回归预测 | MATLAB实现GA-RF遗传算法优化随机森林的数据多输入单输出回归预测
回归预测 | MATLAB实现GA-RF遗传算法优化随机森林的数据多输入单输出回归预测
目录
-
- 回归预测 | MATLAB实现GA-RF遗传算法优化随机森林的数据多输入单输出回归预测
-
- 效果一览
- 基本介绍
- 程序设计
- 参考资料
效果一览
基本介绍
1.Matlab实现GA-RF遗传算法优化随机森林多变量回归预测;
2.输入7个特征,输出1个,即多输入单输出;
3.运行环境Matlab2018及以上,运行主程序main即可,其余为函数文件无需运行,所有程序放在一个文件夹,data为数据集;
4.遗传算法优化随机森林树数目、最大深度,命令窗口输出RMSE、MAE、R2、MAPE等评价指标。
程序设计
- 完整程序和数据下载方式1(资源处直接下载):MATLAB实现GA-RF遗传算法优化随机森林的数据多输入单输出回归预测
- 完整程序和数据下载方式2(订阅《RF随机森林》专栏,同时可阅读《RF随机森林》专栏收录的所有内容,数据订阅后私信我获取):MATLAB实现GA-RF遗传算法优化随机森林的数据多输入单输出回归预测
- 完整程序和数据下载方式3(订阅《智能学习》专栏,同时获取《智能学习》专栏收录程序6份,数据订阅后私信我获取):MATLAB实现GA-RF遗传算法优化随机森林的数据多输入单输出回归预测
%% 数据归一化
[p_train, ps_input] = mapminmax(P_train, 0, 1);
p_test = mapminmax('apply', P_test, ps_input);
[t_train, ps_output] = mapminmax(T_train, 0, 1);
t_test = mapminmax('apply', T_test, ps_output);
%% 转置以适应模型
p_train = p_train'; p_test = p_test';
t_train = t_train'; t_test = t_test';
%% 优化参数
dim = 2; % 待优化的变量的个数
NIND = 5; % 种群数目
MAXGEN = 10; % 最大迭代次数
PRECI = 10; % 变量的二进制位数
GGAP = 0.95; % 代沟
px = 0.7; % 交叉概率
pm = 0.01; % 变异概率
nu_min = [100, 1]; % 参数范围最小值(决策树数目,最大深度)
nu_max = [500, f_]; % 参数范围最大值(最大深度小于特征数目)
%% 种群初始化
trace = zeros(dim + 1, MAXGEN); % 寻优结果的初始值
Chrom = crtbp(NIND, PRECI * dim); % 初始种群
FieldD = [repmat(PRECI, 1, dim); ... % 区域描述器
[nu_min; nu_max]; repmat([1; 0; 1; 1], 1, dim)];
%% 迭代优化
gen = 0; % 代计数器
pop = bs2rv(Chrom, FieldD); % 计算初始种群的十进制转换
ObjV = Objfun(pop, p_train, t_train); % 计算目标函数值
while gen < MAXGEN
FitnV = ranking(ObjV); % 分配适应度值
SelCh = select('sus', Chrom, FitnV, GGAP); % 选择
SelCh = recombin('xovsp', SelCh, px); % 重组
SelCh = mut(SelCh, pm); % 变异
pop = bs2rv(SelCh, FieldD); % 子代个体的十进制转换
ObjVSel = Objfun(pop, p_train, t_train); % 计算子代的目标函数值
[Chrom, ObjV] = reins(Chrom, SelCh, 1, 1, ObjV, ObjVSel); % 重插入子代到父代,得到新种群
pop = bs2rv(Chrom, FieldD); % 解码种群
gen = gen + 1; % 代计数器增加
% 获取每代的最优解及其序号,Y为最优解,I为个体的序号
[Y, I] = min(ObjV);
trace(1: dim, gen) = round(pop(I, :)); % 记下每代的最优种群
trace(end, gen) = Y; % 记下每代的最优适应度
end
%% 获取最佳参数
max_tra(1) = trace(1, end);
max_tra(2) = trace(2, end);
%% 建立模型
model = regRF_train(p_train, t_train, max_tra(1), max_tra(2));
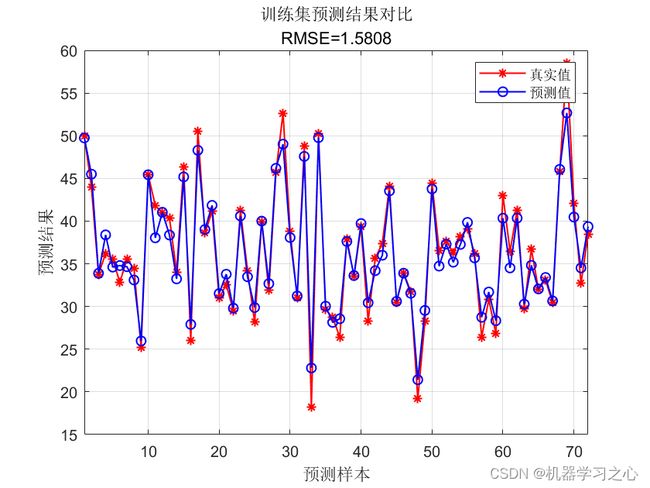
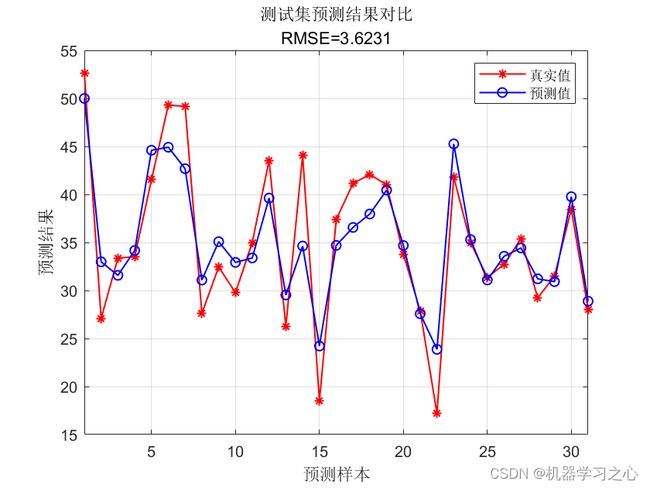
%% 仿真测试
t_sim1 = regRF_predict(p_train, model);
t_sim2 = regRF_predict(p_test , model);
%% 数据反归一化
T_sim1 = mapminmax('reverse', t_sim1, ps_output);
T_sim2 = mapminmax('reverse', t_sim2, ps_output);
%% 均方根误差
error1 = sqrt(sum((T_sim1' - T_train).^2) ./ M);
error2 = sqrt(sum((T_sim2' - T_test ).^2) ./ N);
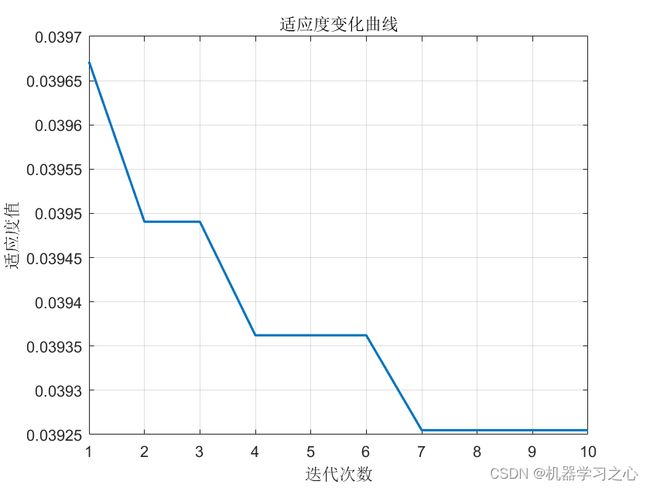
%% 优化迭代图
figure
plot(1: MAXGEN, trace(end, :), 'LineWidth', 1.5);
xlabel('迭代次数');
ylabel('适应度值');
string = {'适应度变化曲线'};
title(string)
grid on
%% 通用选择
% This function performs universal selection. The function handles
% multiple populations and calls the low level selection function
% for the actual selection process.
% Input parameters:
% SEL_F - Name of the selection function
% Chrom - Matrix containing the individuals (parents) of the current
% population. Each row corresponds to one individual.
% FitnV - Column vector containing the fitness values of the
% individuals in the population.
% GGAP - (optional) Rate of individuals to be selected
% if omitted 1.0 is assumed
% SUBPOP - (optional) Number of subpopulations
% if omitted 1 subpopulation is assumed
% Output parameters:
% SelCh - Matrix containing the selected individuals.
%% 检查参数一致性
if nargin < 3
error('Not enough input parameter');
end
%% 确定种群规模 (Nind)
[NindCh, ~] = size(Chrom);
[NindF, VarF] = size(FitnV);
if NindCh ~= NindF
error('Chrom and FitnV disagree');
end
if VarF ~= 1
error('FitnV must be a column vector');
end
if nargin < 5
SUBPOP = 1;
end
if nargin > 4
if isempty(SUBPOP)
SUBPOP = 1;
elseif isnan(SUBPOP)
SUBPOP = 1;
elseif length(SUBPOP) ~= 1
error('SUBPOP must be a scalar');
end
end
if (NindCh / SUBPOP) ~= fix(NindCh / SUBPOP)
error('Chrom and SUBPOP disagree');
end
%% 计算每个亚群的个体数量
Nind = NindCh / SUBPOP;
if nargin < 4
GGAP = 1;
end
if nargin > 3
if isempty(GGAP)
GGAP = 1;
elseif isnan(GGAP)
GGAP = 1;
elseif length(GGAP) ~= 1
error('GGAP must be a scalar');
elseif (GGAP < 0)
error('GGAP must be a scalar bigger than 0');
end
end
%% 计算新个体的数量(供选择)
NSel = max(floor(Nind * GGAP + 0.5), 2);
%% 从种群中选择个体
SelCh = [];
for irun = 1: SUBPOP
FitnVSub = FitnV((irun - 1) * Nind + 1: irun * Nind);
ChrIx = feval(SEL_F, FitnVSub, NSel) + (irun - 1) * Nind;
SelCh = [SelCh; Chrom(ChrIx, :)];
参考资料
[1] https://blog.csdn.net/kjm13182345320/article/details/129215161
[2] https://blog.csdn.net/kjm13182345320/article/details/128105718