算法拾遗二十八之单调栈结构
算法拾遗二十八之单调栈结构
-
-
- 单调栈是什么
- 题目二
- 题目三
- 题目四
- 题目五
-
单调栈是什么


0位置的3左边比他小的为-1,右边比他小的为2位置的2,依次类推
思路:
准备一个栈,让其从小到大到栈顶递增

1位置的4可以直接进来
2位置的2进来需要栈弹出元素了
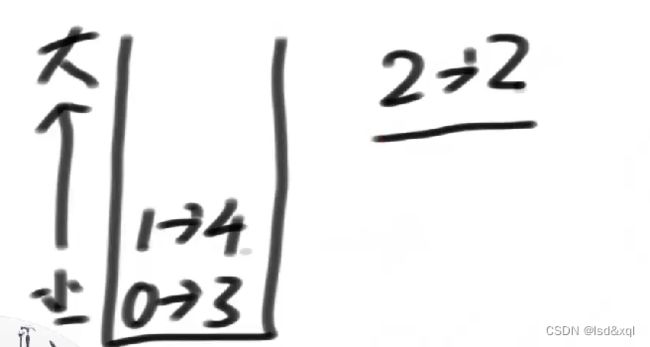
1位置右边离它近的比他小的就是2位置的2,它左边离他近的比他小的就是压着的0位置的3

然后0位置的3弹出,它的下面没有数了说明0位置的3左边没有比它小的填入负一,然后它右边有2位置的2比它小,最后栈空压栈2位置的2

然后3位置的6直接压栈进来,然后压4位置的1

依次弹出3位置的6和2位置的2生成对应信息:


如果最后栈里面还剩东西,则需要将栈里面的元素单独弹出:

7位置的5单独弹出所以右边离它最近比他小的为-1,表示没有,左边离它近的比它小的,为下面压着的数6位置的0。最后剩下6位置的0左右都是-1,表示没有
流程证明(为什么对):
首先来看在某一步:栈中b的下面压着一个a,因为c的出现导致b要从栈中弹出,c小于b才会让b弹出,在数组中b一定在c的左边,b和c中间的数不可能是小于b的,那么c就是离b右边最近的且小于b的,a在数组中一定在b的左边,分为如下情况
1)a到b中间有小于a的数,这种情况是不存在的,因为这种情况下a是被释放了的,就轮不到b和a挨着
2)a到b中间有大于a小于b的,那么a,b中间一定隔着某个数,这种情况不存在
3) 中间的数都是大于b的,那么a就是b的左边离他最近的比他小的

数组无重复值,时间复杂度为O(N)的,对于数组中每个元素最多入栈一次出栈一次
情况二:
数组中有重复值的如何处理:
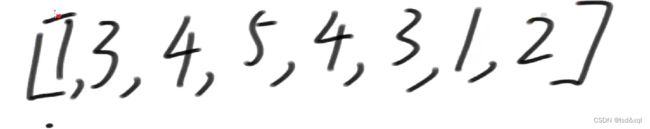
看如上数组:
还是单调栈处理:
0位置搞个小链表进去指向1
1位置搞个小链表进去指向3

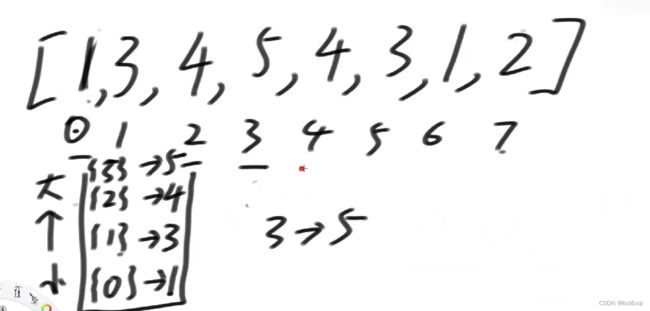
然后4位置的4,4位置的4没法落在3位置的5上,所以要拿答案:
左边的答案就是底下压着的链表的最后一个位置。

然后4位置的4和2位置的4两个值相同都是4,所以需要进行位置合并:
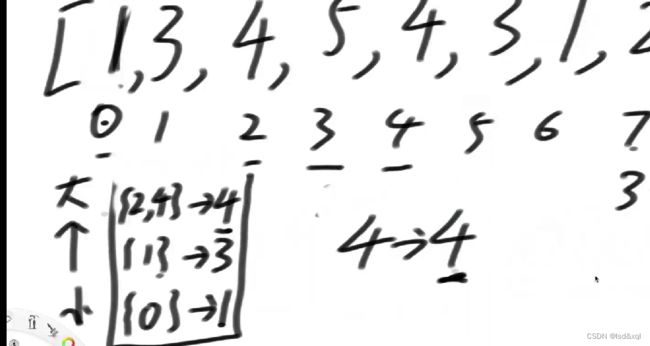
再是5位置的3进入,发现不能继续压栈,所以2位置的4和4位置的4一起结算,
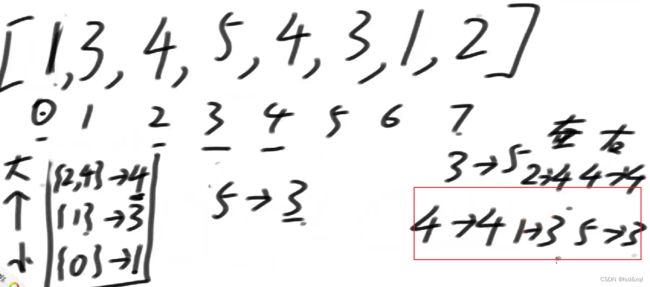
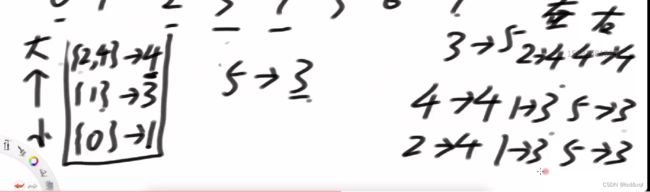
然后再压入5位置的3,发现和1位置的3一样,则构成链表一起指向3

然后结算1位置和5位置的3,
1位置的3右边是6位置的1,左边是0位置的1
5位置的3右边是6位置的1,左边是0位置的1
然后6位置的1进入:
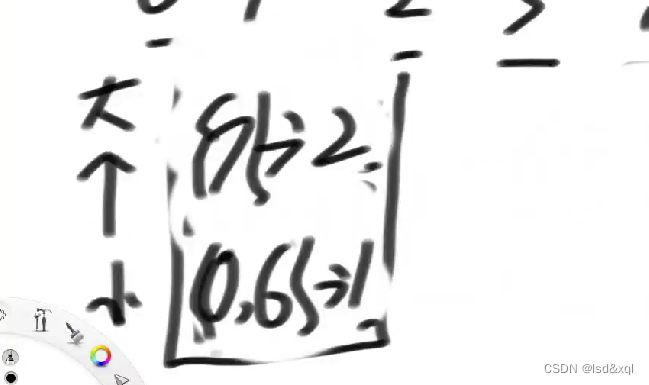
然后单独结算:
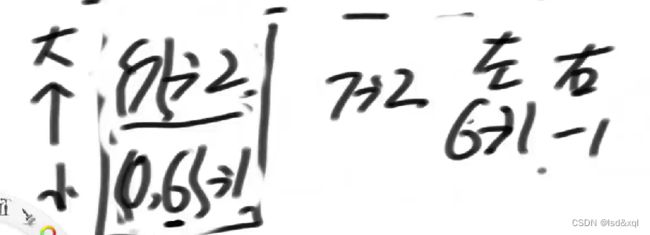
7位置的2左边是下面链表的最后一个位置就是6位置的1
public class MonotonousStack {
// arr = [ 3, 1, 2, 3]
// 0 1 2 3
// [
// 0 : [-1, 1]
// 1 : [-1, -1]
// 2 : [ 1, -1]
// 3 : [ 2, -1]
// ]
//只适用于五重复值
public static int[][] getNearLessNoRepeat(int[] arr) {
//2代表 左边比他小的位置,右边比他小的位置
int[][] res = new int[arr.length][2];
// 只存位置!
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
// 当遍历到i位置的数arr[i]时,当前栈不为空,并且当前数落不上去时
while (!stack.isEmpty() && arr[stack.peek()] > arr[i]) {
int j = stack.pop();
int leftLessIndex = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek();
//j位置左边比它小的为leftlessindex
res[j][0] = leftLessIndex;
//j位置右边比他小的位置为i
res[j][1] = i;
}
//能继续push下去放自己
stack.push(i);
}
//单独结算栈中元素
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
int j = stack.pop();
int leftLessIndex = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek();
//左边比他小的取栈下面一个元素
res[j][0] = leftLessIndex;
//右边比它小的一律没有设置成-1
res[j][1] = -1;
}
return res;
}
//支持重复值
public static int[][] getNearLess(int[] arr) {
int[][] res = new int[arr.length][2];
//栈上放一组一组的小链表
Stack<List<Integer>> stack = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { // i -> arr[i] 进栈
//栈不为空,并且链表里面第0个位置的数大于当前arr[i]则需要生成答案,要严格大于我才能设置答案
while (!stack.isEmpty() && arr[stack.peek().get(0)] > arr[i]) {
//弹出整个链表,每个位置都结算答案
List<Integer> popIs = stack.pop();
//栈不为空获取压着链表的最后一个元素位置
int leftLessIndex = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek().get(stack.peek().size() - 1);
for (Integer popi : popIs) {
res[popi][0] = leftLessIndex;
res[popi][1] = i;
}
}
//栈顶和当前数相等,则加到栈顶的链表中
if (!stack.isEmpty() && arr[stack.peek().get(0)] == arr[i]) {
stack.peek().add(Integer.valueOf(i));
} else {
//如果不相等自己搞个小链表加进去
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(i);
stack.push(list);
}
}
//遍历结束后,栈中还存在答案,单独结算
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> popIs = stack.pop();
int leftLessIndex = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek().get(stack.peek().size() - 1);
for (Integer popi : popIs) {
res[popi][0] = leftLessIndex;
res[popi][1] = -1;
}
}
return res;
}
// for test
public static int[] getRandomArrayNoRepeat(int size) {
int[] arr = new int[(int) (Math.random() * size) + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
int swapIndex = (int) (Math.random() * arr.length);
int tmp = arr[swapIndex];
arr[swapIndex] = arr[i];
arr[i] = tmp;
}
return arr;
}
// for test
public static int[] getRandomArray(int size, int max) {
int[] arr = new int[(int) (Math.random() * size) + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = (int) (Math.random() * max) - (int) (Math.random() * max);
}
return arr;
}
// for test
public static int[][] rightWay(int[] arr) {
int[][] res = new int[arr.length][2];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
int leftLessIndex = -1;
int rightLessIndex = -1;
int cur = i - 1;
while (cur >= 0) {
if (arr[cur] < arr[i]) {
leftLessIndex = cur;
break;
}
cur--;
}
cur = i + 1;
while (cur < arr.length) {
if (arr[cur] < arr[i]) {
rightLessIndex = cur;
break;
}
cur++;
}
res[i][0] = leftLessIndex;
res[i][1] = rightLessIndex;
}
return res;
}
// for test
public static boolean isEqual(int[][] res1, int[][] res2) {
if (res1.length != res2.length) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < res1.length; i++) {
if (res1[i][0] != res2[i][0] || res1[i][1] != res2[i][1]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// for test
public static void printArray(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int size = 10;
int max = 20;
int testTimes = 2000000;
System.out.println("测试开始");
for (int i = 0; i < testTimes; i++) {
int[] arr1 = getRandomArrayNoRepeat(size);
int[] arr2 = getRandomArray(size, max);
if (!isEqual(getNearLessNoRepeat(arr1), rightWay(arr1))) {
System.out.println("Oops!");
printArray(arr1);
break;
}
if (!isEqual(getNearLess(arr2), rightWay(arr2))) {
System.out.println("Oops!");
printArray(arr2);
break;
}
}
System.out.println("测试结束");
}
}
题目二

如下图数组:子数组1,4,2>累加和是7
乘以最小值也是7

思路:
我们想求必须以x位置做最小值的子数组的指标的最大值,如下图必须以3开始且3是最小值的子数组最大为【3,4】的时候得出指标为21
,再推导以4作为最小值的时候得出的结果为16
再推导以2作为最小的时候得到的结果以此类推从而得到最终的结果。

已知i位置的数为x我想求数组必须以x作为最小值,如何能得到哪一个子数组累加和最大,找左边离x最近的比x小的,右边离x最近的比x小的,求中间那一坨就是结果。一定要以x做最小值,那么只需要保证累加和最大

写代码时需要预处理一个前缀和数组以便处理累加和
再看如下例子
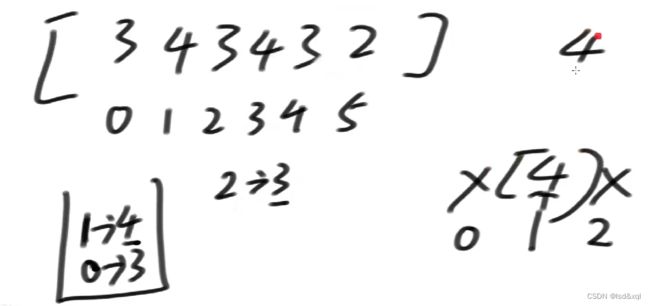
首先0位置的3进去,1位置的4进去,轮到2位置的3发现进不去,需要弹出4,从而得出4的答案,右边离他最近的比他小的到不了,左边离他近的比他小的到不了只能自己乘以自己4乘4等于16
2位置的3此时要进去,此时不压缩,算出0位置3所对应的答案就是(3+4)乘以3,这样没算对,但是我们可以等到算四位置的3的时候把它算对。相等的时候就让他弹出,并且算出答案,压入后一个相等的值进去,让后面的相等值去让他算对。
public static int max1(int[] arr) {
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (int j = i; j < arr.length; j++) {
int minNum = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int sum = 0;
for (int k = i; k <= j; k++) {
sum += arr[k];
minNum = Math.min(minNum, arr[k]);
}
max = Math.max(max, minNum * sum);
}
}
return max;
}
public static int max2(int[] arr) {
int size = arr.length;
int[] sums = new int[size];
sums[0] = arr[0];
//生成前缀和
for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) {
sums[i] = sums[i - 1] + arr[i];
}
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
//涉及单调栈的改进
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
//大于等于就弹出
while (!stack.isEmpty() && arr[stack.peek()] >= arr[i]) {
int j = stack.pop();
max = Math.max(max, (stack.isEmpty() ? sums[i - 1] : (sums[i - 1] - sums[stack.peek()])) * arr[j]);
}
stack.push(i);
}
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
int j = stack.pop();
max = Math.max(max, (stack.isEmpty() ? sums[size - 1] : (sums[size - 1] - sums[stack.peek()])) * arr[j]);
}
return max;
}
public static int[] gerenareRondomArray() {
int[] arr = new int[(int) (Math.random() * 20) + 10];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = (int) (Math.random() * 101);
}
return arr;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int testTimes = 2000000;
System.out.println("test begin");
for (int i = 0; i < testTimes; i++) {
int[] arr = gerenareRondomArray();
if (max1(arr) != max2(arr)) {
System.out.println("FUCK!");
break;
}
}
System.out.println("test finish");
}
题目三


如上图最大长方形面积为10
思路:
求解过程每次以每个格子的高度为基准扩展出最大长方形是多大。
import java.util.Stack;
// 测试链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histogram
public class LargestRectangleInHistogram {
public static int largestRectangleArea1(int[] height) {
if (height == null || height.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int maxArea = 0;
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < height.length; i++) {
while (!stack.isEmpty() && height[i] <= height[stack.peek()]) {
int j = stack.pop();
int k = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek();
int curArea = (i - k - 1) * height[j];
maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, curArea);
}
stack.push(i);
}
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
int j = stack.pop();
int k = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek();
int curArea = (height.length - k - 1) * height[j];
maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, curArea);
}
return maxArea;
}
public static int largestRectangleArea2(int[] height) {
if (height == null || height.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int N = height.length;
int[] stack = new int[N];
int si = -1;
int maxArea = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < height.length; i++) {
while (si != -1 && height[i] <= height[stack[si]]) {
int j = stack[si--];
int k = si == -1 ? -1 : stack[si];
int curArea = (i - k - 1) * height[j];
maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, curArea);
}
stack[++si] = i;
}
while (si != -1) {
int j = stack[si--];
int k = si == -1 ? -1 : stack[si];
int curArea = (height.length - k - 1) * height[j];
maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, curArea);
}
return maxArea;
}
}
题目四

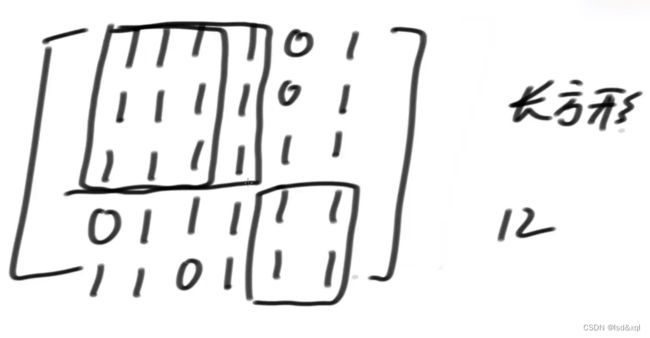
如上图返回12
n*n的矩阵中,子矩阵的数量为n的四次方
思路:
采用压缩数组的方式求解:
时间复杂度O(N方)
和上一题一样每次以一行作为底基,看能构成的直方图有多大,每一行看一次每一行看一次,找到最大的面积。

// 测试链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximal-rectangle/
public class MaximalRectangle {
public static int maximalRectangle(char[][] map) {
if (map == null || map.length == 0 || map[0].length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int maxArea = 0;
int[] height = new int[map[0].length];
for (int i = 0; i < map.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < map[0].length; j++) {
height[j] = map[i][j] == '0' ? 0 : height[j] + 1;
}
maxArea = Math.max(maxRecFromBottom(height), maxArea);
}
return maxArea;
}
// height是正方图数组
public static int maxRecFromBottom(int[] height) {
if (height == null || height.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int maxArea = 0;
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < height.length; i++) {
while (!stack.isEmpty() && height[i] <= height[stack.peek()]) {
int j = stack.pop();
int k = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek();
int curArea = (i - k - 1) * height[j];
maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, curArea);
}
stack.push(i);
}
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
int j = stack.pop();
int k = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek();
int curArea = (height.length - k - 1) * height[j];
maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, curArea);
}
return maxArea;
}
}
题目五
推导公式:
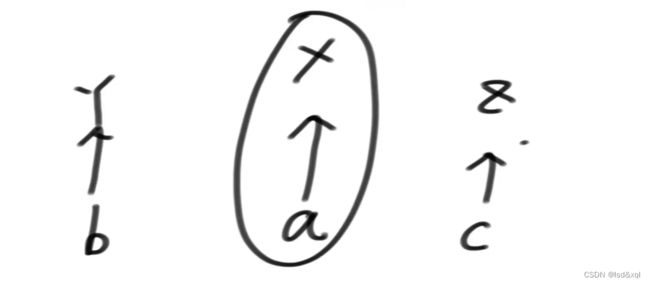
左边离他最近比他小的位置在b值是y,右边离他近的比他小的位置在c值是z,
那么其中的子矩阵数量应为(x-max(y,z))乘以(L*(L+1))/2
看实际例子:
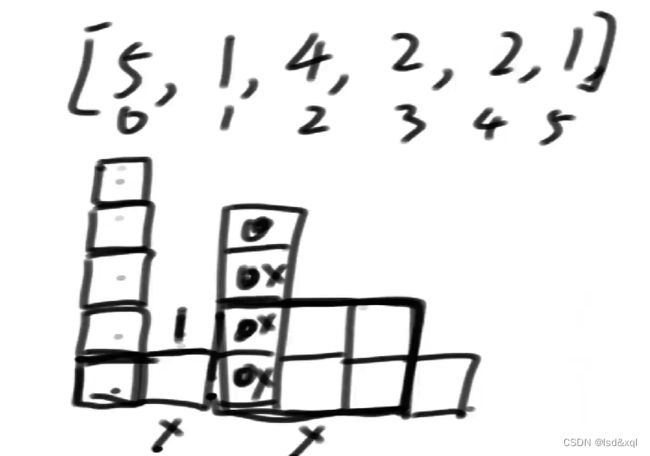
首先零位置的5进来,发现左边比他小的在-1位置,右边比他小的在1位置高度为4,当1位置的1进来的时候需要释放它(结果为:(5-max(0,1))乘以(1*(1+1))/2) = 4
然后1位置的1进去了,二位置的4直接进
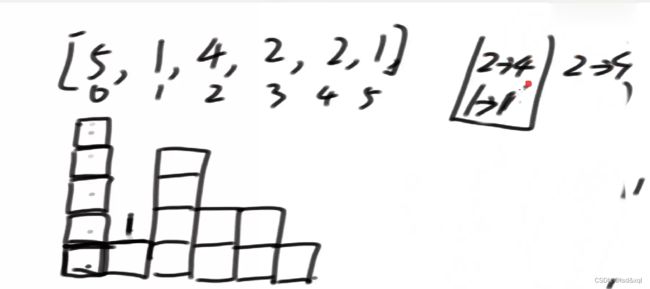
然后3位置的2进来时,2位置的4左边到不了的是1位置的1,右边到不了的是3位置的2,还是只有自己一个单位,通过公式算出结果为2,代表高度为3的自己和高度为4的自己。
然后3位置的2入栈,原2位置的4出栈,然后4位置的2进来发现两个算的一样的值,3位置的2不算了,通过4位置的2找联通区域统一算。
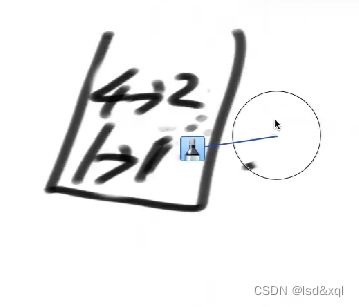
接下来5位置的1进来,要释放4位置的2,比他小的最近的分别是1位置的1和5位置的1。

高度为2对应的情况,(2-max(0,1))乘以(3*(3+1))/2) =6
最后5位置的1进去,弹出1位置1,算整个为1的联通区域长方形
// 测试链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/count-submatrices-with-all-ones
public class Code05_CountSubmatricesWithAllOnes {
public static int numSubmat(int[][] mat) {
if (mat == null || mat.length == 0 || mat[0].length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int nums = 0;
int[] height = new int[mat[0].length];
for (int i = 0; i < mat.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < mat[0].length; j++) {
height[j] = mat[i][j] == 0 ? 0 : height[j] + 1;
}
nums += countFromBottom(height);
}
return nums;
}
// 比如
// 1
// 1
// 1 1
// 1 1 1
// 1 1 1
// 1 1 1
//
// 2 .... 6 .... 9
// 如上图,假设在6位置,1的高度为6
// 在6位置的左边,离6位置最近、且小于高度6的位置是2,2位置的高度是3
// 在6位置的右边,离6位置最近、且小于高度6的位置是9,9位置的高度是4
// 此时我们求什么?
// 1) 求在3~8范围上,必须以高度6作为高的矩形,有几个?
// 2) 求在3~8范围上,必须以高度5作为高的矩形,有几个?
// 也就是说,<=4的高度,一律不求
// 那么,1) 求必须以位置6的高度6作为高的矩形,有几个?
// 3..3 3..4 3..5 3..6 3..7 3..8
// 4..4 4..5 4..6 4..7 4..8
// 5..5 5..6 5..7 5..8
// 6..6 6..7 6..8
// 7..7 7..8
// 8..8
// 这么多!= 21 = (9 - 2 - 1) * (9 - 2) / 2
// 这就是任何一个数字从栈里弹出的时候,计算矩形数量的方式
public static int countFromBottom(int[] height) {
if (height == null || height.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int nums = 0;
int[] stack = new int[height.length];
int si = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < height.length; i++) {
while (si != -1 && height[stack[si]] >= height[i]) {
int cur = stack[si--];
if (height[cur] > height[i]) {
int left = si == -1 ? -1 : stack[si];
int n = i - left - 1;
int down = Math.max(left == -1 ? 0 : height[left], height[i]);
//每个高度乘以算的累加
nums += (height[cur] - down) * num(n);
}
}
stack[++si] = i;
}
while (si != -1) {
int cur = stack[si--];
int left = si == -1 ? -1 : stack[si];
int n = height.length - left - 1;
int down = left == -1 ? 0 : height[left];
nums += (height[cur] - down) * num(n);
}
return nums;
}
public static int num(int n) {
return ((n * (1 + n)) >> 1);
}
}

