OpenRisc-41-or1200的cache模块分析
引言
为CPU提供足够的,稳定的指令流和数据流是计算机体系结构设计中两个永恒的话题。为了给CPU提供指令流,需要设计分支预测机构,为了给CPU提供数据流,就需要设计cache了。其实,无论是insn还是data,都需要访问存储器,所以从这个角度来说,cache需要承担更重要的角色。
本小节我们就分析一下or1200的cache部分的实现。
1,cache产生原因
还是那句话,研究一个东西,首先要了解其来龙去脉,cache也不例外。
cache的出现是为了解决memory wall问题。由于cpu的频率越来越高,处理能力越来越大,但存储系统虽有一定发展,但还是和CPU的距离越来越大。这样就会出现“茶壶里倒饺子”的情况,就是所谓的存储墙问题。cache,正是为了解决这个问题而出现的。
2,cache基础
关于cache,我们需要先了解cache的映射方式,写策略,替换策略,cache的优化技术,等等相关内容。这些内容,我们之前都已介绍过了,这里不再赘述,如有疑问,请参考:http://blog.csdn.net/rill_zhen/article/details/9491095
3,cache工作机制
1>基本工作过程
在分析or1200的cache的具体实现之前,我们有必要先了解cache的一般工作机制。为了清晰的展示这个过程,我假设了一个例子,这个例子是MMU模块分析时,那个例子的延伸。
在分析or1200的MMU时,我们假设了一个例子,那个示例中,MMU将变量test的虚拟地址(0x2008),转换成了物理地址(0x1006008)。
cpu访问内存,虚实地址转换,是其中的第一步,在完成虚实转换之后,并不是直接用这个地址访问外部的SDRAM,而是MMU先将物理地址发送到cache,如果cache hit则直接ack cpu,如果cache miss则才需要访问下一级cache或外部SDRAM。
2>直接映射cache的工作机制
上面我们介绍了cache的大致工作流程,但是,cache的具体工作细节是怎样的呢?
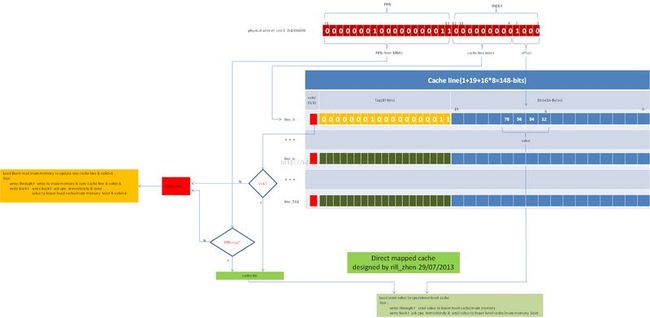
得到test的物理地址之后是如何运作的呢,下面,我们就以直接映射的,大小为8K,line数目为512,line宽度为16-Bytes的一个cache,来说明,如下图所示:
通过这幅图,我们可以很清楚的看到其工作细节。
说明:
a,这个cache的映射方式是direct mapped。
b,cache的总容量是8K,也正好就是一个内存页。
c,整个cache有512个cache line,或者叫cache entry。
d,每个cache line缓存16个字节的数据。
e,由于是直接映射,所以不存在什么替换算法,哪个line出现cache miss就替换哪个。
f,写策略,write through和write back两种。
g,由于cache一般是对软件编程模型透明的,所以很少需要和软件交互,只需要最基本的控制,比如,需要把那个通道lock啊,cache flush啊,如果采用LRU替换算法,及时更新LRU值啊,等等。这一点和MMU大不相同,MMU需要软件的大量的干预和控制。
h,简单介绍一下工作机制:
首先,cache将虚拟地址的index域进行取模运算(%),具体和那个值取模,就看cache line的数量和缓存的数据大小。本例子中cacheline数量是512,缓存数量是16B,所以,需要将index分成cache line index(定位到哪一行),和行内偏移(定位到这一行的哪一个字节)。
cache根据cache line index定位到cache的具体一行,判断这一行的valid标志,如果有效,在将这一行的tag和MMU产生的PPN进行比较(因为一个cache line可能会对应多个内存地址)。如果tag和PPN匹配,那么说明cache hit,如果两个判断条件有一个不满足,说明cache miss,这时,cache会burst access(突发访问,本例子是叠4,每次4B,正好16B),更新这一个cache line。
i,cache的操作
刷新:cache将valid置0即可。
锁定:加入有某个程序运行时间很长,为了防止其他程序在出现cache miss时将这个程序的cache line刷新,可以将这个程序使用的cache line 锁定。具体锁定方式可以是通道锁定,也可以是某一行锁定(将整个cache分成若干组,每个组有若干行,一个组就叫一个通道(way))。
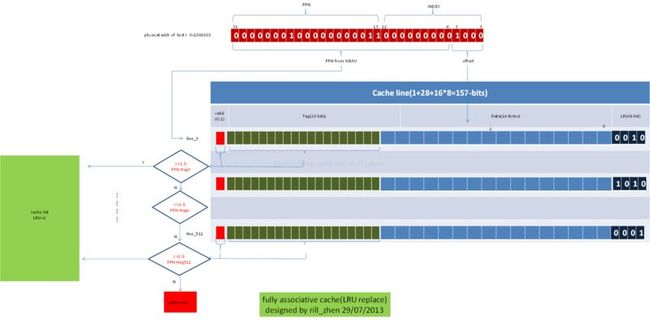
3>全相连映射cache的工作机制
上面我们介绍了直接映射cache的工作机制,其他两种映射方式的cache也大体相同,不同的地方是cache line搜索方法,替换策略,写策略不同。
全相连映射cache的工作机制,如下图所示:
4>组相连映射cache的工作机制
介于直接映射和全相连映射之间,不再赘述。
4,or1200的cache系统分析
了解了cache的工作机制之后,再分析or1200的cache的具体实现就相对容易一些,由于cache只是内存的一个子集,没有独立的编程空间,所以与软件的交互比较少,分析起来就更简单一些。
1>or1200的cache的工作机制
or1200的cache采用直接映射方式,大小是8K,共512个entry,每个line缓存16个字节,每个line由1-bit标志位,19-bit tag和16*8-bit数据组成。
上面我们已经详细说明了这种cache的工作机制,or1200的cache也不例外。
2>or1200的cache组成
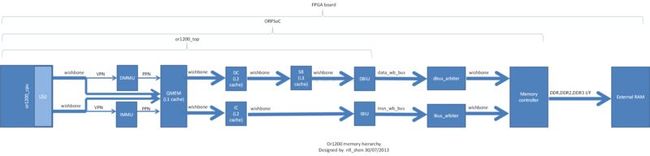
or1200的cache,由qmem模块组成一级cache,dcache/icache组成二级cache,sb模块组成数据的三级cache。
下面是整个ordb2a开饭板的存储系统的框图,从中,我们可以清晰的看出整个系统的存储子系统的数据通路。
3>qmem模块分析
1》整体分析
qmem模块是一级cache,在or1200_define.v中,对qmem有如下描述,从中我们可以知道qmem的作用,意义,容量等信息。
///////////////////////////////////////////////// // // Quick Embedded Memory (QMEM) // // // Quick Embedded Memory // // Instantiation of dedicated insn/data memory (RAM or ROM). // Insn fetch has effective throughput 1insn / clock cycle. // Data load takes two clock cycles / access, data store // takes 1 clock cycle / access (if there is no insn fetch)). // Memory instantiation is shared between insn and data, // meaning if insn fetch are performed, data load/store // performance will be lower. // // Main reason for QMEM is to put some time critical functions // into this memory and to have predictable and fast access // to these functions. (soft fpu, context switch, exception // handlers, stack, etc) // // It makes design a bit bigger and slower. QMEM sits behind // IMMU/DMMU so all addresses are physical (so the MMUs can be // used with QMEM and QMEM is seen by the CPU just like any other // memory in the system). IC/DC are sitting behind QMEM so the // whole design timing might be worse with QMEM implemented. // //`define OR1200_QMEM_IMPLEMENTED // // Base address and mask of QMEM // // Base address defines first address of QMEM. Mask defines // QMEM range in address space. Actual size of QMEM is however // determined with instantiated RAM/ROM. However bigger // mask will reserve more address space for QMEM, but also // make design faster, while more tight mask will take // less address space but also make design slower. If // instantiated RAM/ROM is smaller than space reserved with // the mask, instatiated RAM/ROM will also be shadowed // at higher addresses in reserved space. // `define OR1200_QMEM_IADDR 32'h0080_0000 `define OR1200_QMEM_IMASK 32'hfff0_0000 // Max QMEM size 1MB `define OR1200_QMEM_DADDR 32'h0080_0000 `define OR1200_QMEM_DMASK 32'hfff0_0000 // Max QMEM size 1MB // // QMEM interface byte-select capability // // To enable qmem_sel* ports, define this macro. // //`define OR1200_QMEM_BSEL // // QMEM interface acknowledge // // To enable qmem_ack port, define this macro. // //`define OR1200_QMEM_ACK
2》qmem模块RTL代码分析
qmem模块只有一个RTL文件,就是or1200_qmem_top.v,代码分析,不是代码的复制,粘贴之后加点注释那么简单。为了突出重点,在了解了qmem的大体功能之后,我们需要了解其核心代码,下面,我们分析一下qmem模块的核心,也就是其FSM,如下所示:
`define OR1200_QMEMFSM_IDLE 3'd0 `define OR1200_QMEMFSM_STORE 3'd1 `define OR1200_QMEMFSM_LOAD 3'd2 `define OR1200_QMEMFSM_FETCH 3'd3 // // QMEM control FSM // always @(`OR1200_RST_EVENT rst or posedge clk) if (rst == `OR1200_RST_VALUE) begin state <= `OR1200_QMEMFSM_IDLE; qmem_dack <= 1'b0; qmem_iack <= 1'b0; end else case (state) // synopsys parallel_case `OR1200_QMEMFSM_IDLE: begin if (qmemdmmu_cycstb_i & daddr_qmem_hit & qmemdcpu_we_i & qmem_ack) begin state <= `OR1200_QMEMFSM_STORE; qmem_dack <= 1'b1; qmem_iack <= 1'b0; end else if (qmemdmmu_cycstb_i & daddr_qmem_hit & qmem_ack) begin state <= `OR1200_QMEMFSM_LOAD; qmem_dack <= 1'b1; qmem_iack <= 1'b0; end else if (qmemimmu_cycstb_i & iaddr_qmem_hit & qmem_ack) begin state <= `OR1200_QMEMFSM_FETCH; qmem_iack <= 1'b1; qmem_dack <= 1'b0; end end `OR1200_QMEMFSM_STORE: begin if (qmemdmmu_cycstb_i & daddr_qmem_hit & qmemdcpu_we_i & qmem_ack) begin state <= `OR1200_QMEMFSM_STORE; qmem_dack <= 1'b1; qmem_iack <= 1'b0; end else if (qmemdmmu_cycstb_i & daddr_qmem_hit & qmem_ack) begin state <= `OR1200_QMEMFSM_LOAD; qmem_dack <= 1'b1; qmem_iack <= 1'b0; end else if (qmemimmu_cycstb_i & iaddr_qmem_hit & qmem_ack) begin state <= `OR1200_QMEMFSM_FETCH; qmem_iack <= 1'b1; qmem_dack <= 1'b0; end else begin state <= `OR1200_QMEMFSM_IDLE; qmem_dack <= 1'b0; qmem_iack <= 1'b0; end end `OR1200_QMEMFSM_LOAD: begin if (qmemdmmu_cycstb_i & daddr_qmem_hit & qmemdcpu_we_i & qmem_ack) begin state <= `OR1200_QMEMFSM_STORE; qmem_dack <= 1'b1; qmem_iack <= 1'b0; end else if (qmemdmmu_cycstb_i & daddr_qmem_hit & qmem_ack) begin state <= `OR1200_QMEMFSM_LOAD; qmem_dack <= 1'b1; qmem_iack <= 1'b0; end else if (qmemimmu_cycstb_i & iaddr_qmem_hit & qmem_ack) begin state <= `OR1200_QMEMFSM_FETCH; qmem_iack <= 1'b1; qmem_dack <= 1'b0; end else begin state <= `OR1200_QMEMFSM_IDLE; qmem_dack <= 1'b0; qmem_iack <= 1'b0; end end `OR1200_QMEMFSM_FETCH: begin if (qmemdmmu_cycstb_i & daddr_qmem_hit & qmemdcpu_we_i & qmem_ack) begin state <= `OR1200_QMEMFSM_STORE; qmem_dack <= 1'b1; qmem_iack <= 1'b0; end else if (qmemdmmu_cycstb_i & daddr_qmem_hit & qmem_ack) begin state <= `OR1200_QMEMFSM_LOAD; qmem_dack <= 1'b1; qmem_iack <= 1'b0; end else if (qmemimmu_cycstb_i & iaddr_qmem_hit & qmem_ack) begin state <= `OR1200_QMEMFSM_FETCH; qmem_iack <= 1'b1; qmem_dack <= 1'b0; end else begin state <= `OR1200_QMEMFSM_IDLE; qmem_dack <= 1'b0; qmem_iack <= 1'b0; end end default: begin state <= `OR1200_QMEMFSM_IDLE; qmem_dack <= 1'b0; qmem_iack <= 1'b0; end endcase
分析:
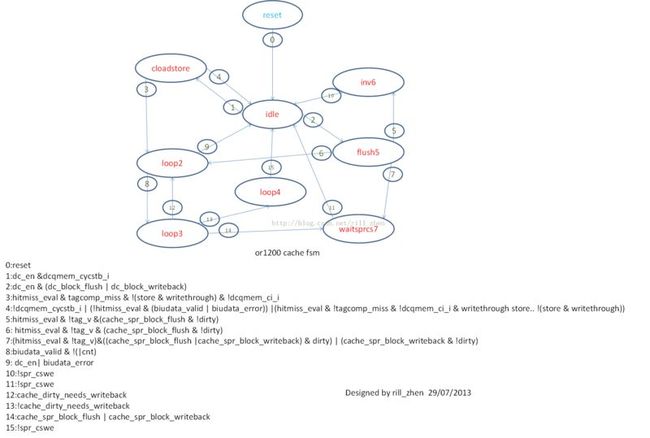
可以看出qmem共有4个状态,为了便于查看,我画出了qmem的状态图,如下所示,有状态和状态转移条件,一目了然,不再赘述。
4>dcache模块分析
data cache和instruction cache机制相似,这里只分析data cache。
1》整体分析
data cache是外部内存的一个子集,其作用也是一般意义上的cache的作用。
这里只说明一下几点:
a,cache的预取,在cache空闲的时候,可以事先将内存中的部分数据填充到cache里,降低cache miss概率。
b,cache的无效控制,如果有些cache line有特殊要求,软件可以设置这些line为无效。
c,cache的锁定,本小节开始部分已经介绍了。
2》代码分析
dcache由四个文件组成,分别是:or1200_dc_top.v,or1200_dc_fsm.v,or1200_dc_tag.v,or1200_dc_ram.v。这里只介绍其核心部分,也就是or1200_dc_fsm.v中的FSM,代码如下所示:
`define OR1200_DCFSM_IDLE 3'd0
`define OR1200_DCFSM_CLOADSTORE 3'd1
`define OR1200_DCFSM_LOOP2 3'd2
`define OR1200_DCFSM_LOOP3 3'd3
`define OR1200_DCFSM_LOOP4 3'd4
`define OR1200_DCFSM_FLUSH5 3'd5
`define OR1200_DCFSM_INV6 3'd6 //invalidate
`define OR1200_DCFSM_WAITSPRCS7 3'd7
//
// Main DC FSM
//
always @(posedge clk or `OR1200_RST_EVENT rst)
begin
if (rst == `OR1200_RST_VALUE)
begin
state <= `OR1200_DCFSM_IDLE;
addr_r <= 32'd0;
hitmiss_eval <= 1'b0;
store <= 1'b0;
load <= 1'b0;
cnt <= `OR1200_DCLS'd0;
cache_miss <= 1'b0;
cache_dirty_needs_writeback <= 1'b0;
cache_inhibit <= 1'b0;
did_early_load_ack <= 1'b0;
cache_spr_block_flush <= 1'b0;
cache_spr_block_writeback <= 1'b0;
end
else
case (state) // synopsys parallel_case
`OR1200_DCFSM_IDLE :
begin
if (dc_en & (dc_block_flush | dc_block_writeback))
begin
cache_spr_block_flush <= dc_block_flush;
cache_spr_block_writeback <= dc_block_writeback;
hitmiss_eval <= 1'b1;
state <= `OR1200_DCFSM_FLUSH5;
addr_r <= spr_dat_i;
end
else if (dc_en & dcqmem_cycstb_i)
begin
state <= `OR1200_DCFSM_CLOADSTORE;
hitmiss_eval <= 1'b1;
store <= dcqmem_we_i;
load <= !dcqmem_we_i;
end
end // case: `OR1200_DCFSM_IDLE
`OR1200_DCFSM_CLOADSTORE:
begin
hitmiss_eval <= 1'b0;
if (hitmiss_eval)
begin
cache_inhibit <= dcqmem_ci_i; // Check for cache inhibit here
cache_miss <= tagcomp_miss;
cache_dirty_needs_writeback <= dirty;
addr_r <= lsu_addr;
end
// Evaluate any cache line load/stores in first cycle:
if (hitmiss_eval & tagcomp_miss & !(store & writethrough) & !dcqmem_ci_i)
begin
// Miss - first either:
// 1) write back dirty line
if (dirty)
begin
// Address for writeback
addr_r <= {tag, lsu_addr[`OR1200_DCINDXH:2],2'd0};
load <= 1'b0;
store <= 1'b1;
`ifdef OR1200_VERBOSE
$display("%t: dcache miss and dirty", $time);
`endif
end
// 2) load requested line
else
begin
addr_r <= lsu_addr;
load <= 1'b1;
store <= 1'b0;
end // else: !if(dirty)
state <= `OR1200_DCFSM_LOOP2;
// Set the counter for the burst accesses
cnt <= ((1 << `OR1200_DCLS) - 4);
end
else if (// Strobe goes low
!dcqmem_cycstb_i |
// Cycle finishes
(!hitmiss_eval & (biudata_valid | biudata_error)) |
// Cache hit in first cycle....
(hitmiss_eval & !tagcomp_miss & !dcqmem_ci_i &
// .. and you're not doing a writethrough store..
!(store & writethrough)))
begin
state <= `OR1200_DCFSM_IDLE;
load <= 1'b0;
store <= 1'b0;
cache_inhibit <= 1'b0;
cache_dirty_needs_writeback <= 1'b0;
end
end // case: `OR1200_DCFSM_CLOADSTORE
`OR1200_DCFSM_LOOP2 :
begin // loop/abort
if (!dc_en| biudata_error)
begin
state <= `OR1200_DCFSM_IDLE;
load <= 1'b0;
store <= 1'b0;
cnt <= `OR1200_DCLS'd0;
end
if (biudata_valid & (|cnt))
begin
cnt <= cnt - 4;
addr_r[`OR1200_DCLS-1:2] <= addr_r[`OR1200_DCLS-1:2] + 1;
end
else if (biudata_valid & !(|cnt))
begin
state <= `OR1200_DCFSM_LOOP3;
addr_r <= lsu_addr;
load <= 1'b0;
store <= 1'b0;
end
// Track if we did an early ack during a load
if (load_miss_ack)
did_early_load_ack <= 1'b1;
end // case: `OR1200_DCFSM_LOOP2
`OR1200_DCFSM_LOOP3:
begin // figure out next step
if (cache_dirty_needs_writeback)
begin
// Just did store of the dirty line so now load new one
load <= 1'b1;
// Set the counter for the burst accesses
cnt <= ((1 << `OR1200_DCLS) - 4);
// Address of line to be loaded
addr_r <= lsu_addr;
cache_dirty_needs_writeback <= 1'b0;
state <= `OR1200_DCFSM_LOOP2;
end // if (cache_dirty_needs_writeback)
else if (cache_spr_block_flush | cache_spr_block_writeback)
begin
// Just wrote back the line to memory, we're finished.
cache_spr_block_flush <= 1'b0;
cache_spr_block_writeback <= 1'b0;
state <= `OR1200_DCFSM_WAITSPRCS7;
end
else
begin
// Just loaded a new line, finish up
did_early_load_ack <= 1'b0;
state <= `OR1200_DCFSM_LOOP4;
end
end // case: `OR1200_DCFSM_LOOP3
`OR1200_DCFSM_LOOP4:
begin
state <= `OR1200_DCFSM_IDLE;
end
`OR1200_DCFSM_FLUSH5:
begin
hitmiss_eval <= 1'b0;
if (hitmiss_eval & !tag_v)
begin
// Not even cached, just ignore
cache_spr_block_flush <= 1'b0;
cache_spr_block_writeback <= 1'b0;
state <= `OR1200_DCFSM_WAITSPRCS7;
end
else if (hitmiss_eval & tag_v)
begin
// Tag is valid - what do we do?
if ((cache_spr_block_flush | cache_spr_block_writeback) & dirty)
begin
// Need to writeback
// Address for writeback (spr_dat_i has already changed so
// use line number from addr_r)
addr_r <= {tag, addr_r[`OR1200_DCINDXH:2],2'd0};
load <= 1'b0;
store <= 1'b1;
`ifdef OR1200_VERBOSE
$display("%t: block flush: dirty block", $time);
`endif
state <= `OR1200_DCFSM_LOOP2;
// Set the counter for the burst accesses
cnt <= ((1 << `OR1200_DCLS) - 4);
end
else if (cache_spr_block_flush & !dirty)
begin
// Line not dirty, just need to invalidate
state <= `OR1200_DCFSM_INV6;
end // else: !if(dirty)
else if (cache_spr_block_writeback & !dirty)
begin
// Nothing to do - line is valid but not dirty
cache_spr_block_writeback <= 1'b0;
state <= `OR1200_DCFSM_WAITSPRCS7;
end
end // if (hitmiss_eval & tag_v)
end
`OR1200_DCFSM_INV6:
begin
cache_spr_block_flush <= 1'b0;
// Wait until SPR CS goes low before going back to idle
if (!spr_cswe)
state <= `OR1200_DCFSM_IDLE;
end
`OR1200_DCFSM_WAITSPRCS7:
begin
// Wait until SPR CS goes low before going back to idle
if (!spr_cswe)
state <= `OR1200_DCFSM_IDLE;
end
endcase // case (state)
end // always @ (posedge clk or `OR1200_RST_EVENT rst)
为了便于理解,我画出了其状态图,如下所示:
5>sb模块分析
1》整体分析
store buffer,其本质是一个FIFO,相当于一个write back的cache,其功能和相关分析,之前已经做过,请参考:http://blog.csdn.net/rill_zhen/article/details/9491095 中的第2.1章节。
关于这个FIFO的depth和width,or1200-define.v中有如下定义:
// // Number of store buffer entries // // Verified number of entries are 4 and 8 entries // (2 and 3 for OR1200_SB_LOG). OR1200_SB_ENTRIES must // always match 2**OR1200_SB_LOG. // To disable store buffer, undefine // OR1200_SB_IMPLEMENTED. // `define OR1200_SB_LOG 2 // 2 or 3 `define OR1200_SB_ENTRIES 4 // 4 or 8
2》代码分析
sb模块包含两个文件,or1200_sb.v和or1200_sb_fifo.v,第二个从文件名就可以看出是一个FIFO,其物理结构是一个双口的RAM,这里只分析第一个,主要代码如下所示:
代码很少,只有150多行。
module or1200_sb(
// RISC clock, reset
clk, rst,
// Internal RISC bus (SB)
sb_en,
// Internal RISC bus (DC<->SB)
dcsb_dat_i, dcsb_adr_i, dcsb_cyc_i, dcsb_stb_i, dcsb_we_i, dcsb_sel_i, dcsb_cab_i,
dcsb_dat_o, dcsb_ack_o, dcsb_err_o,
// BIU bus
sbbiu_dat_o, sbbiu_adr_o, sbbiu_cyc_o, sbbiu_stb_o, sbbiu_we_o, sbbiu_sel_o, sbbiu_cab_o,
sbbiu_dat_i, sbbiu_ack_i, sbbiu_err_i
);
parameter dw = `OR1200_OPERAND_WIDTH;
parameter aw = `OR1200_OPERAND_WIDTH;
//
// RISC clock, reset
//
input clk; // RISC clock
input rst; // RISC reset
//
// Internal RISC bus (SB)
//
input sb_en; // SB enable
//
// Internal RISC bus (DC<->SB)
//
input [dw-1:0] dcsb_dat_i; // input data bus
input [aw-1:0] dcsb_adr_i; // address bus
input dcsb_cyc_i; // WB cycle
input dcsb_stb_i; // WB strobe
input dcsb_we_i; // WB write enable
input dcsb_cab_i; // CAB input
input [3:0] dcsb_sel_i; // byte selects
output [dw-1:0] dcsb_dat_o; // output data bus
output dcsb_ack_o; // ack output
output dcsb_err_o; // err output
//
// BIU bus
//
output [dw-1:0] sbbiu_dat_o; // output data bus
output [aw-1:0] sbbiu_adr_o; // address bus
output sbbiu_cyc_o; // WB cycle
output sbbiu_stb_o; // WB strobe
output sbbiu_we_o; // WB write enable
output sbbiu_cab_o; // CAB input
output [3:0] sbbiu_sel_o; // byte selects
input [dw-1:0] sbbiu_dat_i; // input data bus
input sbbiu_ack_i; // ack output
input sbbiu_err_i; // err output
`ifdef OR1200_SB_IMPLEMENTED
//
// Internal wires and regs
//
wire [4+dw+aw-1:0] fifo_dat_i; // FIFO data in
wire [4+dw+aw-1:0] fifo_dat_o; // FIFO data out
wire fifo_wr;
wire fifo_rd;
wire fifo_full;
wire fifo_empty;
wire sel_sb;
reg sb_en_reg;
reg outstanding_store;
reg fifo_wr_ack;
//
// FIFO data in/out
//
assign fifo_dat_i = {dcsb_sel_i, dcsb_dat_i, dcsb_adr_i};
assign {sbbiu_sel_o, sbbiu_dat_o, sbbiu_adr_o} = sel_sb ? fifo_dat_o : {dcsb_sel_i, dcsb_dat_i, dcsb_adr_i};
//
// Control
//
assign fifo_wr = dcsb_cyc_i & dcsb_stb_i & dcsb_we_i & ~fifo_full & ~fifo_wr_ack;
assign fifo_rd = ~outstanding_store;
assign dcsb_dat_o = sbbiu_dat_i;
assign dcsb_ack_o = sel_sb ? fifo_wr_ack : sbbiu_ack_i;
assign dcsb_err_o = sel_sb ? 1'b0 : sbbiu_err_i; // SB never returns error
assign sbbiu_cyc_o = sel_sb ? outstanding_store : dcsb_cyc_i;
assign sbbiu_stb_o = sel_sb ? outstanding_store : dcsb_stb_i;
assign sbbiu_we_o = sel_sb ? 1'b1 : dcsb_we_i;
assign sbbiu_cab_o = sel_sb ? 1'b0 : dcsb_cab_i;
assign sel_sb = sb_en_reg & (~fifo_empty | (fifo_empty & outstanding_store));
//
// SB enable
//
always @(posedge clk or `OR1200_RST_EVENT rst)
if (rst == `OR1200_RST_VALUE)
sb_en_reg <= 1'b0;
else if (sb_en & ~dcsb_cyc_i)
sb_en_reg <= 1'b1; // enable SB when there is no dcsb transfer in progress
else if (~sb_en & (~fifo_empty | (fifo_empty & outstanding_store)))
sb_en_reg <= 1'b0; // disable SB when there is no pending transfers from SB
//
// Store buffer FIFO instantiation
//
or1200_sb_fifo or1200_sb_fifo (
.clk_i(clk),
.rst_i(rst),
.dat_i(fifo_dat_i),
.wr_i(fifo_wr),
.rd_i(fifo_rd),
.dat_o(fifo_dat_o),
.full_o(fifo_full),
.empty_o(fifo_empty)
);
//
// fifo_rd
//
always @(posedge clk or `OR1200_RST_EVENT rst)
if (rst == `OR1200_RST_VALUE)
outstanding_store <= 1'b0;
else if (sbbiu_ack_i)
outstanding_store <= 1'b0;
else if (sel_sb | fifo_wr)
outstanding_store <= 1'b1;
//
// fifo_wr_ack
//
always @(posedge clk or `OR1200_RST_EVENT rst)
if (rst == `OR1200_RST_VALUE)
fifo_wr_ack <= 1'b0;
else if (fifo_wr)
fifo_wr_ack <= 1'b1;
else
fifo_wr_ack <= 1'b0;
`else // !OR1200_SB_IMPLEMENTED
assign sbbiu_dat_o = dcsb_dat_i;
assign sbbiu_adr_o = dcsb_adr_i;
assign sbbiu_cyc_o = dcsb_cyc_i;
assign sbbiu_stb_o = dcsb_stb_i;
assign sbbiu_we_o = dcsb_we_i;
assign sbbiu_cab_o = dcsb_cab_i;
assign sbbiu_sel_o = dcsb_sel_i;
assign dcsb_dat_o = sbbiu_dat_i;
assign dcsb_ack_o = sbbiu_ack_i;
assign dcsb_err_o = sbbiu_err_i;
`endif
endmodule
6>biu模块分析
1》整体分析
biu(bus ingerface unit)模块,是or1200_top和外界进行数据交换的窗口,对于or1200,例化了两个,分别是dbiu和ibiu。biu模块除了和外界交换数据外,还有判断字节对齐等功能。
这个模块主要是一个wishbone协议的slave和master的一个wrapper,如果你对wishbone总线protocol比较熟悉的话,这个模块看起来就简单多了,我之前也写过wishbone的相关的内容,请参考:http://blog.csdn.net/rill_zhen/article/details/8659788
2》代码分析
biu模块包含一个文件,or1200_wb_biu.v,主要是wishbone协议的时序产生逻辑,这里不做细说,为了保持本文的完整性,其主要代码,如下所示:
module or1200_wb_biu(
// RISC clock, reset and clock control
clk, rst, clmode,
// WISHBONE interface
wb_clk_i, wb_rst_i, wb_ack_i, wb_err_i, wb_rty_i, wb_dat_i,
wb_cyc_o, wb_adr_o, wb_stb_o, wb_we_o, wb_sel_o, wb_dat_o,
`ifdef OR1200_WB_CAB
wb_cab_o,
`endif
`ifdef OR1200_WB_B3
wb_cti_o, wb_bte_o,
`endif
// Internal RISC bus
biu_dat_i, biu_adr_i, biu_cyc_i, biu_stb_i, biu_we_i, biu_sel_i, biu_cab_i,
biu_dat_o, biu_ack_o, biu_err_o
);
parameter dw = `OR1200_OPERAND_WIDTH;
parameter aw = `OR1200_OPERAND_WIDTH;
parameter bl = 4; /* Can currently be either 4 or 8 - the two optional line
sizes for the OR1200. */
//
// RISC clock, reset and clock control
//
input clk; // RISC clock
input rst; // RISC reset
input [1:0] clmode; // 00 WB=RISC, 01 WB=RISC/2, 10 N/A, 11 WB=RISC/4
//
// WISHBONE interface
//
input wb_clk_i; // clock input
input wb_rst_i; // reset input
input wb_ack_i; // normal termination
input wb_err_i; // termination w/ error
input wb_rty_i; // termination w/ retry
input [dw-1:0] wb_dat_i; // input data bus
output wb_cyc_o; // cycle valid output
output [aw-1:0] wb_adr_o; // address bus outputs
output wb_stb_o; // strobe output
output wb_we_o; // indicates write transfer
output [3:0] wb_sel_o; // byte select outputs
output [dw-1:0] wb_dat_o; // output data bus
`ifdef OR1200_WB_CAB
output wb_cab_o; // consecutive address burst
`endif
`ifdef OR1200_WB_B3
output [2:0] wb_cti_o; // cycle type identifier
output [1:0] wb_bte_o; // burst type extension
`endif
//
// Internal RISC interface
//
input [dw-1:0] biu_dat_i; // input data bus
input [aw-1:0] biu_adr_i; // address bus
input biu_cyc_i; // WB cycle
input biu_stb_i; // WB strobe
input biu_we_i; // WB write enable
input biu_cab_i; // CAB input
input [3:0] biu_sel_i; // byte selects
output [31:0] biu_dat_o; // output data bus
output biu_ack_o; // ack output
output biu_err_o; // err output
//
// Registers
//
wire wb_ack; // normal termination
reg [aw-1:0] wb_adr_o; // address bus outputs
reg wb_cyc_o; // cycle output
reg wb_stb_o; // strobe output
reg wb_we_o; // indicates write transfer
reg [3:0] wb_sel_o; // byte select outputs
`ifdef OR1200_WB_CAB
reg wb_cab_o; // CAB output
`endif
`ifdef OR1200_WB_B3
reg [2:0] wb_cti_o; // cycle type identifier
reg [1:0] wb_bte_o; // burst type extension
`endif
`ifdef OR1200_NO_DC
reg [dw-1:0] wb_dat_o; // output data bus
`else
assign wb_dat_o = biu_dat_i; // No register on this - straight from DCRAM
`endif
`ifdef OR1200_WB_RETRY
reg [`OR1200_WB_RETRY-1:0] retry_cnt; // Retry counter
`else
wire retry_cnt;
assign retry_cnt = 1'b0;
`endif
`ifdef OR1200_WB_B3
reg [3:0] burst_len; // burst counter
`endif
reg biu_stb_reg; // WB strobe
wire biu_stb; // WB strobe
reg wb_cyc_nxt; // next WB cycle value
reg wb_stb_nxt; // next WB strobe value
reg [2:0] wb_cti_nxt; // next cycle type identifier value
reg wb_ack_cnt; // WB ack toggle counter
reg wb_err_cnt; // WB err toggle counter
reg wb_rty_cnt; // WB rty toggle counter
reg biu_ack_cnt; // BIU ack toggle counter
reg biu_err_cnt; // BIU err toggle counter
reg biu_rty_cnt; // BIU rty toggle counter
wire biu_rty; // BIU rty indicator
reg [1:0] wb_fsm_state_cur; // WB FSM - surrent state
reg [1:0] wb_fsm_state_nxt; // WB FSM - next state
wire [1:0] wb_fsm_idle = 2'h0; // WB FSM state - IDLE
wire [1:0] wb_fsm_trans = 2'h1; // WB FSM state - normal TRANSFER
wire [1:0] wb_fsm_last = 2'h2; // EB FSM state - LAST transfer
//
// WISHBONE I/F <-> Internal RISC I/F conversion
//
//assign wb_ack = wb_ack_i;
assign wb_ack = wb_ack_i & !wb_err_i & !wb_rty_i;
//
// WB FSM - register part
//
always @(posedge wb_clk_i or `OR1200_RST_EVENT wb_rst_i) begin
if (wb_rst_i == `OR1200_RST_VALUE)
wb_fsm_state_cur <= wb_fsm_idle;
else
wb_fsm_state_cur <= wb_fsm_state_nxt;
end
//
// WB burst tength counter
//
always @(posedge wb_clk_i or `OR1200_RST_EVENT wb_rst_i) begin
if (wb_rst_i == `OR1200_RST_VALUE) begin
burst_len <= 0;
end
else begin
// burst counter
if (wb_fsm_state_cur == wb_fsm_idle)
burst_len <= bl[3:0] - 2;
else if (wb_stb_o & wb_ack)
burst_len <= burst_len - 1;
end
end
//
// WB FSM - combinatorial part
//
always @(wb_fsm_state_cur or burst_len or wb_err_i or wb_rty_i or wb_ack or
wb_cti_o or wb_sel_o or wb_stb_o or wb_we_o or biu_cyc_i or
biu_stb or biu_cab_i or biu_sel_i or biu_we_i) begin
// States of WISHBONE Finite State Machine
case(wb_fsm_state_cur)
// IDLE
wb_fsm_idle : begin
wb_cyc_nxt = biu_cyc_i & biu_stb;
wb_stb_nxt = biu_cyc_i & biu_stb;
wb_cti_nxt = {!biu_cab_i, 1'b1, !biu_cab_i};
if (biu_cyc_i & biu_stb)
wb_fsm_state_nxt = wb_fsm_trans;
else
wb_fsm_state_nxt = wb_fsm_idle;
end
// normal TRANSFER
wb_fsm_trans : begin
wb_cyc_nxt = !wb_stb_o | !wb_err_i & !wb_rty_i &
!(wb_ack & wb_cti_o == 3'b111);
wb_stb_nxt = !wb_stb_o | !wb_err_i & !wb_rty_i & !wb_ack |
!wb_err_i & !wb_rty_i & wb_cti_o == 3'b010 ;
wb_cti_nxt[2] = wb_stb_o & wb_ack & burst_len == 'h0 | wb_cti_o[2];
wb_cti_nxt[1] = 1'b1 ;
wb_cti_nxt[0] = wb_stb_o & wb_ack & burst_len == 'h0 | wb_cti_o[0];
if ((!biu_cyc_i | !biu_stb | !biu_cab_i | biu_sel_i != wb_sel_o |
biu_we_i != wb_we_o) & wb_cti_o == 3'b010)
wb_fsm_state_nxt = wb_fsm_last;
else if ((wb_err_i | wb_rty_i | wb_ack & wb_cti_o==3'b111) &
wb_stb_o)
wb_fsm_state_nxt = wb_fsm_idle;
else
wb_fsm_state_nxt = wb_fsm_trans;
end
// LAST transfer
wb_fsm_last : begin
wb_cyc_nxt = !wb_stb_o | !wb_err_i & !wb_rty_i &
!(wb_ack & wb_cti_o == 3'b111);
wb_stb_nxt = !wb_stb_o | !wb_err_i & !wb_rty_i &
!(wb_ack & wb_cti_o == 3'b111);
wb_cti_nxt[2] = wb_ack & wb_stb_o | wb_cti_o[2];
wb_cti_nxt[1] = 1'b1 ;
wb_cti_nxt[0] = wb_ack & wb_stb_o | wb_cti_o[0];
if ((wb_err_i | wb_rty_i | wb_ack & wb_cti_o == 3'b111) & wb_stb_o)
wb_fsm_state_nxt = wb_fsm_idle;
else
wb_fsm_state_nxt = wb_fsm_last;
end
// default state
default:begin
wb_cyc_nxt = 1'bx;
wb_stb_nxt = 1'bx;
wb_cti_nxt = 3'bxxx;
wb_fsm_state_nxt = 2'bxx;
end
endcase
end
//
// WB FSM - output signals
//
always @(posedge wb_clk_i or `OR1200_RST_EVENT wb_rst_i) begin
if (wb_rst_i == `OR1200_RST_VALUE) begin
wb_cyc_o <= 1'b0;
wb_stb_o <= 1'b0;
wb_cti_o <= 3'b111;
wb_bte_o <= (bl==8) ? 2'b10 : (bl==4) ? 2'b01 : 2'b00;
`ifdef OR1200_WB_CAB
wb_cab_o <= 1'b0;
`endif
wb_we_o <= 1'b0;
wb_sel_o <= 4'hf;
wb_adr_o <= {aw{1'b0}};
`ifdef OR1200_NO_DC
wb_dat_o <= {dw{1'b0}};
`endif
end
else begin
wb_cyc_o <= wb_cyc_nxt;
if (wb_ack & wb_cti_o == 3'b111)
wb_stb_o <= 1'b0;
else
wb_stb_o <= wb_stb_nxt;
`ifndef OR1200_NO_BURSTS
wb_cti_o <= wb_cti_nxt;
`endif
wb_bte_o <= (bl==8) ? 2'b10 : (bl==4) ? 2'b01 : 2'b00;
`ifdef OR1200_WB_CAB
wb_cab_o <= biu_cab_i;
`endif
// we and sel - set at beginning of access
if (wb_fsm_state_cur == wb_fsm_idle) begin
wb_we_o <= biu_we_i;
wb_sel_o <= biu_sel_i;
end
// adr - set at beginning of access and changed at every termination
if (wb_fsm_state_cur == wb_fsm_idle) begin
wb_adr_o <= biu_adr_i;
end
else if (wb_stb_o & wb_ack) begin
if (bl==4) begin
wb_adr_o[3:2] <= wb_adr_o[3:2] + 1;
end
if (bl==8) begin
wb_adr_o[4:2] <= wb_adr_o[4:2] + 1;
end
end
`ifdef OR1200_NO_DC
// dat - write data changed after avery subsequent write access
if (!wb_stb_o) begin
wb_dat_o <= biu_dat_i;
end
`endif
end
end
//
// WB & BIU termination toggle counters
//
always @(posedge wb_clk_i or `OR1200_RST_EVENT wb_rst_i) begin
if (wb_rst_i == `OR1200_RST_VALUE) begin
wb_ack_cnt <= 1'b0;
wb_err_cnt <= 1'b0;
wb_rty_cnt <= 1'b0;
end
else begin
// WB ack toggle counter
if (wb_fsm_state_cur == wb_fsm_idle | !(|clmode))
wb_ack_cnt <= 1'b0;
else if (wb_stb_o & wb_ack)
wb_ack_cnt <= !wb_ack_cnt;
// WB err toggle counter
if (wb_fsm_state_cur == wb_fsm_idle | !(|clmode))
wb_err_cnt <= 1'b0;
else if (wb_stb_o & wb_err_i)
wb_err_cnt <= !wb_err_cnt;
// WB rty toggle counter
if (wb_fsm_state_cur == wb_fsm_idle | !(|clmode))
wb_rty_cnt <= 1'b0;
else if (wb_stb_o & wb_rty_i)
wb_rty_cnt <= !wb_rty_cnt;
end
end
always @(posedge clk or `OR1200_RST_EVENT rst) begin
if (rst == `OR1200_RST_VALUE) begin
biu_stb_reg <= 1'b0;
biu_ack_cnt <= 1'b0;
biu_err_cnt <= 1'b0;
biu_rty_cnt <= 1'b0;
`ifdef OR1200_WB_RETRY
retry_cnt <= {`OR1200_WB_RETRY{1'b0}};
`endif
end
else begin
// BIU strobe
if (biu_stb_i & !biu_cab_i & biu_ack_o)
biu_stb_reg <= 1'b0;
else
biu_stb_reg <= biu_stb_i;
// BIU ack toggle counter
if (wb_fsm_state_cur == wb_fsm_idle | !(|clmode))
biu_ack_cnt <= 1'b0 ;
else if (biu_ack_o)
biu_ack_cnt <= !biu_ack_cnt ;
// BIU err toggle counter
if (wb_fsm_state_cur == wb_fsm_idle | !(|clmode))
biu_err_cnt <= 1'b0 ;
else if (wb_err_i & biu_err_o)
biu_err_cnt <= !biu_err_cnt ;
// BIU rty toggle counter
if (wb_fsm_state_cur == wb_fsm_idle | !(|clmode))
biu_rty_cnt <= 1'b0 ;
else if (biu_rty)
biu_rty_cnt <= !biu_rty_cnt ;
`ifdef OR1200_WB_RETRY
if (biu_ack_o | biu_err_o)
retry_cnt <= {`OR1200_WB_RETRY{1'b0}};
else if (biu_rty)
retry_cnt <= retry_cnt + 1'b1;
`endif
end
end
assign biu_stb = biu_stb_i & biu_stb_reg;
//
// Input BIU data bus
//
assign biu_dat_o = wb_dat_i;
//
// Input BIU termination signals
//
assign biu_rty = (wb_fsm_state_cur == wb_fsm_trans) & wb_rty_i & wb_stb_o & (wb_rty_cnt ~^ biu_rty_cnt);
assign biu_ack_o = (wb_fsm_state_cur == wb_fsm_trans) & wb_ack & wb_stb_o & (wb_ack_cnt ~^ biu_ack_cnt);
assign biu_err_o = (wb_fsm_state_cur == wb_fsm_trans) & wb_err_i & wb_stb_o & (wb_err_cnt ~^ biu_err_cnt)
`ifdef OR1200_WB_RETRY
| biu_rty & retry_cnt[`OR1200_WB_RETRY-1];
`else
;
`endif
endmodule
5,一个小问题
终于可以告一段落了,下面弄个小问题放松一下。
很多人可能曾经遇到过这样一个软件方面的笔试题,题目是,下面两段程序,一般情况下,哪个的执行时间短(假设cache大小为8K)?
6,小结
自此,我们完成了对OpenRISC的MMU,cache系统的分析,对计算机体系结构中很重要的部分--存储器组织有了一个完整,清晰,透彻的了解了。
7,参考文献
1,ORPSoC RTL code
2,OpenRISC arch-manual