uboot启动流程(1)之链接脚本u-boot.lds详解
大部分转载了大神的博客:uboot启动流程(1)之链接脚本u-boot.lds详解_蒋文韬的博客-CSDN博客
部分穿插了对自身平台内容的理解。
=========================================================================
要分析 uboot 的启动流程,首先要找到“入口”,找到第一行程序在哪里。程序的链接是由链接脚本来决定的,所以通过链接脚本可以找到程序的入口。如果没有编译过 uboot 的话链接脚本为arch/arm/cpu/u-boot.lds。但是这个不是最终使用的链接脚本,最终的链接脚本是在这个链接脚本的基础上生成的。编译一下 uboot,编译完成以后就会在 uboot 根目录下生成 u-boot.lds文件
 只有编译 u-boot 以后才会在根目录下出现 u-boot.lds 文件!
只有编译 u-boot 以后才会在根目录下出现 u-boot.lds 文件!
打开 u-boot.lds,内容如下(以下文件内容是我所用的A40/T3平台):
OUTPUT_FORMAT("elf32-littlearm", "elf32-littlearm", "elf32-littlearm")
OUTPUT_ARCH(arm)
ENTRY(_start)
SECTIONS
{
. = 0x4A000000;
. = ALIGN(4);
.head :
{
*(.__image_copy_start)
arch/arm/cpu/armv7/spare_head.o (.data*)
}
.hash :
{
arch/arm/cpu/armv7/uboot_hash.o(.data*)
}
. = ALIGN(4);
.text :
{
*(.vectors)
arch/arm/cpu/armv7/start.o (.text*)
*(.text*)
}
. = ALIGN(4);
.rodata : { *(SORT_BY_ALIGNMENT(SORT_BY_NAME(.rodata*))) }
. = ALIGN(4);
.data :
{
*(.data*)
}
. = ALIGN(4);
. = .;
. = ALIGN(4);
.u_boot_list :
{
KEEP(*(SORT(.u_boot_list*)));
}
. = ALIGN(4);
.image_copy_end :
{
*(.__image_copy_end)
}
.rel_dyn_start :
{
*(.__rel_dyn_start)
}
.rel.dyn :
{
*(.rel*)
}
.rel_dyn_end :
{
*(.__rel_dyn_end)
}
.end :
{
*(.__end)
}
_image_binary_end = .;
. = ALIGN(4096);
.mmutable : {
*(.mmutable)
}
.bss_start __rel_dyn_start (OVERLAY) : {
KEEP(*(.__bss_start));
__bss_base = .;
}
.bss __bss_base (OVERLAY) : {
*(.bss*)
. = ALIGN(4);
__bss_limit = .;
}
.bss_end __bss_limit (OVERLAY) : {
KEEP(*(.__bss_end));
}
.dynsym _image_binary_end : { *(.dynsym) }
.dynbss : { *(.dynbss) }
.dynstr : { *(.dynstr*) }
.dynamic : { *(.dynamic*) }
.plt : { *(.plt*) }
.interp : { *(.interp*) }
.gnu.hash : { *(.gnu.hash) }
.gnu : { *(.gnu*) }
.ARM.exidx : { *(.ARM.exidx*) }
.gnu.linkonce.armexidx : { *(.gnu.linkonce.armexidx.*) }
}
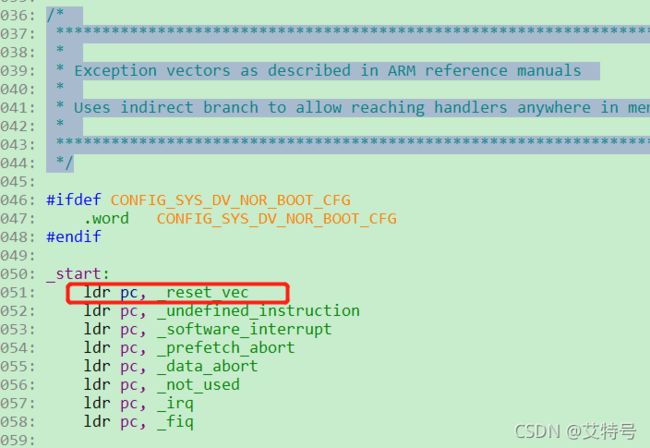
第 3 行为代码当前入口点:_start, _start 在文件 arch/arm/lib/vectors.S 中有定义
=========================================================================
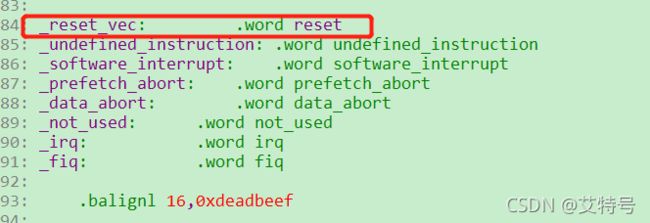
(注:我的A40/T3平台略有不同,使用了一个“reset_vec”变量,但该变量实际指向的还是“reset”)
=========================================================================
可以看出,_start 后面就是中断向量表,从图中的“.section “.vectors”, "ax”可以得到,此代码存放在.vectors 段里面。使用如下命令在 uboot 中查找“__image_copy_start”:
grep -nR “__image_copy_start”打开 u-boot.map
打开 u-boot.map
u-boot.map 是 uboot 的映射文件,可以从此文件看到某个文件或者函数链接到了哪个地址,从图中的 932 行可以看到__image_copy_start 为 0X87800000,而.text 的起始地址也是0X87800000。
=========================================================================
(注:以下时我的A40/T3平台的u-boot.map)
可以看到A40/T3平台'__image_copy_start'的起始地址是0x4a000000,但是.text 的起始地址是0x4a000640,因为在.text前还有个.head段和.hash段,从spare_head.o和uboot_hash.o可以看出这两段代码是在:spare_head.c 和 uboot_hash.c 文件中,如下:
spare_head.c文件:
/*
* (C) Copyright 2007-2013
* Allwinner Technology Co., Ltd.
* Jerry Wang
*
...... 此处略去
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
* along with this program; if not, write to the Free Software
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston,
* MA 02111-1307 USA
*/
#include
#include
extern char uboot_hash_value[64];
#pragma pack(1)
struct spare_boot_head_t uboot_spare_head =
{
{
/* jump_instruction */
...... 此处略去
}
};
#pragma pack()
/*******************************************************************************
*
* 关于Boot_file_head中的jump_instruction字段
*
* jump_instruction字段存放的是一条跳转指令:( B BACK_OF_Boot_file_head ),此跳
*转指令被执行后,程序将跳转到Boot_file_head后面第一条指令。
*
* ARM指令中的B指令编码如下:
* +--------+---------+------------------------------+
* | 31--28 | 27--24 | 23--0 |
* +--------+---------+------------------------------+
* | cond | 1 0 1 0 | signed_immed_24 |
* +--------+---------+------------------------------+
* 《ARM Architecture Reference Manual》对于此指令有如下解释:
* Syntax :
* B{}
* Is the condition under which the instruction is executed. If the
* is ommitted, the AL(always,its code is 0b1110 )is used.
*
* Specified the address to branch to. The branch target address is
* calculated by:
* 1. Sign-extending the 24-bit signed(wro's complement)immediate
* to 32 bits.
* 2. Shifting the result left two bits.
* 3. Adding to the contents of the PC, which contains the address
* of the branch instruction plus 8.
*
* 由此可知,此指令编码的最高8位为:0b11101010,低24位根据Boot_file_head的大小动
*态生成,所以指令的组装过程如下:
* ( sizeof( boot_file_head_t ) + sizeof( int ) - 1 ) / sizeof( int ) 求出文件头
* 占用的“字”的个数
* - 2 减去PC预取的指令条数
* & 0x00FFFFFF 求出signed-immed-24
* | 0xEA000000 组装成B指令
*
*******************************************************************************/
该文件中就是对定义的 “struct spare_boot_head_t uboot_spare_head” 结构体变量赋值,该结构体变量的定义如下:
struct spare_boot_head_t
{
struct spare_boot_ctrl_head boot_head;
struct spare_boot_data_head boot_data;
struct spare_boot_ext_head boot_ext[16];
};
内部是定义了三个结构体变量,这三个结构体的定义可以自行看代码,计算后的大小也是0x600,与.head段的大小相对应。
uboot_hash.c 文件
/*
* (C) Copyright 2007-2013
* Allwinner Technology Co., Ltd.
* Jerry Wang
*
* See file CREDITS for list of people who contributed to this
* project.
*
...... 此处略去
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
* along with this program; if not, write to the Free Software
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston,
* MA 02111-1307 USA
*/
#include
char uboot_hash_value[64] = {0x38};
而uboot_hash.c 文件只是定义了一个64字节的数组,即0x40的大小,与.hash段的大小相对应。
(至于以上两段是用来干嘛的,暂时还未深究,留待后面再去挖掘)
因此该A40/T3平台.text 的起始地址是0x4a000640
=========================================================================
继续回到u-boot.lds中,第 11 行是 vectors 段,vectors 段保存中断向量表,从vector.S中我们知道了 vectors.S 的代码是存在 vectors 段中的。从u-boot.map可以看出,vectors 段的起始地址也是0X87800000,说明整个 uboot 的起始地址就是 0X87800000,这也是为什么我们裸机例程的链接起始地址选择 0X87800000 了,目的就是为了和 uboot一致。
第 12 行将 arch/arm/cpu/armv7/start.s 编译出来的代码放到中断向量表后面。
第 13 行为 text 段,其他的代码段就放到这里
在 u-boot.lds 中有一些跟地址有关的“变量”需要我们注意一下,后面分析 u-boot 源码的时候会用到,这些变量要最终编译完成才能确定的!!!比如我编译完成以后这些“变量”的值
| 变量 | 数值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| __image_copy_start | 0x87800000 | uboot 拷贝的首地址 |
| __image_copy_end | 0x8785dd54 | uboot 拷贝的结束地址 |
| __rel_dyn_start | 0x8785dd54 | .rel.dyn 段起始地址 |
| __rel_dyn_end | 0x878668f4 | .rel.dyn 段结束地址 |
| _image_binary_end | 0x878668f4 | 镜像结束地址 |
| __bss_start | 0x8785dd54 | .bss 段起始地址 |
| __bss_end | 0x878a8e74 | .bss 段结束地址 |
“变量”值可以在 u-boot.map 文件中查找,除了__image_copy_start以外,其他的变量值每次编译的时候可能会变化,如果修改了 uboot 代码、修改了 uboot 配置、选用不同的优化等级等等都会影响到这些值。所以,一切以实际值为准!