Ajax详解
1、什么是Ajax
- ajax 全名
async javascript and XML - 是
前后台交互的能力也就是我们客户端给服务端发送消息的工具,以及接受响应的工具 - 是一个 默认
异步执行机制的功能。
2、 AJAX 的优势
- 不需要插件的支持,
原生 js就可以使用 - 用户体验好(
不需要刷新页面就可以更新数据) 减轻服务端和带宽的负担- 缺点: 搜索引擎的支持度不够,因为数据都不在页面上,搜索引擎搜索不到
3、AJAX 的使用
在 js 中有内置的构造函数来创建 ajax 对象
创建 ajax 对象以后,我们就使用 ajax 对象的方法去发送请求和接受响应
3.1 配置链接信息
onst xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
// xhr 对象中的 open 方法是来配置请求信息的
// 第一个参数是本次请求的请求方式 get / post / put / ...
// 第二个参数是本次请求的 url
// 第三个参数是本次请求是否异步,默认 true 表示异步,false 表示同步
// xhr.open('请求方式', '请求地址', 是否异步)
xhr.open('get', './data.php',true)
//默认是true
上面的代码执行完毕以后,本次请求的基本配
- List item
置信息就写完了
3.2 发送请求
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
xhr.open('get', './data.php', true)
// 使用 xhr 对象中的 send 方法来发送请求
xhr.send()
上面代码是把配置好信息的 ajax 对象发送到服务端
3.3 一个基本的 Ajax 请求
- 一个最基本的 ajax 请求就是上面三步
- 但是光有上面的三个步骤,我们确实能把请求发送的到服务端
- 如果服务端正常的话,响应也能回到客户端
- 但是我们拿不到响应
- 如果想拿到响应,我们有两个前提条件
1、本次 HTTP 请求是成功的,也就是我们之前说的 http 状态码为 200 ~ 299
2、ajax 对象也有自己的状态码,用来表示本次 ajax 请求中各个阶段
3.4 Ajax状态码
ajax 状态码 xhr.readyState
是用来表示一个 ajax 请求的全部过程中的某一个状态
readyState === 0: 表示未初始化完成,也就是 open 方法还没有执行readyState === 1: 表示配置信息已经完成,也就是执行完 open 之后readyState === 2: 表示 send 方法已经执行完成readyState === 3: 表示正在解析响应内容readyState === 4: 表示响应内容已经解析完毕,可以在客户端使用了
这个时候我们就会发现,当一个 ajax 请求的全部过程中,只有当 readyState === 4 的时候,我
们才可以正常使用服务端给我们的数据.
所以,配合 http 状态码为 200 ~ 299
- 一个 ajax 对象中有一个成员叫做
xhr.status - 这个成员就是记录本次请求的
http 状态码的
两个条件都满足的时候,才是本次请求正常完成
3.5 readyStateChange
- 在 ajax 对象中有一个事件,叫做 readyStateChange 事件
- 这个事件是专门用来监听 ajax 对象的 readyState 值改变的的行为
- 也就是说只要 readyState 的值发生变化了,那么就会触发该事件
- 所以我们就在这个事件中来监听 ajax 的 readyState 是不是到 4 了
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
xhr.open('get', './data.php')
xhr.send()
xhr.onreadyStateChange = function () {
// 每次 readyState 改变的时候都会触发该事件
// 我们就在这里判断 readyState 的值是不是到 4
// 并且 http 的状态码是不是 200 ~ 299
if (xhr.readyState === 4 && /^2\d{2}$/.test(xhr.status)) {
// 这里表示验证通过
// 我们就可以获取服务端给我们响应的内容了
}
}
3.6 responseText
- ajax 对象中的 responseText 成员
- 就是用来记录服务端给我们的响应体内容的
- 所以我们就用这个成员来获取响应体内容就可以
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
xhr.open('get', './data.php')
xhr.send()
xhr.onreadyStateChange = function () {
// 每次 readyState 改变的时候都会触发该事件
// 我们就在这里判断 readyState 的值是不是到 4
// 并且 http 的状态码是不是 200 ~ 299
if (xhr.readyState === 4 && /^2\d{2}$/.test(xhr.status)) {
// 我们在这里直接打印 xhr.responseText 来查看服务端给我们返回的内容
console.log(xhr.responseText)
}
}
3.7 Ajax案例
由于时间原因,页面布局就不写了。
<ul class="list">
<li>
<img src="" alt="">
<span></span>
</li>
</ul>
<script>
//创建一个Ajax对象
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
//配置链接信息
xhr.open('GET', 'http://www.xiongmaoyouxuan.com:80/api/tabs')
//发送请求
xhr.send()
//监听 ajax 对象的 readyState 值
xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
//判断eadyState 的值是不是到 4
// 并且 http 的状态码是不是 200 ~ 299
if (xhr.readyState === 4 && /^2\d{2}$/.test(xhr.status)) {
//获取服务端给我们的响应体内容,由于获取过来的是json字符串
//所以我们要通过JSON.parse()转化为json对象
let jsonData = JSON.parse(xhr.responseText)
//调用渲染函数
render(jsonData)
}
}
//创建渲染函数页面
function render(data) {
//对数据进行解构赋值
let { data: { list } } = data
//使用map映射到页面当中
let lists = list.map(function (item) {
return `
 ${item.imageUrl}
${item.imageUrl} " alt="">
${item.name}
`
})
//添加到ul里面
document.querySelector('.list').innerHTML = lists.join('')
//使用join()进行拼接
}
</script>
4、使用 Ajax 发送请求时携带参数
- 我们使用 ajax 发送请求也是可以携带参数的
- 参数就是和后台交互的时候给他的一些信息
- 但是携带参数 get 、 post、put、patch、delete这些方式还是有区别的。
- 在实际开发中常用的还是get 和post,后面三种了解即可
注:我们的接口是利用node.js和json文件来模拟实现。
4.1 发送一个带有参数的 get 请求
- get 请求的参数就直接在 url 后面进行拼接就可以
不带参数默认获取所有数据,带参数获取匹配对应的数据
<button id="myget">get</button>
<button id="mypost">post1</button>
<button id="myput">put</button>
<button id="mypatch">patch</button>
<button id="mydelete">delete</button>
<script>
document.querySelector('#myget').addEventListener('click', () => {
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
xhr.open("GET", "http://localhost:3000/username?name=zwy&password=123")
//获取name等于zwy并且password等于123的数据
xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (xhr.readyState === 4 && /^2\d{2}$/.test(xhr.status)) {
console.log(JSON.parse(xhr.responseText))
}
}
xhr.send()
})
</script>
4.2 发送一个带有参数的 POST 请求
因为live server服务器在发送post请求后会默认刷新页面,所以我们换一个服务器,实现提交后页面不刷新。

安装完,重启VSCode即可。
post 请求的参数是携带在请求体中的,所以不需要再 url 后面拼接
如果是用 ajax 对象发送 post 请求,必须要先设置一下请求头中的 content-type
告诉一下服务端我给你的是一个什么样子的数据格式。
1、如果是表单格式'key=value&key=value'则用application/x-www-form-urlencoded
2、如果是json格式则用application/json
具体实现1:提交表单格式数据
document.querySelector('#mypost').addEventListener('click', () => {
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
xhr.open("POST", "http://localhost:3000/username")
xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (xhr.readyState === 4 && /^2\d{2}$/.test(xhr.status)) {
console.log(JSON.parse(xhr.responseText))
}
}
xhr.setRequestHeader("Content-Type","application/x-www-form-urlencoded")
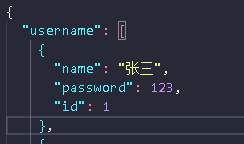
xhr.send(`name=张三&password=136`)
})
具体实现2:提交json格式数据
document.querySelector('#mypost').addEventListener('click', () => {
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
xhr.open("POST", " http://localhost:3000/username")
xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (xhr.readyState === 4 && /^2\d{2}$/.test(xhr.status)) {
console.log(JSON.parse(xhr.responseText))
}
}
xhr.setRequestHeader("Content-Type","application/json") //name=kerwin&age=100
xhr.send(JSON.stringify({
name:"ximen",
password:"789"
}))
})
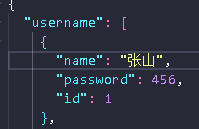
4.3 发送一个PUT请求
put默认修改所有数据
如果send()传递的参数少于该对象的属性,则后面的会被默认删除。
document.querySelector('#myput').addEventListener('click', () => {
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
xhr.open("PUT", " http://localhost:3000/username/1")
//url地址后面必须指定修改哪个数据
// /1表示修改id为1的数据
xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (xhr.readyState === 4 && /^2\d{2}$/.test(xhr.status)) {
console.log(JSON.parse(xhr.responseText))
}
}
xhr.setRequestHeader("Content-Type","application/json")
xhr.send(JSON.stringify({
name:"张"
//只传了一个属性,后面的password属性会被默认删除
}))
})
4.4 发送一个PATCH请求
patch是部分修改,可以弥补put的缺陷。
document.querySelector('#mypatch').addEventListener('click', () => {
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
xhr.open("PATCH", " http://localhost:3000/username/1")
//url地址后面必须指定修改哪个数据
// /1表示修改id为1的数据
xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (xhr.readyState === 4 && /^2\d{2}$/.test(xhr.status)) {
console.log(JSON.parse(xhr.responseText))
}
}
xhr.setRequestHeader("Content-Type","application/json")
xhr.send(JSON.stringify({
name:"李四"
//只传了一个属性,后面的password属性会被保留,不做修改
}))
})
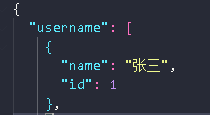
4.5 发送一个DELETE请求
document.querySelector('#mydelete').addEventListener('click', () => {
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
xhr.open("DeLETE", " http://localhost:3000/username/1")
//指定你要删除id为几的数据
xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (xhr.readyState === 4 && /^2\d{2}$/.test(xhr.status)) {
console.log(JSON.parse(xhr.responseText))
}
}
xhr.send()
})
删除后
5、封装Ajax
如果页面中很多个请求,上面这种方法则需要new很多个XMLHttpRequest(),这样会使得代码有很多的重复,显然这样做是不合理的,所有我们需要封装一个Ajax来解决这个问题。
//如果data传入的是json格式,而header设置的是form表单编码
//我们就需要将json字符串进行转换。
function queryStringify(obj) {
let str = ''
for (let k in obj) str += `${k}=${obj[k]}&`
//username=kerwin&password=789&
return str.slice(0, -1)
}
// 封装 ajax
function ajax(options) {
//设置一个options默认值,在我们不传递参数的时候默认是get提交
let defaultoptions = {
url: "",
method: "GET",
async: true,
data: {},
headers: {
"content-type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded"
},
success: function () { },
error: function () { }
}
// 进行解构赋值
let { url, method, async, data, headers, success, error } = {
//展开运算符
...defaultoptions,
...options
}
//判断headers的值是否为json
if (typeof data === 'object' && headers["content-type"]?.indexOf("json") > -1) {
data = JSON.stringify(data)
}
else {
data = queryStringify(data)
}
// // 如果是 get 请求, 并且有参数, 那么直接组装一下 url 信息
if (/^get$/i.test(method) && data) url += '?' + data
// // 4. 发送请求
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
xhr.open(method, url, async)
xhr.onload = function () {
if (!/^2\d{2}$/.test(xhr.status)) {
// console.log(error)
error(`错误状态码:${xhr.status}`) //回调
return
}
// 执行解析
try {
let result = JSON.parse(xhr.responseText)
success(result)
} catch (err) {
error('解析失败 ! 因为后端返回的结果不是 json 格式字符串')
}
}
// // 设置请求头内的信息
for (let k in headers) xhr.setRequestHeader(k, headers[k])
//判断method是不是get
if (/^get$/i.test(method)) {
xhr.send()
} else {
xhr.send(data)
}
}