【算法与数据结构】3 知行合一,线性查找的自定义类测试
![]()
欢迎来到爱书不爱输的程序猿的博客, 本博客致力于知识分享,与更多的人进行学习交流
本文收录于算法与数据结构体系专栏,本专栏对于0基础者极为友好,欢迎与我一起完成算法与数据结构的从0到1的跨越
![]()
线性查找的测试应用
- 1.前言
- 2.使用自定义类测试
-
- 2.1⛏创建Student类并测试
- 2.2 剖析测试结果
- 2.3 自定义equals()
-
- 2.3.1 初窥门径➡️错误的函数声明
- 2.3.2 渐入佳境➡️善用工具
- 2.3.3 略有小成 ➡️完成equals()
- 2.3.4 融会贯通➡️完整的equals()
1.前言
☑️首篇详细讲述线性查找法并且对其进行了初步的优化:传送门:详解什么是算法?什么是线性查找法?
☑️第二篇进行了再次优化,讲述了使用泛型这种语言机制来解决避免重复写一个方法的问题:传送门:线性查找的究极优化
⬇️学习了前面的理论,我们应该学会举一反三:在对于不同的类而言,里面的equals()方法具体的实现逻辑可能不同,在第二篇中使用的是Integer作为例子,对于Java语言而言,已经帮助实现了Integer类的equals()方法,包括8个基本类型对应的包装类或者String类等通常使用的类,Java语言都已经帮我们实现了equals()方法。
当我们使用自己定义的类的时候,是需要自己去将equals()的逻辑实现出来的,那么一起来学习如何实现吧
2.使用自定义类测试
2.1⛏创建Student类并测试
- 创建Student类
public class Student { //Student类
private String name;
public Student(String name){
this.name = name;
}
}
- 进行测试
public class LinearSearch {
private LinearSearch(){}
public static <E> int search(E[] data, E target){
for(int i = 0; i < data.length; i ++)
if(data[i].equals(target))
return i;
return -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args){ //进行测试
Student[] students = {new Student("A"),
new Student("B"),
new Student("C")};
Student b = new Student("B");
int res3 = LinearSearch.search(students, b);
System.out.println(res3);
}
}
2.2 剖析测试结果
- 代码描述: students数组是一个Student类的数组,里面new了三个Student类的对象,分别为A、B、C,然后使用LinearSearch的search()方法——参数为数组students和b,即查找students中是否有名为"B"的学生
- 结果描述: 查询结果是-1,即不存在学生B,很明显,查询结果是有误的
- 结果剖析: 查询结果是-1,是因为
equals()方法默认比较的是两个类对象的地址,而在我们上面代码的逻辑中,我们 更希望的是比较两个类对象所对应的字符串 ——为了实现这个逻辑,我们就必须自己 自定义Student的这个类中的这个equals()
2.3 自定义equals()
2.3.1 初窥门径➡️错误的函数声明
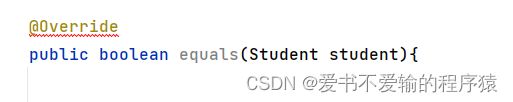
public boolean equals(Student student){...}
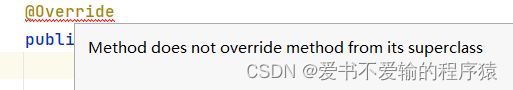
- 结论: equals(Student student):对equals的声明里传的参数和Student类的类型是一样的,这个函数声明是错误的❌
- 原因:
equals()是Object父类的一个函数,我们是覆盖equals这个方法,所以这个函数签名要和Object的函数签名是一样的——Object父类函数传进去的参数的类型是Object,我们需要这样来写⬇️
public boolean equals(Object student){...}
2.3.2 渐入佳境➡️善用工具
-
1️⃣工具之编译器
-
2️⃣工具之Java关键字
2.3.3 略有小成 ➡️完成equals()
- 1️⃣声明
@Override
public boolean equals(Object student){}
Student stu = (Student)student;
- 3️⃣完成比较是否相等的逻辑,并将结果返回
- 该判断仅针对本文中的判断逻辑,因为现实中同名不一定是同一个人
/*此处的equals()其实是调用的String类中的equals
➡️所以,将两个学生类的比较,变成了字符串的比较
如果两个学生的名字所对应的字符串是一样的,即两个学生是一样的
*/
return this.name.equals(stu.name);
- 4️⃣整体逻辑如上⬆️,不过我们仍需要添加一些判断, 因为将Object类型的对象student 强制转换为Student类的对象,可能会抛异常或者无法强制转换
//【判断1】:this,即当前这个类的对象,是否就是Student类的对象,它们的地址是否一样
if(this == student)
/*
如果判断结果为一样,
那么比较的就是同一个对象,就不需要强制转换,true
*/
return true;
//【判断2】:如果判断1是false,那么就判断传来的student是不是一个空对象
if(student == null)
/*当前的Student类的对象肯定是非空的,如果传来的student是空对象,那么直接false*/
return false;
//【判断3】:判断强制转换是否成立
/*
this.getClass()即当前这个类对象所对应的类到底是什么,其实就是Student类
判断this.getClass是否等于传来的student这个对象所对应的类
如果不相等,即二者不属于同一个类,直接false
*/
if(this.getClass() != student.getClass())
return false;
✔️经过4️⃣里的3个判断,如果都通过了,即传的student不为空,且确实是Student类的对象,那么就可以安全的进行强制转换的操作2️⃣
2.3.4 融会贯通➡️完整的equals()
public class Student {
private String name;
public Student(String name){
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object student){
if(this == student)
return true;
if(student == null)
return false;
if(this.getClass() != student.getClass())
return false;
Student another = (Student)student;
return this.name.equals(another.name);
}
}