GeoTools解析GeoJson为要素集(FeatureCollection)含嵌套数组属性
一 概述
GeoJSON是一种基于JSON(JavaScript Object Notation)格式的地理空间数据交换格式。它可以用来描述地理空间数据,如点、线、面、多边形等。GeoJSON是一种开放的标准格式,由IETF(Internet Engineering Task Force)发布的RFC 7946规范定义。
GeoTools是一个开源的Java库,用于处理地理空间数据。它提供了一系列API,可用于读取、写入、处理和分析各种地理空间数据格式,如Shapefile、GeoJSON、KML、GML等。GeoTools还包括一些专门用于地理信息系统(GIS)和地图制图的工具和组件,如渲染引擎、符号化、空间索引、投影转换等。
二 Maven依赖配置
<properties>
<geotool.version>27.0geotools.version>
<geotool.version>28.2geotools.version>
properties>
<dependencies>
....
<dependency>
<groupId>org.geotoolsgroupId>
<artifactId>gt-mainartifactId>
<version>${geotools.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.geotoolsgroupId>
<artifactId>gt-geojson-coreartifactId>
<version>${geotools.version}version>
dependency>
dependencies>
三 解析GeoJson
测试GeoJson数据
{
"type" : "FeatureCollection",
"crs": {
"type": "name",
"properties": {
"name": "urn:ogc:def:crs:OGC:1.3:CRS84"
}
},
"features" : [
{
"type" : "Feature",
"id" : 0,
"geometry" : {
"type" : "Polygon",
"coordinates" : [
[
[
-135.79570815450649,
73.421459227467892
],
[
-82.429184549356194,
84.298712446351942
],
[
-88.207725321888461,
104.35364806866954
],
[
-118.46008583690991,
98.235193133047346
],
[
-135.79570815450649,
73.421459227467892
]
]
]
},
"properties" : {
"FID" : 0,
"Id" : 0,
"name" : "医院"
}
},
{
"type" : "Feature",
"id" : 1,
"geometry" : {
"type" : "Polygon",
"coordinates" : [
[
[
-57.955364806866953,
61.864377682403472
],
[
-80.389699570815424,
73.761373390557935
],
[
-132.05665236051499,
63.563948497854199
],
[
-131.03690987124469,
43.848927038626698
],
[
-57.955364806866953,
61.864377682403472
]
]
]
},
"properties" : {
"FID" : 1,
"Id" : 0,
"name" : "学校"
}
},
{
"type" : "Feature",
"id" : 2,
"geometry" : {
"type" : "MultiPolygon",
"coordinates" : [
[
[
[
-6.3568031535012892,
114.77443915078777
],
[
-6.7137223043758354,
104.06686462455139
],
[
1.13849901486401,
104.42378377542593
],
[
1.13849901486401,
115.13135830166232
],
[
-6.3568031535012892,
114.77443915078777
]
]
],
[
[
[
4.7076905236094717,
115.13135830166232
],
[
5.4215288253585641,
103.70994547367684
],
[
12.916830993724034,
102.6391880210532
],
[
12.202992691974941,
115.84519660341141
],
[
4.7076905236094717,
115.13135830166232
]
]
],
[
[
[
16.129103351594779,
116.20211575428596
],
[
17.199860804218417,
101.56843056842956
],
[
23.267486369085702,
101.92534971930411
],
[
23.267486369085702,
116.5590349051605
],
[
16.129103351594779,
116.20211575428596
]
]
],
[
[
[
26.836677877831164,
117.62979235778414
],
[
26.836677877831164,
102.99610717192775
],
[
35.402737498820045,
103.70994547367684
],
[
35.759656649694591,
118.34363065953323
],
[
26.836677877831164,
117.62979235778414
]
]
]
]
},
"properties" : {
"FID" : 2,
"Id" : 0,
"name" : "停车场"
}
}
]
}
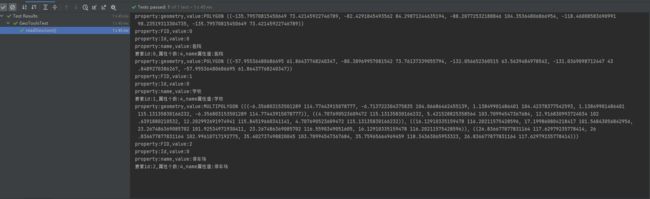
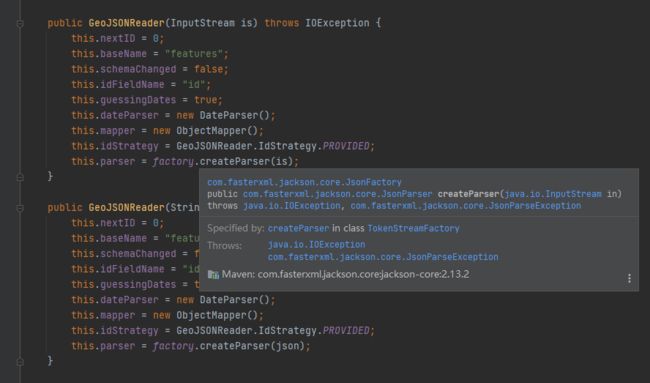
通过GeoJSONReader解析要素集
@Test
public void readGeoJson() throws IOException {
String geoJsonFile = "D:\\MyData\\02_MyTestData\\geojson\\building.geojson";
GeoJSONReader reader = new GeoJSONReader(new FileInputStream(geoJsonFile));
SimpleFeatureCollection featureCollection = reader.getFeatures();
// 遍历要素进行处理
SimpleFeatureIterator features = featureCollection.features();
while (features.hasNext()) {
SimpleFeature feature = features.next();
// 获取要素几何类型
Class<?> binding = feature.getDefaultGeometryProperty().getType().getBinding();
Object defaultGeometry = feature.getDefaultGeometry();
// 具体的几何类型判断
if (defaultGeometry instanceof Point) {
System.out.println(defaultGeometry.toString());
} else if (defaultGeometry instanceof LineString) {
} else if (defaultGeometry instanceof Polygon) {
} else if (defaultGeometry instanceof MultiPoint) {
} else if (defaultGeometry instanceof MultiLineString) {
} else if (defaultGeometry instanceof MultiPolygon) {
}
// 遍历获取要素属性信息
Collection<Property> properties = feature.getProperties();
Iterator<Property> propertyIterator = properties.iterator();
while (propertyIterator.hasNext()){
Property property = propertyIterator.next();
System.out.println(StrUtil.format("property:{},value:{}",property.getName().toString(),property.getValue()));
}
// 获取指定属性信息
int attributeCount = feature.getAttributeCount(); //属性个数
Object attribute_name_value = feature.getAttribute("name"); //获取指定属性值
System.out.println(StrUtil.format("要素id:{},属性个数:{},name属性值:{}", feature.getID(), attributeCount, attribute_name_value));
// 需要注意,获取到的属性集合中包含了几何字段
}
// 要素集迭代器用完记得关闭
features.close();
}
五 避坑
1 产生异常情况的数据
GeoJson是Json的子集,换句话说,本身GeoJson就是一个Json。因此就很有可能属性对象的值为一个对象或者为一个数组,数组中又是某个结构的对象集合,看下面的例子:
{
"type": "FeatureCollection",
"crs": {
"type": "name",
"properties": {
"name": "urn:ogc:def:crs:OGC:1.3:CRS84"
}
},
"features": [
{
"type": "Feature",
"id": 0,
"geometry": {
"type": "Point",
"coordinates": [
104.1111,
34.1111
]
},
"properties": {
"FID": 0,
"Id": 0,
"name": "医院",
"regions": [
"a",
"b",
"c"
],
"workers": [
{
"id": "worker_1",
"name": "billy",
"age": "26"
},
{
"id": "worker_2",
"name": "bille",
"age": "25"
}
],
"code": "yy_0001"
}
}
]
}
1 通过FeatureJSON实例解析
通过GeoTools工具包解析GeoJson为要素集合,网上较多的方法就是通过FeatureJSON实例以读取文件流的形式解析要素集。如果说GeoJson文件中各要素的属性字段不包含嵌套类型,此方法可用。
@Test
public void featureJsonTest() throws IOException {
String geoJsonFile = "D:\\MyData\\02_MyTestData\\geojson\\point_withNestedProperties.geojson";
SimpleFeatureCollection featureCollection = (SimpleFeatureCollection) new FeatureJSON().readFeatureCollection(new FileInputStream(geoJsonFile));
SimpleFeatureIterator featureIterator = featureCollection.features();
while (featureIterator.hasNext()) {
SimpleFeature feature = featureIterator.next();
Iterator<Property> propertyIterator = feature.getProperties().iterator();
while (propertyIterator.hasNext()) {
Property property = propertyIterator.next();
System.out.println(StrUtil.format("要素ID:{},属性:{},值:{}", feature.getID(), property.getName().toString(), property.getValue()));
}
}
featureIterator.close();
}
(1)包含了嵌套属性对象会怎么样?
要素ID:0,属性:FID,值:0
要素ID:0,属性:Id,值:0
要素ID:0,属性:name,值:医院
要素ID:0,属性:regions,值:[a, b, c]
要素ID:0,属性:workers,值:null
要素ID:0,属性:code,值:null
要素ID:0,属性:geometry,值:POINT (104.1111 34.1111)
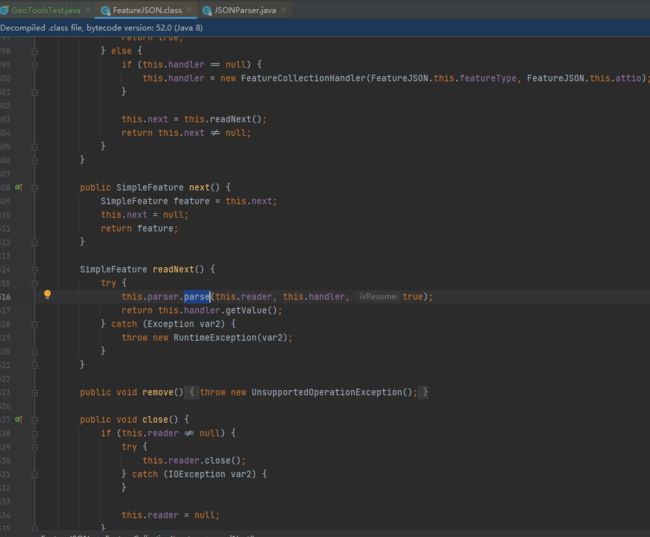
可以发现,使用FeatureJson进行解析,regions属性(字符串数组)解析正确,但是workers(嵌套数组)解析就发生了问题,workers读取失败,并且workers之后的属性也读取失败了,比如code。
简单看一下源码后有些震惊,一串的switch case嵌套,本想追一下源码分析一下问题,看到这里就算了。大致意思应该就是读取输入流形成迭代器,逐个构建成Feature返回。有问题的地方可能就是判断某个要素的流的开始、结束位置出现了问题,发生错误要素属性构建部分就跳过了。
2 通过GeoJSONReader解析
使用这个Reader工具类解析是比较好的选择,但是也有坑!先看一下正常的解析结果。
@Test
public void featureJsonTest() throws IOException {
String geoJsonFile = "D:\\MyData\\02_MyTestData\\geojson\\point_withNestedProperties.geojson";
//SimpleFeatureCollection featureCollection = (SimpleFeatureCollection) new FeatureJSON().readFeatureCollection(new FileInputStream(geoJsonFile));
GeoJSONReader reader = new GeoJSONReader(new FileInputStream(geoJsonFile));
SimpleFeatureCollection featureCollection = reader.getFeatures();
SimpleFeatureIterator featureIterator = featureCollection.features();
while (featureIterator.hasNext()) {
SimpleFeature feature = featureIterator.next();
Iterator<Property> propertyIterator = feature.getProperties().iterator();
while (propertyIterator.hasNext()) {
Property property = propertyIterator.next();
System.out.println(StrUtil.format("要素ID:{},属性:{},值:{}", feature.getID(), property.getName().toString(), property.getValue()));
}
}
featureIterator.close();
}
要素ID:0,属性:geometry,值:POINT (104.1111 34.1111)
要素ID:0,属性:FID,值:0
要素ID:0,属性:Id,值:0
要素ID:0,属性:name,值:医院
要素ID:0,属性:regions,值:[a, b, c]
要素ID:0,属性:workers,值:[{"id":"worker_1","name":"billy","age":"26"}, {"id":"worker_2","name":"bille","age":"25"}]
要素ID:0,属性:code,值:yy_0001
可以看到workers属性是正确解析的!为什么呢?
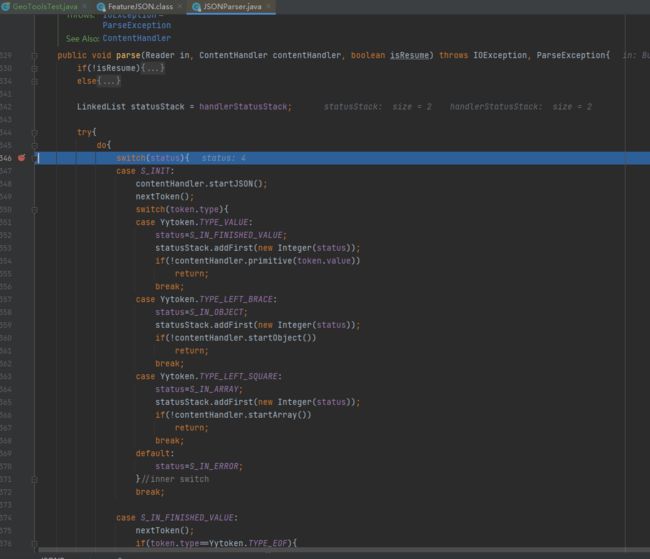
(1)GeoJSONReader的执行流程
- 首先构造函数中就明确了文件流内容,同时内部使用jackson(Json库)将数据先解析为了Json对象
- 内部处理也是逐个完整的对象获取,进行关键字的判定
- 属性构建时,会根据读取到属性节点中各个属性kv键值对中值的类型,去确定要素属性值的类型
(方法:private SimpleFeature getNextFeature(ObjectNode node) throws IOException)
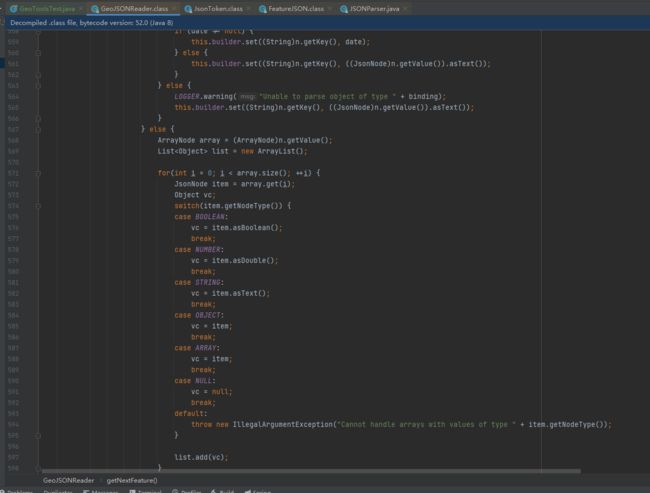
(2)坑在哪?
看执行过程中的第三步,也就是”属性构建时,会根据读取到属性节点中各个属性kv键值对中值的类型,去确定要素属性值的类型“,这里是一个switch-case语句,对通过jackson读取到的json对象的属性值类型进行了处理,当前我使用的geotools的版本是:
28.2
但是我之前使用的geotools版本是:
27.0
让我们对比一下两个版本中这段switch-case有什么不同!
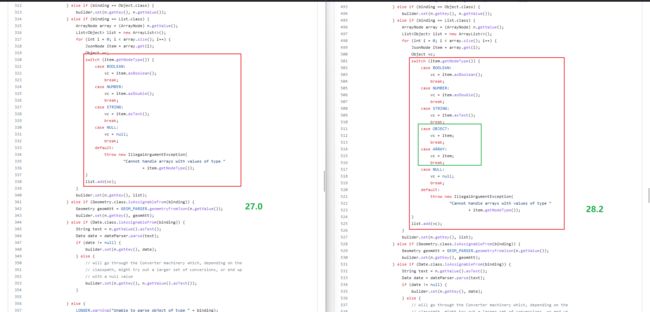
没错,27.0版本中switch分支中并没有对OBJECT、ARRAY等Json节点类型的处理!
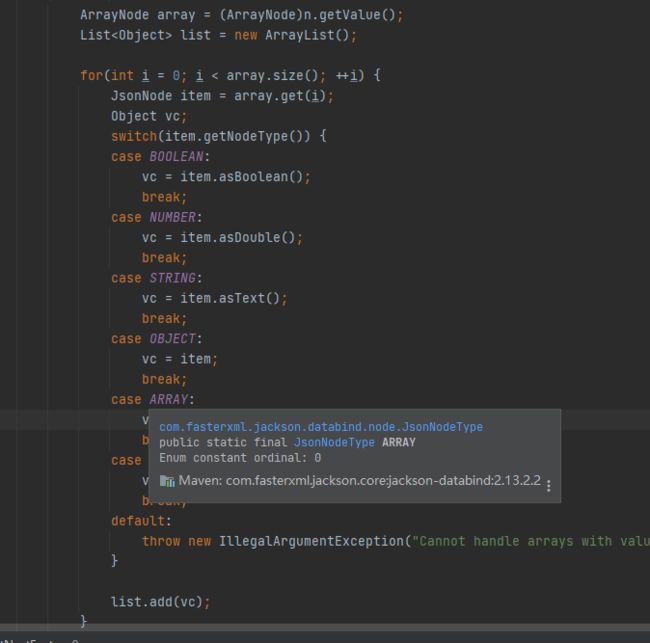

(3)建议
- 为什么之前用27.0?
秉持着老项目用啥我用啥的原则,本想避坑,结果踩坑。
- 为什么只升级到28.2,不使用最新版GeoTools?
因为较新版本对Java版本有要求,目前GeoTools对java 8最高应该就是支持到28.2!