ML 100day fiveday(逻辑回归、数据归一化、评估预测、matplotlib数据展示)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
dataset = pd.read_csv(‘C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\ml 100day\Social_Network_Ads.csv’)
dataset.head()
User ID Gender Age EstimatedSalary Purchased
0 15624510 Male 19 19000 0
1 15810944 Male 35 20000 0
2 15668575 Female 26 43000 0
3 15603246 Female 27 57000 0
4 15804002 Male 19 76000 0
#划分XY
X = dataset.iloc[:, [2, 3]].values
Y = dataset.iloc[:,4].values
#使用model_selection来划分训练集和测试集
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size = 0.25, random_state
#Feature Scaling,归一化,缩小范围,加速梯度下降收敛(注意:针对树类算法没有必要)
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
sc = StandardScaler()
#相同规则进行训练 而不是X_test = sc.fit_transform(X_test)l
X_train = sc.fit_transform(X_train) 注意这里fit_transform和transform
X_test = sc.transform(X_test)
#logistic Regression to the Train set
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
classifier = LogisticRegression()
classifier.fit(X_train, y_train)
#使用训练好的模型预测值
y_pred = classifier.predict(X_test)
#评估预测:我们预测了测试集。现在我们将评估模型是否正确的学习和理解。因此这个混淆矩阵包含我们模型的正确和错误的预测
#生成混淆矩阵,只有在对角线上的才是预测正确的数据
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test,y_pred)
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
X_set,y_set=X_train,y_train
#numpy.meshgrid()——生成网格点坐标矩阵。
X1,X2=np. meshgrid(np. arange(start=X_set[:,0].min()-1, stop=X_set[:, 0].max()+1, step=0.01),
np. arange(start=X_set[:,1].min()-1, stop=X_set[:,1].max()+1, step=0.01))
#contour和contourf都是画三维等高线图的,不同点在于contourf会对等高线间的区域进行填充
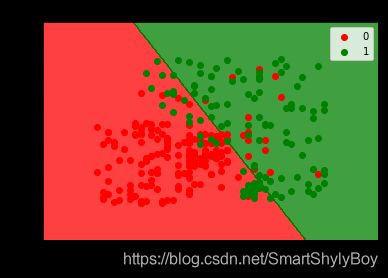
plt.contourf(X1, X2, classifier.predict(np.array([X1.ravel(),X2.ravel()]).T).reshape(X1.shape),
alpha = 0.75, cmap = ListedColormap((‘red’, ‘green’)))
plt.xlim(X1.min(),X1.max())
plt.ylim(X2.min(),X2.max())
for i,j in enumerate(np. unique(y_set)):
plt.scatter(X_set[y_setj,0],X_set[y_setj,1],
c = ListedColormap((‘red’, ‘green’))(i), label=j)
plt. title(’ LOGISTIC(Training set)’)
plt. xlabel(’ Age’)
plt. ylabel(’ Estimated Salary’)
plt. legend()
plt. show()