数据库优化之sql语句优化
网站打破了有此站以来就长的因错误而无法访问的记录,错误很简单就是执行超时。通过分析发现问题出现在产品表上,没有对这个表有相关联系的页面正常。数据表不过3-4万条记录,关联两个表,怎么可能查询都出现超时呢。直接在查询分析器里执行,竟然要3分钟左右才能出现结果。
难道此表被锁定了,重启下sql server服务,一样;语句太复杂了吧,先写个简单sql试下,同样都在30秒以上,K,郁闷了。。。。。。。。
下午的时候神经病般的又正常了。。。。。。。。。
鉴于此次灾难,做了些试验了解下数据库方面的优化,先从sql语句入手,看看sql语句的优化对数据库的优化有多大用处。
实验平台:我的工作电脑,winxp+sql server 2000 (还真是落后。。。)
1,Order by 对查询有影响吗??
 sql语句
sql语句
2 select * from protuct_city order by productid desc 23.86
3 select * from protuct 35.67
4 select * from protuct order by id desc 35.67
前面是sql语句,后面的数字是执行时产生的此条语句相对整个批处理的查询成本的百分数。
结论:
对于有主键的表,不加order by 和以主键排序(asc,desc)查询成本没有变化,从3,4的结果得出。
对于没有主键的表,就算是排序的因子加了索引,查询成本还是有大幅度的提升,从1,2条的结果得出。
(通过1,3条比较,所查询的表的数据量对查询成本也是有很大的影响。protuct表50个字段,而protuct_city只有5个字段。)
再来看一段代码:
2 select * from protuct order by addtime desc 68.13
上面两条查询出的数据完全一样,但是查询成本却有很大的差别。
结论:
排序因子对整个查询也是有很大的影响的。
2,select字段数对查询有影响吗??
2 select id from protuct 2.90
3 select name from protuct 31.38
4 select id,name from protuct 31.38
5 select * from protuct 31.44
protuct表有50个字段,id是主键
有以上我们可以得出结论:
只查询索引的字段,显然比其它节省很多的资源和时间。
当select字段中出现一个不是索引过的字段时,其它再多的字段(承受范围之内)对查询成本是没有太大的影响的。(但是这只是查询成本,并不代表写的时候就直接上select * 了,考虑传输时的成本和其它因素,尽量还是只提取有用数据)
3,查询条件对查询影响有多大??
2 select * from protuct p inner join protuct_city c on p.id = c.productid where c.city = 410100 41.27
加了条件查询成本反而降低了!!!????
呵呵,我K,第一个你提的所有的数据,第二个可能数据很少,当然降低啦
是的,看下面
2 select * from protuct p inner join protuct_city c on p.id = c.productid where id > 0 49.41
id是主键,从1开始的自增,这次提取的数据完全一样了吧,但是查询成本还是有小点的节省的,这TMD何解啊???
2 select * from protuct p inner join protuct_city c on p.id = c.productid where name <> '' 50.71
其中name永远不会为空,两者提的数据量也是一样的。
出现这个结果可能在意料之内,但是这相差也真出乎意料的小。
再来看看提取的数据量对查询的影响
 代码
代码
2 select * from protuct p inner join protuct_city c on p.id = c.productid where id > 10 21.88
3 select * from protuct p inner join protuct_city c on p.id = c.productid where id > 100 21.87
4 select * from protuct p inner join protuct_city c on p.id = c.productid where id > 1000 21.10
5 select * from protuct p inner join protuct_city c on p.id = c.productid where id > 10000 13.26
不说了,结果就这样,大家都知道
重点来啦,条件的多少对查询的影响,原来印象就是条件越多肯定成本越高,执行越慢啊。
 代码
代码
2 select * from protuct p inner join protuct_city c on p.id = c.productid where c.city = 410100 and p.state != 100 24.94
3 select * from protuct p inner join protuct_city c on p.id = c.productid where c.city = 410100 and p.state != 100 and p.state1 != 100 25.09
4 select * from protuct p inner join protuct_city c on p.id = c.productid where c.city = 410100 and p.state != 100 and p.state1 != 100 and name != '' 25.19
首先,我先说明这4句提取出来的数据是一模一样的,因为state和state1永远不会等于100,name也永远不为空。只是条件一个比一个多。
结论也是正确的,成本确定是提高了,但是差别真的不是太大,并且实际中,可能条件越多,数据越少,可能摊薄这部分的损失,因此查询条件多(别太多了)并不会显著的影响程序的性能。那么,原来一出现网站的time out,给老板的回答就是这个表数据多,又太多的查询条件,因此慢了,这原因不太成立啊。。。。说啥原因呢,说机器神经病(别说有时候还真神经),我K,找死的,哎,还是为机器、程序好好运行找些解决措施吧。
4,子查询和inner join
 代码
代码
2 select * from protuct where id in ( select productid from protuct_city where city = 410100 ) and state = 1 49.95
查询结果是一样的,查询成本也出奇的相似,竟然子查询还低那么一点。。。。。
更让人惊奇的是两个语句的执行计划竟然是一样的。有小图为证。
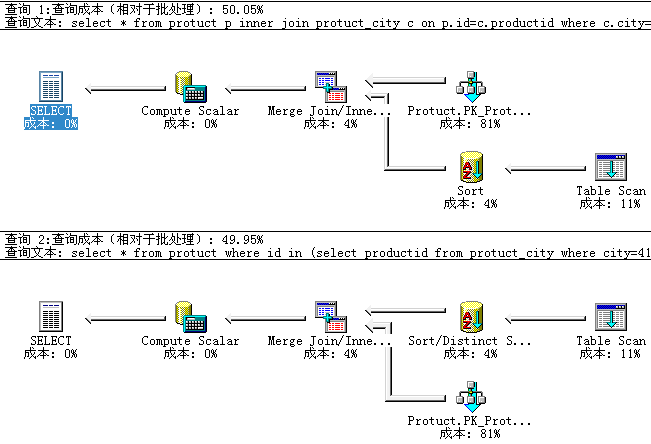
难道这类子查询和inner join根子里是一个人吗,K。
总体感觉:数据库优化方面sql语句的优化空间不大,真正的优化应该在表的设计上下功夫。
实验还在继续,结论有待更新。(我写文章的速度、速率,自己都惭愧。。。。。)
