Python每日一练(20230416)
![]()
目录
1. 有效数字
2. 二叉树的最大深度
3. 单词搜索
每日一练刷题专栏
Golang每日一练 专栏
Python每日一练 专栏
C/C++每日一练 专栏
Java每日一练 专栏
1. 有效数字
有效数字(按顺序)可以分成以下几个部分:
- 一个 小数 或者 整数
- (可选)一个
'e'或'E',后面跟着一个 整数
小数(按顺序)可以分成以下几个部分:
- (可选)一个符号字符(
'+'或'-') - 下述格式之一:
- 至少一位数字,后面跟着一个点
'.' - 至少一位数字,后面跟着一个点
'.',后面再跟着至少一位数字 - 一个点
'.',后面跟着至少一位数字
- 至少一位数字,后面跟着一个点
整数(按顺序)可以分成以下几个部分:
- (可选)一个符号字符(
'+'或'-') - 至少一位数字
部分有效数字列举如下:
["2", "0089", "-0.1", "+3.14", "4.", "-.9", "2e10", "-90E3", "3e+7", "+6e-1", "53.5e93", "-123.456e789"]
部分无效数字列举如下:
["abc", "1a", "1e", "e3", "99e2.5", "--6", "-+3", "95a54e53"]
给你一个字符串 s ,如果 s 是一个 有效数字 ,请返回 true 。
示例 1:
输入:s = "0" 输出:true
示例 2:
输入:s = "e" 输出:false
示例 3:
输入:s = "." 输出:false
示例 4:
输入:s = ".1" 输出:true
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 20s仅含英文字母(大写和小写),数字(0-9),加号'+',减号'-',或者点'.'。
以下程序实现了这一功能,请你填补空白处内容:
```python
class Solution(object):
def isNumber(self, s):
s = s.strip()
ls, pos = len(s), 0
if ls == 0:
return False
if s[pos] == '+' or s[pos] == '-':
pos += 1
isNumeric = False
while pos < ls and s[pos].isdigit():
pos += 1
isNumeric = True
_____________________________;
elif pos < ls and s[pos] == 'e' and isNumeric:
isNumeric = False
pos += 1
if pos < ls and (s[pos] == '+' or s[pos] == '-'):
pos += 1
while pos < ls and s[pos].isdigit():
pos += 1
isNumeric = True
if pos == ls and isNumeric:
return True
return False
# %%
s = Solution()
print(s.isNumber(s = "0"))
```
出处:
https://edu.csdn.net/practice/25740860
代码:
class Solution(object):
def isNumber(self, s):
s = s.strip()
ls, pos = len(s), 0
if ls == 0:
return False
if s[pos] == '+' or s[pos] == '-':
pos += 1
isNumeric = False
while pos < ls and s[pos].isdigit():
pos += 1
isNumeric = True
if pos < ls and s[pos] == '.':
pos += 1
while pos < ls and s[pos].isdigit():
pos += 1
isNumeric = True
elif pos < ls and s[pos] == 'e' and isNumeric:
isNumeric = False
pos += 1
if pos < ls and (s[pos] == '+' or s[pos] == '-'):
pos += 1
while pos < ls and s[pos].isdigit():
pos += 1
isNumeric = True
if pos == ls and isNumeric:
return True
return False
# %%
s = Solution()
print(s.isNumber(s = "0"))
print(s.isNumber(s = "e"))
print(s.isNumber(s = "."))
print(s.isNumber(s = ".1"))
输出:
True
False
False
True
2. 二叉树的最大深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回它的最大深度 3 。
出处:
https://edu.csdn.net/practice/25740861
代码:
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
def listToTree(lst: list) -> TreeNode:
if not lst:
return None
root = TreeNode(lst[0])
queue = [root]
i = 1
while i < len(lst):
node = queue.pop(0)
if lst[i] is not None:
node.left = TreeNode(lst[i])
queue.append(node.left)
i += 1
if i < len(lst) and lst[i] is not None:
node.right = TreeNode(lst[i])
queue.append(node.right)
i += 1
return root
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
if root is None:
return 0
maxdepth = max(self.maxDepth(root.left),self.maxDepth(root.right)) + 1
return maxdepth
# %%
s = Solution()
null = None
nums = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
root = listToTree(nums)
print(s.maxDepth(root))输出:
3
代码2:DFS
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
def listToTree(lst: list) -> TreeNode:
if not lst:
return None
root = TreeNode(lst[0])
queue = [root]
i = 1
while i < len(lst):
node = queue.pop(0)
if lst[i] is not None:
node.left = TreeNode(lst[i])
queue.append(node.left)
i += 1
if i < len(lst) and lst[i] is not None:
node.right = TreeNode(lst[i])
queue.append(node.right)
i += 1
return root
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: TreeNode):
if not root:
return 0
depth = []
def dfs(node, nodes=[]):
if not node:
return
nodes.append(node.val)
if node.left or node.right:
dfs(node.left, nodes)
dfs(node.right, nodes)
else:
depth.append(len(nodes))
nodes.pop()
dfs(root)
return max(depth)
# %%
s = Solution()
null = None
nums = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
root = listToTree(nums)
print(s.maxDepth(root))3. 单词搜索
给定一个 m x n 二维字符网格 board 和一个字符串单词 word 。如果 word 存在于网格中,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
单词必须按照字母顺序,通过相邻的单元格内的字母构成,其中“相邻”单元格是那些水平相邻或垂直相邻的单元格。同一个单元格内的字母不允许被重复使用。
示例 1:
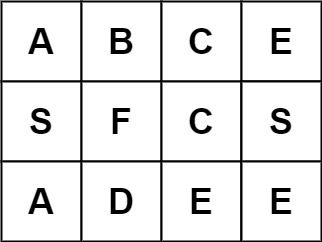
输入:board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCCED" 输出:true
示例 2:
输入:board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "SEE" 输出:true
示例 3:
输入:board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCB" 输出:false
提示:
m == board.lengthn = board[i].length1 <= m, n <= 61 <= word.length <= 15board和word仅由大小写英文字母组成
进阶:你可以使用搜索剪枝的技术来优化解决方案,使其在 board 更大的情况下可以更快解决问题?
出处:
https://edu.csdn.net/practice/25740862
代码:
class Solution(object):
def exist(self, board, word):
"""
:type board: List[List[str]]
:type word: str
:rtype: bool
"""
check_board = [[True] * len(board[0]) for _ in range(len(board))]
for i in range(len(board)):
for j in range(len(board[0])):
if board[i][j] == word[0] and check_board:
check_board[i][j] = False
res = self.check_exist(check_board, board, word, 1, len(word), i, j)
if res:
return True
check_board[i][j] = True
return False
def check_exist(self, check_board, board, word, index, ls, row, col):
if index == ls:
return True
for temp in [(0, 1),(0, -1),(1, 0),(-1, 0)]:
curr_row = row + temp[0]
curr_col = col + temp[1]
if curr_row >= 0 and curr_row < len(board) and curr_col >= 0 and curr_col < len(board[0]):
if check_board[curr_row][curr_col] and board[curr_row][curr_col] == word[index]:
check_board[curr_row][curr_col] = False
res = self.check_exist(check_board, board, word, index + 1, len(word), curr_row, curr_col)
if res:
return res
check_board[curr_row][curr_col] = True
return False
if __name__ == "__main__":
s = Solution()
print (s.exist(board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCCED"))输出:
True
每日一练刷题专栏
✨ 持续,努力奋斗做强刷题搬运工!
点赞,你的认可是我坚持的动力!
收藏,你的青睐是我努力的方向!
✎ 评论,你的意见是我进步的财富!
☸ 主页:https://hannyang.blog.csdn.net/
Golang每日一练 专栏 |
|
Python每日一练 专栏 |
|
C/C++每日一练 专栏 |
|
Java每日一练 专栏 |