@Configuration 和 @Component 的区别
一句话概括就是 @Configuration 中所有带 @Bean 注解的方法都会被动态代理,因此调用该方法返回的都是同一个实例。
理解:调用@Configuration类中的@Bean注解的方法,返回的是同一个示例;而调用@Component类中的@Bean注解的方法,返回的是一个新的实例。
注意:上面说的调用,而不是从spring容器中获取! 见最下面的示例 1 及 示例 2
下面看看实现的细节。
@Configuration 注解:
@Component
@Documented
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Configuration {
String value() default "";
}从定义来看, @Configuration注解本质上还是@Component,因此 @ComponentScan 都能处理@Configuration注解的类。
@Configuration标记的类必须符合下面的要求:
-
配置类必须以类的形式提供(不能是工厂方法返回的实例),允许通过生成子类在运行时增强(cglib 动态代理)。
-
配置类不能是final 类(没法动态代理)。
-
配置注解通常为了通过
@Bean注解生成 Spring 容器管理的类, -
配置类必须是非本地的(即不能在方法中声明,不能是 private)。
-
任何嵌套配置类都必须声明为static。
-
@Bean方法可能不会反过来创建进一步的配置类(也就是返回的 bean 如果带有@Configuration,也不会被特殊处理,只会作为普通的 bean)。
@Bean 注解方法执行策略
先给一个简单的示例代码:
@Configuration
public class MyBeanConfig {
@Bean
public Country country(){
return new Country();
}
@Bean
public UserInfo userInfo(){
return new UserInfo(country());
}
}大多数人第一次看到上面 userInfo() 中调用 country()时,会认为这里的 Country和上面 @Bean方法返回的 Country 可能不是同一个对象,因此可能会通过下面的方式来替代这种方式:
-
@Autowired -
private Country country;
实际上不需要这么做(后面会给出需要这样做的场景),直接调用country()方法返回的是同一个实例。
@Component 注解
@Component注解并没有通过 cglib 来代理@Bean 方法的调用,因此像下面这样配置时,就是两个不同的 country。
@Component
public class MyBeanConfig {
@Bean
public Country country(){
return new Country();
}
@Bean
public UserInfo userInfo(){
return new UserInfo(country());
}
}有些特殊情况下,我们不希望 MyBeanConfig被代理(代理后会变成WebMvcConfig$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$8bef3235293)时,就得用 @Component,这种情况下,上面的写法就需要改成下面这样:
@Component
public class MyBeanConfig {
@Autowired
private Country country;
@Bean
public Country country(){
return new Country();
}
@Bean
public UserInfo userInfo(){
return new UserInfo(country);
}
}这种方式可以保证使用的同一个 Country 实例。
示例 1:调用@Configuration类中的@Bean注解的方法,返回的是同一个示例
第一个bean类
package com.xl.test.logtest.utils;
public class Child {
private String name = "the child";
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}第二个bean类
package com.xl.test.logtest.utils;
public class Woman {
private String name = "the woman";
private Child child;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Child getChild() {
return child;
}
public void setChild(Child child) {
this.child = child;
}
}@Configuration类
package com.xl.test.logtest.utils;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
//@Component
@Configuration
public class Human {
@Bean
public Woman getWomanBean() {
Woman woman = new Woman();
//直接调用@Bean注解的方法方法getChildBean()
woman.setChild(getChildBean());
return woman;
}
@Bean
public Child getChildBean() {
return new Child();
}
}测试类 I
本测试类为一个配置类,这样启动项目是就可以看到测试效果,更加快捷;也可以使用其他方式测试见下面的测试类 II
package com.xl.test.logtest.utils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
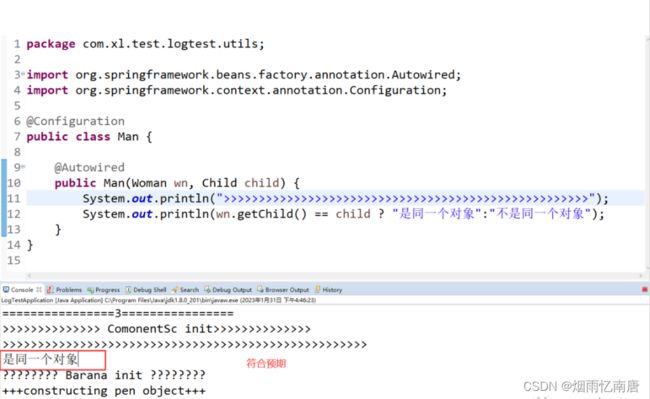
public class Man {
@Autowired
public Man(Woman wn, Child child) {
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");
System.out.println(wn.getChild() == child ? "是同一个对象":"不是同一个对象");
}
}启动项目,查看输出结果:
测试类 II
package com.xl.test.logtest.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.xl.test.logtest.utils.Child;
import com.xl.test.logtest.utils.Woman;
@RestController
public class LogTestController {
@Autowired
Woman woman ;
@Autowired
Child child;
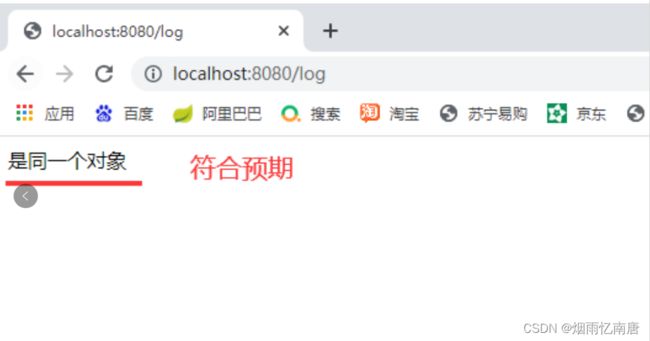
@GetMapping("/log")
public String log() {
return woman.getChild() == child ? "是同一个对象":"不是同一个对象";
}
} 浏览器访问项目,查看结果;输入localhost:8080/log
示例 2 :调用@Component类中的@Bean注解的方法,返回的是一个新的实例。
测试代码,只需要将@Configuration改为@Component即可!其他的均不变
package com.xl.test.logtest.utils;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
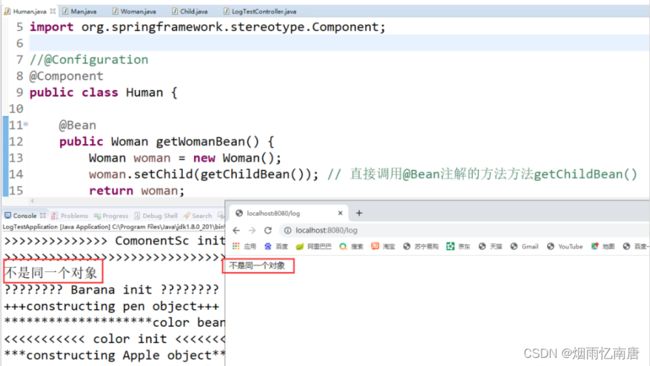
@Component
//@Configuration
public class Human {
@Bean
public Woman getWomanBean() {
Woman woman = new Woman();
//直接调用@Bean注解的方法方法getChildBean()
woman.setChild(getChildBean());
return woman;
}
@Bean
public Child getChildBean() {
return new Child();
}
}测试 :
控制台和浏览器展示,均符合预期!