做很多需求或者是技术细节验证的时候会用到 Runtime 技术,用了挺久的了,本文就写一些场景和源码分析相关的文章。
先问几个小问题:
- class_rw_t的结构是数组,数组里面的元素是数组,那它是二维数组吗?
- 为什么16字节对齐的?
- 有类对象、为什么设计元类对象?
- Super 原理的什么?
阅读完本文,你会掌握 Runtime 的原理和细节
动态语言
Runtime 是实现 OC 语言动态的 API。
静态语言:在编译阶段确定了变量数据类型、函数地址等,无法动态修改。
动态语言:只有在运行的时候才可以决定变量属于什么类型、方法真正的地址,
对象 objc_object 存了:isa、成员变量的值
类 objc_class: superclass、成员变量、实例变量
@interface Person : NSObject
{
NSString *_name;
}
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *hobby;
@end
malloc_size((__bridge const void *)(p)) // 24 isa占8字节 + _name 指针占8字节 + hobby 指针占8字节 = 24
class_getInstanceSize(p.class) // 32 ,系统内存对齐 为什么系统是由16字节对齐的?
成员变量占用8字节对齐,每个对象的第一个都是 isa 指针,必须要占用8字节。举例一个极端 case,假设 n 个对象,其中 m 个对象没有成员变量,只有 isa 指针占用8字节,其中的 n-m个对象既有 isa 指针,又有成员变量。每个类交错排列,那么 CPU 在访问对象的时候会耗费大量时间去识别具体的对象。很多时候会取舍,这个 case 就是时间换空间。以16字节对齐,会加快访问速度(参考链表和数组的设计)
class_rw_t、class_ro_t、class_rw_ext_t 区别?
class_ro_t 在编译时期生成的,class_rw_t 是在运行时期生成的。
那么什么是 class_rw_ext_t?首先明确2个概念
- clean memory:加载后不会被修改。当系统内存紧张时,可以从内存中移除,需要时可以再次加载
- dirty memory:加载后会被修改,一直处于内存中
Runtime 初始化的时候,遇到一个类,则会利用类的 class_ro_t 中的基础信息(methods、properties、protocols)来创建 class_rw_t 对象。class_rw_t 设计的目的就是为了 Runtime 所需(Category 增加属性、协议、动态增加方法等),但是实际上那么多类大多数情况只有少部分类才需要 Runtime 能力。所以 Apple 为了内存优化,在 iOS 14 对 class_rw_t 拆分出 class_rw_ext_t,用来存储 Methods、Protocols、Properties 信息,会在使用的时候才创建,节省更多内存。
比如访问 method 的过程
// 新版
const method_array_t methods() const {
auto v = get_ro_or_rwe();
if (v.is()) {
return v.get(&ro_or_rw_ext)->methods;
} else {
return method_array_t{v.get(&ro_or_rw_ext)->baseMethods};
}
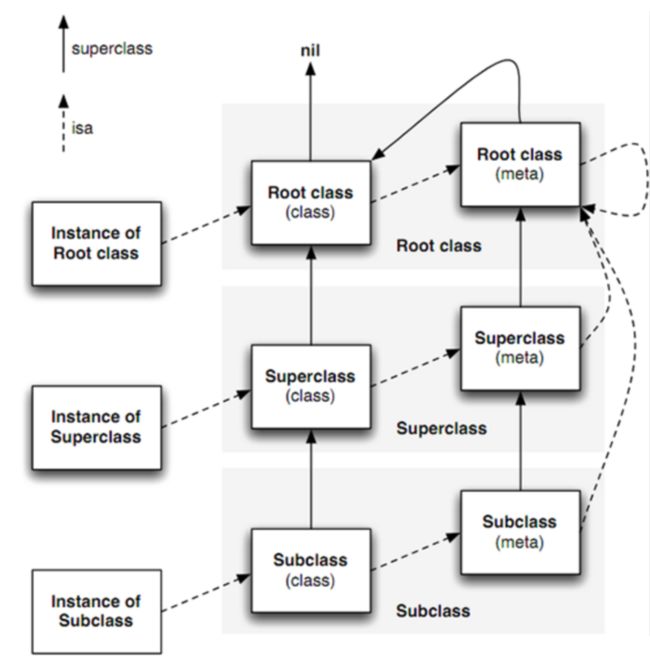
} 有类对象、为什么设计元类对象
复用消息机制。比如 [Person new]。
元类对象: isa、元类方法、
objc_msgSend 设计初衷就是为了消息发送很快。假如没有元类,则类方法也存储在类对象的方法信息中,则可能需要加额外的字段来标记某个方法是类方法还是对象方法。遍历或者寻找会比较慢。所以引入元类(单一职责),设计元类的目的就是为了提高 objc_msgSend 的效率。
isa 本质
在 arm64 架构之前,isa 就是一个普通的指针,存储着 Class或Meta-Class 对象的内存地址。
在 arm64 之后,对 isa 进行了优化,变成了一个共用体(union)结构,还使用位域来存储更多的信息。
union isa_t
{
Class cls;
uintptr_t bits;
# if __arm64__
# define ISA_MASK 0x0000000ffffffff8ULL
# define ISA_MAGIC_MASK 0x000003f000000001ULL
# define ISA_MAGIC_VALUE 0x000001a000000001ULL
struct {
uintptr_t nonpointer : 1;
uintptr_t has_assoc : 1;
uintptr_t has_cxx_dtor : 1;
uintptr_t shiftcls : 33; // MACH_VM_MAX_ADDRESS 0x1000000000
uintptr_t magic : 6;
uintptr_t weakly_referenced : 1;
uintptr_t deallocating : 1;
uintptr_t has_sidetable_rc : 1;
uintptr_t extra_rc : 19;
# define RC_ONE (1ULL<<45)
# define RC_HALF (1ULL<<18)
};
};struct 内部的成员变量可以指定占用内存位数, uintptr_t nonpointer : 1 代表占用1个字节
其中,结构体里面的属于”位域“
- nonpointer:0,代表普通的指针,存储着Class、Meta-Class对象的内存地址;1,代表优化过,使用位域存储更多的信息
- has_assoc:是否有设置过关联对象,如果没有,释放时会更快
- has_cxx_dtor:是否有C++的析构函数(.cxx_destruct),如果没有,释放时会更快
- shiftcls:存储着Class、Meta-Class对象的内存地址信息
- magic:用于在调试时分辨对象是否未完成初始化
- weakly_referenced:是否有被弱引用指向过,如果没有,释放时会更快
- deallocating:对象是否正在释放
- extra_rc:里面存储的值是引用计数器减1(刚创建出的对象,查看这个信息位0,因为存储着-1之后的引用计数)
- has_sidetable_rc:引用计数器是否过大无法存储在isa中;如果为1,那么引用计数会存储在一个叫SideTable的类的属性中
上面说的更快,是如何得出结论的?
查看 objc4 源代码看到对象执行销毁函数的时候会判断对象是否有关联对象、析构函数,有的话分别调用析构函数、移除关联对象等逻辑。
/***********************************************************************
* objc_destructInstance
* Destroys an instance without freeing memory.
* Calls C++ destructors.
* Calls ARC ivar cleanup.
* Removes associative references.
* Returns `obj`. Does nothing if `obj` is nil.
**********************************************************************/
void *objc_destructInstance(id obj)
{
if (obj) {
// Read all of the flags at once for performance.
bool cxx = obj->hasCxxDtor();
bool assoc = obj->hasAssociatedObjects();
// This order is important.
if (cxx) object_cxxDestruct(obj);
if (assoc) _object_remove_assocations(obj);
obj->clearDeallocating();
}
return obj;
}isa 在 arm64 之后必须通过 ISA_MASK 去查询 class(类对象、元类对象) 真正的地址
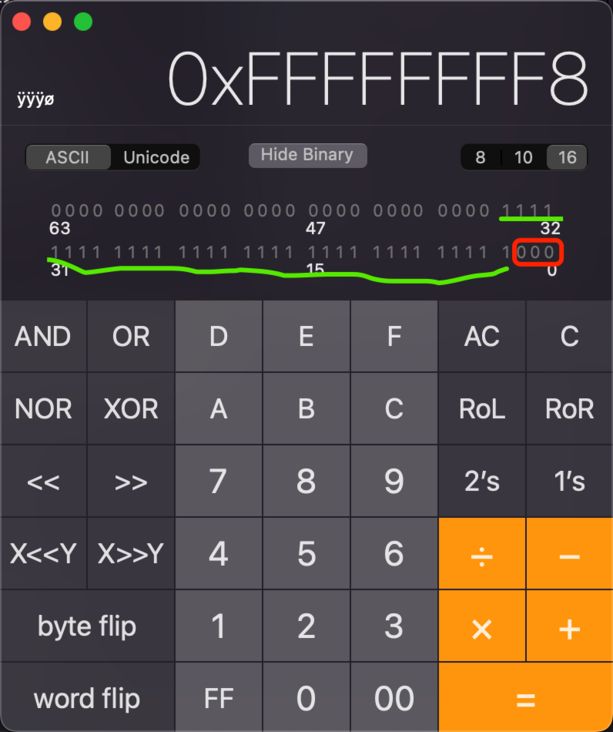
0x0000000ffffffff8ULL 用程序员模式打开计算器
其中,结构体中的数据存放大体是下面的结构:
extra_rc、has_sidetable_rc、deallocating、weakly_referenced、magic、shiftcls、has_has_cxx_dtor、assoc、nonpointer
知道结构体可以指定存储大小这个功能后,可以看到 isa_t 联合体与 ISA_MASK 按位与之后的地址,其实就是类真实的地址信息(可能是类对象、也有可能是元类对象)
如果要找出下面中间的 1010 如何实现?按位与即可,且要找的位置补充位1,其他位置为0
0b0010 1000
0b0011 1100
-----------
0b0010 1000结论:根据按位与的效果。ISA_MASK 的后3位都是0,所以我们找到的类地址二进制表示时后3位一定为0
我们可以验证下
Person *p = [[Person alloc] init];
NSLog(@"%p", [p class]); // 0x1000081d8
NSLog(@"%p", object_getClass([Person class])); // 0x100008200
NSLog(@"%p", object_getClass([NSObject class])); // 0x7ff84cb29fe0
NSLog(@"%p", object_getClass([NSString class])); // 0x7ff84c9dcc28为什么有的结尾是8?
16进制的8转为二进制,0x1000
关于这部分的调试,需要在真机上运行,真机上 arm64,拷贝对象地址到系统自带的运算器(程序员模式),查看64位地址。按照下面的顺序一一查看
extra_rc、has_sidetable_rc、deallocating、weakly_referenced、magic、shiftcls、has_has_cxx_dtor、assoc、nonpointer
所以可以根据 isa 信息查看对象是否创建过关联对象、有没有设置弱引用、
模仿系统位运算设计 API
系统很多 API 都有位或运算。比如 KVO 中的 options,可以传递 NSKeyValueObservingOptionNew | NSKeyValueObservingOptionOld ,那么系统是如何知道我到底传递了哪几个值?
按位或运算
0b0000 0001 // 1
0b0000 0010 // 2
0b0000 0100 // 4
------------
0b0000 0111 // 7可以看到上面3个数,按位或之后的结果为 0b0000 0111
按位与运算。
0b0000 0111
0b0000 0001
-----------
0b0000 0001
0b0000 0111
0b0000 0010
-----------
0b0000 0010
0b0000 0111
0b0000 0100
-----------
0b0000 0100
0b0000 0111
0b0000 1000
-----------
0b0000 0000我们发现上面3个数按位或之后的数字,分别与每个数按位与,得到的结果就是数据本身。
与一个不是3个数之一的数按位与,得到的结果为0b0000 0000。利用这个特性我们可以判断传递来的参数是不是包含了某个值
typedef enum {
OptionsEast = 1<<0, // 0b0001
OptionsSouth = 1<<1, // 0b0010
OptionsWest = 1<<2, // 0b0100
OptionsNorth = 1<<3 // 0b1000
} Options;
- (void)setOptions:(Options)options
{
if (options & OptionsEast) {
NSLog(@"我自东边来");
}
if (options & OptionsSouth) {
NSLog(@"我自南边来");
}
if (options & OptionsWest) {
NSLog(@"我自西边来");
}
if (options & OptionsNorth) {
NSLog(@"我自北边来");
}
}
[self setOptions: OptionsWest | OptionsNorth];
// 我自西边来
// 我自北边来类对象 Class 的结构
查看 objc4 源代码看看
struct objc_object {
private:
isa_t isa;
}
struct objc_class : objc_object {
// Class ISA;
Class superclass;
cache_t cache; // formerly cache pointer and vtable
class_data_bits_t bits; // class_rw_t * plus custom rr/alloc flags
};结构体继承于 objc_object 等同于下面代码
struct objc_class : objc_object {
isa_t isa;
Class superclass;
cache_t cache; // 方法缓存
class_data_bits_t bits; // 用于获取具体的类信息
};struct class_rw_t {
// Be warned that Symbolication knows the layout of this structure.
uint32_t flags;
uint32_t version;
const class_ro_t *ro;
method_array_t methods; // 方法列表
property_array_t properties; // 属性列表
protocol_array_t protocols; // 协议列表
Class firstSubclass;
Class nextSiblingClass;
char *demangledName;
};
struct class_data_bits_t {
// Values are the FAST_ flags above.
uintptr_t bits;
public:
class_rw_t* data() {
return (class_rw_t *)(bits & FAST_DATA_MASK);
}
}可以看到 objc_class 获取 bits 里的真实数据需要经过按位与 FAST_DATA_MASK
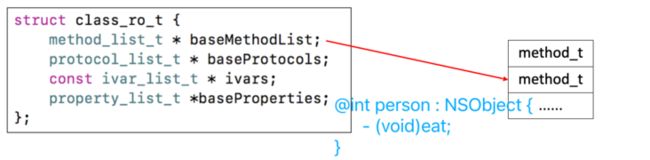
struct class_ro_t {
uint32_t flags;
uint32_t instanceStart;
uint32_t instanceSize; // instance 对象占用的内存空间
#ifdef __LP64__
uint32_t reserved;
#endif
const uint8_t * ivarLayout;
const char * name; // 类名
method_list_t * baseMethodList;
protocol_list_t * baseProtocols;
const ivar_list_t * ivars; // 成员变量列表
const uint8_t * weakIvarLayout;
property_list_t *baseProperties;
method_list_t *baseMethods() const {
return baseMethodList;
}
};说明:
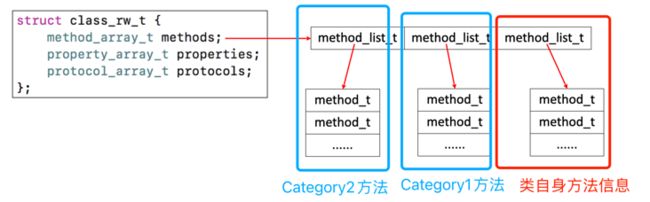
class_rw_t里面的 methods、properties、protocols 是数组(数组元素是也是方法组成的 Array),是可读可写的,包含了类的初始内容、分类的内容。为什么不是二维数组?因为Array 中的子 Array长度不一致,且不能补空
static void remethodizeClass(Class cls) { category_list *cats; bool isMeta; runtimeLock.assertWriting(); isMeta = cls->isMetaClass(); // Re-methodizing: check for more categories if ((cats = unattachedCategoriesForClass(cls, false/*not realizing*/))) { if (PrintConnecting) { _objc_inform("CLASS: attaching categories to class '%s' %s", cls->nameForLogging(), isMeta ? "(meta)" : ""); } attachCategories(cls, cats, true /*flush caches*/); free(cats); } } static void attachCategories(Class cls, category_list *cats, bool flush_caches) { if (!cats) return; if (PrintReplacedMethods) printReplacements(cls, cats); bool isMeta = cls->isMetaClass(); // fixme rearrange to remove these intermediate allocations method_list_t **mlists = (method_list_t **) malloc(cats->count * sizeof(*mlists)); property_list_t **proplists = (property_list_t **) malloc(cats->count * sizeof(*proplists)); protocol_list_t **protolists = (protocol_list_t **) malloc(cats->count * sizeof(*protolists)); // Count backwards through cats to get newest categories first int mcount = 0; int propcount = 0; int protocount = 0; int i = cats->count; bool fromBundle = NO; while (i--) { auto& entry = cats->list[i]; method_list_t *mlist = entry.cat->methodsForMeta(isMeta); if (mlist) { mlists[mcount++] = mlist; fromBundle |= entry.hi->isBundle(); } property_list_t *proplist = entry.cat->propertiesForMeta(isMeta, entry.hi); if (proplist) { proplists[propcount++] = proplist; } protocol_list_t *protolist = entry.cat->protocols; if (protolist) { protolists[protocount++] = protolist; } } auto rw = cls->data(); prepareMethodLists(cls, mlists, mcount, NO, fromBundle); rw->methods.attachLists(mlists, mcount); free(mlists); if (flush_caches && mcount > 0) flushCaches(cls); rw->properties.attachLists(proplists, propcount); free(proplists); rw->protocols.attachLists(protolists, protocount); free(protolists); }查看 objc4 源码发现针对类自身信息、Category 信息会进行组合。
class_ro_t里面的 baseMethodList、baseProtocols、ivars、baseProperties 是一维数组,是只读的,包含了类的(原始信息)初始内容
Method_t
method_t 是对方法\函数的封装
struct method_t {
SEL name; // 函数名、方法名
const char *types; // 编码(返回值类型、参数类型)
IMP imp; // 指向函数的指针(函数地址)
}IMP 代表函数的具体实现
typedef id _Nullable (*IMP)(id _Nonnull, SEL _Nonnull, ...); SEL 代表方法、函数名,一般叫做选择器,底层结构跟 char * 类似
typedef struct objc_selector *SEL;- 可以通过
@selector()和sel_registerName()获得 - 可以通过
sel_getName()和NSStringFromSelector()转成字符串 - 不同类中相同名字的方法,所对应的方法选择器是相同的
types 包含了函数返回值、参数编码的字符串。返回值|参数1|参数2| ... | 参数n
Type Encoding
iOS 中提供了一个叫做 @encode 的指令,可以将具体的类型表示成字符串编码
- (int)calcuate:(int)age heigith:(float)height;比如这个方法的 type encoding 为 i24@0:8i16f20
解读下,上面的方法其实携带了2个基础参数。
(id)self _cmd:(SEL)_cmd
i 代表方法返回值为 int
24 代表参数共占24个字节大小。4个参数分别为 id 类型的 self、SEL 类型的 _cmd, int 类型的 age、float 类型的 height。8+8+4+4 共24个字节(id、SEL 都为指针,长度为8)
@ 代表第一个参数为 object 类型,从第0个字节开始
:代表第二个参数为 SEL,从第8个字节开始
i 代表第三个参数为 int,从第16个字节开始
f 代表第四个参数为 float,从第20个字节开始
方法缓存
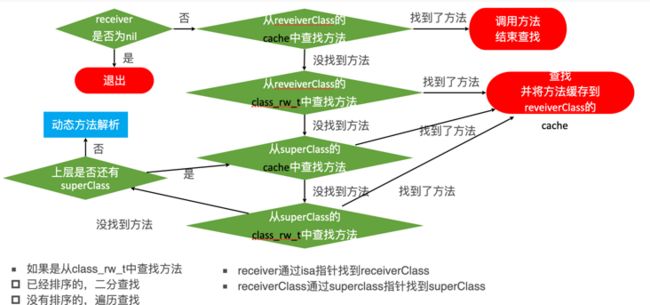
调用方法的本质,比如说对象方法,先根据对象的 isa 找到类对象,在类对象的 method_list_t 类型的 methods 方法数组(Array 中的元素是方法 Array)中(类的Category1、类的 Category2... 类自身的方法)查找方法,找不到则调用 superclass 查找父类的 methods 方法数组(Array 中的元素是方法 Array),效率较低,所以为了方便,给类设置了方法缓存。比如调用 Student 对象的 eat 方法,eat 在 student 中不存在,通过 isa 不断找,在 Person 类中找到了,则将 Person 类中的 eat 方法缓存在 Student 的 cache_t 类型的 cache 中。
Class 内部结构中有个方法缓存(cache_t),用散列表(哈希表)来缓存曾经调用过的方法,可以提高方法的查找速度
所以完整结构为:先根据对象的 isa 找到类对象,在类对象的 cache 列表中查找方法实现,如果找不到,则去 method_list_t 类型的 methods 方法数组(Array 中的元素是方法 Array)中(类的Category1、类的 Category2... 类自身的方法)查找方法,找不到则调用 superclass 查找父类的 cache 中查找,找到则调用方法,同时将父类 cache 缓存中的方法,在子类的 cache 中缓存一边。父类 cache 没找到,则在 methods 方法数组(Array 中的元素是方法 Array)查找,找到则调用,同时在子类 cache 中缓存一份。父类 methods 方法数组(Array 中的元素是方法 Array)没找到则继续调用 superclass,依次类推
struct cache_t {
struct bucket_t *_buckets; // 散列表
mask_t _mask; // 散列表的参数 -1
mask_t _occupied; // 已经缓存的方法数量
}struct bucket_t {
private:
cache_key_t _key; // SEL 作为 key
IMP _imp; // 函数的内存地址
}_buckets -> | bucket_t |bucket_t |bucket_t |bucket_t |...
方法缓存查找原理,散列表查找
objc4 源码 objc-cache.mm
bucket_t * cache_t::find(cache_key_t k, id receiver)
{
assert(k != 0);
bucket_t *b = buckets();
mask_t m = mask();
mask_t begin = cache_hash(k, m);
mask_t i = begin;
do {
if (b[i].key() == 0 || b[i].key() == k) {
return &b[i];
}
} while ((i = cache_next(i, m)) != begin);
// hack
Class cls = (Class)((uintptr_t)this - offsetof(objc_class, cache));
cache_t::bad_cache(receiver, (SEL)k, cls);
}散列表不够了,则会哈希拓容,此时缓存会释放 cache_collect_free
void cache_t::expand()
{
cacheUpdateLock.assertLocked();
uint32_t oldCapacity = capacity();
uint32_t newCapacity = oldCapacity ? oldCapacity*2 : INIT_CACHE_SIZE;
if ((uint32_t)(mask_t)newCapacity != newCapacity) {
// mask overflow - can't grow further
// fixme this wastes one bit of mask
newCapacity = oldCapacity;
}
reallocate(oldCapacity, newCapacity);
}
void cache_t::reallocate(mask_t oldCapacity, mask_t newCapacity)
{
bool freeOld = canBeFreed();
bucket_t *oldBuckets = buckets();
bucket_t *newBuckets = allocateBuckets(newCapacity);
// Cache's old contents are not propagated.
// This is thought to save cache memory at the cost of extra cache fills.
// fixme re-measure this
assert(newCapacity > 0);
assert((uintptr_t)(mask_t)(newCapacity-1) == newCapacity-1);
setBucketsAndMask(newBuckets, newCapacity - 1);
if (freeOld) {
cache_collect_free(oldBuckets, oldCapacity);
cache_collect(false);
}
}哈希查找元素核心是一个求 key 的过程,Java 中是求余,iOS 中是按位与 key & mask。
static inline mask_t cache_hash(cache_key_t key, mask_t mask)
{
return (mask_t)(key & mask);
}空间换时间的一个实现。
查找类的方法缓存 Demo
#import
#ifndef MockClassInfo_h
#define MockClassInfo_h
# if __arm64__
# define ISA_MASK 0x0000000ffffffff8ULL
# elif __x86_64__
# define ISA_MASK 0x00007ffffffffff8ULL
# endif
#if __LP64__
typedef uint32_t mask_t;
#else
typedef uint16_t mask_t;
#endif
typedef uintptr_t cache_key_t;
struct bucket_t {
cache_key_t _key;
IMP _imp;
};
struct cache_t {
bucket_t *_buckets;
mask_t _mask;
mask_t _occupied;
};
struct eint main () {
GoodStudent *goodStudent = [[GoodStudent alloc] init];
mock_objc_class *goodStudentClass = (__bridge mj_objc_class *)[GoodStudent class];
[goodStudent goodStudentTest];
[goodStudent studentTest];
[goodStudent personTest];
return 0;
}ntsize_list_tt {
uint32_t entsizeAndFlags;
uint32_t count;
};
struct method_t {
SEL name;
const char *types;
IMP imp;
};
struct method_list_t : entsize_list_tt {
method_t first;
};
struct ivar_t {
int32_t *offset;
const char *name;
const char *type;
uint32_t alignment_raw;
uint32_t size;
};
struct ivar_list_t : entsize_list_tt {
ivar_t first;
};
struct property_t {
const char *name;
const char *attributes;
};
struct property_list_t : entsize_list_tt {
property_t first;
};
struct chained_property_list {
chained_property_list *next;
uint32_t count;
property_t list[0];
};
typedef uintptr_t protocol_ref_t;
struct protocol_list_t {
uintptr_t count;
protocol_ref_t list[0];
};
struct class_ro_t {
uint32_t flags;
uint32_t instanceStart;
uint32_t instanceSize; // instance对象占用的内存空间
#ifdef __LP64__
uint32_t reserved;
#endif
const uint8_t * ivarLayout;
const char * name; // 类名
method_list_t * baseMethodList;
protocol_list_t * baseProtocols;
const ivar_list_t * ivars; // 成员变量列表
const uint8_t * weakIvarLayout;
property_list_t *baseProperties;
};
struct class_rw_t {
uint32_t flags;
uint32_t version;
const class_ro_t *ro;
method_list_t * methods; // 方法列表
property_list_t *properties; // 属性列表
const protocol_list_t * protocols; // 协议列表
Class firstSubclass;
Class nextSiblingClass;
char *demangledName;
};
#define FAST_DATA_MASK 0x00007ffffffffff8UL
struct class_data_bits_t {
uintptr_t bits;
public:
class_rw_t* data() {
return (class_rw_t *)(bits & FAST_DATA_MASK);
}
};
/* OC对象 */
struct mock_objc_object {
void *isa;
};
/* 类对象 */
struct mock_objc_class : mock_objc_object {
Class superclass;
cache_t cache;
class_data_bits_t bits;
public:
class_rw_t* data() {
return bits.data();
}
mock_objc_class* metaClass() {
return (mock_objc_class *)((long long)isa & ISA_MASK);
}
};
#endif /* MockClassInfo_h */
@interface Person : NSObject
- (void)personSay;
@end
@interface Student : Person
- (void)studentSay;
@end
@interface GoodStudent : Student
- (void)goodStudentSay;
@end
int main () {
GoodStudent *goodStudent = [[GoodStudent alloc] init];
mock_objc_class *goodStudentClass = (__bridge mj_objc_class *)[GoodStudent class];
// breakpoints1
[goodStudent goodStudentSay];
// breakpoints2
[goodStudent studentSay];
// breakpoints3
[goodStudent personSay];
// breakpoints4
[goodStudent goodStudentSay];
// breakpoints5
[goodStudent studentSay];
// breakpoints6
NSLog(@"well donw");
return 0;
} 流程:
断点1的地方可以看到 mock_objc_class 结构体 cache 的 _occupied 为1,_mask 为3,初始化哈希表长度为4
在断点1的地方,_occupied 为1则代表只有 init 方法被缓存,本行代码执行完,_occupied 为2.
在断点2的地方,_occupied 为2则代表只有 init、goodStudentSay 方法被缓存。本行代码执行完,_occupied 为3
在断点3的地方,_occupied 为3则代表只有 init 、goodStudentSay 、studentSay方法被缓存。本行代码执行完,_occupied 为1,且 _mask 为7。
奇了怪了,为什么 _occupied为1,且_mask 为7?
因为哈希表长度为4,缓存3个方法后,到第4个方法需要缓存的时候会执行哈希表拓容,缓存会失效。拓容策略为乘以2 即 uint32_t newCapacity = oldCapacity ? oldCapacity*2 : INIT_CACHE_SIZE; 所以长度为8,mask 为长度-1 ,则为7,第4个方法刚好被缓存下来,_occupied 为1。
void cache_t::expand()
{
cacheUpdateLock.assertLocked();
uint32_t oldCapacity = capacity();
uint32_t newCapacity = oldCapacity ? oldCapacity*2 : INIT_CACHE_SIZE;
if ((uint32_t)(mask_t)newCapacity != newCapacity) {
// mask overflow - can't grow further
// fixme this wastes one bit of mask
newCapacity = oldCapacity;
}
reallocate(oldCapacity, newCapacity);
}继续运行
在断点4的地方,_occupied 为1则代表只有 personSay方法被缓存。本行代码执行完,_occupied 为2,且 _mask 为7。
在断点5的地方,_occupied 为2则代表只有 personSay、goodStudentSay 方法被缓存。本行代码执行完,_occupied 为3,且 _mask 为7。
在断点6的地方,_occupied 为3则代表只有 personSay、goodStudentSay、studentSay 方法被缓存, _mask 为7。
如何根据方法散列表查找某个方法
GoodStudent *student = [[GoodStudent alloc] init];
mock_objc_class *studentClass = (__bridge mock_objc_class *)[GoodStudent class];
[student goodStudentSay];
[student studentSay];
[student personSay];
NSLog(@"Well done");
cache_t cache = studentClass->cache;
bucket_t *buckets = cache._buckets;
bucket_t bucket = buckets[(long long)@selector(personSay) & cache._mask];
NSLog(@"%s %p", bucket._key, bucket._imp);
// personSay 0xbec8原理就是根据类对象结构体找到 cache 结构体,cache 结构体内部的 _buckets 是一个方法散列表,查看源代码,根据散列表的哈希寻找策略 (key & mask) 找到哈希索引,然后找到方法对象 bucket,其中寻找方法索引的 key 就是 方法 selector。
static inline mask_t cache_hash(cache_key_t key, mask_t mask)
{
return (mask_t)(key & mask);
}objc_msgSend
oc 方法(对象方法、类方法)调用本质就是 objc_msgSend
[person eat];
objc_msgSend(person, sel_registerName("eat"));
[Person initialize];
objc_msgSend([Person class], sel_registerName("initialize")); objc_msgSend 可以分为3个阶段:
- 消息发送
- 动态方法解析
- 消息转发
查看源码 objc-msg-arm64.s
ENTRY _objc_msgSend
UNWIND _objc_msgSend, NoFrame
MESSENGER_START
// x0 寄存器代表消息接受者,receiver。objc_msgSend(person, sel_registerName("eat")) 的 person
cmp x0, #0 // nil check and tagged pointer check
// b 代表指令跳转。le 代表 小于等于。<=0则跳转到 LNilOrTagged
b.le LNilOrTagged // (MSB tagged pointer looks negative)
ldr x13, [x0] // x13 = isa // ldr 代表加载指令。这里的意思是将 x0 寄存器信息写入到 x13中
and x16, x13, #ISA_MASK // x16 = class // 这里就是将 x13 与 ISA_MASK 按位与,然后得到真实的 isa 信息,然后写入到 x16 中
LGetIsaDone:
CacheLookup NORMAL // calls imp or objc_msgSend_uncached // 这里执行 objc_msgSend_uncached 逻辑,CacheLookup 是一个汇编宏,看下面的说明
LNilOrTagged:
// 判断为 nil 则跳转到 LReturnZero
b.eq LReturnZero // nil check
// tagged
mov x10, #0xf000000000000000
cmp x0, x10
b.hs LExtTag
adrp x10, _objc_debug_taggedpointer_classes@PAGE
add x10, x10, _objc_debug_taggedpointer_classes@PAGEOFF
ubfx x11, x0, #60, #4
ldr x16, [x10, x11, LSL #3]
b LGetIsaDone
LExtTag:
// ext tagged
adrp x10, _objc_debug_taggedpointer_ext_classes@PAGE
add x10, x10, _objc_debug_taggedpointer_ext_classes@PAGEOFF
ubfx x11, x0, #52, #8
ldr x16, [x10, x11, LSL #3]
b LGetIsaDone
LReturnZero:
// x0 is already zero
mov x1, #0
movi d0, #0
movi d1, #0
movi d2, #0
movi d3, #0
MESSENGER_END_NIL
// 汇编中 ret 代表 return
ret
END_ENTRY _objc_msgSend
.macro CacheLookup // 汇编宏,可以看到根据 (SEL & mask) 来寻找真正的方法地址
// x1 = SEL, x16 = isa
ldp x10, x11, [x16, #CACHE] // x10 = buckets, x11 = occupied|mask
and w12, w1, w11 // x12 = _cmd & mask
add x12, x10, x12, LSL #4 // x12 = buckets + ((_cmd & mask)<<4)
ldp x9, x17, [x12] // {x9, x17} = *bucket
1: cmp x9, x1 // if (bucket->sel != _cmd)
b.ne 2f // scan more
CacheHit $0 // call or return imp
2: // not hit: x12 = not-hit bucket
CheckMiss $0 // miss if bucket->sel == 0
cmp x12, x10 // wrap if bucket == buckets
b.eq 3f
ldp x9, x17, [x12, #-16]! // {x9, x17} = *--bucket
b 1b // loop
3: // wrap: x12 = first bucket, w11 = mask
add x12, x12, w11, UXTW #4 // x12 = buckets+(mask<<4)
// Clone scanning loop to miss instead of hang when cache is corrupt.
// The slow path may detect any corruption and halt later.
ldp x9, x17, [x12] // {x9, x17} = *bucket
1: cmp x9, x1 // if (bucket->sel != _cmd)
b.ne 2f // scan more
CacheHit $0 // call or return imp
2: // not hit: x12 = not-hit bucket
// 这里是方法查找失败,则走 checkMiss 逻辑,具体看下面
CheckMiss $0 // miss if bucket->sel == 0
cmp x12, x10 // wrap if bucket == buckets
b.eq 3f
ldp x9, x17, [x12, #-16]! // {x9, x17} = *--bucket
b 1b // loop
3: // double wrap
JumpMiss $0
.endmacro
// CheckMiss 汇编宏,上面走 Normal 逻辑,内部走 __objc_msgSend_uncached 流程
.macro CheckMiss
// miss if bucket->sel == 0
.if $0 == GETIMP
cbz x9, LGetImpMiss
.elseif $0 == NORMAL
cbz x9, __objc_msgSend_uncached
.elseif $0 == LOOKUP
cbz x9, __objc_msgLookup_uncached
.else
.abort oops
.endif
.endmacro
// __objc_msgSend_uncached 内部其实走 MethodTableLookup 逻辑
STATIC_ENTRY __objc_msgSend_uncached
UNWIND __objc_msgSend_uncached, FrameWithNoSaves
// THIS IS NOT A CALLABLE C FUNCTION
// Out-of-band x16 is the class to search
MethodTableLookup
br x17
END_ENTRY __objc_msgSend_uncached
// MethodTableLookup 是一个汇编宏,内部指令跳转到 __class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3。
.macro MethodTableLookup
// push frame
stp fp, lr, [sp, #-16]!
mov fp, sp
// save parameter registers: x0..x8, q0..q7
sub sp, sp, #(10*8 + 8*16)
stp q0, q1, [sp, #(0*16)]
stp q2, q3, [sp, #(2*16)]
stp q4, q5, [sp, #(4*16)]
stp q6, q7, [sp, #(6*16)]
stp x0, x1, [sp, #(8*16+0*8)]
stp x2, x3, [sp, #(8*16+2*8)]
stp x4, x5, [sp, #(8*16+4*8)]
stp x6, x7, [sp, #(8*16+6*8)]
str x8, [sp, #(8*16+8*8)]
// receiver and selector already in x0 and x1
mov x2, x16
bl __class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3
// imp in x0
mov x17, x0
// restore registers and return
ldp q0, q1, [sp, #(0*16)]
ldp q2, q3, [sp, #(2*16)]
ldp q4, q5, [sp, #(4*16)]
ldp q6, q7, [sp, #(6*16)]
ldp x0, x1, [sp, #(8*16+0*8)]
ldp x2, x3, [sp, #(8*16+2*8)]
ldp x4, x5, [sp, #(8*16+4*8)]
ldp x6, x7, [sp, #(8*16+6*8)]
ldr x8, [sp, #(8*16+8*8)]
mov sp, fp
ldp fp, lr, [sp], #16
.endmacroTips:c 方法在汇编中使用的时候,需要在方法名前加 _ 。所以在汇编中某个方法为 _xxx,则在其他地方查找实现,需要去掉 _
此时 __class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3 在汇编中没有实现,则按照 _class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3 查找
IMP _class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3(id obj, SEL sel, Class cls)
{
return lookUpImpOrForward(cls, sel, obj,
YES/*initialize*/, NO/*cache*/, YES/*resolver*/);
}
IMP lookUpImpOrForward(Class cls, SEL sel, id inst,
bool initialize, bool cache, bool resolver)
{
IMP imp = nil;
bool triedResolver = NO;
runtimeLock.assertUnlocked();
// Optimistic cache lookup
if (cache) {
imp = cache_getImp(cls, sel);
if (imp) return imp;
}
// runtimeLock is held during isRealized and isInitialized checking
// to prevent races against concurrent realization.
// runtimeLock is held during method search to make
// method-lookup + cache-fill atomic with respect to method addition.
// Otherwise, a category could be added but ignored indefinitely because
// the cache was re-filled with the old value after the cache flush on
// behalf of the category.
runtimeLock.read();
if (!cls->isRealized()) {
// Drop the read-lock and acquire the write-lock.
// realizeClass() checks isRealized() again to prevent
// a race while the lock is down.
runtimeLock.unlockRead();
runtimeLock.write();
realizeClass(cls);
runtimeLock.unlockWrite();
runtimeLock.read();
}
if (initialize && !cls->isInitialized()) {
runtimeLock.unlockRead();
_class_initialize (_class_getNonMetaClass(cls, inst));
runtimeLock.read();
// If sel == initialize, _class_initialize will send +initialize and
// then the messenger will send +initialize again after this
// procedure finishes. Of course, if this is not being called
// from the messenger then it won't happen. 2778172
}
retry:
runtimeLock.assertReading();
// Try this class's cache.
imp = cache_getImp(cls, sel);
if (imp) goto done;
// Try this class's method lists.
{
Method meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(cls, sel);
if (meth) {
log_and_fill_cache(cls, meth->imp, sel, inst, cls);
imp = meth->imp;
goto done;
}
}
// Try superclass caches and method lists.
{
unsigned attempts = unreasonableClassCount();
for (Class curClass = cls->superclass;
curClass != nil;
curClass = curClass->superclass)
{
// Halt if there is a cycle in the superclass chain.
if (--attempts == 0) {
_objc_fatal("Memory corruption in class list.");
}
// Superclass cache.
imp = cache_getImp(curClass, sel);
if (imp) {
if (imp != (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache) {
// Found the method in a superclass. Cache it in this class.
log_and_fill_cache(cls, imp, sel, inst, curClass);
goto done;
}
else {
// Found a forward:: entry in a superclass.
// Stop searching, but don't cache yet; call method
// resolver for this class first.
break;
}
}
// Superclass method list.
Method meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(curClass, sel);
if (meth) {
log_and_fill_cache(cls, meth->imp, sel, inst, curClass);
imp = meth->imp;
goto done;
}
}
}
// No implementation found. Try method resolver once.
if (resolver && !triedResolver) {
runtimeLock.unlockRead();
_class_resolveMethod(cls, sel, inst);
runtimeLock.read();
// Don't cache the result; we don't hold the lock so it may have
// changed already. Re-do the search from scratch instead.
triedResolver = YES;
goto retry;
}
// No implementation found, and method resolver didn't help.
// Use forwarding.
imp = (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache;
cache_fill(cls, sel, imp, inst);
done:
runtimeLock.unlockRead();
return imp;
}消息发送阶段
上面的代码走到 getMethodNoSuper_nolock 寻找类里的方法
static method_t *
getMethodNoSuper_nolock(Class cls, SEL sel)
{
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
assert(cls->isRealized());
// fixme nil cls?
// fixme nil sel?
// 这里根据类结构体找到 data(),然后找到 methods (Array 数组,数组元素是方法 Array)
/*
data() 其实就是 class_rw_t* data() {
return (class_rw_t *)(bits & FAST_DATA_MASK);
}
*/
for (auto mlists = cls->data()->methods.beginLists(),
end = cls->data()->methods.endLists();
mlists != end;
++mlists)
{
method_t *m = search_method_list(*mlists, sel);
if (m) return m;
}
return nil;
}
static method_t *search_method_list(const method_list_t *mlist, SEL sel)
{
int methodListIsFixedUp = mlist->isFixedUp();
int methodListHasExpectedSize = mlist->entsize() == sizeof(method_t);
// 排好序则调用 `findMethodInSortedMethodList`,其内部是二分查找实现。
if (__builtin_expect(methodListIsFixedUp && methodListHasExpectedSize, 1)) {
return findMethodInSortedMethodList(sel, mlist);
} else {
// 没排序则线性查找
// Linear search of unsorted method list
for (auto& meth : *mlist) {
if (meth.name == sel) return &meth;
}
}
#if DEBUG
// sanity-check negative results
if (mlist->isFixedUp()) {
for (auto& meth : *mlist) {
if (meth.name == sel) {
_objc_fatal("linear search worked when binary search did not");
}
}
}
#endif
return nil;
}
static method_t *findMethodInSortedMethodList(SEL key, const method_list_t *list)
{
assert(list);
const method_t * const first = &list->first;
const method_t *base = first;
const method_t *probe;
uintptr_t keyValue = (uintptr_t)key;
uint32_t count;
for (count = list->count; count != 0; count >>= 1) {
probe = base + (count >> 1);
uintptr_t probeValue = (uintptr_t)probe->name;
if (keyValue == probeValue) {
// `probe` is a match.
// Rewind looking for the *first* occurrence of this value.
// This is required for correct category overrides.
while (probe > first && keyValue == (uintptr_t)probe[-1].name) {
probe--;
}
return (method_t *)probe;
}
if (keyValue > probeValue) {
base = probe + 1;
count--;
}
}
return nil;
}cls->data()->methods.beginLists 这里根据类结构体调用到 data() 方法,获取到 class_rw_t
class_rw_t *data() {
return bits.data();
}然后通过 class_rw_t 找到 methods (Array 数组,数组元素是方法 Array)。内部调用 search_method_list 方法。
search_method_list 方法内部判断方法数组是否排好序
- 排好序则调用
findMethodInSortedMethodList,其内部是二分查找实现。 - 没排序,则线性查找 (Linear search of unsorted method list)
getMethodNoSuper_nolock 执行完则会将方法写入到当前类对象的缓存中。
static void
log_and_fill_cache(Class cls, IMP imp, SEL sel, id receiver, Class implementer)
{
#if SUPPORT_MESSAGE_LOGGING
if (objcMsgLogEnabled) {
bool cacheIt = logMessageSend(implementer->isMetaClass(),
cls->nameForLogging(),
implementer->nameForLogging(),
sel);
if (!cacheIt) return;
}
#endif
cache_fill (cls, sel, imp, receiver);
}
void cache_fill(Class cls, SEL sel, IMP imp, id receiver)
{
#if !DEBUG_TASK_THREADS
mutex_locker_t lock(cacheUpdateLock);
cache_fill_nolock(cls, sel, imp, receiver);
#else
_collecting_in_critical();
return;
#endif
}
static void cache_fill_nolock(Class cls, SEL sel, IMP imp, id receiver)
{
cacheUpdateLock.assertLocked();
// Never cache before +initialize is done
if (!cls->isInitialized()) return;
// Make sure the entry wasn't added to the cache by some other thread
// before we grabbed the cacheUpdateLock.
if (cache_getImp(cls, sel)) return;
cache_t *cache = getCache(cls);
cache_key_t key = getKey(sel);
// Use the cache as-is if it is less than 3/4 full
mask_t newOccupied = cache->occupied() + 1;
mask_t capacity = cache->capacity();
if (cache->isConstantEmptyCache()) {
// Cache is read-only. Replace it.
cache->reallocate(capacity, capacity ?: INIT_CACHE_SIZE);
}
else if (newOccupied <= capacity / 4 * 3) {
// Cache is less than 3/4 full. Use it as-is.
}
else {
// Cache is too full. Expand it.
cache->expand();
}
// Scan for the first unused slot and insert there.
// There is guaranteed to be an empty slot because the
// minimum size is 4 and we resized at 3/4 full.
bucket_t *bucket = cache->find(key, receiver);
if (bucket->key() == 0) cache->incrementOccupied();
bucket->set(key, imp);
}摘出 lookUpImpOrForward 方法中的一段代码
// Try this class's cache.
imp = cache_getImp(cls, sel);
if (imp) goto done;
// Try this class's method lists.
{
Method meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(cls, sel);
if (meth) {
log_and_fill_cache(cls, meth->imp, sel, inst, cls);
imp = meth->imp;
goto done;
}
}
// Try superclass caches and method lists.如果代码没有找到,则不会 goto 到 done,开始走父类缓存查找逻辑
// Try superclass caches and method lists.
{
unsigned attempts = unreasonableClassCount();
// for 循环不断查找,找当前类的父类,直到当前类为 nil。
for (Class curClass = cls->superclass;
curClass != nil;
curClass = curClass->superclass)
{
// Halt if there is a cycle in the superclass chain.
if (--attempts == 0) {
_objc_fatal("Memory corruption in class list.");
}
// Superclass cache.
// 先在父类的方法缓存中查找(根据 sel & mask)`cache_getImp` ,找到则将方法写入到自身类的方法缓存中去 `log_and_fill_cache(cls, imp, sel, inst, curClass);`
imp = cache_getImp(curClass, sel);
if (imp) {
if (imp != (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache) {
// Found the method in a superclass. Cache it in this class.
log_and_fill_cache(cls, imp, sel, inst, curClass);
goto done;
}
else {
// Found a forward:: entry in a superclass.
// Stop searching, but don't cache yet; call method
// resolver for this class first.
break;
}
}
// Superclass method list.
// 如果在父类的方法缓存中没找到,则调用 `getMethodNoSuper_nolock` 父类的 方法数组(Array 元素为方法数组),按照排序好和没排序好分别走二分查找和线性查找。
Method meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(curClass, sel);
if (meth) {
// 如果找到则继续填充到当前类的方法缓存中去
log_and_fill_cache(cls, meth->imp, sel, inst, curClass);
imp = meth->imp;
goto done;
}
}
} for 循环不断查找,找当前类的父类,直到当前类为 nil。
先在父类的方法缓存中查找(根据 sel & mask)cache_getImp ,找到则将方法写入到自身类的方法缓存中去 log_and_fill_cache(cls, imp, sel, inst, curClass);
比如 Person 类有 eat 方法,Student 类有 stduy 方法,调用 Student 对象的 eat 方法,则会走到这里,从父类找到方法后写入到 Student 类的方法缓存中去。
如果在父类的方法缓存中没找到,则调用 getMethodNoSuper_nolock 父类的 方法数组(Array 元素为方法数组),按照排序好和没排序好分别走二分查找和线性查找。
如果找到则继续填充到当前类的方法缓存中去 log_and_fill_cache(cls, meth->imp, sel, inst, curClass);,最后 goto done
上面的流程是整个 objc_msgSend 的消息发送阶段的整个流程。可以用下图表示
动态方法解析阶段
接着查看源码
IMP lookUpImpOrForward(Class cls, SEL sel, id inst,
bool initialize, bool cache, bool resolver)
{
//...
// No implementation found. Try method resolver once.
if (resolver && !triedResolver) {
runtimeLock.unlockRead();
_class_resolveMethod(cls, sel, inst);
runtimeLock.read();
// Don't cache the result; we don't hold the lock so it may have
// changed already. Re-do the search from scratch instead.
triedResolver = YES;
goto retry;
}
// ...
}
void _class_resolveMethod(Class cls, SEL sel, id inst)
{
if (! cls->isMetaClass()) {
// try [cls resolveInstanceMethod:sel]
_class_resolveInstanceMethod(cls, sel, inst);
}
else {
// try [nonMetaClass resolveClassMethod:sel]
// and [cls resolveInstanceMethod:sel]
_class_resolveClassMethod(cls, sel, inst);
if (!lookUpImpOrNil(cls, sel, inst,
NO/*initialize*/, YES/*cache*/, NO/*resolver*/))
{
_class_resolveInstanceMethod(cls, sel, inst);
}
}
}判断当前类没有走过动态方法解析阶段,则走动态方法解析阶段,调用 _class_resolveMethod 方法。
内部会判断但前类是不是元类对象、还是类对象走不同逻辑。
类对象走 _class_resolveInstanceMethod 逻辑
static void _class_resolveInstanceMethod(Class cls, SEL sel, id inst)
{
if (! lookUpImpOrNil(cls->ISA(), SEL_resolveInstanceMethod, cls,
NO/*initialize*/, YES/*cache*/, NO/*resolver*/))
{
// Resolver not implemented.
return;
}
BOOL (*msg)(Class, SEL, SEL) = (typeof(msg))objc_msgSend;
bool resolved = msg(cls, SEL_resolveInstanceMethod, sel);
// Cache the result (good or bad) so the resolver doesn't fire next time.
// +resolveInstanceMethod adds to self a.k.a. cls
IMP imp = lookUpImpOrNil(cls, sel, inst,
NO/*initialize*/, YES/*cache*/, NO/*resolver*/);
if (resolved && PrintResolving) {
if (imp) {
_objc_inform("RESOLVE: method %c[%s %s] "
"dynamically resolved to %p",
cls->isMetaClass() ? '+' : '-',
cls->nameForLogging(), sel_getName(sel), imp);
}
else {
// Method resolver didn't add anything?
_objc_inform("RESOLVE: +[%s resolveInstanceMethod:%s] returned YES"
", but no new implementation of %c[%s %s] was found",
cls->nameForLogging(), sel_getName(sel),
cls->isMetaClass() ? '+' : '-',
cls->nameForLogging(), sel_getName(sel));
}
}
}核心就调用 bool resolved = msg(cls, SEL_resolveInstanceMethod, sel); 运行 resolveInstanceMethod 方法。
元类对象走 _class_resolveClassMethod 逻辑
static void _class_resolveClassMethod(Class cls, SEL sel, id inst)
{
assert(cls->isMetaClass());
if (! lookUpImpOrNil(cls, SEL_resolveClassMethod, inst,
NO/*initialize*/, YES/*cache*/, NO/*resolver*/))
{
// Resolver not implemented.
return;
}
BOOL (*msg)(Class, SEL, SEL) = (typeof(msg))objc_msgSend;
bool resolved = msg(_class_getNonMetaClass(cls, inst),
SEL_resolveClassMethod, sel);
// Cache the result (good or bad) so the resolver doesn't fire next time.
// +resolveClassMethod adds to self->ISA() a.k.a. cls
IMP imp = lookUpImpOrNil(cls, sel, inst,
NO/*initialize*/, YES/*cache*/, NO/*resolver*/);
if (resolved && PrintResolving) {
if (imp) {
_objc_inform("RESOLVE: method %c[%s %s] "
"dynamically resolved to %p",
cls->isMetaClass() ? '+' : '-',
cls->nameForLogging(), sel_getName(sel), imp);
}
else {
// Method resolver didn't add anything?
_objc_inform("RESOLVE: +[%s resolveClassMethod:%s] returned YES"
", but no new implementation of %c[%s %s] was found",
cls->nameForLogging(), sel_getName(sel),
cls->isMetaClass() ? '+' : '-',
cls->nameForLogging(), sel_getName(sel));
}
}
}其实就是调用 `bool resolved = msg(_class_getNonMetaClass(cls, inst),
SEL_resolveClassMethod, sel);`
最后还是走到了 goto retry; 继续走完整的消息发送流程(因为添加了方法,所以会按照方法查找再去执行的逻辑)
完整流程如下
上 Demo
Person *person = [[Person alloc] init];
[person eat];调用不存在方法则报错 ***** Terminating app due to uncaught exception 'NSInvalidArgumentException', reason: '-[Person eat]: unrecognized selector sent to instance 0x101b2d900'**
因为调用对象不存在的方法,所以会 Crash
知道 objc_msgSend 的流程,我们尝试给它修正下
- (void)customEat {
NSLog(@"我的假的 eat 方法,为了解决奔溃问题");
}
+ (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel {
if (sel == @selector(eat)) {
// 对象方法,存在于对象上。
Method method = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(customEat));
class_addMethod(self, sel, method_getImplementation(method), method_getTypeEncoding(method));
return YES;
}
return [super resolveInstanceMethod:sel];
}也可以添加 c 语音方法
void customEat (id self, SEL _cmd) {
NSLog(@"%@-%s-%s", self, sel_getName(_cmd), __func__);
}
+ (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel
{
if (sel == @selector(eat)) {
// 对象方法,存在于对象上。
class_addMethod(self, sel, (IMP)customEat, "v16@0:8");
return YES;
}
return [super resolveInstanceMethod:sel];
}因为 c 语言方法名就是函数地址,所以不需要直接传递即可,需要做下类型转换 (IMP)customEat
也可以给类方法做动态方法解析。需要注意的是类方法。
- 调用
-(BOOL)resolveClassMethod:(SEL)sel class_addMethod方法中的第一个参数,需要加到类的元类对象中,所以是object_getClass
Person *person = [[Person alloc] init];
[Person drink];
void customDrink (id self, SEL _cmd) {
NSLog(@"假喝水");
}
+ (BOOL)resolveClassMethod:(SEL)sel
{
if (sel == @selector(drink)) {
// 类方法,存在于元类对象上。
class_addMethod(object_getClass(self), sel, (IMP)customDrink, "v16@0:8");
return YES;
}
return [super resolveClassMethod:sel];
}消息转发阶段
能走到消息转发,说明
- 类自身没有该方法(
objc_msgSend的消息发送) objc_msgSend动态方法解析失败或者没有做
说明类自身和父类没有可以处理该消息的能力,此时应该将该消息转发给其他对象。
查看 objc4 的源码
IMP lookUpImpOrForward(Class cls, SEL sel, id inst,
bool initialize, bool cache, bool resolver)
{
//...
// No implementation found, and method resolver didn't help.
// Use forwarding.
imp = (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache;
cache_fill(cls, sel, imp, inst);
// ...
}继续查找 _objc_msgForward_impcache
STATIC_ENTRY __objc_msgForward_impcache
MESSENGER_START
nop
MESSENGER_END_SLOW
// No stret specialization.
b __objc_msgForward
END_ENTRY __objc_msgForward_impcache
ENTRY __objc_msgForward
adrp x17, __objc_forward_handler@PAGE
ldr x17, [x17, __objc_forward_handler@PAGEOFF]
br x1
END_ENTRY __objc_msgForward查找 __objc_forward_handler 没有找到,可以猜想是一个 c 方法,去掉最前面的 _,按照 _objc_forward_handler 查找得到
__attribute__((noreturn)) void
objc_defaultForwardHandler(id self, SEL sel)
{
_objc_fatal("%c[%s %s]: unrecognized selector sent to instance %p "
"(no message forward handler is installed)",
class_isMetaClass(object_getClass(self)) ? '+' : '-',
object_getClassName(self), sel_getName(sel), self);
}
void *_objc_forward_handler = (void*)objc_defaultForwardHandler;消息转发的代码是不开源的,查找资料找到一份靠谱的 __forwarding 方法实现
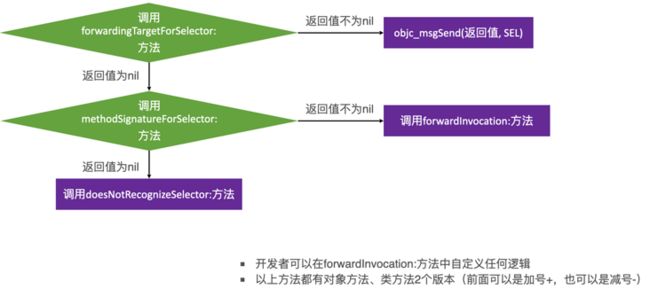
为什么是 __forwarding__ 方法。我们可以根据 Xcode 崩溃窥探一二
int __forwarding__(void *frameStackPointer, int isStret) {
id receiver = *(id *)frameStackPointer;
SEL sel = *(SEL *)(frameStackPointer + 8);
const char *selName = sel_getName(sel);
Class receiverClass = object_getClass(receiver);
// 调用 forwardingTargetForSelector:
if (class_respondsToSelector(receiverClass, @selector(forwardingTargetForSelector:))) {
id forwardingTarget = [receiver forwardingTargetForSelector:sel];
if (forwardingTarget && forwardingTarget != receiver) {
return objc_msgSend(forwardingTarget, sel, ...);
}
}
// 调用 methodSignatureForSelector 获取方法签名后再调用 forwardInvocation
if (class_respondsToSelector(receiverClass, @selector(methodSignatureForSelector:))) {
NSMethodSignature *methodSignature = [receiver methodSignatureForSelector:sel];
if (methodSignature && class_respondsToSelector(receiverClass, @selector(forwardInvocation:))) {
NSInvocation *invocation = [NSInvocation _invocationWithMethodSignature:methodSignature frame:frameStackPointer];
[receiver forwardInvocation:invocation];
void *returnValue = NULL;
[invocation getReturnValue:&value];
return returnValue;
}
}
if (class_respondsToSelector(receiverClass,@selector(doesNotRecognizeSelector:))) {
[receiver doesNotRecognizeSelector:sel];
}
// The point of no return.
kill(getpid(), 9);
}具体地址可以参考 __frowarding
完整流程如下
上 Demo
Person 类不存在 drink 方法,Bird 类存在
@implementation Bird
- (void)drink
{
NSLog(@"一只鸟儿在喝水");
}
@end
Person *person = [[Person alloc] init];
[person drink];方法1
@implementation Person
- (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector
{
if (aSelector == @selector(drink)) {
return [[Bird alloc] init];
}
return [super forwardingTargetForSelector:aSelector];
}
@end方法2
- (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector
{
if (aSelector == @selector(drink)) {
return nil;
}
return [super forwardingTargetForSelector:aSelector];
}
- (NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector
{
NSMethodSignature *signature = [NSMethodSignature signatureWithObjCTypes:"v16@0:8"];
return signature;
}
- (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation
{
[anInvocation invokeWithTarget:[[Bird alloc] init]];
}注意:methodSignatureForSelector 如果返回 nil,则 forwardInvocation 不会执行
给 Person 类方法进行消息转发处理
方法1
+ (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector
{
if (aSelector == @selector(drink)) {
return [Bird class];
}
return [super forwardingTargetForSelector:aSelector];
}方法2
+ (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector
{
if (aSelector == @selector(drink)) {
return nil;
}
return [super forwardingTargetForSelector:aSelector];
}
+ (NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector
{
if (aSelector == @selector(drink)) {
return [[Bird class] methodSignatureForSelector:@selector(drink)];
}
return [super methodSignatureForSelector:aSelector];
}
+ (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation
{
[anInvocation invokeWithTarget:[Bird class]];
}方法签名的获取
方法1: 自己根据方法的返回值类型,方法2个基础参数参数:id self、SEL _cdm,其他参数类型按照 Encoding 自己拼。 类似 v16@0:8
方法2 :根据某个类的对象,去调用 methodSignatureForSelector 方法获取。
[[[Bird alloc] init] methodSignatureForSelector:**@selector**(drink)];
- (NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector
{
if (aSelector == @selector(drink)) {
return [[[Bird alloc] init] methodSignatureForSelector:@selector(drink)];
}
return [super methodSignatureForSelector:aSelector];
}Super 原理
@implementation Person
@end
@implementation Student
- (instancetype)init
{
if (self = [super init]) {
NSLog(@"%@", [self class]); // Student
NSLog(@"%@", [self superclass]); // Person
NSLog(@"%@", [super class]); // Student
NSLog(@"%@", [super superclass]); // Person
}
return self;
}
@end后面2个的打印似乎不符合预期?转成 c++ 代码看看
static instancetype _I_Student_init(Student * self, SEL _cmd) {
if (self = ((Student *(*)(__rw_objc_super *, SEL))(void *)objc_msgSendSuper)((__rw_objc_super){(id)self, (id)class_getSuperclass(objc_getClass("Student"))}, sel_registerName("init"))) {
NSLog((NSString *)&__NSConstantStringImpl__var_folders_z5_ksvb7q252lbdfg78236t7tt00000gn_T_Student_91af5b_mi_0, ((Class (*)(id, SEL))(void *)objc_msgSend)((id)self, sel_registerName("class")));
NSLog((NSString *)&__NSConstantStringImpl__var_folders_z5_ksvb7q252lbdfg78236t7tt00000gn_T_Student_91af5b_mi_1, ((Class (*)(id, SEL))(void *)objc_msgSend)((id)self, sel_registerName("superclass")));
NSLog((NSString *)&__NSConstantStringImpl__var_folders_z5_ksvb7q252lbdfg78236t7tt00000gn_T_Student_91af5b_mi_2, ((Class (*)(__rw_objc_super *, SEL))(void *)objc_msgSendSuper)((__rw_objc_super){(id)self, (id)class_getSuperclass(objc_getClass("Student"))}, sel_registerName("class")));
NSLog((NSString *)&__NSConstantStringImpl__var_folders_z5_ksvb7q252lbdfg78236t7tt00000gn_T_Student_91af5b_mi_3, ((Class (*)(__rw_objc_super *, SEL))(void *)objc_msgSendSuper)((__rw_objc_super){(id)self, (id)class_getSuperclass(objc_getClass("Student"))}, sel_registerName("superclass")));
}
return self;
}[super class] 这句代码底层实现为 objc_msgSendSuper((__rw_objc_super){self, class_getSuperclass(objc_getClass("Student"))}, sel_registerName("class"));
__rw_objc_super 是什么?
struct objc_super {
__unsafe_unretained _Nonnull id receiver;
__unsafe_unretained _Nonnull Class super_class;
};objc_msgSendSuper 如下
/**
* Sends a message with a simple return value to the superclass of an instance of a class.
*
* @param super A pointer to an \c objc_super data structure. Pass values identifying the
* context the message was sent to, including the instance of the class that is to receive the
* message and the superclass at which to start searching for the method implementation.
* @param op A pointer of type SEL. Pass the selector of the method that will handle the message.
* @param ...
* A variable argument list containing the arguments to the method.
*
* @return The return value of the method identified by \e op.
*
* @see objc_msgSend
*/
objc_msgSendSuper(struct objc_super * _Nonnull super, SEL _Nonnull op, ...)所以 objc_msgSendSuper((__rw_objc_super){self, class_getSuperclass(objc_getClass("Student"))}, sel_registerName("class")); 等同于下面代码
struct objc_super arg = {self, class_getSuperclass(self)};
objc_msgSendSuper(arg, sel_registerName("class"))[super class] super 调用的 receiver 还是 self
结构体的目的是为了在类对象查找的过程中,直接从当前类的父类中查找,而不是本类(比如 Student 类的 [super init] 会直接从 Person 的类对象中查找 init,找不到则通过 superclass 向上查找)
大致推测系统的 class、superclass 方法实现如下
@implementation Person
- (Class)class{
return object_getClass(self);
}
- (Class)superclass {
return class_getSuperclass(object_getClass(self));
}
@endclass 方法是在 NSObject 类对象的方法列表中的。所以
[self class] 等价于 objc_msgSend(self, sel_registerName("class"))
[super class] 等价于 objc_msgSendSuper({self, class_getSuperclass(self)}, sel_registerName("class"))
其实2个方法本质上消息 receiver 都是 self,也就是当前的 Student,所以打印都是 Student
结论:[super message] 有2个特征
- super 消息的调用者还是 self
- 方法查找是根据当前 self 的父类开始查找
通过将代码转为 c++ 发现,super 调用本质就是 objc_msgSendSuper,实际不然
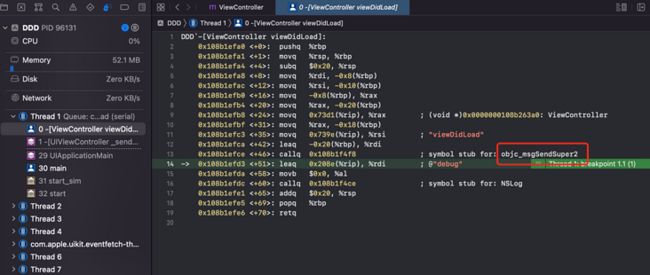
我们对 iOS 项目[super viewDidLoad] 下符号断点,发现objc_msgSendSuper2
查看 objc4 源代码发现是一段汇编实现。
ENTRY _objc_msgSendSuper2
UNWIND _objc_msgSendSuper2, NoFrame
MESSENGER_START
ldp x0, x16, [x0] // x0 = real receiver, x16 = class
ldr x16, [x16, #SUPERCLASS] // x16 = class->superclass
CacheLookup NORMAL
END_ENTRY _objc_msgSendSuper2所以 super viewDidLoad本质上就是
struct objc_super arg = {
self,
[UIViewController class]
};
objc_msgSendSuper2(arg, sel_registerName("viewDidLoad"));objc_msgSendSuper2 和 objc_msgSendSuper 区别在于第二个参数
objc_msgSendSuper2 底层源码(汇编代码 objc-msg-arm64.s 422 行)会将第二个参数找到父类,然后进行方法缓存查找
objc_msgSendSuper 直接从第二个参数查找方法。
总结:clang 转 c++ 可以窥探系统实现,可以作为研究参考。super 本质上就是 objc_msgSendSuper2,传递2个参数,第一个参数为结构体,第二个参数是sel。
为什么转为 c++ 和真正实现不一样?思考下
源代码变为机器码之前,会经过 LLVM 编译器转换为中间代码(Intermediate Representation),最后转为汇编、机器码
我们来验证下 super 在中间码上是什么
clang -emit-llvm -S Student.mllvm 中间码如下,可以看到确实内部是 objc_msgSendSuper2
; Function Attrs: noinline optnone ssp uwtable
define internal void @"\01-[Student sayHi]"(%0* %0, i8* %1) #1 {
%3 = alloca %0*, align 8
%4 = alloca i8*, align 8
%5 = alloca %struct._objc_super, align 8
store %0* %0, %0** %3, align 8
store i8* %1, i8** %4, align 8
%6 = load %0*, %0** %3, align 8
%7 = bitcast %0* %6 to i8*
%8 = getelementptr inbounds %struct._objc_super, %struct._objc_super* %5, i32 0, i32 0
store i8* %7, i8** %8, align 8
%9 = load %struct._class_t*, %struct._class_t** @"OBJC_CLASSLIST_SUP_REFS_$_", align 8
%10 = bitcast %struct._class_t* %9 to i8*
%11 = getelementptr inbounds %struct._objc_super, %struct._objc_super* %5, i32 0, i32 1
store i8* %10, i8** %11, align 8
%12 = load i8*, i8** @OBJC_SELECTOR_REFERENCES_.6, align 8, !invariant.load !12
call void bitcast (i8* (%struct._objc_super*, i8*, ...)* @objc_msgSendSuper2 to void (%struct._objc_super*, i8*)*)(%struct._objc_super* %5, i8* %12)
notail call void (i8*, ...) @NSLog(i8* bitcast (%struct.__NSConstantString_tag* @_unnamed_cfstring_.8 to i8*))
ret void
}指令介绍
@ - 全局变量
% - 局部变量
alloca - 在当前执行的函数的堆栈帧中分配内存,当该函数返回到其调用者时,将自动释放内存
i32 - 32位4字节的整数
align - 对齐
load - 读出,store 写入
icmp - 两个整数值比较,返回布尔值
br - 选择分支,根据条件来转向label,不根据条件跳转的话类似 goto
label - 代码标签
call - 调用函数isKindOfClass、isMemberOfClass
Demo
Student *student = [[Student alloc] init];
NSLog(@"%hhd", [student isMemberOfClass:[Student class]]); // 1
NSLog(@"%hhd", [student isKindOfClass:[Person class]]); // 1
NSLog(@"%hhd", [Student isMemberOfClass:[Student class]]); // 0
NSLog(@"%hhd", [Student isKindOfClass:[Student class]]); // 0有些人答对了,有些人错了。
上面2个判断都是调用对象方法的 isMemberOfClass 、isKindOfClass
由于 objc4 是开源的,查看 object.mm
- (BOOL)isKindOfClass:(Class)cls {
for (Class tcls = [self class]; tcls; tcls = tcls->superclass) {
if (tcls == cls) return YES;
}
return NO;
}
- (BOOL)isMemberOfClass:(Class)cls {
return [self class] == cls;
}isMemberOfClass 判断当前对象是不是传递进来的对象
isKindOfClass 内部是一个 for 循环,第一次循环先拿当前类的类对象,判断是不是和传递进来的对象一样,一样则 return YES,否则先给 tlcs 赋值当前类的父类,然后走第二次判断,直到 cls 不存在位置(NSObject 的父类为 nil)。所以 isKindOfClass 其实判断的是当前类是传递进来的类,或者传递进来类的子类
下面面2个判断都是调用类方法的 isMemberOfClass 、isKindOfClass
+ (BOOL)isMemberOfClass:(Class)cls {
return object_getClass((id)self) == cls;
}
+ (BOOL)isKindOfClass:(Class)cls {
for (Class tcls = object_getClass((id)self); tcls; tcls = tcls->superclass) {
if (tcls == cls) return YES;
}
return NO;
}可以看到 +(BOOL)isMemberOfClass:(Class)cls 方法内部就是对当前类获取类对象,然后与传递进来的 cls 判断是否相等。由于是 [Student isMemberOfClass:[Student class]]) Student 类调用类方法 +isMemberOfClass 所以类对象的类对象也就是元类对象,cls 参数也就是 [Student class] 是一个类对象,元类对象等于类对象吗?显然不是
想让判断成立,可以改为 [Student isMemberOfClass:object_getClass([Student class])] 或者 [[Student **class**] isMemberOfClass:object_getClass([Student class])]
+(BOOL)isKindOfClass:(Class)cls 同理分析。作用是当前类的元类,是否是右边传入对象的元类或者元类的子类。
来个特殊 case
NSLog(@"%hhd", [[Student class] isKindOfClass:[NSObject class]]); // NO输出 1。为什么?
看坐右边的部分,调用 isKindOfClass 方法,本质上就是 Student 类的类对象,也就是 Student 元类,和传入的右边 [NSObject class]判断是否想通过
第一次 for 循环当然不同,所以不能 return,会将 tcls 走步长改变逻辑 tcls = tcls->superclass,也就是找到当前 Student 元类对象的父类。
第二次 for 循环也一样不相等,Person 元类不等于 [NSObject class] 继续向上,直到 tcls = NSObject。此时还是不等,这时候 tcls 走步长改变逻辑,tcls = tcls->superclass NSObject 元类的 superclass 还是 NSObject。所以 for 循环内部的判断编委 [NSObject class] == [NSObject class],return YES。
tips:基类的元类对象指向基类的类对象。
+ (BOOL)isKindOfClass:(Class)cls {
for (Class tcls = object_getClass((id)self); tcls; tcls = tcls->superclass) {
if (tcls == cls) return YES;
}
return NO;
}Quiz
NSLog(@"%hhd", [NSObject isKindOfClass:[NSObject class]]); // 1
NSLog(@"%hhd", [NSObject isMemberOfClass:[NSObject class]]); //0
NSLog(@"%hhd", [Person isKindOfClass:[Person class]]); // 0
NSLog(@"%hhd", [Person isMemberOfClass:[Person class]]); //0Runtime 刁钻题
@interface Person : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *name;
- (void)sayHi;
@end
@implementation Person
- (void)sayHi{
NSLog(@"hi,my name is %@", self->_name); // hi,my name is 杭城小刘
}
@end
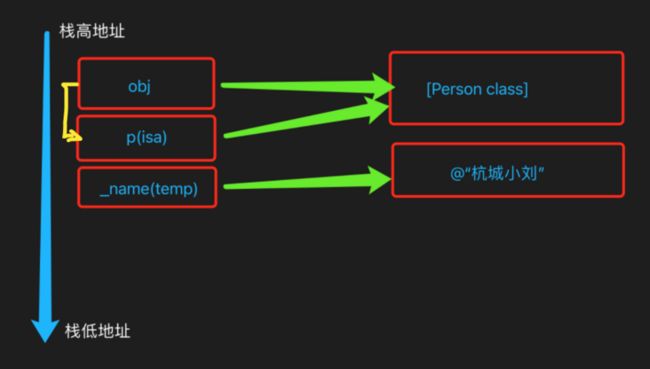
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
NSString *temp = @"杭城小刘";
id obj = [Person class];
void *p = &obj;
[(__bridge id)p sayHi];
test();
}
return 0;
}程序运行什么结果?
hi,my name is 杭城小刘为什么会方法调用成功?为什么 name 打印出为 @"杭城小刘"
我们来分析下:
1.方法调用本质就是寻找 isa 进行消息发送
Person *person = [[Person alloc] init];
[person sayHi];[[Person alloc] init]在内存中分配一块内存,然后 isa 指向这块内存,然后 person 指针,指向结构体,结构体的第一个成员。
2.栈空间数据内存向下生长。第一个变量地址高,其次降低。且每个变量的内存地址是连续的。
这个流程其实和上面的代码一样的。所以可以正常调用
void test () {
long long a = 4; // 0x7ff7bfeff2d8
long long b = 5; // 0x7ff7bfeff2d0
long long c = 6; // 0x7ff7bfeff2c8
NSLog(@"%p %p %p", &a, &b, &c);
}方法内的变量存储在栈上,堆向上增长,栈向下增长。
3.实例对象的本质就是一个结构体,存储所有成员变量(isa 是一个特殊成员变量,其他的成员变量,这里就是 _name),sayHi 方法内部的 self 就是 obj,找成员变量的本质就是找内存地址的过程(此时就是偏移8个字节)
上面代码可以类比类调用方法的流程。 obj 指针指向 Person 这块内存,给类对象发送 sayHi 消息也就是通过 obj 指针找到 isa,恰好 obj 指针指向的地址就是类对象的类结构体的地址,结构体成员变量第一个就是 isa 指针,结构体的其他成员变量就是类的其他属性,这里也就是 _name,所以我们给自定义的指针 void *p 调用 sayHi 方法,系统 runtime 在打印 name 的时候,会在 p 附近(下8个字节,因为 isa 是指针,长度为8)找 _name 属性,此时也就找到了 temp 字符串。
struct Person_IMPL {
Class isa; // 8字节
NSString *_name; // 8字节
}再看一个变体1
NSObject *temp = [[NSObject alloc] init];
id obj = [Person class];
void *p = &obj;
[(__bridge id)p sayHi];
// hi,my name is 再看一个变体2(将代码放在 ViewController中)
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
id obj = [Person class];
void *p = &class;
NSObject *temp = [[NSObject alloc] init];
[(__bridge id)p sayHi];
}
// hi,my name is 搞懂的小伙伴不迷惑了。没搞懂其实就是没搞懂栈地址由高到低,向下生长 和 super 调用的本质。
再强调一句,根据指针寻找成员变量 _name 的过程其实就是根据内存偏移找对象的过程。在变体2中,isa 地址就是 class 的地址,所以按照地址 +8 的策略,其实前一个局部变量。
[super viewDidLoad]; 本质就是 objc_msgSendSuper({self, class_getSuperclass(self)}, sel_registerName("viewDidLoad"))
struct objc_super arg = {self, class_getSuperclass(self)};
objc_msgSendSuper(arg, sel_registerName("viewDidLoad"));所以此时的“前一个局部变量” 也就是结构体 objc_super 类型的 arg。arg 是一个结构体,结构体第一个成员变量就是 self,所以“前一个局部变量” 也就是 self(ViewController)
应用场景
1.统计 App 中未响应的方法。给 NSObject 添加分类
- (NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector
{
// 本来能调用的方法
if ([self respondsToSelector:aSelector]) {
return [super methodSignatureForSelector:aSelector];
}
// 找不到的方法
return [NSMethodSignature signatureWithObjCTypes:"v@:"];
}
// 找不到的方法,都会来到这里
- (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation
{
NSLog(@"找不到%@方法", NSStringFromSelector(anInvocation.selector));
}
@end2.修改类的 isa
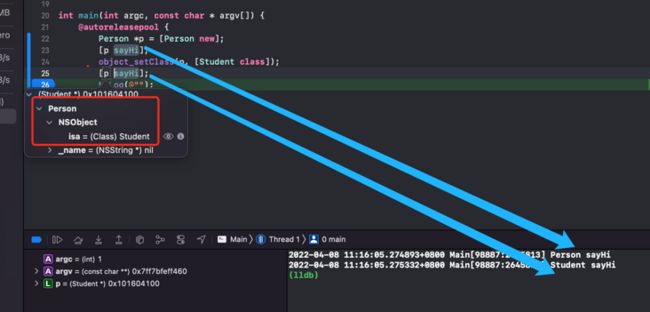
object_setClass 实现
Person *p = [Person new];
object_setClass(p, [Student class]);3.动态创建类
objc_allocateClassPair、objc_registerClassPair 成对存在
动态创建类、添加属性、方法
void study (id self, SEL _cmd) {
NSLog(@"在学习了");
}
void createClass (void) {
Class newClass = objc_allocateClassPair([NSObject class], "GoodStudent", 0);
class_addIvar(newClass, "_score", 4, 1, "i");
class_addIvar(newClass, "_height", 4, 1, "i");
class_addMethod(newClass, @selector(study), (IMP)study, "v16@0:8");
objc_registerClassPair(newClass);
id student = [[newClass alloc] init];
[student setValue:@100 forKey:@"_score"];
[student setValue:@177 forKey:@"_height"];
[student performSelector:@selector(study)];
NSLog(@"%@ %@", [student valueForKey:@"_score"], [student valueForKey:@"_height"]);
}runtime 中 copy、create 等出来的内存,不使用的时候需要手动释放objc_disposeClassPair(newClass>)
4.访问成员变量信息
void ivarInfo (void) {
Ivar nameIvar = class_getInstanceVariable([Person class], "_name");
NSLog(@"%s %s", ivar_getName(nameIvar), ivar_getTypeEncoding(nameIvar)); //_name @"NSString"
// 设置、获取成员变量
Person *p = [[Person alloc] init];
Ivar ageIvar = class_getInstanceVariable([Person class], "_age");
object_setIvar(p, ageIvar, (__bridge id)(void *)27);
NSLog(@"%d", p.age);
}runtime 设置值 api object_setIvar(id _Nullable obj, Ivar _Nonnull ivar, id _Nullable value) 第三个参数要求为 id 类型,但是我们给 int 类型的属性设置值,怎么办?可以将27这个数字的地址传进去,同时需要类型转换为 id (__bridge id)(void *)27)
KVC 可以根据具体的值,去取出 NSNumber ,然后调用 intValue
[p setValue:@27 forKey:@"_age"];
5.访问对象的所有成员变量信息
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *name;
@property (nonatomic, assign) int age;
@end
unsigned int count;
// 数组指针
Ivar *properties = class_copyIvarList([Person class], &count);
for (int i =0 ; i根据这个可以做很多事情,比如设置解模型、给 UITextField 设 placeholder 的颜色
先根据 class_copyIvarList 访问到 UITextFiled 有很多属性,然后找到可疑累_placeholderLabel,通过打印 class、superclass 得到类型为 UILabel。所以用 UILabel 对象设置 color 即可,要么通过 KVC 直接设置
[self.textFiled setValue:[UIColor redColor] forKeyPath:@"_placeholderLabel.textColor"];或者设置字典转模型(不够健壮,随便写的。具体可以参考 YYModel)
+ (instancetype)lbp_modelWithDic:(NSDictionary *)dict
{
id obj = [[self alloc] init];
unsigned int count;
Ivar *properties = class_copyIvarList([self class], &count);
for (int i =0 ; i6.替换方法实现
注意
- 类似 NSMutableArray 的时候,+load 方法进行方法替换的时候需要注意类簇的存在,比如
__NSArrayM - 方法交换一般写在类的
+load方法中,且为了防止出问题,比如别人手动调用 load,代码需要加dispatch_once
void studentSayHi (void) {
NSLog(@"Student say hi");
}
void changeMethodImpl (void){
class_replaceMethod([Person class], @selector(sayHi), (IMP)studentSayHi, "v16@0:8");
Person *p = [[Person alloc] init];
[p sayHi];
}
// Student say hi上述代码可以换一种写法
class_replaceMethod([Person class], @selector(sayHi), imp_implementationWithBlock(^{
NSLog(@"Student say hi");
}), "v16@0:8");
Person *p = [[Person alloc] init];
[p sayHi];imp_implementationWithBlock(id _Nonnull block) 该方法将方法实现替换为包装好的 block
Person *p = [[Person alloc] init];
Method sleep = class_getInstanceMethod([Person class], @selector(sleep));
Method sayHi = class_getInstanceMethod([Person class], @selector(sayHi));
method_exchangeImplementations(sleep, sayHi);
[p sayHi]; // 人生无常,抓紧睡觉
[p sleep]; // Person sayHi7.无痕埋点
对 App 内所有的按钮点击事件进行监听并上报。发现 UIButton 继承自 UIControl,所以添加分类,在 load 方法内,替换方法实现。UIControl 存在方法 sendAction:to:forEvent:
@implementation UIControl (Monitor)
+ (void)load {
Method method1 = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(sendAction:to:forEvent:));
Method method2 = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(lbp_sendAction:to:forEvent:));
method_exchangeImplementations(method1, method2);
}
- (void)lbp_sendAction:(SEL)action to:(id)target forEvent:(UIEvent *)event {
NSLog(@"%@-%@-%@", self, target, NSStringFromSelector(action));
// 调用系统原来的实现
[self mj_sendAction:action to:target forEvent:event];
// [target performSelector:action];
}
@end为了对业务代码无影响,在 hook 代码内部又要调用回去,所以需要调用原来的方法,此时因为交换方法实现,所以原来的方法应该是 lbp_sendAction:to:forEvent:
method_exchangeImplementations 方法实现交换了,系统会清空缓存,调用 flushCaches 方法,内部调用 cache_erase_nolock 来清空方法缓存。
void method_exchangeImplementations(Method m1, Method m2)
{
if (!m1 || !m2) return;
rwlock_writer_t lock(runtimeLock);
IMP m1_imp = m1->imp;
m1->imp = m2->imp;
m2->imp = m1_imp;
// RR/AWZ updates are slow because class is unknown
// Cache updates are slow because class is unknown
// fixme build list of classes whose Methods are known externally?
flushCaches(nil);
updateCustomRR_AWZ(nil, m1);
updateCustomRR_AWZ(nil, m2);
}
static void flushCaches(Class cls)
{
runtimeLock.assertWriting();
mutex_locker_t lock(cacheUpdateLock);
if (cls) {
foreach_realized_class_and_subclass(cls, ^(Class c){
cache_erase_nolock(c);
});
}
else {
foreach_realized_class_and_metaclass(^(Class c){
cache_erase_nolock(c);
});
}
}总结:
OC 是一门动态性很强的编程语言,允许很多操作推迟到程序运行时决定。OC 动态性其实就是由 Runtime 来实现的,Runtime 是一套 c 语言 api,封装了很多动态性相关函数。平时写的 oc 代码,底层大多都是转换为 Runtime api 进行调用的。
- 关联对象
- 遍历类的所有成员变量(可以访问私有变量,比如修改 UITextFiled 的 placeholder 颜色、字典转模型、自动归档接档)
- 交换方法实现
- 扩大点击区域
- 利用消息转发机制,解决消息找不到的问题
- 无痕埋点
- 热修复(热修复方案有几大类:内置虚拟机、下发脚本关联到 runtime 修改原始行为、AST 解析处理)
- 安全气垫(使用场景褒贬不一:比如责任边界问题、虽然兜住了 crash,但是问题没有充分暴露。一个优雅的策略是线上兜住 crash,但是同时收集案发数据,走业务异常报警,开发立马去根据数据分析这个问题是业务异常还是什么情况,要不要发布热修,还是后端数据/逻辑错误)