imgaug Augment Polygons 对标注图片和polygons的数据增强
对于本地化进行图像的增强,大家都是非常好操作的。但是,对于标注信息一起增强,还是稍微有一些难度的,麻烦很多。
我是遇到一个数据集非常少的任务,只有40张图。就直接标记了去训练,发现几乎不拟合,当然这里使用的是yolo v8,而不是UNet。
于是,先本地化给增强到50倍数据集,然后再去训练,说不定是个好的方法。这里采用的就是imgaug的开源库,学习参考如下:
- imgaug 地址
- 官方文档
- Augment Polygons
一、单张实验下
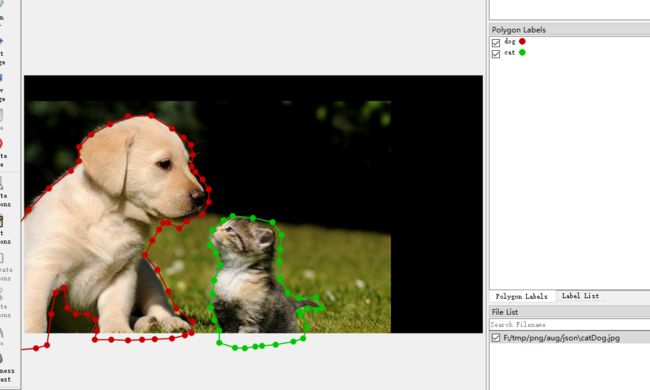
1、首先,是采用labelme标注的一张图像,如下,是用labelme打开时候看到的内容:
用imgaug查看原图和标记内容,如下:
import imageio
import imgaug as ia
import json
import numpy as np
from imgaug.augmentables.polys import Polygon, PolygonsOnImage
class LabelJson(object):
def __init__(self, abs_path=None) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.abs_path = abs_path
self.read()
def read(self):
with open(self.abs_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
lj = json.load(f)
self.wh = [lj.get('imageWidth'), lj.get('imageHeight')]
shapes = lj.get('shapes')
self.cls = [i.get('label') for i in shapes] # '1305' if i.get('label') == '14' else
points = [i.get('points') for i in shapes]
points = [np.array(i, dtype=np.int32).reshape((-1, 2)) for i in points]
self.loc = points
self.box = [[j[:, 0].min(), j[:, 1].min(), j[:, 0].max(), j[:, 1].max()] for j in points]
self.img_name = lj.get('imagePath')
self.is_pos = bool(self.cls)
return self
img_path = r"F:\tmp\png/catDog.jpg"
json_path = r'F:\tmp\png\catDog.json'
image = imageio.imread(img_path)
json_info = LabelJson(json_path)
print(image.shape)
ia.imshow(image)
image_polys = np.copy(image)
for point in json_info.loc:
meerkat = Polygon(point)
image_polys = meerkat.draw_on_image(image_polys, alpha_face=0.2, size_points=7)
ia.imshow(image_polys)
显示的图片内容:
2、开始进行第一次数据增强,不改变形状,加入高斯噪声等等操作
# let's convert our polygons to an PolygonsOnImage instance:
psoi = ia.PolygonsOnImage([Polygon(point) for point in json_info.loc],
shape=image.shape)
import imgaug.augmenters as iaa
ia.seed(1)
# add aug
aug = iaa.Sequential([
iaa.AdditiveGaussianNoise(scale=10),
iaa.CoarseDropout(0.1, size_px=8),
iaa.AddToHueAndSaturation((-50, 50))
])
image_aug, psoi_aug = aug(image=image, polygons=psoi)
ia.imshow(psoi_aug.draw_on_image(image_aug, alpha_face=0.2, size_points=7))
下面就是增强后的结果:
3、接下来进行第二次的增强,这次加入形状和位置调整。
# add aug 2
aug = iaa.Sequential([
iaa.Affine(translate_percent={"x": 0.2, "y": 0.1}),
iaa.Fliplr(1.0)
])
image_aug, psoi_aug = aug(image=image, polygons=psoi)
ia.imshow(psoi_aug.draw_on_image(image_aug, alpha_face=0.2, size_points=7))
展示如下所示:
4、增强后的坐标,转化为labelme可以读取的json形式保存,再打开查看,这也是大多数我们需要做的目的。如下操作:
import base64, os
from PIL import Image
import io
import json
import cv2
def base64encode_img(src_image):
# src_image = Image.open(image_path)
src_image = Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(src_image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
output_buffer = io.BytesIO()
src_image.save(output_buffer, format='JPEG')
byte_data = output_buffer.getvalue()
base64_str = base64.b64encode(byte_data).decode('utf-8')
return base64_str
def savejson(points_list, clses_list, img_tmp, filename, save_dir):
A = dict()
listbigoption = []
for cls, points in zip(clses_list, points_list):
listobject = dict()
listobject['points'] = points
listobject['line_color'] = 'null'
listobject['label'] = cls
listobject['fill_color'] = 'null'
listbigoption.append(listobject)
A['imageData'] = base64encode_img(img_tmp)
A['imagePath'] = filename
A['shapes'] = listbigoption
A['flags'] = {}
print(A)
saveJson_path = os.path.join(save_dir, 'json')
os.makedirs(saveJson_path, exist_ok=True)
suffix = os.path.splitext(filename)[-1]
with open(saveJson_path + "/" + filename.replace(suffix, ".json"), 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
json.dump(A, f, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False)
image_aug, psoi_aug = aug(image=image, polygons=psoi)
print(psoi_aug)
points_list = []
for pos in psoi_aug:
print('pos:', pos)
points = [list(xy.astype(np.float64)) for xy in pos]
print('points:', points)
points_list.append(points)
image_augRGB = cv2.cvtColor(image_aug, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
savejson(points_list, json_info.cls, image_augRGB, os.path.basename(img_path), r'F:\tmp\png\aug')
# ia.imshow(psoi_aug.draw_on_image(image_aug, alpha_face=0.2, size_points=7))
ia.imshow(image_aug)
cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(r'F:\tmp\png\aug', os.path.basename(img_path)), image_augRGB)
直接保存的是BGR,需要转到RGB进行保存
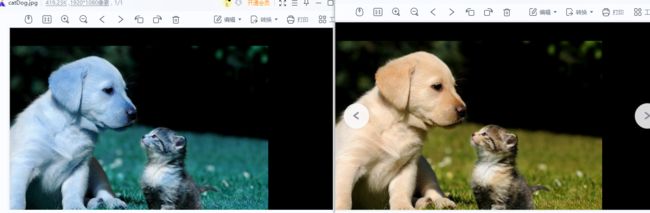
增强后,存储到本地,用labelme再次打开查看,如下(暂未做小于0的截断处理):
加入截断操作,如下:
image_aug, psoi_aug = aug(image=image, polygons=psoi)
print(psoi_aug)
nw, nh, _ = image_aug.shape
points_list = []
for pos in psoi_aug:
print('pos:', pos)
points = [list(xy.astype(np.float64)) for xy in pos]
print('points:', points)
for p in points:
if p[0]<0:
p[0] = 0
elif p[0]>nh:
p[0] = nh
if p[1]<0:
p[1] = 0
elif p[1]>nw:
p[1] = nw
points_list.append(points)
展示如下:
数据增强,随机的产生2*4个图像,用于展示:
ia.seed(2)
aug = iaa.Sequential([
iaa.OneOf([
iaa.AdditiveGaussianNoise(scale=10),
iaa.GaussianBlur(sigma=(0.0, 3.0)),
]),
iaa.Affine(rotate=(-20, 20), translate_percent=(-0.2, 0.2), scale=(0.8, 1.2),
mode=["constant", "edge"], cval=0), # 放射变换
iaa.OneOf([
iaa.Fliplr(0.5), # 水平翻转
iaa.Flipud(0.5), # 上下翻转
]),
iaa.OneOf([
iaa.GammaContrast((0.5, 2.0)),
iaa.LinearContrast((0.8, 1.2), per_channel=0.5),
]),
iaa.AddToHueAndSaturation((-20, 20)), # 通过随机值增加或减少色调和饱和度。
iaa.Sometimes(0.75, iaa.Snowflakes())
])
images_polys_aug = []
for _ in range(2*4):
image_aug, psoi_aug = aug(image=image, polygons=psoi)
image_polys_aug = psoi_aug.draw_on_image(image_aug, alpha_face=0.2, size_points=11)
images_polys_aug.append(ia.imresize_single_image(image_polys_aug, 0.5))
ia.imshow(ia.draw_grid(images_polys_aug, cols=2))
展示如下:
二、汇总
最后,做下汇总:
目标:根据采用labelme标注的pylygons标记信息,批量对图像和标注信息同时增强变换
步骤:
- 读取图像和json文件信息
- 增强操作
- 保存到本地
- 再次采用labelme,查看生成的结果,是否正常
代码如下:
import imageio
import imgaug as ia
import numpy as np
from imgaug.augmentables.polys import Polygon, PolygonsOnImage
import imgaug.augmenters as iaa
class LabelJson(object):
def __init__(self, abs_path=None) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.abs_path = abs_path
self.read()
def read(self):
with open(self.abs_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
lj = json.load(f)
self.wh = [lj.get('imageWidth'), lj.get('imageHeight')]
shapes = lj.get('shapes')
self.cls = [i.get('label') for i in shapes] # '1305' if i.get('label') == '14' else
points = [i.get('points') for i in shapes]
points = [np.array(i, dtype=np.int32).reshape((-1, 2)) for i in points]
self.loc = points
self.box = [[j[:, 0].min(), j[:, 1].min(), j[:, 0].max(), j[:, 1].max()] for j in points]
self.img_name = lj.get('imagePath')
self.is_pos = bool(self.cls)
return self
import base64, os
from PIL import Image
import io
import json
import cv2
def base64encode_img(src_image):
# src_image = Image.open(image_path)
src_image = Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(src_image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
output_buffer = io.BytesIO()
src_image.save(output_buffer, format='JPEG')
byte_data = output_buffer.getvalue()
base64_str = base64.b64encode(byte_data).decode('utf-8')
return base64_str
def savejson(points_list, clses_list, img_tmp, filename, save_dir):
A = dict()
listbigoption = []
for cls, points in zip(clses_list, points_list):
listobject = dict()
listobject['points'] = points
listobject['line_color'] = 'null'
listobject['label'] = cls
listobject['fill_color'] = 'null'
listbigoption.append(listobject)
A['imageData'] = base64encode_img(img_tmp)
A['imagePath'] = filename
A['shapes'] = listbigoption
A['flags'] = {}
suffix = os.path.splitext(filename)[-1]
with open(save_dir + "/" + filename.replace(suffix, ".json"), 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
json.dump(A, f, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False)
def saveJsonImg_main(image_aug, psoi_aug, cls_list, img_path, num, save_dir):
nw, nh, _ = image_aug.shape
points_list = []
for pos in psoi_aug:
points = [list(xy.astype(np.float64)) for xy in pos]
for p in points:
if p[0] < 0:
p[0] = 0
elif p[0] > nh:
p[0] = nh
if p[1] < 0:
p[1] = 0
elif p[1] > nw:
p[1] = nw
points_list.append(points)
image_augRGB = cv2.cvtColor(image_aug, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
savejson(points_list, cls_list, image_augRGB, str(num)+'_'+os.path.basename(img_path), save_dir)
# ia.imshow(psoi_aug.draw_on_image(image_aug, alpha_face=0.2, size_points=7))
cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(save_dir, str(num)+'_'+os.path.basename(img_path)), image_augRGB)
ia.seed(2)
aug = iaa.Sequential([
iaa.OneOf([
iaa.SaltAndPepper(0.01),
iaa.AdditiveGaussianNoise(scale=5),
iaa.GaussianBlur(sigma=(0.0, 3.0)),
]),
iaa.OneOf([
iaa.Affine(rotate=(-20, 20), translate_percent=(-0.2, 0.2), scale=(0.8, 1.2),
mode=["constant", "edge"], cval=0), # 放射变换
iaa.Affine(scale={"x": (0.5, 1.5), "y": (0.5, 1.5)}),
iaa.Affine(translate_px={"x": (-20, 20), "y": (-20, 20)}),
iaa.TranslateX(px=(-20, 20)),
iaa.Rotate((-45, 45))
]),
iaa.OneOf([
iaa.Fliplr(0.7), # 水平翻转
iaa.Flipud(0.7), # 上下翻转
]),
iaa.OneOf([
iaa.GammaContrast((0.5, 2.0)),
iaa.LinearContrast((0.8, 1.2), per_channel=0.5),
iaa.WithBrightnessChannels(iaa.Add((-50, 50))), # Augmenter to apply child augmenters to brightness-related image channels.
iaa.AddToHueAndSaturation((-20, 20)), # 通过随机值增加或减少色调和饱和度。
]),
iaa.Sometimes(0.75, iaa.Snowflakes())
])
def main():
img_dir = r"./images"
json_dir = r'./label'
save_dir = r'./aug'
for file in os.listdir(img_dir):
img_path = os.path.join(img_dir, file)
json_path = os.path.join(json_dir, file.replace('.jpg', '.json'))
# read image and get json info
image = imageio.imread(img_path)
json_info = LabelJson(json_path)
# let's convert our polygons to an PolygonsOnImage instance:
psoi = ia.PolygonsOnImage([Polygon(point) for point in json_info.loc],
shape=image.shape)
# one labelme image aug to 50 image
for num in range(50):
# aug
image_aug, psoi_aug = aug(image=image, polygons=psoi)
# save json and image
saveJsonImg_main(image_aug, psoi_aug, json_info.cls, img_path, num, save_dir)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
至此结束,感兴趣的可以赶紧去学习下。如果恰好对你也有帮助,点个赞,再走啦。