【04】插件化换肤技术实战
(1)使用插件化的方案为App换肤
(2)不需要重启App就能够换肤
(3)市场上所有的APP都可以当成自己的皮肤包来用。
(4)无闪烁
(5)便于扩展与维护,入侵性很小。
(6)只需要在Application初始化一次即可使用
(7)喜欢什么样的皮肤包,就可以将它的apk包拿过来就可以了。
【04】插件化换肤技术实战
文章目录
- 【04】插件化换肤技术实战
-
- 1.插件化换肤需要了解的技术
-
- 1.1LayoutInflater.inflate
- 1.2Factory2
- 2.动态换肤实现
-
- 2.1自定义控件实现换肤的接口
- 2.2换肤方案信息的存储
- 2.3换肤资源的获取
- 2.4变更Theme主题中的样式
- 2.5存放需要换肤的View及View所对应的属性
- 2.6寻找并记录需要换肤的属性
- 2.7通过反射控件构造方法的方式生成布局中的控件
- 2.8换肤的过程应该放在什么时间点
- 2.9换肤过程封装在工具类中
-
- 2.9.1创建被观察者
- 2.9.2创建被观察者
- 2.9.3为被观察者添加观察者
- 2.10小结
- 2.11测试
- 3.打赏鼓励
-
- 3.1微信打赏
- 3.2支付宝打赏
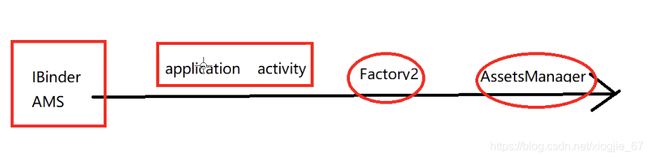
1.插件化换肤需要了解的技术
1.1LayoutInflater.inflate
(1)从PhoneWindow中进入到setContentView方法
(2)installDecor()完成了之后,Activity的整个布局就是Activity上面放了一个PhoneWindow,PhoneWindow上面又放了一个DecorView.
(3)DecorView的加载实际上加载的是预编译时期选择的不同的主题,在frameWork里面去搜过文件可以清楚其具体的布局。
(4)Activity的布局文件是通过LayoutInflater进行加载的,其最主要的功能是通过带3个参数的inflate方法实现的。
-
createviewFromTag是通过反射来生成对象,这个对象实际上是不带参数的,会帮我们造一个参数。
-
如果根布局存在,就通过generateLayoutParams()将根布局的参数造出来,造出来之后,需要根据inflate()的第三个参数attachToRoot为false的情况,才将参数填充进去。
-
正常的代码,系统在运行的时候,基本上值都是为true的,都是通过往root上去添加这个View.然后直接将参数填充进去。
-
用第三个参数,实际上就是将系统使用的与用户用的将它隔离开来。
-
我们自己在使用的时候,经常将第三个参数写为false,如果为true,就直接报出异常。
android.view.LayoutInflater#inflate(org.xmlpull.v1.XmlPullParser, android.view.ViewGroup, boolean)
是因为系统在设计View系统的时候,它的希望值是所有的View能够以树形结构来摆放。树形结构的特点就是每一个节点都只有一个父亲。
即在调用addView方法的时候,只要这个View有父亲,就抛出异常,因此childView是不能够有父亲的。
android.view.ViewGroup#addViewInner
if (child.getParent() != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("The specified child already has a parent. " +
"You must call removeView() on the child's parent first.");
}
也就是说inflate方法的第三个参数为false的时候,没有去调用addView方法。
没有addView在实现代码中,在LinearLayout自己去写了一个属性,虽然在布局文件中看起来有一个属性,例如layout_width=“110dp”,在没有addView之前,这个值是毫无意义的,是取不到的。即在父控件上去拿这个值是拿不到的。
1.2Factory2
android.view.LayoutInflater.Factory2
android.view.LayoutInflater#tryCreateView
(1)这个factory是一个空的接口,仅仅声明了一个onCreateView方法
(2)它将createVeiw的过程交给了程序员,如果我们去设置一个工厂,在View里面只创建了一个Button,程序执行之后,就只能看到Button.
(3)具体重写Factory2创建View的方法,后续加上。
(4)android.view.LayoutInflater#createViewFromTag(android.view.View, java.lang.String, android.content.Context, android.util.AttributeSet, boolean)
这个方法是不是只执行了一次
android.view.LayoutInflater#rInflateChildren
android.view.LayoutInflater#rInflate
它会通过一个循环用pull解析,不断遍历标签,只要不到根节点,就用一个where循环去加载我们的View,还是调用的createViewFromTag(),所以整个布局里面的每一个View都会执行这一个方法。
while (((type = parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.END_TAG ||
parser.getDepth() > depth) && type != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) {
if (type != XmlPullParser.START_TAG) {
continue;
}
final String name = parser.getName();
if (TAG_REQUEST_FOCUS.equals(name)) {
pendingRequestFocus = true;
consumeChildElements(parser);
} else if (TAG_TAG.equals(name)) {
parseViewTag(parser, parent, attrs);
} else if (TAG_INCLUDE.equals(name)) {
if (parser.getDepth() == 0) {
throw new InflateException("(5)因此我们自己写工厂是为了去收集这些View用的。
2.动态换肤实现
(1)好处是进入项目之后,可以随时无屏闪的将皮肤换掉。
(2)采用插件化的方案,任何一个APP的apk都可以复制之后拿过来使用,可以在里边儿加一些自定义的属性,整个APK的包就可以直接去使用了。
2.1自定义控件实现换肤的接口
/**
* @author XiongJie
* @version appVer
* @Package com.gdc.lib.interfaces
* @file
* @Description:
* 1.接口用于帮助写自定义控件时能够让控件自己提供换肤的方案
* (1)自定义控件实现换肤的接口
* @date 2021-6-14 07:01
* @since appVer
*/
public interface SkinViewSupport {
void applySkin();
}
2.2换肤方案信息的存储
/**
* @author XiongJie
* @version appVer
* @Package com.gdc.lib.interfaces
* @file
* @Description:
* 1.换肤方案信息的存储
* @date 2021-6-14 07:44
* @since appVer
*/
public class SkinPreference {
//1.目录是skins中的
private static final String SKIN_SHARED = "skins";
/**
* 1.用一个键值对保存一下最后一个皮肤包的文件名,即文件名的路径
*/
private static final String KEY_SKIN_PATH = "skin-path";
private volatile static SkinPreference instance;
private final SharedPreferences mPref;
public static void init(Context context) {
if (instance == null) {
synchronized (SkinPreference.class) {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new SkinPreference(context.getApplicationContext());
}
}
}
}
public static SkinPreference getInstance() {
return instance;
}
private SkinPreference(Context context) {
mPref = context.getSharedPreferences(SKIN_SHARED, Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
}
/**
* 1.设置皮肤包的路径
* (1)如果这个皮肤包里面没有数据,那么就证明使用的是整个皮肤包里面最原始的一个皮肤。
* (2)如果这个皮肤包里面有数据,就会找到目录里面的那一个皮肤。
* @param skinPath
*/
public void setSkin(String skinPath) {
mPref.edit().putString(KEY_SKIN_PATH, skinPath).apply();
}
/**
* 重新设置主题的路径
*/
public void reset() {
mPref.edit().remove(KEY_SKIN_PATH).apply();
}
/**
* 获取主题的路径
* @return
*/
public String getSkin() {
return mPref.getString(KEY_SKIN_PATH, null);
}
}
2.3换肤资源的获取
(1)设置背景色,setBackgroundColor实际上是对应着主APK 某一个View的属性,以及某个资源的值。
案例代码:
new View().setBackgroundColor(R.color.xxxx);
(2)setColor() 改颜色就要给颜色填写一个颜色R.color.xxxx,而这个颜色是有一个真实的数据的。我们在set的时候,就是在主APP里面,setColor是一个控件属性。对于系统来说是一个颜色属性。最终想要的效果是将#223344这样的颜色值填写上去。在主app里面根据id是能够找得到这个颜色值所对应的名称的。
(3)在插件包里面, 唯一的区别是#23122442颜色的值不一样,因此只需要从主APP的id找到这一个名称,再利用这个名称对应插件中的颜色值,如果拿到这个值,再去setColor,去设置这一个值,皮肤就按照插件中的颜色改掉了。
(4)R.color.xxxx怎么去拿到?
可以通过AssetsManager去拿到。
- AssetsManager是包了三层了的,最上层是Resources,Resources里面又有一个ResourceImpl,在ResourcesImpl里面包含了一个AssetsManager.
- 即只要能够拿到Resources,对于资源文件就可以全部操作了。不管是用AssetsManager操作还是使用Resources操作,都是可以通用的。
public class SkinResources {
/**
* 1.皮肤包的包名
* (1)用来保存皮肤包的包名
*/
private String mSkinPkgName;
/**
* 1.是否使用默认的皮肤。
* (1)正常情况下,一打开APP,就是一个默认的皮肤,使用的是原生的参数
*/
private boolean isDefaultSkin = true;
/**
* 1.app原始的resource
* (1)主APP使用的资源
* (2)根据主APP的名字,然后将名字传到另外一个APP,再去找那个值。
*/
private Resources mAppResources;
/**
* 1.皮肤包的resource
*/
private Resources mSkinResources;
/**
* 双重松测单例
*/
private volatile static SkinResources instance;
private SkinResources(Context context){
mAppResources = context.getResources();
}
public static void init(Context context){
if(null == instance){
synchronized (SkinResources.class){
if(null == instance){
instance = new SkinResources(context);
}
}
}
}
public static SkinResources getInstance(){
return instance;
}
/**
* 1.复位
* (1)将皮肤包,皮肤包名,是否为默认值将其置空。
* (2)假如不去加载皮肤包了,只需要将这几个属性值置空就可以了。
*/
public void reset(){
mSkinResources = null;
mSkinPkgName = null;
isDefaultSkin = true;
}
/**
* 使用皮肤
* @param resources
* @param pkgName
*/
public void applySkin(Resources resources, String pkgName){
mSkinResources = resources;
mSkinPkgName = pkgName;
isDefaultSkin = TextUtils.isEmpty(pkgName) || resources == null;
}
/**
* 1.通过原始app中的resId(R.color.XX)获取到自己的名字
* 2.根据名字和类型获取皮肤包中的ID号
* 3.mAppResources就是apk中的resources.arsc文件中的一些信息,也就是ID,Name,值。
* 4.能够拿到插件包中的id号,将来需要数据值的时候,比如需要填充颜色,就可以调用这个方法去拿值。
* new View().setBackgroundColor(getIdentifier(resId));
* 即自己APK中的颜色值就可以被插件中的颜色值替换掉。
* 5.插件就是一个单独的APK,在市场上下载的任何一个APK包都能用,或者自己新建的一个APK都可以用,
* 也就是市场上任何一个APK的皮肤都可以拿来用的。
* 6.正常情况是无论放在手机的哪一目录都可以,一般是从服务器下载之后,放在手机的任一目录,但一定是
* 可以访问的目录,一般处在data/data....的某个地方。
*/
public int getIdentifier(int resId){
//(1)默认皮肤的,就返回当前这个资源的id值
if(isDefaultSkin){
return resId;
}
//(2)拿自己APP里面对应的id的名称,id的类型,以及
String resName = mAppResources.getResourceEntryName(resId);
String restType = mAppResources.getResourceTypeName(resId);
//(3)从皮肤包中根据名称及资源类型以及包名获取插件包中的ID号
int skinId = mSkinResources.getIdentifier(resName,restType,mSkinPkgName);
return skinId;
}
/**
* 1.输入主APP的ID,到皮肤包APK文件中去找到对应的ID的颜色值
* (1)即实现动态的获取
* (2)APP
* (3)皮肤.apk
* (4)调用一下getColor,对应在皮肤.apk中的值就可以拿到,拿到之后,在APP中就可以通过setColor
* 进行设置,屏幕上的效果就可以动态改变了。
* @param resId
* @return
*/
public int getColor(int resId){
//(1)如果是默认的情况,返回的是自己的主APP里面的颜色
if(isDefaultSkin){
return mAppResources.getColor(resId);
}
//(2)否则返回的是皮肤包中的资源的id
int skinId = getIdentifier(resId);
//(3)如果没有相同的值,就还是返回自己的资源
if(skinId == 0){
return mAppResources.getColor(resId);
}
//(4)如果有相同的值,就根据得到的插件中的资源id,获取其资源值。
return mSkinResources.getColor(skinId);
}
/**
* 1.输入主APP的ID,到皮肤包APK文件中去找到对应的ID的颜色状态列表
* @param resId
* @return
*/
public ColorStateList getColorStateList(int resId) {
if (isDefaultSkin) {
return mAppResources.getColorStateList(resId);
}
int skinId = getIdentifier(resId);
if (skinId == 0) {
return mAppResources.getColorStateList(resId);
}
return mSkinResources.getColorStateList(skinId);
}
/**
* 1.输入主APP的ID,到皮肤包APK文件中去找到对应的ID的图片
* @param resId
* @return
*/
public Drawable getDrawable(int resId) {
if (isDefaultSkin) {
return mAppResources.getDrawable(resId);
}
//通过 app的resource 获取id 对应的 资源名 与 资源类型
//找到 皮肤包 匹配 的 资源名资源类型 的 皮肤包的 资源 ID
int skinId = getIdentifier(resId);
if (skinId == 0) {
return mAppResources.getDrawable(resId);
}
return mSkinResources.getDrawable(skinId);
}
/**
* 1.输入主APP的ID,到皮肤包APK文件中去找到对应的ID的背景
* (1)可能是Color
* (2)也可能是drawable
* @param resId
* @return
*/
public Object getBackground(int resId) {
String resourceTypeName = mAppResources.getResourceTypeName(resId);
if ("color".equals(resourceTypeName)) {
return getColor(resId);
} else {
// drawable
return getDrawable(resId);
}
}
}
(1)如果在项目中还有其他的属性,都按以上逻辑进行编写。找到自己的API,将自己的逻辑加进去。
2.4变更Theme主题中的样式
public class SkinThemeUtils {
private static int[] APPCOMPAT_COLOR_PRIMARY_DARK_ATTRS = {
androidx.appcompat.R.attr.colorPrimaryDark
};
private static int[] STATUSBAR_COLOR_ATTRS = {
android.R.attr.statusBarColor,android.R.attr.navigationBarColor
};
/**
* 1.获得theme属性中定义的资源id
* (1)obtainStyledAttributes从theme中寻找attrIdArray的值
* (2)参考地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34224268/article/details/102900281
* @param context
* @param attrs
* @return
*/
public static int[] getResId(Context context,int[] attrs){
int [] resIds = new int[attrs.length];
TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs);
for(int i = 0 ; i < attrs.length; i++){
resIds[i] = a.getResourceId(i,0);
}
a.recycle();
return resIds;
}
public static void updateStatusBarColor(Activity activity){
//(1)要求Android5.0以上系统
if(Build.VERSION.SDK_INT<Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP){
return;
}
//(2)获得theme属性中定义的资源id
int [] resIds = getResId(activity,STATUSBAR_COLOR_ATTRS);
int statusBarColorResId = resIds[0];
int navigationBarColor = resIds[1];
/**
* (3)设置状态栏颜色
* - 如果直接在style中写入固定颜色值(而不是 @color.xx )获得0
* - 获得 colorPrimaryDark
*/
if(0 != statusBarColorResId){
int color = SkinResources.getInstance().getColor(statusBarColorResId);
activity.getWindow().setStatusBarColor(color);
}else{
int colorPrimaryDarkResId = getResId(activity,
APPCOMPAT_COLOR_PRIMARY_DARK_ATTRS)[0];
if(0 != colorPrimaryDarkResId){
int color =
SkinResources.getInstance().getColor(colorPrimaryDarkResId);
activity.getWindow().setStatusBarColor(color);
}
}
/**
* (4)设置导航条颜色
*/
if(0 != navigationBarColor){
int color = SkinResources.getInstance().getColor(navigationBarColor);
activity.getWindow().setNavigationBarColor(color);
}
}
}
2.5存放需要换肤的View及View所对应的属性
public class SkinAttribute {
//记录换肤需要操作的View与属性信息
private List<SkinView> skinViews = new ArrayList<>();
static class SkinView{
/**
* 一个View
*/
View view;
/**
* 这个View能被换肤的属性与它对应id的集合
*/
List<SkinPair> skinPairs;
}
static class SkinPair{
/**
* 属性名
*/
String attributeName;
/**
* 对应的资源id
*/
int resId;
public SkinPair(String attributeName, int resId) {
this.attributeName = attributeName;
this.resId = resId;
}
}
}
2.6寻找并记录需要换肤的属性
/**
* 1.查找需要换肤的属性是否出现在自己定义的需要换肤的属性列表中
* (1)记录一个View的哪几个属性需要换肤textColor/src
* (2)带?的属性,都是系统私有的属性,属于主题包中的属性。就到主题中寻找。
* (3)@是在app的xml文件中能够找到的属性,到xml文件中去找。
* (4)#开始的属性值,换肤没有任何意义,因为它已经写死了。
*/
public void look(View view, AttributeSet attrs){
List<SkinPair> skinPairs = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0 ; i < attrs.getAttributeCount();i++){
//1.1获得属性名 textColor/background
String attributeName = attrs.getAttributeName(i);
if(mAttributes.contains(attributeName)){
/**
* 能换肤的包含:
* #
* ?87878787:?表示的是系统私有的属性
* @12126543:@是在app的xml文件中能够找到的属性
*/
//(1)获取属性名对应的属性值
String attributeValue = attrs.getAttributeValue(i);
//(2)比如color以#开头表示写死的颜色,不可用于换肤
if(attributeValue.startsWith("#")){
continue;
}
int resId;
if(attributeValue.startsWith("?")){
//(3)以?开头的表示使用属性
int attrId = Integer.parseInt(attributeValue.substring(1));
resId = SkinThemeUtils.getResId(view.getContext(),
new int[]{attrId})[0];
}else{
//(4)正常以@开头
resId = Integer.parseInt(attributeValue.substring(1));
}
SkinPair skinPair = new SkinPair(attributeName,resId);
skinPairs.add(skinPair);
}
}
//1.记录自定义View需要换肤的属性
if(!skinPairs.isEmpty()||view instanceof SkinViewSupport){
SkinView skinView = new SkinView(view,skinPairs);
skinView.applySkin();
skinViews.add(skinView);
}
}
2.7通过反射控件构造方法的方式生成布局中的控件
/**
* (1)通过反射控件构造方法的方式生成布局中的控件
*
* - 自定义控件、扩展包中的控件,即包名+类名的书写方式
* - 系统的控件,布局中的TextView,ImageView...
* - 如果这个工厂被配置,都是调用View的带两个参数的构造方法进行生成,是通过反射来创建的。
*
* (2)通过反射生成view之后,记录该view的哪些属性需要被修改,即换肤。
*
* @param parent
* @param name
* @param context
* @param attrs
* @return
*/
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(@Nullable View parent, @NonNull String name, @NonNull Context context, @NonNull AttributeSet attrs) {
//(1)如果控件需要使用皮肤,则通过控件包名+控件名拼接为构造方法名的方式反射生成对应的view.
View view = createSDKView(name,context,attrs);
//(2)如果控件是自定义view或者是扩展包中的view,则直接通过反射构造方法的方式生成view
if(null == view){
view = createView(name,context,attrs);
}
/*
*(3)在通过反射生成view的过程中,只要这个view被生成出来了,就记录这个view的哪些属性需要被修改
*/
if(null != view){
skinAttribute.look(view,attrs);
}
return view;
}
/**
* 1.参考sdk中创建View的过程
* @return
*/
private View createSDKView(String name, Context context, AttributeSet attrs){
/*
*(1).如果包含 . 则不是SDK中的view,可能是自定义view,包括support库中的View
* 即如果是自定义控件或者扩展包中的控件,即带包名与类名的view,就不需要走工厂生成控件的流程
*/
if (-1 != name.indexOf('.')) {
return null;
}
/*
* (2)不包含就要在解析的节点 name前,拼上: android.widget. 等尝试去反射生成对象
* 如果是需要使用皮肤的控件(系统的控件TextView,ImageView...),则通过反射生成View,
* 由控件前辍即包名+控件类名反射生成。
*/
for (int i = 0; i < mClassPrefixList.length; i++) {
View view = createView(mClassPrefixList[i] + name, context, attrs);
if(view!=null){
return view;
}
}
return null;
}
private View createView(String name, Context context, AttributeSet attrs){
//1.如果可以通过名字找到构造方法,则直接构建view。
Constructor<? extends View> constructor = findConstructor(context, name);
try {
//2.通过反射构造方法生成view
return constructor.newInstance(context, attrs);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
return null;
}
/**
* 1.先到系统中寻找构造方法
* 2.如果没有找到则通过反射的方式去寻找构造方法。
* @param context
* @param name
* @return
*/
private Constructor<? extends View> findConstructor(Context context,
String name){
Constructor<? extends View> constructor = mConstructorMap.get(name);
if(null == constructor){
try {
//查找是否存在View的子类
Class<? extends View> clazz =
context.getClassLoader().loadClass(name).asSubclass(View.class);
constructor = clazz.getConstructor(mConstructorSignature);
//缓存构造方法
mConstructorMap.put(name,constructor);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return constructor;
}
2.8换肤的过程应该放在什么时间点
(1)如果是动态换肤,可以在任何一个时间点,去点击换肤按钮在屏幕中都会有换肤后的效果。如果有BaseActivity这种方式入侵性会比较强。
(2)监听android.app.Application.ActivityLifecycleCallbacks中的生命周期回调,当所有类的onActivityCreated(android.app.Activity, android.os.Bundle)生命周期方法被执行时,将SkinLayoutInflaterFactory生成view控件的接口配置进去。
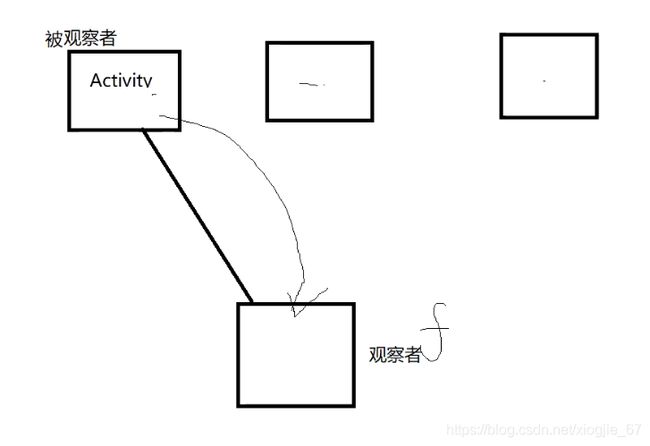
(3)同时配置监听器,如果点击一个按钮需要更新UI的时候,就将当前Activity作为一个被观察者,将工厂作为一个观察者,当需要换肤的时候,让被观察者Activity发一个通知,通知观察者工厂,通过一个com.gdc.lib.SkinAttribute#applySkin() API让被观察者进行换肤。
(4)绑定不是一直绑定的,哪个Activity onActivityCreated()后就往谁身上进行绑定,绑定完之后,就由这个Activity去通知观察者去执行一下换肤的功能com.gdc.lib.SkinAttribute#applySkin(),整个UI上的皮肤即可全部替换掉。
2.9换肤过程封装在工具类中
2.9.1创建被观察者
(1)将布局加载工厂作为被观察者
/**
* @author XiongJie
* @version appVer
* @Package com.gdc.skin
* @file
* @Description:
*
* 1.用来管理布局文件中View的创建过程
*
* @date 2021-6-21 09:57
* @since appVer
*/
public class SkinLayoutInflaterFactory implements LayoutInflater.Factory2, Observer {
/**
* 项目中view的前辍
*/
private static final String[] mClassPrefixList = {
"android.widget.",
"android.webkit.",
"android.app.",
"android.view."
};
//1.记录对应VIEW的构造函数,每个构造方法都是填写Context与AttributeSet两个内容
private static final Class<?>[] mConstructorSignature = new Class[] {
Context.class, AttributeSet.class};
//1.记录View的构造函数是否已经找到过
private static final HashMap<String, Constructor<? extends View>> mConstructorMap =
new HashMap<String, Constructor<? extends View>>();
/**
* 1.当选择新皮肤后需要替换View与之对应的属性
* (1)面属性管理器
*/
private SkinAttribute skinAttribute;
// 用于获取窗口的状态框的信息
private Activity activity;
public SkinLayoutInflaterFactory(Activity activity) {
this.activity = activity;
skinAttribute = new SkinAttribute();
}
/**
* (1)通过反射控件构造方法的方式生成布局中的控件
*
* - 自定义控件、扩展包中的控件,即包名+类名的书写方式
* - 系统的控件,布局中的TextView,ImageView...
* - 如果这个工厂被配置,都是调用View的带两个参数的构造方法进行生成,是通过反射来创建的。
*
* (2)通过反射生成view之后,记录该view的哪些属性需要被修改,即换肤。
*
* @param parent
* @param name
* @param context
* @param attrs
* @return
*/
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(@Nullable View parent, @NonNull String name, @NonNull Context context, @NonNull AttributeSet attrs) {
//(1)如果控件需要使用皮肤,则通过控件包名+控件名拼接为构造方法名的方式反射生成对应的view.
View view = createSDKView(name,context,attrs);
//(2)如果控件是自定义view或者是扩展包中的view,则直接通过反射构造方法的方式生成view
if(null == view){
view = createView(name,context,attrs);
}
/*
*(3)在通过反射生成view的过程中,只要这个view被生成出来了,就记录这个view的哪些属性需要被修改
*/
if(null != view){
skinAttribute.look(view,attrs);
}
return view;
}
/**
* 1.参考sdk中创建View的过程
* @return
*/
private View createSDKView(String name, Context context, AttributeSet attrs){
/*
*(1).如果包含 . 则不是SDK中的view,可能是自定义view,包括support库中的View
* 即如果是自定义控件或者扩展包中的控件,即带包名与类名的view,就不需要走工厂生成控件的流程
*/
if (-1 != name.indexOf('.')) {
return null;
}
/*
* (2)不包含就要在解析的节点 name前,拼上: android.widget. 等尝试去反射生成对象
* 如果是需要使用皮肤的控件(系统的控件TextView,ImageView...),则通过反射生成View,
* 由控件前辍即包名+控件类名反射生成。
*/
for (int i = 0; i < mClassPrefixList.length; i++) {
View view = createView(mClassPrefixList[i] + name, context, attrs);
if(view != null){
return view;
}
}
return null;
}
private View createView(String name, Context context, AttributeSet attrs){
//1.如果可以通过名字找到构造方法,则直接构建view。
Constructor<? extends View> constructor = findConstructor(context, name);
try {
//2.通过反射构造方法生成view
return constructor.newInstance(context, attrs);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
return null;
}
/**
* 1.先到系统中寻找构造方法
* 2.如果没有找到则通过反射的方式去寻找构造方法。
* @param context
* @param name
* @return
*/
private Constructor<? extends View> findConstructor(Context context,
String name){
Constructor<? extends View> constructor = mConstructorMap.get(name);
if(null == constructor){
try {
//查找是否存在View的子类
Class<? extends View> clazz =
context.getClassLoader().loadClass(name).asSubclass(View.class);
constructor = clazz.getConstructor(mConstructorSignature);
//缓存构造方法
mConstructorMap.put(name,constructor);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return constructor;
}
/**
* 不需要用
* @param name
* @param context
* @param attrs
* @return
*/
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(@NonNull String name, @NonNull Context context, @NonNull AttributeSet attrs) {
return null;
}
/**
* 1.将此工厂作为观察者
* (1)当Activity被观察者发生改变,就会发送通知给观察者,该方法就会获得执行。
* (2)将状态栏与UI全部进行变更。
*
* 2.由谁通知
* (1)可以写一个Activity,也可以自己写一个工具类,将来谁需要用的时候,就谁来使用。
* (2)写一个单独管理所有皮肤的类。
* @param o
* @param arg
*/
@Override
public void update(Observable o, Object arg) {
SkinThemeUtils.updateStatusBarColor(activity);
skinAttribute.applySkin();
}
}
2.9.2创建被观察者
(1)将换肤工具类作为被观察者
/**
* @author XiongJie
* @version appVer
* @Package com.gdc.skin
* @file
* @Description:
*
* 1.将SkinManager作为一个被观察者
*
* (1)让其具备发通知给观察者的能力
*
* (2)即这个被观察者指的是任何一个对象(Activity,控件)都可以发通知,这个用法是为了发通知
* 因此才写了这样一个观察者模式。
*
* (3)写这个观察者模式,是因为不确定将来在哪里去通知(是在Activity里的某个生命周期中,还是控件上)
* 观察者去更新.
*
* (4)不能使用调用一个方法,然后返回一个值的方式去使用,那种方式是一种到处都是同样的代码。即都去调用
* 换肤的API,就比较麻烦。而改用这个管理工具类,即可方便的实现换肤。
*
* @date 2021-6-23 22:34
* @since appVer
*/
public class SkinManager extends Observable {
/**
* Activity生命周期回调
*/
private Application mContext;
private ApplicationActivityLifecycle skinActivityLifecycle;
/**
* 双重校验检查单例
*/
private volatile static SkinManager instance;
private SkinManager(Application application){
mContext = application;
//(1)共享首选项,用于记录当前使用的皮肤
SkinPreference.init(application);
//(2)资源管理类,用于从app/皮肤包中加载资源
SkinResources.init(application);
//(3)注册Activity生命周期,并设置被观察者
skinActivityLifecycle = new ApplicationActivityLifecycle(this);
application.registerActivityLifecycleCallbacks(skinActivityLifecycle);
//(4)加载上次所使用的皮肤
loadSkin(SkinPreference.getInstance().getSkin());
}
public static void init(Application application){
if(null == instance){
synchronized (SkinManager.class){
if(null == instance){
instance = new SkinManager(application);
}
}
}
}
public static SkinManager getInstance(){
return instance;
}
/**
* 1.加载皮肤并应用
*
* @param skinPath 皮肤路径,如果路径为空,则使用默认的皮肤
*/
public void loadSkin(String skinPath){
if(TextUtils.isEmpty(skinPath)){
//1.1没有换肤的情况
//(1)还原为默认的皮肤
SkinPreference.getInstance().reset();
SkinResources.getInstance().reset();
}else{
try {
//(1)宿主app的resources
Resources appResource = mContext.getResources();
/**
* =====================加载插件APK=======================
*/
//(2)反射创建AssetManager与Resource
AssetManager assetManager = AssetManager.class.newInstance();
//(3)资源路径设置,目录或压缩包
Method addAssetPath = assetManager.getClass().getMethod(
"addAssetPath",String.class);
addAssetPath.invoke(assetManager,skinPath);
/**
* (4)根据当前设备显示器信息与配置(横竖屏、语言等)创建Resources
* - 用插件APK中的AssetManager来获取插件的资源
*/
Resources skinResource = new Resources(assetManager,
appResource.getDisplayMetrics(),
appResource.getConfiguration());
//(5)获取外部(插件)Apk(皮肤包)包名
PackageManager pm = mContext.getPackageManager();
PackageInfo info = pm.getPackageArchiveInfo(skinPath,
PackageManager.GET_ACTIVITIES);
String packageName = info.packageName;
//用皮肤包中的资源,替换宿主app的资源
SkinResources.getInstance().applySkin(skinResource,packageName);
//(6)记录本次使用的皮肤,确保下次去加载皮肤的时候,能够加载到当前皮肤
// //data/data/packageName/skin/skin.apk
SkinPreference.getInstance().setSkin(skinPath);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* (7)换肤
* - 通知采集的View更新皮肤被观察者(当前类SkinManager)改变,通知所有的观察者更新
* - 即通过观察者模式通知所有观察者,即通知com.gdc.lib.ApplicationActivityLifecycle所
* 添加的观察者com.gdc.lib.SkinLayoutInflaterFactory,执行
* com.gdc.lib.SkinLayoutInflaterFactory#update(java.util.Observable, java.lang.Object)
*/
setChanged();
notifyObservers(null);
}
}
2.9.3为被观察者添加观察者
/**
* @author XiongJie
* @version appVer
* @Package com.gdc.lib
* @file
* @Description:
*
* 1.Activity生命周期回调监听
*
* 2.让所有的Activity都可以绑定布局加载工厂,用布局加载工厂实现布局控件的生成。
*
* (1)如果换肤进行过一次之后,就不能继续换第二次,这是由Android布局加载过程决定的。为了能够让换肤
* 之后能够继续换,需要变更mFactorySet属性。
*
* 3.该生命周期回调监听类只要被注册,可以提供一个给用户使用的API。
*
* (1)记录观察者
* (2)记录每一个Activity所对应的布局加载工厂
*
* 4.无论哪一个Activity在执行的过程中,自己所对应的观察者被保存下来,在destory的时候将观察者移除.
* (1)打开一个Activity,即将观察者与被观察者建立关联。
*
* @date 2021-6-23 22:42
* @since appVer
*/
public class ApplicationActivityLifecycle implements Application.ActivityLifecycleCallbacks {
/**
* 1.将Activity设置为被观察者
*/
private Observable mObserable;
/**
* 记录Activity以及其布局加载工厂
*/
private ArrayMap<Activity,SkinLayoutInflaterFactory> mLayoutInflaterFactories =
new ArrayMap<>();
public ApplicationActivityLifecycle(Observable observable) {
mObserable = observable;
}
@Override
public void onActivityCreated(@NonNull Activity activity, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
//1.更新Activity的状态栏
SkinThemeUtils.updateStatusBarColor(activity);
/**
* 2.更新布局视图
* (1)获取Activity
*/
LayoutInflater layoutInflater = activity.getLayoutInflater();
/**
* 3.为了满足换肤的条件,设置mFactorySet标签为false,确保任一时刻都可以使用自定义工厂加载布局。(看源码)
* (1)Android布局加载器,使用mFactorySet标记是否设置过Factory
* (2)如果设置过一次,会抛出异常,因此需要在此将其设置为false,让其按照自定义的方案加载布局并
* 生成View
*/
try {
Field field = LayoutInflater.class.getDeclaredField("mFactorySet");
field.setAccessible(true);
field.setBoolean(layoutInflater,false);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
/**
* 4.使用factory2,设置布局加载工厂
*/
SkinLayoutInflaterFactory skinLayoutInflaterFactory =
new SkinLayoutInflaterFactory(activity);
//4.1设置布局解析器,及布局加载工厂
LayoutInflaterCompat.setFactory2(layoutInflater,skinLayoutInflaterFactory);
//4.2记录每一个Activity所对应的布局加载工厂
mLayoutInflaterFactories.put(activity,skinLayoutInflaterFactory);
/**
* 5.添加观察者
* (1)打开一个Activity,即将观察者SkinLayoutInflaterFactory与被观察者SkinManager建立关联。
* (2)如果用户在Activity中使用换肤工具类SkinManager执行换肤,就会调用SkinLayoutInflaterFactory中的
* update()方法.
*/
mObserable.addObserver(skinLayoutInflaterFactory);
}
@Override
public void onActivityStarted(@NonNull Activity activity) {
}
@Override
public void onActivityResumed(@NonNull Activity activity) {
}
@Override
public void onActivityPaused(@NonNull Activity activity) {
}
@Override
public void onActivityStopped(@NonNull Activity activity) {
}
@Override
public void onActivitySaveInstanceState(@NonNull Activity activity, @NonNull Bundle outState) {
}
@Override
public void onActivityDestroyed(@NonNull Activity activity) {
//1.移除观察者
SkinLayoutInflaterFactory observer =
mLayoutInflaterFactories.remove(activity);
SkinManager.getInstance().deleteObserver(observer);
}
}
2.10小结
(1)Factory2的添加都是在每个Activity执行完onCreate之后
(2)在SkinManager中使用观察者模式通知factory去更新UI。
(3)在SkinManager的loadSkin里面完成初始化。
2.11测试
(1)插件APK
-
可以是任意一个APK
-
插件APK就是去掉代码之后的apk,只需要用到其中的资源,可以将插件中的资源命名成自己APK中使用到的资源名称,即可以实现换肤.即用插件中的资源替换原来APP中的同名资源值。
(2)可以新建一个项目,作为插件apk,在其中写好自己项目中需要用到的换肤资源。
(3)编译插件apk,将生成了apk文件。
(4)运行宿主app,通过Device File Explorer在程序包名之下新建存放插件apk的目录
(5)通过Device File Explorer传递插件apk文件到宿主app中的插件目录中
(6)重新运行宿主APP,查看换肤效果
注意:插件apk的加载可以通过网络进行下载,然后存储。
3.打赏鼓励
感谢您的细心阅读,您的鼓励是我写作的不竭动力!!!