access log requests the TLS info. Requesting it now causes it
// to be cached in the request.
request.getAttribute(Globals.CERTIFICATES_ATTR);
}
for (CachedElement element : cachedElements) {
element.cache(request);
}
getNext().invoke(request, response);//调用下一个valve
}
d10)StandardHostValve关联合适的classloader到当前线程。同时也会检索session关联给到request,如果有session的话,session的acess()方法会被调用来keep alive
d11)StandardHostValve调用pipeline的invoke(request, response)方法
d12)首先是FormAuthenticator的invoke(Request request, Response response)被调用,然后再调用getNext().invoke(request, response);,继而走到StandardContextValve的invoke(Request request, Response response)
源码如下StandardContextValve类:
public final void invoke(Request request, Response response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
...
// Select the Wrapper to be used for this Request
Wrapper wrapper = request.getWrapper();//wrapper会关联一个servlet
...
wrapper.getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);
}
d13)StandardWrapperValve的invoke方法中,jsp会被编译成servlet,然后调用真正的servlet
e)servlet被调用
补充:
在d13)调用过程中,其实是构造了一个filterChain,调用filterChain.doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response),在这个方法中最终会调用到servlet.service(request, response);,这之后就是根据请求的方法调用doGet/doPost之类的方法了
源码如下ApplicationFilterChain类:
private void internalDoFilter(ServletRequest request,
ServletResponse response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
...
// We fell off the end of the chain -- call the servlet instance
try {
if (ApplicationDispatcher.WRAP_SAME_OBJECT) {
lastServicedRequest.set(request);
lastServicedResponse.set(response);
}
if (request.isAsyncSupported() && !servletSupportsAsync) {
request.setAttribute(Globals.ASYNC_SUPPORTED_ATTR,
Boolean.FALSE);
}
// Use potentially wrapped request from this point
if ((request instanceof HttpServletRequest) &&
(response instanceof HttpServletResponse) &&
Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED ) {
final ServletRequest req = request;
final ServletResponse res = response;
Principal principal =
((HttpServletRequest) req).getUserPrincipal();
Object[] args = new Object[]{req, res};
SecurityUtil.doAsPrivilege("service",
servlet,
classTypeUsedInService,
args,
principal);
} else {
servlet.service(request, response);//调用servlet,如果是jsp,其实是在这个方法才编译的
}
} catch (IOException | ServletException | RuntimeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
e = ExceptionUtils.unwrapInvocationTargetException(e);
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
throw new ServletException(sm.getString("filterChain.servlet"), e);
} finally {
if (ApplicationDispatcher.WRAP_SAME_OBJECT) {
lastServicedRequest.set(null);
lastServicedResponse.set(null);
}
}
}
2.2时序图
可以直接下载官方的
https://tomcat.apache.org/tomcat-9.0-doc/architecture/startup/serverStartup.pdf
3.请求处理流程
3.1请求处理时序图

https://tomcat.apache.org/tomcat-9.0-doc/architecture/requestProcess/request-process.png
3.2权限认证时序图:
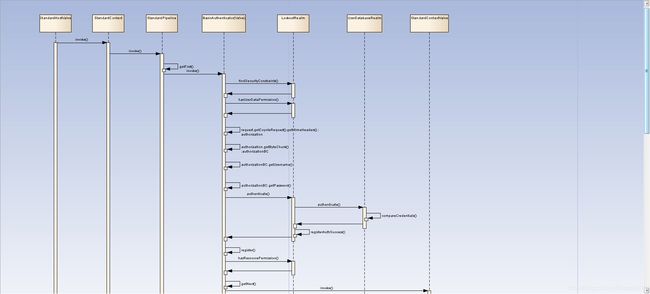
https://tomcat.apache.org/tomcat-9.0-doc/architecture/requestProcess/authentication-process.png
4.源码编译
如果想编译源码,可以查看这篇(https://tomcat.apache.org/tomcat-9.0-doc/building.html)文章,但Tomcat默认是用ant编译的,如果想用maven编译,大家另外再找参考教程吧。我个人是用ant编译的,改了不少地方才编译成功…