AVL平衡二叉搜索树 (介绍+例题)
定义:
平衡二叉树(AVL):是一种平衡的二叉搜索树。
平衡因子:将二叉树上节点的左子树高度减去右子树高度的值称为该节点的平衡因子BF(Balance Factor),|BF|<=1。
性质:
- 空二叉树是一个 AVL 树
- 如果 T 是一棵 AVL 树,那么其左右子树也是 AVL 树,并且|h(ls)-h(rs)| <= 1 ,h 是其左右子树的高度
- 树高为O(log n)
- 它必须是二叉搜索树。
插入节点:
与 BST(二叉搜索树)中类似,先进行一次失败的查找来确定插入的位置,插入节点后根据平衡因子来决定是否需要调整。
参考代码
//获取高度
int getHeight(Node *root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
return max(getHeight(root->l), getHeight(root->r)) + 1;
}
//获取平衡因子
int getBalance(Node *root)
{
return getHeight(root->l) - getHeight(root->r);
}
//节点插入
void insert(Node *&root, int x)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
root = new Node();
root->data = x;
root->l = root->r = NULL;
return;
}
if (x <= root->data)
{
//插入完成后
insert(root->l, x);
//进行平衡调整
if (getBalance(root) == 2)
{
// LL型,右旋
if (getBalance(root->l) == 1)
{
R(root);
}
// LR型,先对左子树左旋,再整体右旋
else if (getBalance(root->l) == -1)
{
LR(root);
}
}
}
else
{
insert(root->r, x);
if (getBalance(root) == -2)
{
// RR型,左旋
if (getBalance(root->r) == -1)
{
L(root);
}
// RL型,先对右子树右旋再整体左旋
else if (getBalance(root->r) == 1)
{
RL(root);
}
}
}
}
删除节点(未实现,待补):
- 删除和 BST 类似,将结点与后继交换后再删除。
- 删除会导致树高以及平衡因子变化,这时需要沿着被删除结点到根的路径来调整这种变化。
平衡的维护:
主要分以下4种平衡维护情况:
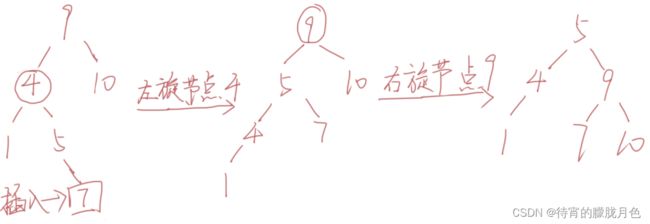
1.LL型
由于在A的左子树(L)的左子树(L)上插入新结点,使原来平衡二叉树变得不平衡,此时A的平衡因子由1增至2。下图是LL型的最简单形式,显然,按照大小关系,结点B应作为新的根结点,其余两个节点分别作为左右孩子节点才能平衡,A结点就好像是绕结点B顺时针旋转一样。(这里我们称为右旋)

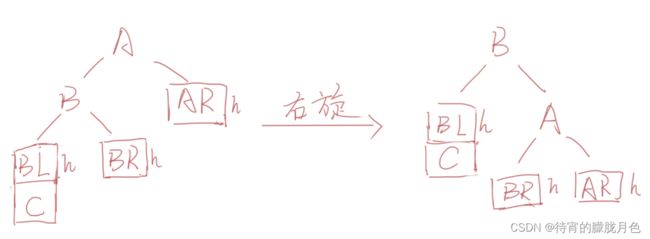
一般形式如下图所示,表示在A的左孩子B的左子树BL(不一定为空)中插入结点C而导致不平衡( h 表示子树的深度)。
这种情况调整如下:
a.将A的左孩子B提升为新的根结点;
b.将原来的根结点A降为B的右孩子;
c.各子树按大小关系连接(BL和AR不变,BR调整为A的左子树)。
参考代码
//右旋
void R(Node *&root)
{
Node *tmp = root->l;
root->l = tmp->r;
tmp->r = root;
root = tmp;
}
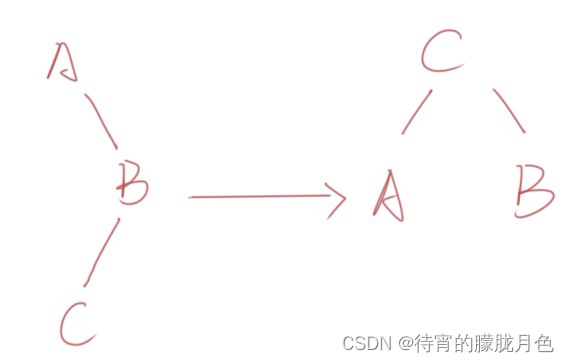
2.RR型
由于在A的右子树(R)的右子树(R)上插入新结点,使原来平衡二叉树变得不平衡,此时A的平衡因子由-1变为-2。下图是RR型的最简单形式。显然,按照大小关系,结点B应作为新的根结点,其余两个节点分别作为左右孩子节点才能平衡,A结点就好像是绕结点B逆时针旋转一样。(这里我们称为左旋)
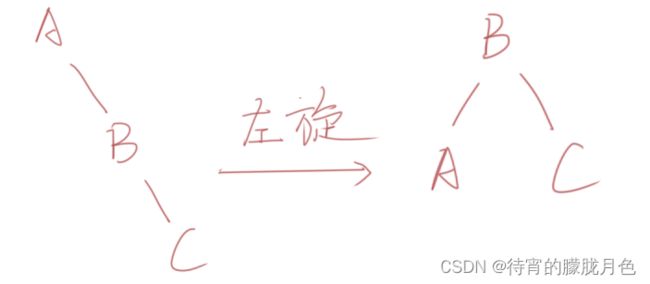
RR型调整的一般形式如下图所示,表示在A的右孩子B的右子树BR(不一定为空)中插入结点C而导致不平衡( h 表示子树的深度)。
这种情况调整如下:
a.将A的右孩子B提升为新的根结点;
b.将原来的根结点A降为B的左孩子
c.各子树按大小关系连接(AL和BR不变,BL调整为A的右子树)。
参考代码
//左旋
void L(Node *&root)
{
Node *tmp = root->r;
root->r = tmp->l;
tmp->l = root;
root = tmp;
}
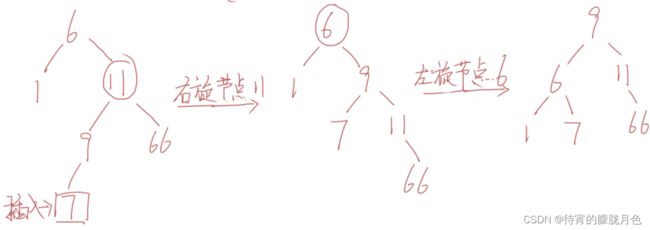
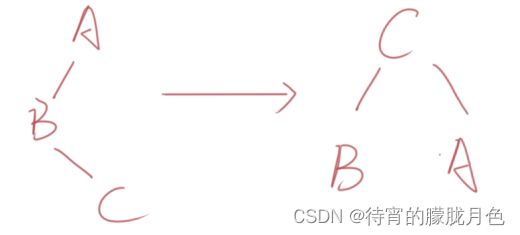
3.LR型
由于在A的左孩子(L)的右子树(R)上插入新结点,使原来平衡二叉树变得不平衡,此时A的平衡因子由1变为2。下图是LR型的最简单形式。显然,按照大小关系,结点C应作为新的根结点,其余两个节点分别作为左右孩子节点才能平衡。
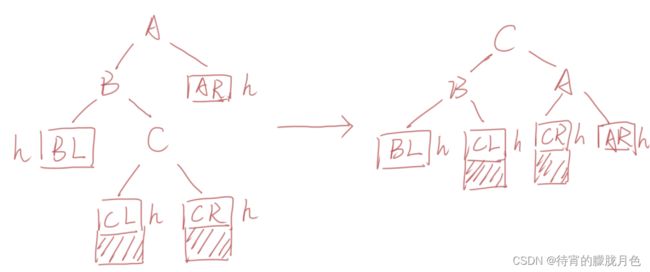
LR型调整的一般形式如下图所示,表示在A的左孩子B的右子树(根结点为C,不一定为空)中插入结点(图中两个阴影部分之一)而导致不平衡( h 表示子树的深度)。
这种情况调整如下:
将B的左孩子C提升为新的根结点;
将原来的根结点A降为C的右孩子;
各子树按大小关系连接(BL和AR不变,CL和CR分别调整为B的右子树和A的左子树)。
参考代码
//先左旋再右旋
void LR(Node *&root)
{
L(root->l);
R(root);
}
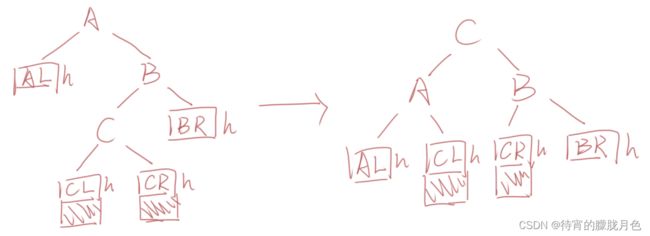
4.RL型
由于在A的右孩子(R)的左子树(L)上插入新结点,使原来平衡二叉树变得不平衡,此时A的平衡因子由-1变为-2。下图是RL型的最简单形式。显然,按照大小关系,结点C应作为新的根结点,其余两个节点分别作为左右孩子节点才能平衡。
RL型调整的一般形式如下图所示,表示在A的右孩子B的左子树(根结点为C,不一定为空)中插入结点(图中两个阴影部分之一)而导致不平衡( h 表示子树的深度)。
这种情况调整如下:
将B的左孩子C提升为新的根结点;
将原来的根结点A降为C的左孩子;
各子树按大小关系连接(AL和BR不变,CL和CR分别调整为A的右子树和B的左子树)。
参考代码
//先右旋再左旋
void RL(Node *&root)
{
R(root->r);
L(root);
}
例题:PAT-甲级 1123 Is It a Complete AVL Tree(板子题)
Question:
An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child subtrees of any node differ by at most one; if at any time they differ by more than one, rebalancing is done to restore this property. Figures 1-4 illustrate the rotation rules.
Now given a sequence of insertions, you are supposed to output the level-order traversal sequence of the resulting AVL tree, and to tell if it is a complete binary tree.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤ 20). Then N distinct integer keys are given in the next line. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, insert the keys one by one into an initially empty AVL tree. Then first print in a line the level-order traversal sequence of the resulting AVL tree. All the numbers in a line must be separated by a space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line. Then in the next line, print YES if the tree is complete, or NO if not.
Sample Input 1:
5
88 70 61 63 65
Sample Output 1:
70 63 88 61 65
YES
Sample Input 2:
8
88 70 61 96 120 90 65 68
Sample Output 2:
88 65 96 61 70 90 120 68
NO
参考代码:
#include
#define io ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0)
#define LL long long
#define PII pair
#define PLL pair
#define PIII pair
#define PSI pair
#define PIIS pair>
#define PDD pair
using namespace std;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int N = 2e5 + 5;
const int M = 1e5;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
struct Node
{
int data, pos;
Node *l, *r;
};
//获取高度
int getHeight(Node *root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
return max(getHeight(root->l), getHeight(root->r)) + 1;
}
//获取平衡因子
int getBalance(Node *root)
{
return getHeight(root->l) - getHeight(root->r);
}
//左旋
void L(Node *&root)
{
Node *tmp = root->r;
root->r = tmp->l;
tmp->l = root;
root = tmp;
}
//右旋
void R(Node *&root)
{
Node *tmp = root->l;
root->l = tmp->r;
tmp->r = root;
root = tmp;
}
// LR型
void LR(Node *&root)
{
L(root->l);
R(root);
}
// RL型
void RL(Node *&root)
{
R(root->r);
L(root);
}
void insert(Node *&root, int x)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
root = new Node();
root->data = x;
root->l = root->r = NULL;
return;
}
if (x <= root->data)
{
//插入完成后
insert(root->l, x);
//进行平衡调整
if (getBalance(root) == 2)
{
// LL型,右旋
if (getBalance(root->l) == 1)
{
R(root);
}
// LR型,先对左子树左旋,再整体右旋
else if (getBalance(root->l) == -1)
{
L(root->l);
R(root);
}
}
}
else
{
insert(root->r, x);
if (getBalance(root) == -2)
{
// RR型,左旋
if (getBalance(root->r) == -1)
{
L(root);
}
// RL型,先对右子树右旋再整体左旋
else if (getBalance(root->r) == 1)
{
R(root->r);
L(root);
}
}
}
}
int n;
int main()
{
// io;
cin >> n;
Node *root = NULL;
for (int i = 0, x; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> x;
insert(root, x);
}
queue heap;
root->pos = 1;
heap.push(root);
int m = 0;
while (heap.size())
{
auto tmp = heap.front();
heap.pop();
if (tmp->pos == 1)
cout << tmp->data;
else
cout << " " << tmp->data;
m = max(m, tmp->pos);
if (tmp->l != NULL)
{
tmp->l->pos = (tmp->pos) * 2;
heap.push(tmp->l);
}
if (tmp->r != NULL)
{
tmp->r->pos = (tmp->pos) * 2 + 1;
heap.push(tmp->r);
}
}
if (m <= n)
cout << "\nYES";
else
cout << "\nNO";
// system("pause");
return 0;
}
/*
*/