Google C++ Testing Framework之参数化
回到第一节所编写的测试案例上,我们看到虽然只有短短的六个检查点,但我已经可以使用复制粘帖5次之多。
而在大型项目的单元测试上,一个案例往往具有更多 的测试点,而如此多的测试点都编写一行代码的话,一来代码量过大浪费时间,二来也使得编译器不够美观。
不过呢,GoogleTest AdvanceGuide 的参数化功能很好的帮我们解决了这个问题。
开始。
1. 首先,我们先定义一个类,继承自 ::testing::TestWithParam<T> , 这里的 T 就是我们需要参数化的参数类型了。而 TestWithParam<T> 则是继承自 ::testing:Test 。所以第一节所定义的类为:
class FooTest : public ::testing::TestWithParam<const char*>
{ // You can implement all the usual fixture class members here.
// To access the test parameter, call GetParam() from class
// TestWithParam<T>.
};
2. 使用宏 TEST_P 定义你所想要进行的测试。
1
TEST_P(IsPrimeParamTest, TrueReturn)
2
{
3
//
在一个测试案例里面,使用GetParam()传递参数
4
int
n
=
GetParam();
5
EXPECT_TRUE(IsPrime(n));
6
}
3. 使用INSTANTIATE_TEST_CASE_P告诉gtest你所要测的参数范围。
1
INSTANTIATE_TEST_CASE_P(TrueCondition,
2
IsPrimeParamTest,
3
::testing::Values(
2
,
3
,
5
,
7
,
11
,
17
));
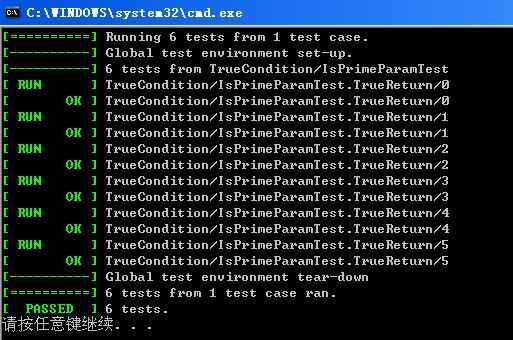
至此,大功告成。运行之,得结果:
另:INSTANTIATE_TEST_CASE_P 的第三个函数为参数生成器,有如下一系列函数:
| Range(begin, end[, step]) | Yields values {begin, begin+step, begin+step+step, ...}. The values do not include end. step defaults to 1. |
| Values(v1, v2, ..., vN) | Yields values {v1, v2, ..., vN}. |
| ValuesIn(container) and ValuesIn(begin, end) | Yields values from a C-style array, an STL-style container, or an iterator range [begin, end). |
| Bool() | Yields sequence {false, true}. |
| Combine(g1, g2, ..., gN) | Yields all combinations (the Cartesian product for the math savvy) of the values generated by the N generators. This is only available if your system provides the <tr1/tuple> header. If you are sure your system does, and Google Test disagrees, you can override it by defining GTEST_HAS_TR1_TUPLE=1. |
总结。
gtest的参数化功能真正做到了为程序员和编译器减负!