Python语言 期末大作业 五子棋 (资源在博主资源拿)
博主代码仅供参考,由于是边做边打补丁补功能,也没有时间去重构代码,所以质量不敢保证(doge)QAQ。。。。
当然给大家给个参考,同样作为模板也能较好的去修改,怕麻烦的uu也可以直接cv过去应付大作业(bushi)
阅读格式:代码+解释
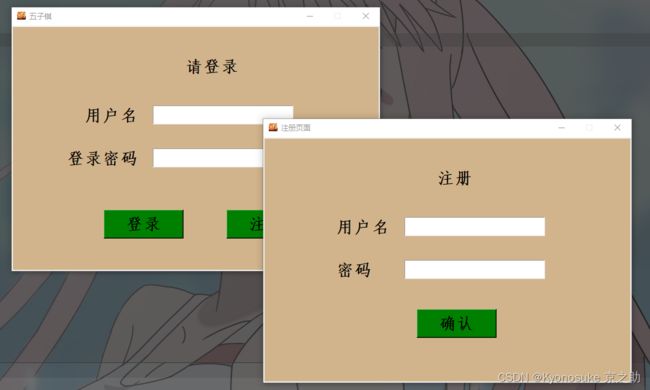
效果展示
这就是主要的三个界面,是调用tkinter包做的(第一次用TK,勿喷),其中注册登录界面,积分胜率需要去写入和读出txt文件,至于游戏界面增加了悔棋和人机(剩下的来不及肝了QAQ),接下来我们进行代码段的解读。
一.登录界面
代码段:
def framLogin():
global user_entry, ss_entry, title_lab, login_btn, userlab, sslab, user, ss, w3,user_goal
w3 = Canvas(game, width=600, height=400, background='tan')
w3.pack()
title_lab = tk.Label(w3, text="请登录", bg='tan', font="仿宋 20 bold")
title_lab.place(x=280, y=50, )
userlab = tk.Label(w3, text="用户名", bg='tan', font="仿宋 20 bold", width=8)
userlab.place(x=100, y=130)
user_entry = tk.Entry(w3, width=15, bg="white", font="仿宋 20 bold")
user_entry.place(x=230, y=130)
sslab = tk.Label(w3, text="登录密码", bg='tan', font="仿宋 20 bold", width=8)
sslab.place(x=85, y=200)
ss_entry = tk.Entry(w3, width=15, bg="white", font="仿宋 20 bold", show="*")
ss_entry.place(x=230, y=200)
login_btn = tk.Button(w3, text="登录", command=judge, font="仿宋 20 bold", bg="green", width=8)
regist_btn = tk.Button(w3, text="注册", command=resgister, font="仿宋 20 bold", bg="green", width=8)
login_btn.place(x=150, y=300)
regist_btn.place(x=350, y=300)framLogin()函数:
可以看到,这段代码就是调用TK做的可视化界面,因为root(桌子)在另一个函数已经初始化了,所以我们在这直接引用,将建立好的Canvas直接放在桌子上就好,这段代码比较简单,我们直接跳过。
def judge():
global user_entry, ss_entry, game,user_goal
temp = False
with open("sql", "r") as f:
data = f.readlines()
for i in range(0, len(data), 4):
data[i] = data[i].strip("\n")
data[i+1] = data[i+1].strip("\n")
print(user_entry.get())
if str(data[i]) == user_entry.get() and str(data[i + 1]) == ss_entry.get():
user_goal = user_entry.get()
temp = True
break
if temp:
game.destroy()
game = Tk()
game.title("五子棋")
game.iconphoto(True, tk.PhotoImage(file='image.png'))
game.geometry("600x710")
game.resizable(False,False)
locating()
framinit()
mainloop()
else:
tkinter.messagebox.showinfo('提示', '密码或用户名不正确')judge()函数:
judge = 判断,旨在判断我们名为sql.txt的文件里是否存在用户输入的用户名及密码,temp为临时判别,遍历txt如果没有此用户或密码不正确,都会向用户报错。在if temp后,则为通过验证的代码段,通过locating(),framinit()这两个自定义函数去完成用户信息定位,游戏界面初始化两个功能(这两个函数后面有解读)
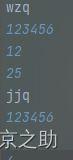
sql.txt补充:因为是大作业,也没有想到去用更高级的手段储存(懒),所以这是我的txt:
可以看到,第一行是用户名,接下来是密码,三四行分别是储存的玩家胜场和机器胜场(12:25,被机器暴打)
二.注册界面
def resgister():
global w4, u_entry, s_entry, re
re = Tk()
re.title("注册页面")
re.geometry("600x400")
re.resizable(False,False)
w4 = Canvas(re, width=600, height=400, background='tan')
title = tk.Label(w4, text="注册", bg='tan', font="仿宋 20 bold")
title.place(x=280, y=50, )
user = tk.Label(w4, text="用户名", bg='tan', font="仿宋 20 bold", width=8)
user.place(x=100, y=130)
u_entry = tk.Entry(w4, width=15, bg="white", font="仿宋 20 bold")
u_entry.place(x=230, y=130)
slab = tk.Label(w4, text="密码", bg='tan', font="仿宋 20 bold", width=8)
slab.place(x=85, y=200)
s_entry = tk.Entry(w4, width=15, bg="white", font="仿宋 20 bold", show="*")
s_entry.place(x=230, y=200)
agree_btn = tk.Button(w4, text="确认", command=registing, font="仿宋 20 bold", bg="green", width=8)
agree_btn.place(x=250, y=280)
w4.pack()resgister()函数:
这个函数一眼顶针,大家可能一下子就看出来是什么作用了,不就是注册界面的页面元素么,当然,重点是agree_btn = tk.Button(w4, text="确认", command=registing, font="仿宋 20 bold", bg="green", width=8)这句中的command—> registing
如下列代码:
def registing():
temp = True
global userID, userSS, u_entry, s_entry
with open("sql", "r") as f:
data = f.readlines()
for i in range(0, len(data), 4):
data[i] = data[i].strip("\n")
if str(data[i]) == u_entry.get():
tkinter.messagebox.showinfo('提示', '该用户名已被注册')
temp = False
break
if temp:
with open("sql", "a") as f:
f.write(f'\r{u_entry.get()}')
f.write(f'\r{s_entry.get()}')
f.write("\r0")
f.write("\r1")
re.destroy()registing()函数:
首先,一个注册界面就需要我们去判断用户是否存在,参照judge()函数,我们建一个temp变量,通过对文本的操作去判别是否存在,如果存在就对用户抛出错误提示。但如果符合条件,就去追加文件,添加用户信息。
三.游戏界面初始化
def framinit():
global im, image, w2, w2q, w2s, w2t
im = Image.open('1.jpeg').resize((600, 600))
image = ImageTk.PhotoImage(im)
w2 = Canvas(game, width=600, height=600)
w2.create_image(300, 300, image=image)
w2t = Button(game, text="双人模式", width=10, height=1, command=framGame, font=('楷体', 15))
w2s = Button(game, text="单人模式", width=10, height=1, command=act, font=('楷体', 15))
w2q = Button(game, text="退出", width=10, height=1, command=quit, font=('楷体', 15))
w2.pack()
w2t.pack()
w2s.pack()
w2q.pack()framinit()函数:
看一下文本可以知道,此段代码对应效果展示的第二张图,这里要提一下im,image两个变量,这两个变量要设为全局变量以此来保留,不然会被删除,由于TK模块只支持gif形式的图片,所以这里我们通过调用PIL.Image 和PIL.ImageTk,去解析这张'1.jpeg',剩下的就是常规的按钮及其绑定的command(命令)。
def act():
global act
framGame()
act = 1act()函数:
act()函数比较好理解,就是激活一个变量act = 1,以进入人机功能,然后激活framGame()函数进入游戏。
def framGame():
global w2, w1,text1,text2
w2s.destroy()
w2.destroy()
w2q.destroy()
w2t.destroy()
w1 = Canvas(width=600, height=600, background='tan')
for i in range(0, 15):
if i != 0 and i != 14:
w1.create_line(i * 40 + 20, 20, i * 40 + 20, 580)
w1.create_line(20, i * 40 + 20, 580, i * 40 + 20)
else:
w1.create_line(i * 40 + 20, 20, i * 40 + 20, 580, width=3)
w1.create_line(20, i * 40 + 20, 580, i * 40 + 20, width=3)
w1.create_oval(135, 135, 145, 145, fill='black')
w1.create_oval(135, 455, 145, 465, fill='black')
w1.create_oval(465, 135, 455, 145, fill='black')
w1.create_oval(455, 455, 465, 465, fill='black')
w1.create_oval(295, 295, 305, 305, fill='black')
text1 = tk.Text(game,width=13,height=1.4,font=('楷体',30))
text1.insert(tk.INSERT, f'黑棋 {b_score}:{w_score} 白棋')
h_score,rate = calculate()
text2 = tk.Text(game, width=33, height=1.4, font=('楷体', 12))
text2.insert(tk.INSERT,f'用户{user_goal}: 胜率 = {rate} 积分 = {h_score}')
u = Button(game, text="认输", width=10, height=1, command=run, font=('楷体', 15))
r = Button(game, text="悔棋", width=10, height=1, command=laterstep, font=('楷体', 15))
q = Button(game, text="退出", width=10, height=1, command=quit, font=('楷体', 15))
w1.bind("framGame()函数:
这段代码是主体代码之一,我们来详细解释下,开头四个destroy()是为了清除前朝余党,然后for循环中绘制棋盘,其中create_line中的参数和创建的Canvas画布的大小也有绝对关系,请根据大小来调参,w1.create_oval(455, 455, 465, 465, fill='black')这行代码是为了绘制五个定位点,同样的思路,等会我们绘制棋子也可以使用create_oval函数来完成,接下来text1,text2,u,r,q分别是对应的几个页面元素,看看即可,但是注意w1.bind("这段代码,是响应函数,其中"是绑定鼠标左键,也是后面完成落子交互的重要函数,start是定义的游戏程序,此处作用和Button函数的commond作用一致。
def start(event):
global num, record, A, B, point, i, j, act, text2
for j in range(0, 15):
for i in range(0, 15):
if (event.x - 20 - 40 * i) ** 2 + (event.y - 20 - 40 * j) ** 2 <= 2 * 20 ** 2:
break
if (event.x - 20 - 40 * i) ** 2 + (event.y - 20 - 40 * j) ** 2 <= 2 * 20 ** 2:
break
if num % 2 == 0 and A[i][j] != 1:
point = w1.create_oval(40 * i + 5, 40 * j + 5, 40 * i + 35, 40 * j + 35, fill='black', tags='ob')
A[i][j] = 1
B[i][j] = 'b'
num += 1
elif num % 2 != 0 and A[i][j] != 1:
point = w1.create_oval(40 * i + 5, 40 * j + 5, 40 * i + 35, 40 * j + 35, fill='white', tags='ob')
A[i][j] = 1
B[i][j] = 'w'
num += 1
record = (i, j)
f = [[-1, 0], [-1, 1], [0, 1], [1, 1]]
for z in range(0, 4):
a, b = f[z][0], f[z][1]
count1, count2 = 0, 0
x, y = i, j
while B[x][y] == B[i][j]:
count1 += 1
if x + a > 0 and y + b > 0 and x + a < 15 and y + b < 15 and B[x + a][y + b] == B[i][j]:
[x, y] = np.array([x, y]) + np.array([a, b])
else:
x, y = i, j
break
while B[x][y] == B[i][j]:
count2 += 1
if x - a < 15 and y - b < 15 and x - a > 0 and y - b > 0 and B[x - a][y - b] == B[i][j]:
[x, y] = np.array([x, y]) - np.array([a, b])
else:
break
if count1 + count2 >= 6:
if B[i][j] == 'b':
tkinter.messagebox.showinfo('提示', '黑棋获胜')
SqlReScore('w')
Refresh('b')
elif B[i][j] == 'w':
tkinter.messagebox.showinfo('提示', '白棋获胜')
SqlReScore('l')
Refresh('w')
w1.delete('ob')
A = np.full((15, 15), 0)
B = np.full((15, 15), '')
num = 0
if act == 1 and num % 2 == 1:
draw()
mainloop()start(event)函数:
接下来,这段代码,就是这个程序的核心代码段之一,灰常滴重要,用event来传递用户鼠标的信息,在第一个嵌套for循环中,去锁定两个直线的交叉点,然后利用num变量的奇偶性,完成黑棋,白棋轮番下祺
if num % 2 == 0 and A[i][j] != 1:
point = w1.create_oval(40 * i + 5, 40 * j + 5, 40 * i + 35, 40 * j + 35, fill='black', tags='ob')
A[i][j] = 1
B[i][j] = 'b'
num += 1我们截取完成绘制棋子的代码段进行分析,在2 line中,我们定义变量point去不断追踪最近一次的落子,以便于完成后面的悔棋功能,可以看到这句的尾巴有tag = 'ob'这个参数,目的在于为每一次绘制的棋子打上标签,为的是之后便于清空棋盘。3,4 line中的A,B两个二维数组,其中A是记录在(i,j)点是否有落子,B则是记录该点的颜色。
接着往下读码,紧接着是一个变量record,目的和point相同,目的在于记录位置便于重置A,B两个二维列表的数据。
接下来一个超巨的for循环,就是去判断胜负,是否是五子连珠,可以看到w1.delete()这个函数,目的就是为了清空棋盘
在最后一段:
if act == 1 and num % 2 == 1:
draw()
mainloop()可以看到,act==1,这是为了人机模式完成交互,draw()是人机下棋的函数,在文章后面会讲
四.人机对战实现
首先,在开始这段讲解之前,大家思考一个问题,当我们自己去下棋的时候,是怎么思考的呢?当对手要五子时,我们肯定首先去进行围堵,达到防守;当对手的棋子对我们威胁不大时,我们肯定要尽量使我们的棋子对对手威胁更大。
所以,我们的思路是,给每个未下棋点打一个分数,当对手棋子的分数更高时,我们去进行防守,当我们分数高于对手时,我们进攻。然后按照这个思路,我们实现代码即可。
def Count(color, x, y):
global A, B
res = 0
tempres = 0
f = [[-1, 0], [-1, 1], [0, 1], [1, 1], [1, 0], [1, -1], [-1, -1], [0, -1]]
if A[x][y] != 1:
if color == 'w':
for road in f:
tempx, tempy = x, y
tempx += road[0]
tempy += road[1]
while 0 <= tempx <= 14 and 0 <= tempy <= 14 and B[tempx][tempy] == 'w':
tempres += 1
tempx += road[0]
tempy += road[1]
if tempres >= 3 and res >= 2:
res += 10000
elif tempres >= 3:
res += 1000
res += tempres
if res >= 3:
res += 100
tempres = 0
else:
for road in f:
tempx, tempy = x, y
tempx += road[0]
tempy += road[1]
while 0 <= tempx < 15 and 0 <= tempy < 15 and B[tempx][tempy] == 'b':
tempres += 1
tempx += road[0]
tempy += road[1]
if tempres >= 3 and res >= 2:
res += 10000
elif tempres >= 3:
res += 1000
res += tempres
if res >= 3:
res += 100
tempres = 0
return res
else:
return -1Count(color, x, y)函数:
这段代码是计数,进行分数评估,可以看到三个参数color,x,y,其中,(x,y)代表坐标,而color则是代表不同颜色棋子在(x,y)处的各自的分数,可以看到有不同权值(10000,1000,100),代表不同的组合方式下的分数,比如四子则要打一个绝对高的分数。
MachineJudge(current):
global num
maxw = 0
maxb = 0
wi, wj, bi, bj = 7, 7, 7, 7
dpw = np.full((15, 15), 0)
dpb = np.full((15, 15), 0)
for i in range(15):
for j in range(15):
dpw[i][j] = Count('w', i, j)
dpb[i][j] = Count('b', i, j)
if dpw[i][j] > maxw:
wi, wj = i, j
if dpb[i][j] > maxb:
bi, bj = i, j
maxw = max(maxw, dpw[i][j])
maxb = max(maxb, dpb[i][j])
if current == 'w':
if maxb > 1000 and maxw > 1000:
return [bi, bj]
elif maxw == 0:
return [bi, bj]
elif maxw > maxb > -1:
return [wi, wj]
elif maxw == maxb > -1:
return [bi, bj]
elif -1 < maxw < maxb:
return [bi, bj]
else:
if maxw > 1000 and maxb > 1000:
return [bi, bj]
elif maxw > 100:
return [wi, wj]
elif maxb == 0:
return [wi, wj]
elif maxb > maxw > -1:
return [bi, bj]
elif maxb == maxw > -1:
return [bi, bj]MachineJudge(current)函数:
machine—judge,机器判别,这段代码根据已打分的两个二维列表来进行判断,看哪个位置有更好的分数,cruuent则是当前回合是黑子或白子。
def draw():
global num, A, B, point1, record1,text2,text3
if num % 2 == 0:
i, j = MachineJudge('b')[0], MachineJudge('b')[1]
B[i][j] = 'b'
A[i][j] = 1
point1 = w1.create_oval(40 * i + 5, 40 * j + 5, 40 * i + 35, 40 * j + 35, fill='black', tags='ob')
else:
i, j = MachineJudge('w')[0], MachineJudge('w')[1]
point1 = w1.create_oval(40 * i + 5, 40 * j + 5, 40 * i + 35, 40 * j + 35, fill='white', tags='ob')
B[i][j] = 'w'
A[i][j] = 1
record1 = [i, j]
A[i][j] = 1
num += 1
f = [[-1, 0], [-1, 1], [0, 1], [1, 1]]
for z in range(0, 4):
a, b = f[z][0], f[z][1]
count1, count2 = 0, 0
x, y = i, j
while B[x][y] == B[i][j]:
count1 += 1
if x + a > 0 and y + b > 0 and x + a < 15 and y + b < 15 and B[x + a][y + b] == B[i][j]:
[x, y] = np.array([x, y]) + np.array([a, b])
else:
x, y = i, j
break
while B[x][y] == B[i][j]:
count2 += 1
if x - a < 15 and y - b < 15 and x - a > 0 and y - b > 0 and B[x - a][y - b] == B[i][j]:
[x, y] = np.array([x, y]) - np.array([a, b])
else:
break
if count1 + count2 >= 6:
if B[i][j] == 'b':
tkinter.messagebox.showinfo('提示', '黑棋获胜')
SqlReScore('w')
Refresh('b')
elif B[i][j] == 'w':
tkinter.messagebox.showinfo('提示', '白棋获胜')
SqlReScore('l')
Refresh('w')
w1.delete('ob')
A = np.full((15, 15), 0)
B = np.full((15, 15), '')
num = 0draw()函数:
这段就是根据 MachineJudge(current)函数返回的结果绘制,然后进行落子判断,因为博主大懒b(QAQ),所以直接复制了前面的代码。
五.完结
好了,基本几个比较联系紧密的代码已经解读完了,完整代码和页面图片在博主资源里,不用积分,免费下载,有问题的小伙伴可以直接留言!