Ansible 变量使用详解(二)
前一篇文章中已经初步的总结了变量的一些使用方法,这篇文章我们继续,只不过,这篇文章所涉及到的内容需要借助两个模块,所以在详细的总结变量的相关使用方法之前,会先描述一下这两个模块的用法。
当我们运行一个playbook时,默认都会运行一个名为"[Gathering Facts]"的任务,前文中已经大致的介绍过这个默认的任务,ansible通过"[Gathering Facts]"这个默认任务收集远程主机的相关信息(例如远程主机的IP地址,主机名,系统版本,硬件配置等信息),其实,这些被收集到的远程主机信息会保存在对应的变量中,当我们想要使用这些信息时,我们可以获取对应的变量,从而使用这些信息。
如果想要查看"[Gathering Facts]"任务收集的信息内容,我们可以借助一个模块:setup模块
当执行playbook时,playbook其实就是自动调用了setup模块从而执行了"[Gathering Facts]"任务,所以我们可以通过手动执行setup模块查看"[Gathering Facts]"任务收集到的信息,示例如下:
ansible test70 -m setup上述ad-hoc命令表示收集test70主机的相关信息,执行上述命令后,远程主机test70的相关信息将会输出到ansible主机的控制台上,返回的信息的格式是json格式,我的返回信息如下。
注:由于返回的信息比较多,此处为了方便示例,我将部分内容删除(或折叠省略)了,所以如下返回信息并不完全,只用于示意。
test70 | SUCCESS =>
{
"ansible_facts":{
"ansible_all_ipv4_addresses":[
"192.168.122.1",
"192.168.1.106",
"10.1.1.70",
"172.16.66.70"
],
"ansible_all_ipv6_addresses":Array[2],
"ansible_apparmor":Object{...},
"ansible_architecture":"x86_64",
"ansible_bios_date":"05/19/2017",
"ansible_bios_version":"6.00",
"ansible_cmdline":Object{...},
"ansible_date_time":Object{...},
"ansible_default_ipv4":Object{...},
"ansible_default_ipv6":Object{...},
"ansible_device_links":Object{...},
"ansible_devices":Object{...},
"ansible_distribution":"CentOS",
"ansible_distribution_file_parsed":true,
"ansible_distribution_file_path":"/etc/redhat-release",
"ansible_distribution_file_variety":"RedHat",
"ansible_distribution_major_version":"7",
"ansible_distribution_release":"Core",
"ansible_distribution_version":"7.4.1708",
"ansible_dns":Object{...},
"ansible_domain":"",
"ansible_effective_group_id":0,
"ansible_effective_user_id":0,
"ansible_ens33":Object{...},
"ansible_ens34":Object{...},
"ansible_ens35":{
"active":true,
"device":"ens35",
"features":{
"busy_poll":"off [fixed]",
"fcoe_mtu":"off [fixed]",
"generic_receive_offload":"on",
"generic_segmentation_offload":"on",
"highdma":"off [fixed]",
"hw_tc_offload":"off [fixed]",
"l2_fwd_offload":"off [fixed]",
"large_receive_offload":"off [fixed]",
"loopback":"off [fixed]",
"netns_local":"off [fixed]",
"ntuple_filters":"off [fixed]",
"receive_hashing":"off [fixed]",
"rx_all":"off",
"rx_checksumming":"off",
"rx_fcs":"off",
"rx_vlan_filter":"on [fixed]",
"rx_vlan_offload":"on",
"rx_vlan_stag_filter":"off [fixed]",
"rx_vlan_stag_hw_parse":"off [fixed]",
"scatter_gather":"on",
"tcp_segmentation_offload":"on",
"tx_checksum_fcoe_crc":"off [fixed]",
"tx_checksum_ip_generic":"on",
"tx_checksum_ipv4":"off [fixed]",
"tx_checksum_ipv6":"off [fixed]",
"tx_checksum_sctp":"off [fixed]",
"tx_checksumming":"on",
"tx_fcoe_segmentation":"off [fixed]",
"tx_gre_csum_segmentation":"off [fixed]",
"tx_gre_segmentation":"off [fixed]",
"tx_gso_partial":"off [fixed]",
"tx_gso_robust":"off [fixed]",
"tx_ipip_segmentation":"off [fixed]",
"tx_lockless":"off [fixed]",
"tx_mpls_segmentation":"off [fixed]",
"tx_nocache_copy":"off",
"tx_scatter_gather":"on",
"tx_scatter_gather_fraglist":"off [fixed]",
"tx_sctp_segmentation":"off [fixed]",
"tx_sit_segmentation":"off [fixed]",
"tx_tcp6_segmentation":"off [fixed]",
"tx_tcp_ecn_segmentation":"off [fixed]",
"tx_tcp_mangleid_segmentation":"off",
"tx_tcp_segmentation":"on",
"tx_udp_tnl_csum_segmentation":"off [fixed]",
"tx_udp_tnl_segmentation":"off [fixed]",
"tx_vlan_offload":"on [fixed]",
"tx_vlan_stag_hw_insert":"off [fixed]",
"udp_fragmentation_offload":"off [fixed]",
"vlan_challenged":"off [fixed]"
},
"hw_timestamp_filters":[
],
"ipv4":{
"address":"10.1.1.70",
"broadcast":"10.1.1.255",
"netmask":"255.255.255.0",
"network":"10.1.1.0"
},
"ipv6":[
{
"address":"fe80::250:56ff:fe25:5fb0",
"prefix":"64",
"scope":"link"
}
],
"macaddress":"00:50:56:25:5f:b0",
"module":"e1000",
"mtu":1500,
"pciid":"0000:02:03.0",
"promisc":false,
"speed":1000,
"timestamping":[
"tx_software",
"rx_software",
"software"
],
"type":"ether"
},
"ansible_env":Object{...},
"ansible_fips":false,
"ansible_form_factor":"Other",
"ansible_fqdn":"test70",
"ansible_hostname":"test70",
"ansible_interfaces":Array[6],
"ansible_kernel":"3.10.0-693.el7.x86_64",
"ansible_lo":Object{...},
"ansible_local":Object{...},
"ansible_lsb":Object{...},
"ansible_lvm":Object{...},
"ansible_machine":"x86_64",
"ansible_machine_id":"f6d15ac15f624d3db89e843639a52cc0",
"ansible_memfree_mb":1121,
"ansible_memory_mb":{
"nocache":{
"free":1467,
"used":356
},
"real":{
"free":1121,
"total":1823,
"used":702
},
"swap":{
"cached":0,
"free":1023,
"total":1023,
"used":0
}
},
"changed":false
}返回信息如上,是一个json格式的字符串,为了方便你阅读,ansible已经将格式化后的json信息返回到了控制台中,返回的信息很全面,比如:
- "ansible_all_ipv4_addresses"表示远程主机中的所有ipv4地址,从其对应的值可以看出,test70主机上一共有4个ipv4地址。
- "ansible_distribution"表示远程主机的系统发行版,从其对应的值可以看出test70主机的系统发行版为centos
- "ansible_distribution_version"表示远程主机的系统版本号,从其对应的值与 "ansible_distribution" 的值可以看出test70主机的系统版本为centos7.4
- "ansible_ens35"表示远程主机ens35网卡的相关信息,细心如你一定也发现了,我还有两个名为"ens33"和"ens34"的网卡,只不过为了方便示例,这两个网卡的信息被我省略了。
- "ansible_memory_mb"表示远程主机的内存配置信息。
返回的信息的确很多,很全面,但是,并不是每一次我们都需要看这么多信息,如果你只是想查看某一类信息,你可以通过关键字对信息进行过滤,比如,我只是想要查看远程主机的内存配置信息,那么我可以使用如下命令:
ansible test70 -m setup -a 'filter=ansible_memory_mb'上述命令表示通过"ansible_memory_mb"关键字对返回信息进行过滤,如你所见,通过setup模块的filter参数可以指定需要过滤的关键字,这样ansible就只会将"ansible_memory_mb"的相关信息返回,返回如下:
test70 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_memory_mb": {
"nocache": {
"free": 1467,
"used": 356
},
"real": {
"free": 1119,
"total": 1823,
"used": 704
},
"swap": {
"cached": 0,
"free": 1023,
"total": 1023,
"used": 0
}
}
},
"changed": false
}这样就精简很多了,因为精准的返回了你需要的信息,我知道,有的朋友可能跟我一样,记性不好,所以通常记不住准确的关键字,所以我们可以使用通配符,进行相对模糊的过滤,示例如下
ansible test70 -m setup -a "filter=*mb*"上述命令表示返回所有包含mb的关键字对应的信息,返回信息如下:
test70 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_memfree_mb": 1140,
"ansible_memory_mb": {
"nocache": {
"free": 1475,
"used": 348
},
"real": {
"free": 1140,
"total": 1823,
"used": 683
},
"swap": {
"cached": 0,
"free": 1023,
"total": 1023,
"used": 0
}
},
"ansible_memtotal_mb": 1823,
"ansible_swapfree_mb": 1023,
"ansible_swaptotal_mb": 1023
},
"changed": false
}其实,setup模块返回的这些信息都存在了对应的变量中,我们可以通过引用变量从而使用对应的信息,但是别急,我们先来了解一下另外一个模块,这个模块叫"debug模块"。
见名知义,debug模块的作用就是帮助我们进行调试的,debug模块可以帮助我们把信息输出到ansible控制台上,以便我们能够定位问题。
那么我们先来看一个debug模块的playbook小示例,如下:
---
- hosts: test70
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: touch testfile
file:
path: /testdir/testfile
state: touch
- name: debug demo
debug:
msg: this is debug info,The test file has been touched上例中,我们先在test70主机上touch了对应的文件,然后,利用debug模块在控制台中输出了我们想要显示的信息,如你所见,debug模块的msg参数可以指定我们想要输出的信息,上述playbook表示touch完对应的文件以后,在ansible控制台中输出我们指定的信息,那么我们运行一下这个测试剧本,看一下效果,如下:
如图所示,自定义信息已经输出在ansible控制台中。
debug模块除了能够使用msg参数输出自定义的信息,还能够直接输出变量中的信息,通过debug模块直接输出变量信息需要使用var参数,示例如下:
---
- hosts: test70
remote_user: root
vars:
testvar: value of test variable
tasks:
- name: debug demo
debug:
var: testvar上例虽然连接到了test70远程主机,但是并没有对test70做任何操作,只是在playbook中定义了一个变量,并且通过debug的var参数输出了这个变量的内容,只是为了单纯的演示debug模块的var参数的使用方法,上述playbook的执行效果如下:
变量的名称以及变量的值都输出到了屏幕上,这个功能可以帮助我们调试playbook中变量,让我们了解变量的值是否符合我们的要求。
当然,使用debug的msg参数时也可以引用变量的值,这样我们自定义的信息就更加灵活了,示例如下。
---
- hosts: test70
remote_user: root
vars:
testvar: testv
tasks:
- name: debug demo
debug:
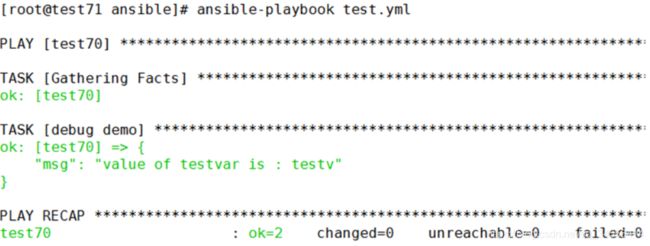
msg: "value of testvar is : {{testvar}}"上例中的msg自定义信息中引用了testvar变量的值
注:上例中msg的值需要使用引号引起,因为{{testvar}}变量前包含"冒号",如果不使用引号会报语法错误。
上例输出效果如下
setup模块与debug模块了解完了,现在绕回一开始的话题,playbook在运行时默认都会运行"[Gathering Facts]"任务,"[Gathering Facts]"任务会收集远程主机的相关信息,这些信息会保存在对应的变量中,我们在playbook中可以使用这些变量,从而利用这些信息,那么我们怎样在playbook获取到这些变量的值呢?
在setup模块的示例中,我们可以通过"ansible_memory_mb"关键字获取远程主机的内存信息,其实,"ansible_memory_mb"就是一个变量名,换句话说就是,我们可以在playbook中直接引用名为"ansible_memory_mb"的变量,从而获取到远程主机的内存信息,示例如下:
---
- hosts: test70
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: debug demo
debug:
msg: "Remote host memory information: {{ansible_memory_mb}}"上例执行效果如下:
如图所示,我们自定义的信息中包含了远程主机的内存信息,同时被输出了,只是格式上没有手动执行setup模块返回的信息格式易读,手动执行setup模块获取到的内存信息返回如下:
test70 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_memory_mb": {
"nocache": {
"free": 1487,
"used": 336
},
"real": {
"free": 1151,
"total": 1823,
"used": 672
},
"swap": {
"cached": 0,
"free": 1023,
"total": 1023,
"used": 0
}
}
},
"changed": false
}如上述返回信息所示,"ansible_memory_mb"中其实包含了 "nocache"、"real"、 "swap"三个部分的信息,如果我们只想获得"real"部分的信息,在playbook中引用变量时可以使用如下两种语法。
语法一示例:
debug:
msg: "Remote host memory information : {{ansible_memory_mb.real}}"
语法二示例:
debug:
msg: "Remote host memory information : {{ansible_memory_mb['real']}}"
上述两种语法前文中已经进行过示例,此处不再赘述。其实,这些远程主机的变量信息不仅仅能够用于输出,我们通常会获取到这些信息以后,对这些信息的值进行判断,判断是否符合我们的要求,然后再执行下一步动作,比如,先获取到远程主机的系统发行版信息,然后判断发行版是centos6还是centos7,如果是centos6,我们就将准备好的A文件拷贝到远程主机中,如果是centos7,我们就将准备好的B文件拷贝到远程主机中,不过由于我们还没有总结条件判断的相关使用方法,所以此处就不进行示例了,这篇文章就先总结到这里,希望能够对你有所帮助。