面试高频代码题
文章目录
-
- 链表
-
- 1.删除有序链表中的重复链表
- 2.删除有序链表的重复数组并只保留只出现过一次的结点
- 3. 无序单链表升序排列
- 数组
-
- 1. 冒泡排序
- 2. 折半查找
- 3. 快排
- 4.给1001个数,有一个是重复的,如何不使用额外空间找出来这个数?(微软)
- 5.给一个整数判单是否是2的n次幂
- 6.和为K的最长连续子数组的长度
- 7.矩阵乘法
- 8.最长公共前序
- 字符串
-
- 1.字符串压缩
- 3.最长不重复字符的最长子串(百度)
- 4.旋转字符串
- 二叉树
-
- 1.返回二叉树的层次遍历结果
- 3. 计算二叉树的个数
- 2.二叉树的前中后遍历
- 3.二叉树中和为某一值的路径
- 4.二叉树的非递归前序遍历
- 5.二叉树的非递归中序遍历
- SQL
-
-
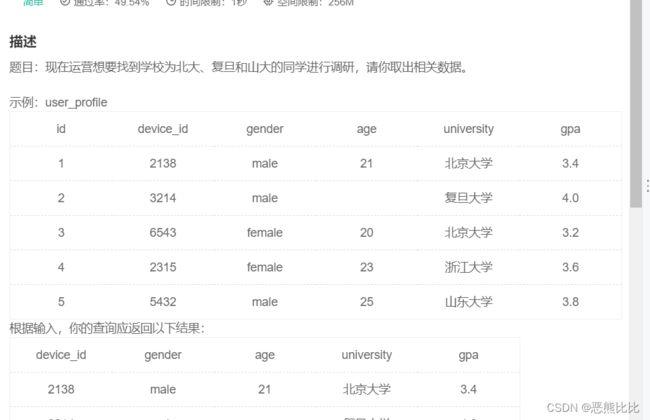
- 1.去重加模糊查询
- 2.过滤空值
- 3. in he not in
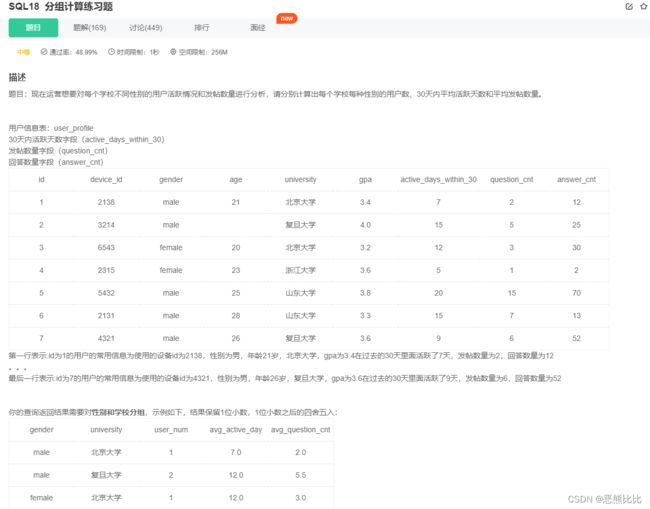
- 4.分组计算
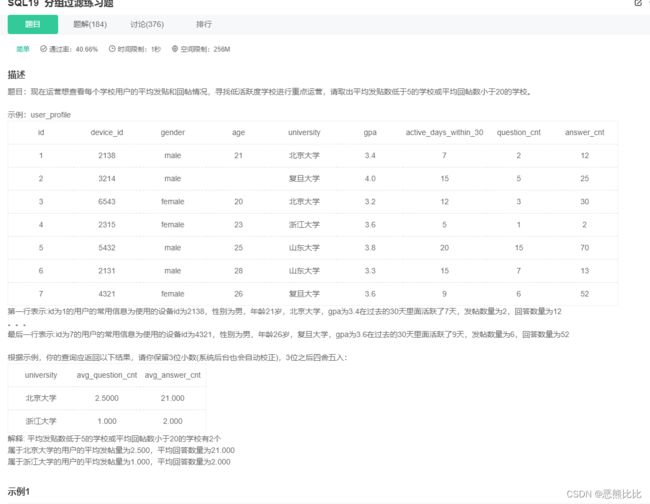
- 5.分组过滤
- 6.多表查询
-
链表
1.删除有序链表中的重复链表
来源:ali
leetcode 83
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
ListNode p=head;
while(p!=null && p.next !=null){
ListNode pre=p.next;
if(pre.val==p.val){
p.next=pre.next;
}else{
p=p.next;
}
}
return head;
}
}
2.删除有序链表的重复数组并只保留只出现过一次的结点
新建一个虚拟头节点dummy,将其next指针指向原链表头节点head。使用指针变量p遍历链表,如果发现当前节点及其后继节点的值相等,则使用一个循环将所有重复的节点跳过,直到找到第一个不重复的节点。如果当前节点和后继节点的值不相等,则将指针p向后移动一个位置。
最后返回虚拟头节点dummy的后继节点,即为修改后的链表的头节点。
import java.util.*;
/*
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next = null;
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param head ListNode类
* @return ListNode类
*/
public ListNode deleteDuplicates (ListNode head) {
// write code here
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode dummyhead = new ListNode(0);
dummyhead.next = head;
ListNode p = dummyhead;
while (p.next != null && p.next.next != null) {
//遇到相邻结点相同
if (p.next.val==p.next.next.val) {
int temp=p.next.val;
//将所有相同的都跳过
while(p.next!=null &&p.next.val==temp){
p.next=p.next.next;
}
} else {
p=p.next;
}
}
//返回时去掉表头
return dummyhead.next;
}
}
3. 无序单链表升序排列
import java.util.*;
/*
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next = null;
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param head ListNode类 the head node
* @return ListNode类
*/
public ListNode sortInList (ListNode head) {
// 归并排序
//只有一个或没有结点
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
//将链表分成两半
ListNode mid = getMid(head);
ListNode next = mid.next;
mid.next = null;
//左右链表继续递归排序
ListNode left = sortInList(head);
ListNode right = sortInList(next);
return meger(left, right);
}
public static ListNode getMid(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
public static ListNode meger(ListNode left, ListNode right) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode p = dummy;
while (left != null && right != null) {
if (left.val < right.val) {
p.next = left;
left = left.next;
} else {
p.next = right;
right = right.next;
}
p=p.next;
}
p.next = (left != null) ? left : right;
return dummy.next;
}
}
数组
1. 冒泡排序
#冒泡排序
arr = [13,44,54,23,9,15,93,65]
def BS(arr):
for i in range(len(arr)-1,0,-1):
count =0
for j in range(0,i):
if(arr[j]>arr[j+1]):
count=count+1
arr[j],arr[j+1] = arr[j+1],arr[j]
if(count==0):
return arr
print(BS(arr))
2. 折半查找
#二分查找
arr = [9, 13, 15, 23, 44, 54, 65, 93]
flag = 13
def Sb(arr,flag):
start = 0
end = len(arr)-1
while(start<=end):
mid = (start+end)//2
if(arr[mid]==flag):
return mid
elif(arr[mid]<flag):
start=mid+1
else:
end=mid-1
return start
print(Sb(arr,flag))
3. 快排
基本思路是
选择一个元素作为基准值(pivot),将待排序序列划分成两个子序列,其中一个子序列中的元素都小于等于基准值,另一个子序列中的元素都大于等于基准值,然后再对这两个子序列分别进行递归排序,直到整个序列有序
具体实现过程如下:
-
选择一个基准值pivot,通常是待排序序列中的第一个或最后一个元素。
-
将待排序序列中小于等于pivot的元素放在pivot的左边,大于等于pivot的元素放在pivot的右边,这个过程称为分区(partition)。
-
对左右两个子序列分别进行递归排序,直到子序列长度为1或0时停止递归。
快速排序的优点在于实现简单、运行速度快,在大多数情况下可以达到O(nlogn)的时间复杂度,相比其他排序算法具有更高的效率。但它的缺点也比较明显,当待排序序列近乎有序时,会导致快排的时间复杂度退化为O(n^2),因此需要针对不同的数据情况进行优化。
arr = [13,44,54,23,9,15,93,65]
def quicksort(arr):
if len(arr)==0 or len(arr)==1:
return arr
pivot = arr[0]
left=[]
right=[]
for i in range(1,len(arr)):
if arr[i]<pivot:
left.append(arr[i])
else:
right.append(arr[i])
return quicksort(left)+[pivot]+quicksort(right)
print(quicksort(arr))
4.给1001个数,有一个是重复的,如何不使用额外空间找出来这个数?(微软)
方法1:如果加条件说是在不重复的数在1-1000之间
直接将数字总和加起来-(1+1000)1000/2
方法2:亦或运算
private static int findnumber2(int[] i) {
{
int re = i[0];
for(int k=1;k<i.length;k++)
{
re = re^i[k];
}
return re;
}
5.给一个整数判单是否是2的n次幂
方法1:暴力破解,如果一个数是2的n次幂,你们它的二进制表示只有一个1
nums = 5
def is_power_of_two(n):
return n > 0 and (n & (n - 1)) == 0
print(is_power_of_two(nums))
该函数首先检查n是否为正整数(因为负数和零都不可能是2的n次幂)。然后,它使用按位与运算符来比较n和n-1的值,以检查二进制表示中是否只有一个1。如果结果为0,则n是2的n次幂;否则,它不是。
(n & (n-1)) == 0 是一个用于判断一个整数 n 是否为2的n次幂的常见技巧。该表达式基于以下性质:如果 n 是2的n次幂,则它的二进制表示中只有一位是1,也就是说,n 的二进制表示为100…00(共有 n 个0)。
因此,如果我们将 n 减去1,得到的结果二进制表示为011…11(共有 n 个1)。然后,如果我们将 n 和 n-1 进行按位与运算,得到的结果应该为0,因为 n 和 n-1 的二进制表示除了最高位以外都是相同的。换句话说,按位与运算会消除 n 中的那个唯一的1。
public static boolean isPowerOfTwo(int n) {
return n > 0 && (n & (n - 1)) == 0;
}
6.和为K的最长连续子数组的长度
解题思路:
暴力破解 将对该数组存在的每个子数组都进行一个判断
import java.util.*;
public class sumK {
/**
* max length of the subarray sum = k
* @param arr int整型一维数组 the array
* @param k int整型 target
* @return int整型
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {5,-1,-2,-3,3,2,1};
int k = 0;
System.out.println(maxlenEqualK(nums, k));
}
public static int maxlenEqualK (int[] arr, int k) {
// write code here
//滑动窗口+双指针
int temp=0,res=0;
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
temp = arr[i];
for(int j=i+1;j<arr.length;j++){
temp+=arr[j];
if(temp==k){
res = Math.max(res,j-i+1);
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
解释:
基本思想是:如果第i个位置总和为a,第j个位置总和为b,那么在j位置时若发现b-a=k,则a-b之间就是总和为k的子数组
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**
* max length of the subarray sum = k
* @param arr int整型一维数组 the array
* @param k int整型 target
* @return int整型
*/
public int maxlenEqualK (int[] arr, int k) {
// write code here
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
//map用于存储当前滑动窗口的子数组总和和当前滑动窗口的左边界
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
map.put(0, -1);
//res表示最终结果
//temp表示滑动窗口的子数组总和
int res = 0;
int temp = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
temp += arr[i];
//判断temp-k是否等于当前左边界的那个数
if (map.containsKey(temp - k)) {
res = Math.max(i - map.get(temp - k), res);
}
if (!map.containsKey(temp)) {
map.put(temp, i);
}
}
return res;
}
}
7.矩阵乘法
三层循环直接背吧
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
* @param a int整型二维数组 第一个矩阵
* @param b int整型二维数组 第二个矩阵
* @return int整型二维数组
*/
public int[][] solve (int[][] a, int[][] b) {
// write code here
int n = a.length;
int[][] res = new int[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++){
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++){
res[i][j] += a[i][k]*b[k][j];
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
8.最长公共前序
leetcode 14
思路:
将数组中的第一个字符作为基准
每次遍历,先判断字符串长度,判断两个字符串最短的长度,先对结果字符串进行切割;
然后根据最小长度开始二层循环遍历,如果找到不同的字符,再次切割跳出循环;
class Solution {
public String longestCommonPrefix(String[] strs) {
String res = "";
res = strs[0];
for(String s:strs){
int len = Math.min(res.length(),s.length());
res = res.substring(0,len);
for(int j=0;j<res.length();j++){
char c1 = s.charAt(j);
char c2 = res.charAt(j);
if(c1!=c2){
res = res.substring(0,j);
break;
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
作者:meini
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/longest-common-prefix/solution/java-by-meini-3m9j/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
字符串
1.字符串压缩
来源:ali
leetcode地址:https://leetcode.cn/problems/compress-string-lcci/
算法思想:借助双指针,左指针指向最左边的一个字符,右指针开始遍历,直至遍历到的字符于左指针的不同,统计他们之间的子字符串个数;
左指针指向下一个字符
class Solution {
public String compressString(String S) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int left=0,right=0;
while(left<S.length()){
while(right<S.length() && S.charAt(right)==S.charAt(left)){
right++;
}
sb.append(S.charAt(left)).append(right-left);
left=right;
}
return S.length()>sb.toString().length()?sb.toString():S;
}
}
3.最长不重复字符的最长子串(百度)
3
方法:滑动窗口+双指针
算法思想:
类似于创建了一个队列,不断的从队列尾部添加字符,如果添加的这个字符原来的队列里没有,加入并统计当前队列的个数,判断是否大于最长的临时结果,如果是则替换;如果添加的这个字符原来的队列中有,从对头开始移除元素,
import java.util.HashSet;
//输出最大字串的大小
public class MaxSubString_nums {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "abcabcbb";
System.out.println(subNums(s));
}
private static int subNums(String s) {
//双指针+滑动窗口
int maxS = 0;
int start=0,end=0;
HashSet<Character> set = new HashSet<>();
while (end<s.length()){
char c = s.charAt(end);
if(!set.contains(c)){
set.add(c);
end++;
if(end-start>maxS){
maxS=end-start;
}
}else {
set.remove(s.charAt(start));
start++;
}
}
return maxS;
}
}
4.旋转字符串
1 判断A和B字符串大小是否相等
2 枚举所有可能的子字符串 substring()
3.判断
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**
* 旋转字符串
* @param A string字符串
* @param B string字符串
* @return bool布尔型
*/
public boolean solve (String A, String B) {
// 暴力破解
if(A.length()!=B.length()){
return false;
}
for (int i=0;i<A.length();i++){
String left = A.substring(0,i);
String right = A.substring(i);
String res = right+left;
if(res.equals(B)){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
二叉树
1.返回二叉树的层次遍历结果
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return new ArrayList<>();
}
//创建一个列表用于存储结果
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
//创建队列用于遍历二叉树
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int count = queue.size();
while(count>0){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
temp.add(node.val);
if(node.left!=null){
queue.add(node.left);
}
if(node.right!=null){
queue.add(node.right);
}
count--;
}
res.add(temp);
}
return res;
}
}
3. 计算二叉树的个数
222
public static int numberTreeNode(TreeNode root) {
int nodes = 0;
if ( root == null) {
return nodes;
}
nodes = 1 + numberTreeNode(root.left) + numberTreeNode(root.right);
return nodes;
}
2.二叉树的前中后遍历
import java.util.*;
/*
* public class TreeNode {
* int val = 0;
* TreeNode left = null;
* TreeNode right = null;
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param root TreeNode类 the root of binary tree
* @return int整型二维数组
*/
public int[][] threeOrders (TreeNode root) {
// write code here
//三个集合,分别存储三种遍历结果
List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> list3 = new ArrayList<>();
preOrder(root, list1);
midOrder(root, list2);
aftOrder(root, list3);
int[][] res = new int[3][list1.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < list1.size(); i++) {
res[0][i] = list1.get(i);
res[1][i] = list2.get(i);
res[2][i] = list3.get(i);
}
return res;
}
public static void preOrder(TreeNode root, List list) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
list.add(root.val);
preOrder(root.left,list);
preOrder(root.right,list);
}
public static void midOrder(TreeNode root, List list) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
midOrder(root.left,list);
list.add(root.val);
midOrder(root.right,list);
}
public static void aftOrder(TreeNode root, List list) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
aftOrder(root.left,list);
aftOrder(root.right,list);
list.add(root.val);
}
}
3.二叉树中和为某一值的路径
要计算是否有一条到叶子结点的路径的和等于sum
转换成用sum减去除了叶子结点以外的结点值 结果是否等于叶子结点的值
import java.util.*;
/*
* public class TreeNode {
* int val = 0;
* TreeNode left = null;
* TreeNode right = null;
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param root TreeNode类
* @param sum int整型
* @return bool布尔型
*/
public boolean hasPathSum (TreeNode root, int sum) {
// write code here
if (root==null){
return false;
}
//判断叶子结点是否等于(sum-当前路径上的其他结点的值)
if(root.right==null&&root.left==null){
return(sum==root.val);
}
//递归
return hasPathSum (root.left, sum-root.val)||hasPathSum (root.right, sum-root.val);
}
}
4.二叉树的非递归前序遍历
//利用栈的思想,每次先入右节点在入左结点
import java.util.*;
/*
* public class TreeNode {
* int val = 0;
* TreeNode left = null;
* TreeNode right = null;
* public TreeNode(int val) {
* this.val = val;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param root TreeNode类
* @return int整型一维数组
*/
public int[] preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
if (root == null){
return new int[0];
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()){
//处理根节点
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
list.add(node.val);
//根左右,由于栈是先进后出,所以要让左节点后入栈,这样才能先弹出来
if (node.right!=null){
stack.push(node.right);
}
if (node.left != null){
stack.push(node.left);
}
}
return list.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
}
}
5.二叉树的非递归中序遍历
可以通过模拟递归的方式,使用栈来实现二叉树的中序遍历。具体步骤如下:
初始化一个栈和一个指向根节点的指针。 将指针指向的节点以及左子树全部入栈,直到指针为空。 弹出栈顶元素作为当前节点,并输出该节点的值。
将指针指向当前节点的右子树,重复步骤2-4,直到栈为空或者指针为空
import java.util.*;
/*
* public class TreeNode {
* int val = 0;
* TreeNode left = null;
* TreeNode right = null;
* public TreeNode(int val) {
* this.val = val;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param root TreeNode类
* @return int整型一维数组
*/
public int[] inorderTraversal (TreeNode root) {
// write code here
if (root == null) {
return new int[0];
}
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();
TreeNode p = root;
while (!stack.isEmpty() || p != null) {
while (p != null) {
stack.push(p);
p = p.left;
}
p = stack.pop();
res.add(p.val);
p = p.right;
}
return res.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
}
}
SQL
1.去重加模糊查询
select
count(distinct device_id) as did_cnt,
count(question_id) as question_cnt
from
question_practice_detail
where date like "%21-08-%";
2.过滤空值
select device_id,gender,age,university
from user_profile
where age is not null;
3. in he not in
select device_id, gender, age, university ,gpa
from user_profile
where university in("北京大学" , "山东大学" ,"复旦大学");
4.分组计算
select
gender,
university,
count(id) as user_num,
avg(active_days_within_30) as avg_active_day,
avg(question_cnt) as avg_question_cnt
from user_profile
group by university,gender;
5.分组过滤
select
university,
avg(question_cnt) as avg_question_cnt,
avg(answer_cnt) as avg_answer_cnt
from
user_profile
group by
university
having
avg_question_cnt < 5
or avg_answer_cnt < 20;
6.多表查询
https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/55f3d94c3f4d47b69833b335867c06c1?tpId=199&tqId=1975672&ru=%2Fpractice%2Fddbcedcd9600403296038ee44a172f2d&qru=%2Fta%2Fsql-quick-study%2Fquestion-ranking&sourceUrl=%2Fexam%2Fcompany
方法1:多表连接查询
select
a1.device_id,
question_id,
result
from
question_practice_detail as a1,
user_profile as a2
where
a1.device_id = a2.device_id
and university = "浙江大学";
方法2:子查询
select
device_id,
question_id,
result
from
question_practice_detail
where
device_id IN (
select
device_id
from
user_profile
where
university = "浙江大学"
)
方法3:内连接
select
q.device_id,
question_id,
result
from
question_practice_detail q
inner join user_profile u on q.device_id = u.device_id
where
university = '浙江大学'