java学习之接口二
目录
一、接口vs继承
一、继承
二、接口
二、接口多态特性
一、多态参数
二、多态数组
三、多态传递
三、接口练习
一、接口vs继承
一、继承
package com.hspedu.interface_;
public class ExtendsVsInterface {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LittleMonkey wuKong = new LittleMonkey("悟空");
wuKong.climbing();
}
}
//父类
class Monkey{
private String name;
public Monkey(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
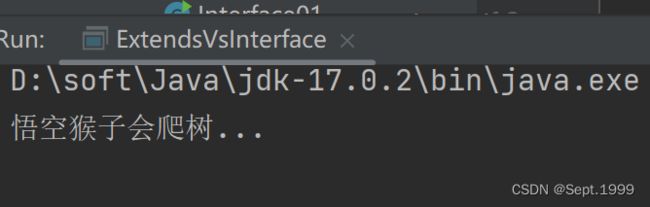
public void climbing(){
System.out.println(name + "猴子会爬树...");
}
}
class LittleMonkey extends Monkey{
public LittleMonkey(String name) {
super(name);
}
}子类继承了父类,也继承了父类的方法,根据继承查找原则,就会输出以下内容
二、接口
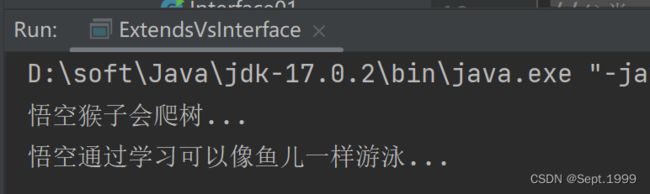
但是如果希望“悟空”能像鱼一样游泳,像鸟儿一样飞翔,就只能通过实现接口来完成
package com.hspedu.interface_;
public class ExtendsVsInterface {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LittleMonkey wuKong = new LittleMonkey("悟空");
wuKong.climbing();
wuKong.swim();
}
}
//父类
class Monkey{
private String name;
public Monkey(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void climbing(){
System.out.println(name + "猴子会爬树...");
}
}
//接口
interface Fishable{
void swim();
}
class LittleMonkey extends Monkey implements Fishable{
public LittleMonkey(String name) {
super(name);
}
@Override
public void swim() {
System.out.println(getName() + "通过学习可以像鱼儿一样游泳...");
}
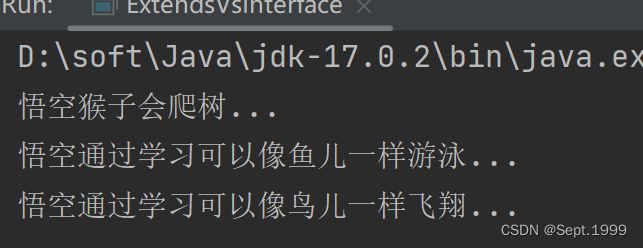
}由于一个类可以实现多个接口,所以也可以实现像鸟儿一样飞翔
package com.hspedu.interface_;
public class ExtendsVsInterface {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LittleMonkey wuKong = new LittleMonkey("悟空");
wuKong.climbing();
wuKong.swim();
wuKong.fly();
}
}
//父类
class Monkey{
private String name;
public Monkey(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void climbing(){
System.out.println(name + "猴子会爬树...");
}
}
//接口
interface Fishable{
void swim();
}
interface Birdable{
void fly();
}
class LittleMonkey extends Monkey implements Fishable,Birdable{
public LittleMonkey(String name) {
super(name);
}
@Override
public void swim() {
System.out.println(getName() + "通过学习可以像鱼儿一样游泳...");
}
@Override
public void fly() {
System.out.println(getName() + "通过学习可以像鸟儿一样飞翔...");
}
} 小结: 当子类继承了父类, 就自动的拥有父类的功能
如果子类需要扩展功能, 可以通过实现接口的方式扩展.
可以理解实现接口 是 对 java 单继承机制的一种补充.
二、接口多态特性
一、多态参数
package com.hspedu.interface_;
public class Computer {
//编写一个方法,计算机工作
//解读:
//1.UsbInterface usbInterface形参是接口类型UsbInterface
//2.可以接收Camera类和Phone类的对象实例(实参),因为这两个类实现了UsbInterface接口
public void work(UsbInterface usbInterface){
usbInterface.start();
usbInterface.stop();
}
}package com.hspedu.interface_;
public class Interface01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建手机、相机对象
Phone phone = new Phone();
Camera camera = new Camera();
//创建计算机
Computer computer = new Computer();
computer.work(phone);//把手机接入到计算机
System.out.println("=============");
computer.work(camera);//把相机接入到计算机
}
}
进一步说明
package com.hspedu.interface_;
public class InterfacePolyParameter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//接口的多态体现:类似父类引用指向子类对象
//接口类型的变量ig1 可以指向 实现了IG接口的类(Monster、Car)的对象实例
IG ig1 = new Monster();
ig1 = new Car();
//继承体现的多态
//父类的对象引用指向子类对象本身
A02 a02 = new B02();
a02 = new C02();
}
}
interface IG{}
class Monster implements IG{}
class Car implements IG{}
class A02{
}
class B02 extends A02{}
class C02 extends A02{}二、多态数组
package com.hspedu.interface_;
public class InterfacePolyArr {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Usb[] usbs = new Usb[2];
usbs[0] = new Phone_();
usbs[1] = new Camera_();
for (int i = 0; i < usbs.length; i++) {
usbs[i].work();//动态绑定机制
if(usbs[i] instanceof Phone_){
//向上转型之后不能调用子类特有的成员,所以必须再向下转型
Phone_ phone_ = (Phone_) usbs[i];
phone_.call();
}
}
}
}
interface Usb{
void work();
}
class Phone_ implements Usb{
@Override
public void work() {
System.out.println("手机正在工作...");
}
public void call(){
System.out.println("有电话进来了...");
}
}
class Camera_ implements Usb{
@Override
public void work() {
System.out.println("相机正在工作...");
}
}
三、多态传递
package com.hspedu.interface_;
public class InterfacePolyPass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//可以指向实现了接口的类的对象实例
IH ih = new Teacher();
IJ ij = new Teacher();
}
}
//接口多态的传递性
interface IJ{ }
interface IH{ }
class Teacher implements IH{
}
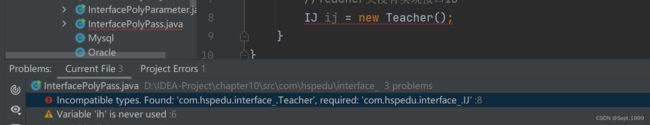
由于Teacher类没有实现接口IJ,所以上述写法是会报错的
但是如果让IH继承IJ,就可以了,这就是接口多态的传递
package com.hspedu.interface_;
public class InterfacePolyPass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//接口类型的变量可以指向实现了接口的类的对象实例
IH ih = new Teacher();
//Teacher类没有实现接口IJ,但是IH继承了IJ,也是可以的
IJ ij = new Teacher();
}
}
//接口多态的传递性
interface IJ{ }
interface IH extends IJ{ }
class Teacher implements IH{
}
同样的,如果接口IJ中有抽象方法,那么Teacher类也需要去实现这些抽象方法
package com.hspedu.interface_;
public class InterfacePolyPass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//接口类型的变量可以指向实现了接口的类的对象实例
IH ih = new Teacher();
//Teacher类没有实现接口IJ,但是IH继承了IJ,也是可以的
IJ ij = new Teacher();
}
}
//接口多态的传递性
interface IJ{
void hi();
}
interface IH extends IJ{ }
class Teacher implements IH{
@Override
public void hi() {
System.out.println("hi。。。");
}
}
三、接口练习
package com.hspedu.interface_;
public class InterfaceExercise02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new C().pX();
}
}
interface A03{
int x = 0;
}
class B03 {
int x = 1;
}
//class C既继承了B03,又实现了A03
//也就是说既可以访问B03中的x,也可以访问A03中的x,所以会报错说x ambiguous
class C extends B03 implements A03 {
public void pX() {
//接口,接口的属性是 public static final int x = 0;
//静态属性可以直接使用 类名.变量名 访问
System.out.println(A03.x);
//父类的属性,使用super关键字
System.out.println(super.x);
}
}总结:继承和实现接口的等级是一样的,所以如果父类和接口中的变量名重合的话,在实现类(子类)中访问时就会提示ambiguous(模棱两可)