数据结构——链式队列【c语言版】
队列(quque)简称队,只允许在表的一端输入,在表的另一端删除(操作受限制的线性表),
把进行插入的一段叫做队尾(表尾),把进入删除的一端叫做队首或队头(表头)。
队列最主要的特点:先进先出,FIFO(first in first out)
队列有其实有三种:顺序队列、 循环队列、链式队列
采用链式存储结构实现的队列称为链队
下面是采用单链表来实现链式队列的过程:
在链队中只允许单链表的表头进行删除操作(出队),表尾进行插入操作(入队),因此需要使用两个指针(一个是对头指针front【指向队首结点】,另一个是队尾指针rear【指向队尾结点】)。
链队数据结点类型DataNode如下:
typedef int ElemType;
//值节点--多个
typedef struct Node
{
ElemType data;//存储队列的元素值
struct Node *next;//存储下一个元素节点的地址
}DataNode;
链队存储结构如图:
链队头结点类型LinkQueue如下:
//头节点--1个
typedef struct
{
DataNode *front;//存储队头元素节点的地址 (队首指针)
DataNode *rear;//存储队尾元素节点的地址 (队尾指针)
}LinkQueue;
链队的动态变化过程如图:
对于链式队列来说,有以下四个非常重要的要素:
1.队空条件:q->front==NULL && q->rear==NULL
2.队满条件:与链栈一样,链队一般不会满,不存在队满上溢情况
3.进队操作:新建一个结点存放元素e,将结点t插入作为尾结点
4.出队操作:构造一个结点t,让t指向队首元素节点,把队首元素存储到*e中,删除队头元 素节点
1)链队初始化
构造一个空的队列,既创建一个链队结点,将front和rear域都设置为NULL,代码如下:
LinkQueue *InitQueue()
{
LinkQueue *q;
q=(LinkQueue *)malloc(sizeof(LinkQueue));
q->front=NULL;
q->rear=NULL;
return q;
}
2)销毁队列
释放队列占用的全部存储空间,包括链队结点与所以数据结点的存储空间,代码如下:
void DestroyQueue(LinkQueue *q)
{
int deQueue(LinkQueue *q,ElemType *e);
ElemType m;
while(q->front!=NULL||q->rear!=NULL)//非空
{
//出队
deQueue(q,&m);
}
free(q);
}
3)判断队列是否为空
链式队列中,判断队列是否为空,只需要判断q->front==NULL && q->rear==NULL的条件成立即可,代码如下:
//判断队列为空
int QueueEmpty(LinkQueue *q)
{
if(q->front==NULL && q->rear==NULL)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
} 4)入队
构造一个节点t,data域存储e,next域存储NULL,若原链队为空,则将链队结点的两个域都指向结点t,否则将结点t链接到单链表末尾,并让链队结点的rear域指向它,代码如下:
void enQueue(LinkQueue *q,ElemType e)
{
DataNode *t;
//1.构造一个节点t,data域存储e,next域存储NULL
t=(DataNode *)malloc(sizeof(DataNode));
t->data=e;
t->next=NULL;
//2.添加
if(q->front!=NULL||q->rear!=NULL)//非空
{
/*队非空*/
q->rear->next=t;
q->rear=t;
}
else
{
/*队空 */
q->front=t;
q->rear=t;
}
} 5)出队
若原链队为空,则下溢,提示,返回0,否则将队首结点的data域赋值给*e,并删除队首结点,若原链队只有一个结点,则需要将链队结点的两个域都设置为NULL,表示此时链队已空,代码如下:
/*
若队列非空,出队,返回1;
否则,提示,返回0
*/
int deQueue(LinkQueue *q,ElemType *e)
{
DataNode *t;
if(q->front!=NULL||q->rear!=NULL)//非空
{
//1.让t指向队头元素节点
t=q->front;
//2.把队头元素存储到*e中
*e=t->data;
//3.删除队头元素节点
if(q->front->next==NULL)//只有1个元素
{
/*只有1个元素*/
q->front=NULL;
q->rear=NULL;
}
else
{
/*多于1个元素*/
q->front=t->next;
}
//4.释放t所占的存储空间
free(t);
return 1;
}
else
{
printf("队空,不能出队!\n");
return 0;
}
}
6)求队列长度
代码如下:
/*
6.求链式队列的长度
*/
int lenghtLinkQueue(LinkQueue *q)
{
int len;
if (QueueEmpty(&q))
{
len = 0;
return len;
}
DataNode *t;
//1.构造一个节点t,让它指向队首元素front
t=(DataNode *)malloc(sizeof(DataNode));
t=q->front;
len = 1;
while(t->next != NULL)
{
len++;
t = t->next;
}
printf("队列长度为%d\n",len);
} 7)打印队列中的元素
从队首到队尾,代码如下:
//打印队列中的与元素
void DispQueue(LinkQueue *q)
{
DataNode *p;
p=q->front;
printf("队列元素为:");
while(p!=NULL)
{
printf("%d ",p->data);
p=p->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
下面是入队、出栈和打印出队列以及销毁队列元素的操作:
int main()
{
LinkQueue lq;
lq = *InitQueue();
enQueue(&lq,1);
enQueue(&lq,2);
enQueue(&lq,3);
enQueue(&lq,4);
enQueue(&lq,5);
enQueue(&lq,6);
enQueue(&lq,7);
enQueue(&lq,8);
enQueue(&lq,9);
DispQueue(&lq);
lenghtLinkQueue(&lq);
ElemType *e;
e = (ElemType *)malloc(sizeof(ElemType));
deQueue(&lq,e);
printf("出队元素:%d\n",*e);
deQueue(&lq,e);
printf("出队元素:%d\n",*e);
printf("队列为空返回1,否则返回0:%d\n",QueueEmpty(&lq));
DispQueue(&lq);
lenghtLinkQueue(&lq);
DestroyQueue(&lq); //销毁队列
return 1;
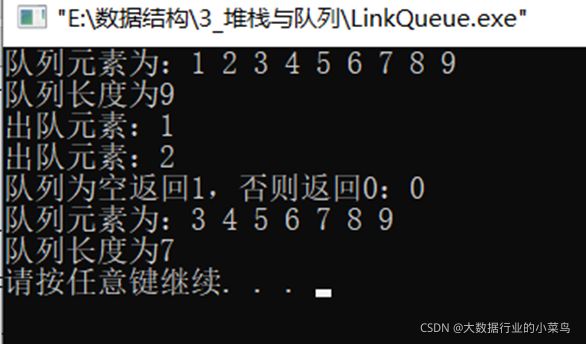
} 测试结构如下
最后再附上完整代码:
#include
typedef int ElemType;
//值节点--多个
typedef struct Node
{
ElemType data;//存储队列的元素值
struct Node *next;//存储下一个元素节点的地址
}DataNode;
//头节点--1个
typedef struct
{
DataNode *front;//存储队头元素节点的地址 (队首指针)
DataNode *rear;//存储队尾元素节点的地址 (队尾指针)
}LinkQueue;
/*
空:q->front==NULL && q->rear==NULL
满:与链栈一样,链队一般不会满,不存在队满上溢情况
*/
/*
1.初始化
*/
LinkQueue *InitQueue()
{
LinkQueue *q;
q=(LinkQueue *)malloc(sizeof(LinkQueue));
q->front=NULL;
q->rear=NULL;
return q;
}
/*
2.销毁
*/
void DestroyQueue(LinkQueue *q)
{
int deQueue(LinkQueue *q,ElemType *e);
ElemType m;
while(q->front!=NULL||q->rear!=NULL)//非空
{
//出队
deQueue(q,&m);
}
free(q);
}
/*
3.判断是否为空
若为空,返回1;
否则,返回0
*/
int QueueEmpty(LinkQueue *q)
{
if(q->front==NULL && q->rear==NULL)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
/*
4.进队
*/
void enQueue(LinkQueue *q,ElemType e)
{
DataNode *t;
//1.构造一个节点t,data域存储e,next域存储NULL
t=(DataNode *)malloc(sizeof(DataNode));
t->data=e;
t->next=NULL;
//2.添加
if(q->front!=NULL||q->rear!=NULL)//非空
{
/*队非空*/
q->rear->next=t;
q->rear=t;
}
else
{
/*队空 */
q->front=t;
q->rear=t;
}
}
/*
5.出队
若队列非空,出队,返回1;
否则,提示,返回0
*/
int deQueue(LinkQueue *q,ElemType *e)
{
DataNode *t;
if(q->front!=NULL||q->rear!=NULL)//非空
{
//1.让t指向队头元素节点
t=q->front;
//2.把队头元素存储到*e中
*e=t->data; // 其实是q->front->data
//3.删除队头元素节点
if(q->front->next==NULL)//只有1个元素
{
/*只有1个元素*/
q->front=NULL;
q->rear=NULL;
}
else
{
/*多于1个元素*/
q->front=t->next;
}
//4.释放t所占的存储空间
free(t);
return 1;
}
else
{
printf("队空,不能出队!\n");
return 0;
}
}
/*
6.求链式队列的长度
*/
int lenghtLinkQueue(LinkQueue *q)
{
int len;
if (QueueEmpty(&q))
{
len = 0;
return len;
}
DataNode *t;
//1.构造一个节点t,让它指向队首元素front
t=(DataNode *)malloc(sizeof(DataNode));
t=q->front;
len = 1;
while(t->next != NULL)
{
len++;
t = t->next;
}
printf("队列长度为%d\n",len);
}
/*
7.输出
*/
void DispQueue(LinkQueue *q)
{
DataNode *p;
p=q->front;
printf("队列元素为:");
while(p!=NULL)
{
printf("%d ",p->data);
p=p->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
LinkQueue lq;
lq = *InitQueue();
enQueue(&lq,1);
enQueue(&lq,2);
enQueue(&lq,3);
enQueue(&lq,4);
enQueue(&lq,5);
enQueue(&lq,6);
enQueue(&lq,7);
enQueue(&lq,8);
enQueue(&lq,9);
DispQueue(&lq);
lenghtLinkQueue(&lq);
ElemType *e;
e = (ElemType *)malloc(sizeof(ElemType));
deQueue(&lq,e);
printf("出队元素:%d\n",*e);
deQueue(&lq,e);
printf("出队元素:%d\n",*e);
printf("队列为空返回1,否则返回0:%d\n",QueueEmpty(&lq));
DispQueue(&lq);
lenghtLinkQueue(&lq);
DestroyQueue(&lq); //销毁队列
return 1;
}