linux 通用时钟框架CCF
linux CCF 时钟框架
简单介绍
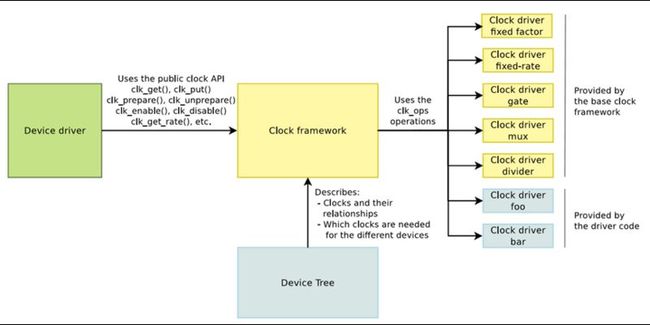
这里讲的时钟是给soc各组件提供时钟的树状框架,并非内核使用的时间,和其它模块一样,clk也有框架,用以适配不同的平台。适配层之上是客户代码和接口,也就是各模块(如须要时钟信号的外设,usb等)的驱动。适配层之下是详细的soc平台的时钟操作细节。
内核中另外一个具有类似树状框架特点的是regulator框架。对照regulator框架,clk框架不确定性更大,内核中只提供了少数的适配规范,struct clk都是各平台自己的clk驱动实现。 在3.4.5内核里基本上还是这样的状态,可是新的3.10内核非常多soc的clk驱动已经改为common clock framework(CCF)。各平台採用CCF的的clock驱动都统一在drivers/clk文件夹。
common clock framework由Mike Turquette在2012.5引入kernel 3.4。
下图引用自Emb edded Linux Conference 2013上Gregory CLEMENT的一篇介绍elc2013_clement.pdf。
内核版本号: linux-linaro-stable-android-3.10.37-2014.04
CCF相关的内核配置宏
CONFIG_COMMON_CLK
CCF core

CCF core主要代码在drivers/clk/clk.c里。主要维护时钟树以及操作,相互排斥锁,通知链。
主要结构体定义
仅仅有定义了CONFIG_COMMON_CLK才会有CCF框架。
include/linux/clk- private.h:
#ifdef CONFIG_COMMON_CLK
struct clk {
const char *name; //名字用来在全局链表里查找clk用的
const struct clk_ops *ops; //抽象的标准ops操作
struct clk_hw *hw; //clk_hw后面有专门介绍
struct clk *parent; //父时钟
const char **parent_names; //父时钟的个数
struct clk **parents;
u8 num_parents; //父时钟的名字字符串数组
unsigned long rate; //频率
unsigned long new_rate;
unsigned long flags;
unsigned int enable_count; //
unsigned int prepare_count;
struct hlist_head children;
struct hlist_node child_node;
unsigned int notifier_count;
#ifdef CONFIG_COMMON_CLK_DEBUG
struct dentry *dentry;
#endif
};
…
#endif
struct clk_ops {
int (*prepare)(struct clk_hw *hw); //开时钟前调用,可能会造成休眠,所以把休眠部分放到这里,能够原子操作的放到enable里
void (*unprepare)(struct clk_hw *hw); //prepare的反操作
int (*is_prepared)(struct clk_hw *hw); //是否prepared
void (*unprepare_unused)(struct clk_hw *hw); //仅仅在clk_disable_unused里特殊需求调用,可能会休眠
int (*enable)(struct clk_hw *hw); //原子操作,打开时钟,这个函数必须在产生实际可用的时钟信号后才干返回
void (*disable)(struct clk_hw *hw); //原子操作,关闭时钟
int (*is_enabled)(struct clk_hw *hw);
void (*disable_unused)(struct clk_hw *hw); //仅仅在clk_disable_unused里特殊需求调用,不能休眠
unsigned long (*recalc_rate)(struct clk_hw *hw,
unsigned long parent_rate); //查询硬件,又一次计算频率
long (*round_rate)(struct clk_hw *hw, unsigned long,
unsigned long *); //计算最接近要求的频率
int (*set_parent)(struct clk_hw *hw, u8 index); //MUX会使用
u8 (*get_parent)(struct clk_hw *hw); //MUX会使用
int (*set_rate)(struct clk_hw *hw, unsigned long, //设置频率
unsigned long);
void (*init)(struct clk_hw *hw); //初始化
};
struct clk_init_data {
const char *name;
const struct clk_ops *ops; //操作函数集,和其它框架的ops作用一样,提供实际的操作函数。
const char **parent_names; //父时钟的名字字符串数组
u8 num_parents; //父时钟的个数
unsigned long flags;
};
//用来连接clk结构体和实际硬件的关系
struct clk_hw {
struct clk *clk;
const struct clk_init_data *init;
};
时钟的基本种类
CCF将soc抽象出5个基本种类,能够快捷的定义。
| 固定速率 |
不能设置的时钟 |
| 门时钟 |
和上级时钟同频,仅仅能打开和关闭操作 |
| MUX |
多选一 |
| 固定倍频 |
上级时钟的频率有固定倍频或者分频,不能关闭 |
| 分频 |
上级时钟的频率分频,能够选择不同的分频比 |
5种时钟类型都有不同的注冊函数和结构体,如MUX时钟
结构体毫无例外是封装包括struct clk_hw,然后加上该种类的特性的成员。
struct clk_mux {
struct clk_hw hw;
void __iomem *reg;
u32 *table;
u32 mask;
u8 shift;
u8 flags;
spinlock_t *lock;
};
struct clk *clk_register_mux(struct device *dev, const char *name,
const char **parent_names, u8 num_parents, unsigned long flags,
void __iomem *reg, u8 shift, u8 width,
u8 clk_mux_flags, spinlock_t *lock);
一般SOC都有大量的时钟,用数组变量定义批量时钟是最方便的,可是内核不推荐这样做。新开发的驱动用clk_init_data和clk_register()定义。
时钟标准驱动层
CCF提供的API,实际是调用了clk_ops的实际操作函数,这些函数是依照5种主要的时钟分类来的。
值得注意的是,一般的驱动框架,比方网卡,usb,regulator,都是内核的core层提供管理逻辑,由芯片驱动提供实际的操作。可是clk的实际操作是由CCF API完毕,而不是芯片驱动完毕的。之所以可以做到这一点,是由于芯片的时钟操作方法比較类似。soc平台注冊时钟的时候,仅仅须要提供操作的信息,就行由CCF的统一操作函数对这些信息进行操作。
以MUX的clk_set_parent分析为例
clk_set_parent->__clk_set_parent->clk->(ops->set_parent)
ops->set_parent的定义例如以下,在注冊时钟的时候就设置好了。
const struct clk_ops clk_mux_ops = {
.get_parent = clk_mux_get_parent,
.set_parent = clk_mux_set_parent,
};
static int clk_mux_set_parent(struct clk_hw *hw, u8 index)
{
struct clk_mux *mux = to_clk_mux(hw);
u32 val;
unsigned long flags = 0;
if (mux->table)
index = mux->table[index];
else {
if (mux->flags & CLK_MUX_INDEX_BIT)
index = (1 << ffs(index));
if (mux->flags & CLK_MUX_INDEX_ONE)
index++;
}
if (mux->lock)
spin_lock_irqsave(mux->lock, flags);
val = readl(mux->reg);
val &= ~(mux->mask << mux->shift);
val |= index << mux->shift;
writel(val, mux->reg);
if (mux->lock)
spin_unlock_irqrestore(mux->lock, flags);
return 0;
}
可见,平台代码并没有提供实际的ops,仅仅是提供table,bit和reg等信息就能够了。CCF的ops能够直接调用writel操作硬件。
驱动例子分析
准备5类时钟信息
每一个soc有非常多时钟,依照CCF的5个种类分开定义.
struct samsung_mux_clock {
unsigned int id;
const char *dev_name;
const char *name;
const char **parent_names;
u8 num_parents;
unsigned long flags;
unsigned long offset;
u8 shift;
u8 width;
u8 mux_flags;
const char *alias;
};
struct samsung_mux_clock exynos5250_mux_clks[] __initdata = {
MUX_A(none, "mout_apll", mout_apll_p, SRC_CPU, 0, 1, "mout_apll"),
MUX(none, "mout_mpll_fout", mout_mpll_fout_p, PLL_DIV2_SEL, 4, 1),
MUX_A(none, "sclk_mpll", mout_mpll_p, SRC_CORE1, 8, 1, "mout_mpll"),
……
}
參考MUX(none, "mout_mpll_fout", mout_mpll_fout_p, PLL_DIV2_SEL, 4, 1),
#define __MUX(_id, dname, cname, pnames, o, s, w, f, mf, a) \
{ \
.id = _id, \
.dev_name = dname, \
.name = cname, \
.parent_names = pnames, \
.num_parents = ARRAY_SIZE(pnames), \
.flags = f, \
.offset = o, \
.shift = s, \
.width = w, \
.mux_flags = mf, \
.alias = a, \
}
#define MUX(_id, cname, pnames, o, s, w) \
__MUX(_id, NULL, cname, pnames, o, s, w, 0, 0, NULL)
实际上就是利用宏简化赋值代码。mout_mpll_fout展开例如以下
struct samsung_mux_clock –》
{ \
.id = none, \
.dev_name = NULL, \
.name = "mout_mpll_fout", \
.parent_names = mout_mpll_fout_p, \
.num_parents = ARRAY_SIZE(mout_mpll_fout_p), \
.flags = 0, \
.offset = PLL_DIV2_SEL, \
.shift = 4, \
.width = 1, \
.mux_flags = NULL, \
.alias = NULL, \
}
结合时钟标准驱动层int clk_set_parent(struct clk *clk, struct clk *parent)来看。对mout_mpll_fout设置mux的方法分为下面几个步骤:
1. 将本clk和父clk为參数输入clk_set_parent
2. 用for循环在本clk的parents成员数组查找指针和入參clk *parent相等的。返回数组的index
3. 找到偏移为PLL_DIV2_SEL的寄存器,将index左移4bit设置为1就能够。
从上面能够看出,定义clk的时候,父时钟的顺序必须和寄存器设置的顺序匹配才干够。不支持这样的规律的芯片,是不能用CCF的。
注冊5类时钟
void __init exynos5250_clk_init(struct device_node *np)
{
…
samsung_clk_register_fixed_rate(exynos5250_fixed_rate_clks,
ARRAY_SIZE(exynos5250_fixed_rate_clks));
samsung_clk_register_fixed_factor(exynos5250_fixed_factor_clks,
ARRAY_SIZE(exynos5250_fixed_factor_clks));
samsung_clk_register_mux(exynos5250_mux_clks,
ARRAY_SIZE(exynos5250_mux_clks));
…
}
准备非5类时钟信息
出了标准的5类时钟类型,不标准的时钟类型须要单独准备clk_init_data init;
注冊非5类时钟
apll = samsung_clk_register_pll35xx("fout_apll", "fin_pll",
reg_base + 0x100);
struct samsung_clk_pll35xx {
struct clk_hw hw;
const void __iomem *con_reg;
};
struct clk * __init samsung_clk_register_pll35xx(const char *name,
const char *pname, const void __iomem *con_reg)
{
struct samsung_clk_pll35xx *pll;
struct clk *clk;
struct clk_init_data init;
//假设是标准类型,调用标准类型的注冊函数里会分配时钟结构体的内存
pll = kzalloc(sizeof(*pll), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!pll) {
pr_err("%s: could not allocate pll clk %s\n", __func__, name);
return NULL;
}
//配置clk_init_data
init.name = name;
init.ops = &samsung_pll35xx_clk_ops;
init.flags = CLK_GET_RATE_NOCACHE;
init.parent_names = &pname;
init.num_parents = 1;
pll->hw.init = &init;
pll->con_reg = con_reg;
//通用注冊函数,标准类型的注冊函数终于也是调用这个
clk = clk_register(NULL, &pll->hw);
if (IS_ERR(clk)) {
pr_err("%s: failed to register pll clock %s\n", __func__,
name);
kfree(pll);
}
//注冊到clocks全局链表。clk_register_clkdev会申请struct clk_lookup,不用caller关心。
if (clk_register_clkdev(clk, name, NULL))
pr_err("%s: failed to register lookup for %s", __func__, name);
return clk;
}
//因为是私有函数,能够随便写了。
static const struct clk_ops samsung_pll35xx_clk_ops = {
.recalc_rate = samsung_pll35xx_recalc_rate,
};
clk api的用法
和regulator框架类似,首先调用clk_get()得到struct clk *,然后将struct clk *作为入參调用CCF提供的API,如int clk_prepare(struct clk *clk)。