Spring 缓存 AOP 实现
Spring 缓存 AOP 实现
文章目录
- Spring 缓存 AOP 实现
-
- 前言
- 1.项目环境
- 2.Spring @Cacheable 示例
- 3.实现猜想
- 4.实现源码核心API
- 5.Spring AOP API 示例
- 6.源码分析
-
- 6.1 @EnableCaching
- 6.2 ProxyCachingConfiguration
-
- 6.2.1 Advisor 实现
- 6.2.2 Pointcut 实现
- 6.2.3 Interceptor 实现
- 6.2.4 CacheOperationSource 实现
- 6.2.5 小结
- 6.3 AutoProxyRegistrar
-
- 6.3.1 源码分析
- 6.3.2 源码调试
- 7.参考
前言
本章我们来讨论下 Spring 中缓存框架的实现,结合简单的示例,猜测实现方式;最后我们再一探源码来看看 Spring 中的实现。
前提是要对 Spring AOP 和 IoC 有一定的基础,因为本文主要是讲 Spring 如何利用 AOP 和 IoC 的有机结合来实现缓存框架。
1.项目环境
- jdk 1.8
- spring 5.2.2.RELEASE
- github 地址:https://github.com/huajiexiewenfeng/thinking-in-spring
- 本章模块:aop-features
2.Spring @Cacheable 示例
测试启动类 SpringCachingDemo
@EnableCaching
public class SpringCachingDemo {
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(){
CacheManager cacheManager = new ConcurrentMapCacheManager();
return cacheManager;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext configApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
configApplicationContext.register(SpringCachingDemo.class,UserImpl.class);
configApplicationContext.refresh();
UserService userService = configApplicationContext.getBean(UserService.class);
System.out.println(userService.getUser("xwf"));
configApplicationContext.close();
}
}
UserService
public interface UserService {
User getUser(String name);
}
UserImpl
@Service
public class UserImpl implements UserService {
@Override
@Cacheable(value = {"getUser"}, key = "#name")
public User getUser(String name) {
return User.createUser(name);
}
}
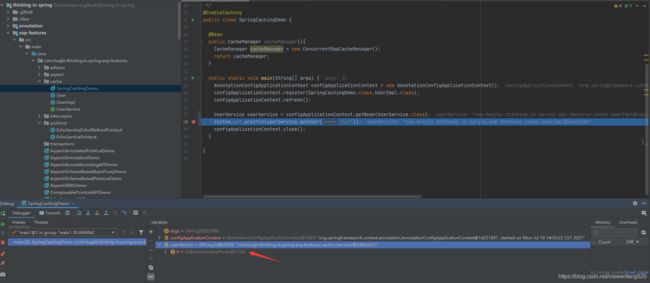
debug 执行
可以看到通过 Spring IoC 依赖查找的 UserService 对象实际上是 JdkDynamicAopProxy 对象,及 JDK 生成的动态代理对象。
执行结果:
User{name='xwf', age=18}
@Cacheable 的作用:多次掉用该接口获取数据,在过期时间内,获取到的都是框架缓存的数据;假设 getUser 方法是通过数据库来获取,且时间较长,那么第一次查询数据缓存之后,后面的查询会通过缓存直接返回,不会再经过数据库,起到优化查询速度的效果。
3.实现猜想
问题:在 Spring 中实现一个缓存 AOP 框架需要做哪些事情?
1.拦截所有的 Spring Bean,判断哪些 Bean 需要处理换成 Proxy 对象
- 根据上面的示例截图,我们可以知道 userService 对象实际上已经被替换成了 JDK 动态代理对象
2.创建 Proxy 代理对象
3.在拦截方法(Advice)中实现缓存功能
4.Spring AOP API 的使用
4.实现源码核心API
- Spring 缓存 @Enable 模块驱动 - @EnableCaching
- 缓存操作注解 - @Caching、@Cachable、@CachePut、@CacheEvict
- 缓存配置注解 - @CacheConfig
- 缓存注解操作数据源 - AnnotationCacheOperationSource
- Spring 缓存注解解释器 - SpringCacheAnnotationParser
- Spring 缓存管理器 - CacheManager
- Spring 缓存接口 - Cache
- Spring 缓存代理配置 - ProxyCachingConfiguration
- Spring 缓存 PointcutAdvisor 实现 - BeanFactoryCacheOperationSourceAdvisor
- Spring 缓存 MethodInterceptor 实现 - CacheInterceptor
5.Spring AOP API 示例
在看源码之前,我们先看一个 Spring AOP API使用的简单示例,这一步可以帮助我们了解猜想中的第 4 项,如何使用 AOP API
- 其中 EchoServicePointcut extends StaticMethodMatcherPointcut 来实现 Pointcut
public class PointcutAPIDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EchoServicePointcut echoServicePointcut = new EchoServicePointcut("echo", EchoService.class);
// 将 Pointcut 适配成 Advisor
DefaultPointcutAdvisor advisor = new DefaultPointcutAdvisor();
advisor.setPointcut(echoServicePointcut);
advisor.setAdvice(new EchoServiceMethodInterceptor());
DefaultEchoService echoService = new DefaultEchoService();
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory(echoService);
proxyFactory.addAdvisor(advisor);
EchoService proxy = (EchoService) proxyFactory.getProxy();
System.out.println(proxy.echo("hello,world"));
}
}
EchoServiceMethodInterceptor 方法拦截器
public class EchoServiceMethodInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
String methodName = invocation.getMethod().getName();
System.out.printf("拦截 EchoService 方法:%s\n", methodName);
return invocation.proceed();
}
}
执行结果:
拦截 EchoService 方法:echo
[Echo] hello,world
通过示例我们可以知道,如果要用 API 的方式使用 Spring AOP
-
需要自己构建 Advisor,这是一个 Advice 的容器,在 Spring 设计中是 1:1 的关系
-
设置 Advice 通知对象,这里用的是方法拦截器实现
-
然后使用 ProxyFactory 添加 Advisor
-
通过 ProxyFactory#getProxy() 获取代理对象,从而达到代理效果
其中 advisor.setAdvice(new EchoServiceMethodInterceptor()) 可以设置我们的方法拦截器,在执行方法之前之后来进行相应的处理,最终达到 AOP 的效果。
6.源码分析
6.1 @EnableCaching
激活 Spring Caching 缓存功能
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(CachingConfigurationSelector.class)
public @interface EnableCaching {
boolean proxyTargetClass() default false;
AdviceMode mode() default AdviceMode.PROXY;
int order() default Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE;
}
这里导入的是 CachingConfigurationSelector,采用的是实现 ImportSelector 接口的方式来进行激活的,相关内容可以参考 Spring boot 编程思想|@Enable 模块驱动。
核心代码
- org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachingConfigurationSelector#selectImports
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AdviceMode adviceMode) {
switch (adviceMode) {
case PROXY:
return getProxyImports();
case ASPECTJ:
return getAspectJImports();
default:
return null;
}
}
判断如果是 PROXY 就执行 getProxyImports(),如果是 ASPECTJ 就执行 getAspectJImports();而这个 adviceMode 其实是 @EnableCaching 中的第二个参数传入的,默认是 PROXY,AdviceMode mode() default AdviceMode.PROXY,其实就是两种不同的 AOP 实现方式。这里我们主要看默认方式:
private String[] getProxyImports() {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>(3);
result.add(AutoProxyRegistrar.class.getName());
result.add(ProxyCachingConfiguration.class.getName());
if (jsr107Present && jcacheImplPresent) {
result.add(PROXY_JCACHE_CONFIGURATION_CLASS);
}
return StringUtils.toStringArray(result);
}
AutoProxyRegistrar:AutoProxyCreator 注册器,这块的作用主要是将 Spring 缓存 AOP 与 Spring IoC Bean 生命周期串联起来,后面我们再看。
ProxyCachingConfiguration:缓存代理的配置类
6.2 ProxyCachingConfiguration
接着我们再来看 Spring 中如何来使用 API 完成 AOP 的配置,这块和 Spring AOP API 示例结合来看
@Configuration
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public class ProxyCachingConfiguration extends AbstractCachingConfiguration {
@Bean(name = CacheManagementConfigUtils.CACHE_ADVISOR_BEAN_NAME)
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public BeanFactoryCacheOperationSourceAdvisor cacheAdvisor() {
BeanFactoryCacheOperationSourceAdvisor advisor = new BeanFactoryCacheOperationSourceAdvisor();
advisor.setCacheOperationSource(cacheOperationSource());
advisor.setAdvice(cacheInterceptor());
if (this.enableCaching != null) {
advisor.setOrder(this.enableCaching.<Integer>getNumber("order"));
}
return advisor;
}
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public CacheOperationSource cacheOperationSource() {
return new AnnotationCacheOperationSource();
}
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public CacheInterceptor cacheInterceptor() {
CacheInterceptor interceptor = new CacheInterceptor();
interceptor.configure(this.errorHandler, this.keyGenerator, this.cacheResolver, this.cacheManager);
interceptor.setCacheOperationSource(cacheOperationSource());
return interceptor;
}
}
这个类中完成了三个Bean的配置
- Advisor
- 实现类 - org.springframework.cache.interceptor.BeanFactoryCacheOperationSourceAdvisor
- Interceptor
- 实现类 - org.springframework.cache.interceptor.CacheInterceptor
- CacheOperationSource
- 实现类 - org.springframework.cache.annotation.AnnotationCacheOperationSource
其中 Advisor 和 Interceptor 是 AOP 的关键项,我们在上面的 Demo 中也用过了;CacheOperationSource 是帮助实现缓存功能的类,比如获取 targetClass 或者 method 中的 CacheOperation 集合,提供缓存注解解析器等等。
6.2.1 Advisor 实现
org.springframework.aop.support.AbstractBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor
public class BeanFactoryCacheOperationSourceAdvisor extends AbstractBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor {
@Nullable
private CacheOperationSource cacheOperationSource;
private final CacheOperationSourcePointcut pointcut = new CacheOperationSourcePointcut() {
@Override
@Nullable
protected CacheOperationSource getCacheOperationSource() {
return cacheOperationSource;
}
};
/**
* Set the cache operation attribute source which is used to find cache
* attributes. This should usually be identical to the source reference
* set on the cache interceptor itself.
*/
public void setCacheOperationSource(CacheOperationSource cacheOperationSource) {
this.cacheOperationSource = cacheOperationSource;
}
/**
* Set the {@link ClassFilter} to use for this pointcut.
* Default is {@link ClassFilter#TRUE}.
*/
public void setClassFilter(ClassFilter classFilter) {
this.pointcut.setClassFilter(classFilter);
}
@Override
public Pointcut getPointcut() {
return this.pointcut;
}
}
CacheOperationSourcePointcut 是一个内部的实现,同样的 CacheOperationSourcePointcut extends StaticMethodMatcherPointcut,和我们上面的 Demo 一样,Pointcut 的主要作用是对类方法的筛选,只有 matches 方法返回 true 的情况,才会进入到切面中。
6.2.2 Pointcut 实现
org.springframework.cache.interceptor.CacheOperationSourcePointcut
关键代码如下:
abstract class CacheOperationSourcePointcut extends StaticMethodMatcherPointcut implements Serializable {
protected CacheOperationSourcePointcut() {
setClassFilter(new CacheOperationSourceClassFilter());
}
@Override
public boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {
CacheOperationSource cas = getCacheOperationSource();
return (cas != null && !CollectionUtils.isEmpty(cas.getCacheOperations(method, targetClass)));
}
...
- 继承了 StaticMethodMatcherPointcut
- matches() 用来过滤满足条件的方法
- cas.getCacheOperations 判断 Method 有缓存操作,比如添加了 @Cacheable 等相关注解
只要满足了 matches() 的条件,就可以进入到该方法的切面,执行相关的拦截操作。
6.2.3 Interceptor 实现
org.springframework.cache.interceptor.CacheInterceptor
缓存拦截器,同样也是实现了 MethodInterceptor,来进行方法的拦截,可想而知拦截方法之后,获取到方法的返回值,来进行一系列的缓存操作。
public class CacheInterceptor extends CacheAspectSupport implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable {
@Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(final MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
Method method = invocation.getMethod();
CacheOperationInvoker aopAllianceInvoker = () -> {
try {
return invocation.proceed();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new CacheOperationInvoker.ThrowableWrapper(ex);
}
};
try {
return execute(aopAllianceInvoker, invocation.getThis(), method, invocation.getArguments());
}
catch (CacheOperationInvoker.ThrowableWrapper th) {
throw th.getOriginal();
}
}
}
缓存实现的核心方法,后面我们会进行源码的调试
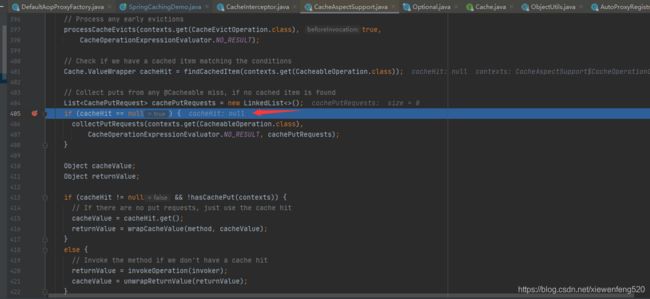
org.springframework.cache.interceptor.CacheAspectSupport#execute()
- 第一次进入,缓存为空
- 将返回值存储到缓存中
- 第二此进入,通过 key 值查询到缓存,返回缓存值
我们将断点打在 org.springframework.cache.interceptor.CacheAspectSupport#execute() 405 行
修改下上面的 Demo 多加一次 userService.getUser("xwf") 方法的调用
第一次调用 getUser 方法
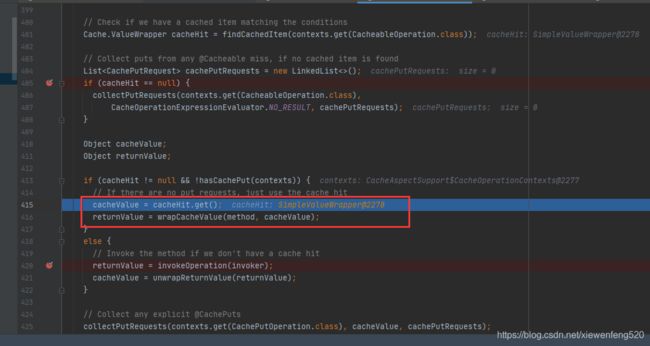
可以看到 cacheHit 为 null,继续往下,断点打在 420 行
返回值 returnValue 是通过 invoker.invoke(); 也就是通过反射执行方法本身拿到返回值。
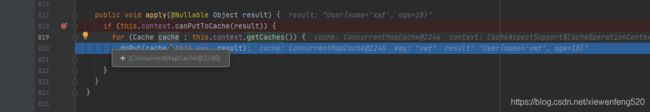
继续往下,断点达到 CacheAspectSupport.CachePutRequest#apply 820行
可以看到 Cahce 的实现类是 ConcurrentMapCache,这个类的get方法源码如下:
public <T> T get(Object key, Callable<T> valueLoader) {
return (T) fromStoreValue(this.store.computeIfAbsent(key, k -> {
try {
return toStoreValue(valueLoader.call());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ValueRetrievalException(key, valueLoader, ex);
}
}));
}
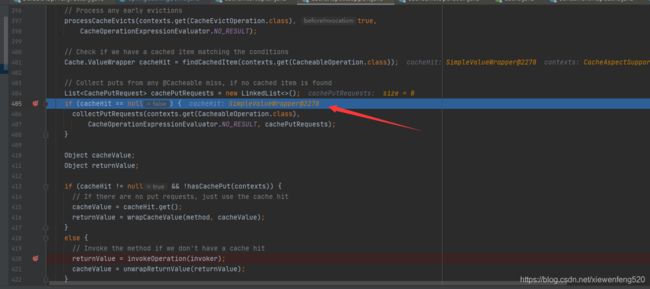
返回 User{name='xwf', age=18} 的结果,然后我们看第二次调用 getUser 方法
cacheHit 不为 null,为 SimpleValueWrapper 对象
会通过 cacheHit.get() 获取缓存对象,而不是通过执行方法的方式。
控制台输出结果如下:
User{name='xwf', age=18}
User{name='xwf', age=18}
其实第一次是通过 Java 反射执行 invoker.invoke(); 也就是执行方法本身拿到的结果,而第二次则是 cacheHit.get() 从缓存中获取。
6.2.4 CacheOperationSource 实现
具体实现类
- AnnotationCacheOperationSource
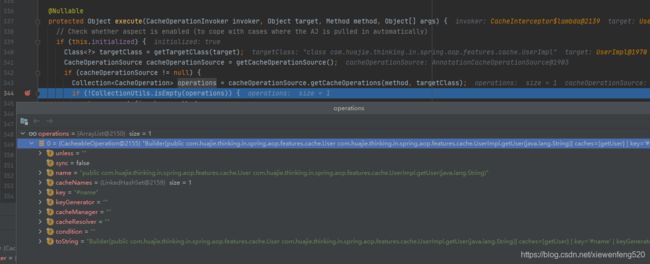
通过 cacheOperationSource.getCacheOperations(method, targetClass); 获取到的信息如下:
通过 method 和 targetClass ,获取改方法的元信息,包括类的信息,注解的信息等等。
其中比如 key = “#name” ,包括一些其他信息需要 Spring 进行解析,这个类中又包含缓存解析器
- SpringCacheAnnotationParser
org.springframework.cache.annotation.SpringCacheAnnotationParser#parseCacheAnnotations()
解析 targetClass 和 method ,获取 @Caching、@Cachable、@CachePut、@CacheEvict 等相关信息。
6.2.5 小结
其实到讨论到这里,我们已经知道了 Spring 是如何使用 AOP API,其实还是 Advisor、Pointcut、Interceptor 这些 API 的使用,在 Interceptor 中来实现缓存效果。
但是还有猜想中的前两个问题我们还不知道 Spring 如何实现
-
1.Spring 如何创建 Proxy 代理对象?
-
2.Spring 如何将普通的 Spring Bean 替换成 Proxy 代理对象?
我们继续往下看
6.3 AutoProxyRegistrar
6.3.1 源码分析
在 @EnableCaching 中注入了两个类,一个是前面讲的 ProxyCachingConfiguration 配置类,还一个就是 AutoProxyRegistrar 。
- org.springframework.aop.config.AopConfigUtils#registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary()
public static BeanDefinition registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable Object source) {
return registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired(InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.class, registry, source);
}
将 InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator 注册到 Spring IoC 容器中
public abstract class AbstractAutoProxyCreator extends ProxyProcessorSupport
implements SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor, BeanFactoryAware {
......
而这个类的父类 AbstractAutoProxyCreator 实现了 SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 接口,postProcessAfterInitialization方法,所以每个 Spring Bean 的生命周期的 初始化后阶段,都会进入到该方法中。
具体可以参考 第十四章:Spring Bean 生命周期-下篇
此方法做的主要功能就是,判断这个 Bean 是否需要被动态代理。
假设这个 Class 中的方法上标注有 @Cacheable 相关的注解,那么就会通过以下代码
Object proxy = createProxy(beanClass, beanName, specificInterceptors, targetSource);
来创建代理对象。
6.3.2 源码调试
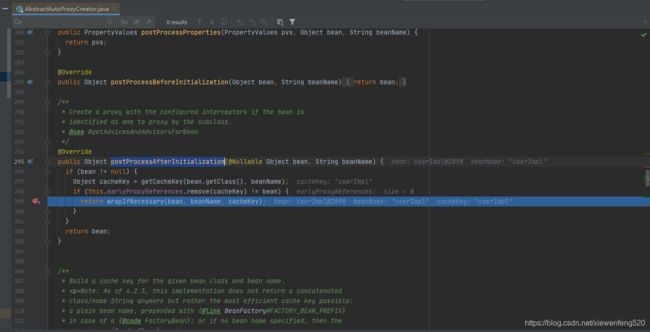
在方法 org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator#postProcessAfterInitialization 299 行打上断点,设置条件 beanName.equals("userImpl")
继续往下,断点打在 350 行
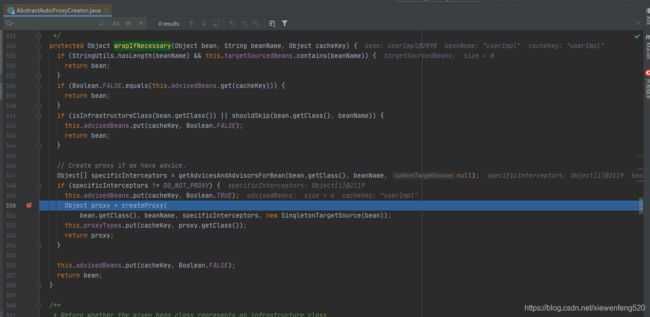
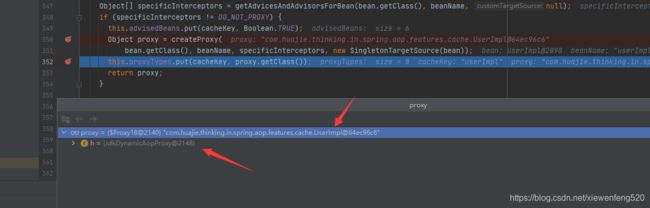
org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator#wrapIfNecessary
可以看到通过 createProxy 方法来创建代理对象。这个创建的代码其实就和我们前面 demo 中的差不多,因为我们这里的 UserImpl 是实现的 UserService 接口,所以 AOP 会使用 JdkDynamicAopProxy 也就是 JDK 动态代理的方式来创建 Proxy 对象 。
最后将这个 Proxy 代理对象返回,存储到 Spring IoC 容器中,类型为 UserService;当我们再通过 Spring IoC 容器获取对象时,就会得到这个有缓存功能的代理对象。
7.参考
- 极客时间-小马哥《小马哥讲Spring AOP编程思想》