《C++高级编程》读书笔记(一:C++和标准库速成)
1、参考引用
- C++高级编程(第4版,C++17标准)马克·葛瑞格尔
2、建议先看《21天学通C++》 这本书入门,笔记链接如下
- 21天学通C++读书笔记(文章链接汇总)
1. C++ 基础知识
1.1 小程序 “hello world”
// helloworld.cpp
/*
helloworld.cpp
*/
#include -
注释
- 这个程序的前四行分别是单行注释和多行注释,这只是供编程人员阅读的消息,编译器会将其忽略
-
预处理指令
- 生成一个 C++ 程序共有三个步骤:首先,代码在预处理器中运行,预处理器会识别代码中的元信息 (meta-information);其次,代码被编译或转换为计算机可识别的目标文件;最后,独立的目标文件被链接在一起变成一个应用程序。
- #include
为预处理指令,预处理指令以 # 字符开始 - include 指令告诉预处理器:提取
头文件中的所有内容并提供给当前文件 - 头文件最常见的用途是声明在其他地方定义的函数
- 函数声明会通知编译器如何调用这个函数,并声明函数中参数的个数和类型,以及函数的返回类型。而函数定义包含了这个函数的实际代码。在 C++ 中,声明通常放在扩展名为 .h 的文件中,称为头文件,其定义通常包含在扩展名为 .cpp 的文件中,称为源文件
- C 中的标准库头文件在 C++ 中依然存在,但使用以下两个版本
- 不使用 .h 后缀,改用前缀 c,如
,这些版本放在 std 名称空间中 - 使用 .h 后缀,这是旧版本,如
,这些版本不使用名称空间
- 不使用 .h 后缀,改用前缀 c,如
- 下面是使用预处理器指令避免重复包含的一个示例
#ifndef MYHEADER_H #define MYHEADER_H //...the contents of this header filef #endif // 或(上下等价) #pragma once //...the contents of this header filef -
main() 函数
- main() 函数式程序的入口,可以忽略显式的 return 语句
- argc 给出了传递给程序的实参数目,argv 包含了这些实参。注意 argv[0] 可能是程序的名称,也可能是空字符串
-
输入输出流
// std::cout 用于输出信息 // std::cerr 用于输出错误信息 // std::endl 代表序列末尾,换行,表明一行末尾的另一种方法是使用 \n 字符(转义字符) // std::cin 接受键盘输入信息 // 注:printf() 和 scanf() 未提供类型安全,不建议使用
1.2 名称空间
- 名称空间用来处理不同代码段之间的名称冲突问题
// 头文件 namespaces.h namespace mycode { void foo(); }// namespaces.cpp // 名称空间中还可实现方法或函数 #include#include "namespaces.h" void mycode::foo() { std::cout << "foo() called in the mycode namespace" << std::endl; } // usingnamespaces.cpp #include "namespaces.h" using namespace mycode; int main() { mycode::foo(); // 调用 mycode 名称空间中的 foo() 函数 foo(); // 使用 using 后也可隐式调用 return 0; }
切勿在头文件中使用 using 指令或 using 声明,否则添加你的头文件的每个人都必须使用它
- C++17 允许方便地使用嵌套的名称空间,即将一个名称空间放在另一个名称空间中
namespace MyLibraries::Networking::FTP {} - C++17 还可使用名称空间别名,为另一个名称空间指定一个更简短的新名称
namespace MyFTP = MyLibraries::Networking::FTP;
1.3 字面量
- 字面量用于在代码中编写数字或字符串
- 以下字面量指定数字 123
- 十进制字面量 123
- 八进制字面量 0173
- 十六进制字面量 0x7B
- 二进制字面量 0b1111011
- 其他字面量
- 浮点值 (如 3.14f)
- 双精度浮点值 (如 3.14)
- 单个字符 (如 ‘a’)
- 以零结尾的字符数组 (如 "character array”)
- 还可自定义自变量类型
1.4 变量
- 类型转换方法
float myFloat = 3.14f; int i1 = (int)myFloat; // 方法一,目前最常使用,但不建议 int i2 = int(myFloat); // 方法二,很少使用 int i3 = static_cast<int>(myFloat); // 方法三,最建议使用
1.5 运算符
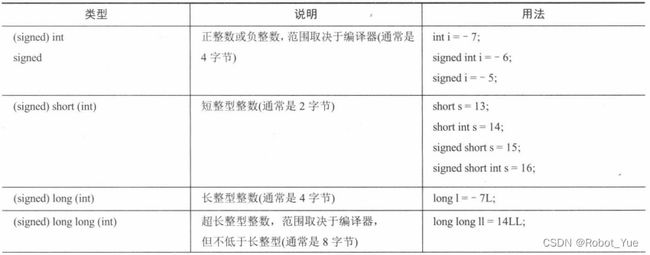
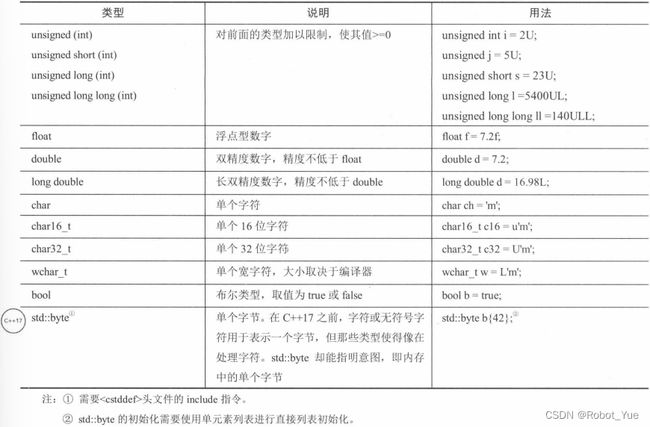
1.6 类型
-
枚举类型
- 枚举类型只是一个整型值,PieceTypeKing 的实际值是 0
- 如果试图对 PieceType 变量执行算术运算或将其作为整数对待,编译器会给出警告或错误信息
enum PieceType { PieceTypeKing, PieceTypeQueen, PieceTypeRook, PieceTypePawn }; -
还可为枚举成员指定整型值
- PieceTypeKing 具有整型值 1,编译器为 PieceTypeQueen 赋予整型值 2,PieceTypeRook 的值为 10,编译器自动为 PieceTypePawn 赋予值 11
enum PieceType { PieceTypeKing = 1, PieceTypeQueen, PieceTypeRook = 10, PieceTypePawn }; -
强类型枚举
- 上面给出的枚举并不是强类型的,这意味着其并非类型安全的。它们总被解释为整型数据,因此可以比较完全不同的枚举类型中的枚举值,强类型的 enum class 枚举解决了这些问题
enum class PieceType { King = 1, Queen, Rook = 10, Pawn }- 对于 enum class,枚举值名不会自动超出封闭的作用域,这表示总要使用作用域解析操作符
PieceType piece = PieceType::King;- 默认情况下,枚举值的基本类型是整型,但可采用以下方式加以改变
enum class PieceType : unsigned long { King = 1, Queen, Rook = 10, Pawn }建议用类型安全的 enum class 枚举替代类型不安全的 enum 枚举
-
结构
- 结构 (struct) 允许将一个或多个已有类型封装到一个新类型中
// employeestruct.h #pragma once struct Employee { char firstInitial; char lastInitial; int employeeNumber; int salary; };// structtest.cpp #include#include "employeestruct.h" using namespace std; int main() { // Create and populate an employee. Employee anEmployee; anEmployee.firstInitial = 'M'; anEmployee.lastInitial = 'G'; anEmployee.employeeNumber = 42; anEmployee.salary = 80000; // Output the values of an employee. cout << "Employee: " << anEmployee.firstInitial << anEmployee.lastInitial << endl; cout << "Number: " << anEmployee.employeeNumber << endl; cout << "Salary: $" << anEmployee.salary << endl; return 0; }
1.7 条件语句
-
if/else 语句
- if 语句的圆括号中的表达式必须是一个布尔值,或者求值的结果必须是布尔值
- 0 为 false,非 0 为 true
if (i > 4) { // Do something. } else if { // Do something else. } else { // Do something else. } -
C++17 允许在 if 语中包括一个初始化器
if (<initializer> ; <conditional expression>) ( <body> } // 示例:初始化器获得一名雇员,以及检查所检索雇员的薪水是否超出 1000 的条件 // 只有满足条件才执行 if 语句体 if (Employee employee = GetEmployee(); employee.salary > 1000) { ... } -
switch 语句
- switch 语句的表达式必须是整型、能转换为整型的类型、枚举类型或强类型枚举,必须与一个常量进行比较,每个常量值代表一种 “情况(case)”,如果表达式与这种情况匹配,随后的代码行将会被执行,直至遇到 break 语句为止
- 此外还可提供 default 情况,如果没有其他情况与表达式值匹配,表达式值将与 default 情况匹配
switch(menuItem) { case OpenMenuItem: // Code to open a file break; case SaveMenuItem: // Code to save a file break; default: // Code to give an error message break; }- 与 if 语句一样,C++17 支持在 switch 语句中使用初始化器
switch (<initializer>; <expression>) {<body>} -
条件运算符
- 也称三目运算符,因为它使用三个操作数
// i 大于 2 吗?如果是真的,结果就是 yes,否则结果就是 no std::cout << ((i > 2) ? "yes" : "no");
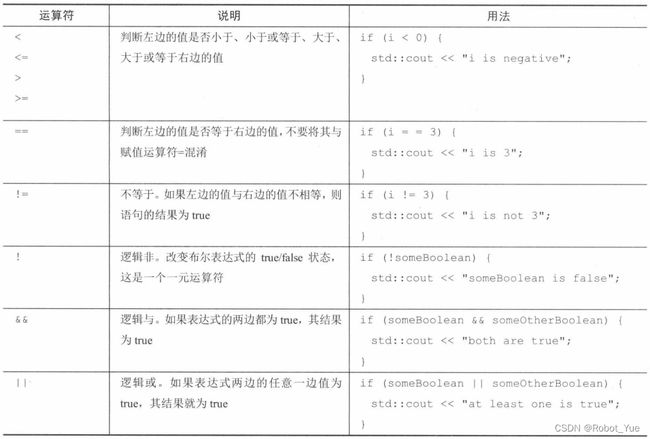
1.8 逻辑比较运算符
1.9 函数
- 在 C++ 中,为让其他代码使用某个函数,首先应该声明该函数
- 如果函数在某个特定的文件内部使用,通常会在源文件中声明并定义这个函数
- 如果函数是供其他模块或文件使用的,通常会在头文件中声明函数,并在源文件中定义函数
// 函数声明 void myFunction(int i, char c); // 函数定义 void myFunction(int i, char c) { std::cout << "the value of i is" << i << std::endl; std::cout << "the value of c is" << c << std::endl; } // 函数调用 myFunction(8,a'); - 函数返回类型的推断
- 要使用这个功能,需要把 auto 指定为返回类型,编译器根据 return 语句使用的表达式推断返回类型
auto addNumbers(int number1, int number2) { return number1 + number2; } - 当前函数的名称
- 每个函数都有一个预定义的局部变量 _func_,其中包含当前函数的名称。这个变量的一个用途是用于日志记录
int addNumbers(int number1, int number2) { std::cout << "Entering function " << _func_ << std::endl; return number1 + number2; }
1.10 C 风格的数组
- C++ 中应尽量避免使用 C 风格的数组,而改用 STL 中的 std::array 和 std::vector
int myArray[3]; myArray[0]; myArray[1]; myArray[2]; int myArray[3] = {0}; int myArray[3] = {}; int myArray[] = {1, 2, 3, 4}; char ticTacToeBoard[3][3]; ticTacToeBoard[1][1] = 'o';
1.11 std::array
- C++ 有一种大小固定的特殊容器 std::array,这种容器在
头文件中定义,用 std:array 替代 C 风格的数组会带来很多好处,如下所示 - 它总是知道自身大小
- 不会自动转换为指针,从而避免了某些类型的 bug
- 具有迭代器,可方便地遍历元素
array<int, 3> arr = {9, 8, 7}; cout << "Array size = " << arr.size() << endl; cout << "2nd element = " << arr[1] << endl;
1.12 std::vector
- 如果希望数组的大小是动态的,推荐使用 std:vector。在 vector 中添加新元素时,vector 会自动增加其大小
#include// 包含头文件 vector<int> myVector = {11, 22}; myVector.push_back(33); // 向 vector 中动态添加元素 myVector.push_back(44); cout << "1st element: " << myVector[0] << endl;
1.13 结构化绑定
- C++17 引入了结构化绑定 (structured bindings) 的概念,允许声明多个变量,这些变量使用数组、结构、pair 或元组中的元素来初始化。例如,假设有下面的数组
std::array<int, 3> values = {11,22,33}; - 可声明三个变量 x、y 和 z,使用其后数组中的三个值进行初始化。注意,必须为结构化绑定使用 auto 关键字
auto [x, y, z] = values; - 使用结构化绑定声明的变量数量必须与右侧表达式中的值数量匹配
1.14 循环
-
while 循环
- 只要条件表达式的求值结果为 true,while 循环就会重复执行一个代码块
int i = 0; while (i < 5) { std::cout << "This is silly." << std::endl; ++i; } -
do/while 循环
- 会首先执行一次代码,而判断是否继续执行的条件检测被放在结尾处。如果想让代码块至少执行一次,并且根据某一条件确定是否多次执行,就可以使用这个循环版本。下面的代码尽管条件为 false,但仍会输出一次
int i = 100; do { std::cout << "This is silly." << std::endl; ++i; } while (i < 5); -
for 循环
- for 循环的语法一般更简便,因为可看到循环的初始表达式、结束条件以及每次迭代结束后执行的语句
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) { std::cout << "This is silly." << std::endl; } -
基于区间的 for 循环
- 这种循环允许方便地迭代容器中的元素,可用于 C 风格的数组、初始化列表,也可用于具有返回迭代器的 begin() 和 end() 函数的类型:例如 std::array、std::vector
std::array<int, 4> arr = {1, 2, 3, 4}; for (int i : arr) { std::cout << i << std::endl; }
1.15 初始化列表
- 初始化列表在
头文件中定义,利用初始化列表,可轻松地编写能接收可变数量参数的函数 - initializer list 类是一个模板,要求在尖括号之间指定列表中的元素类型,这类似于指定 vector 中存储的对象类型
#include#include using namespace std; int makeSum(initializer_list<int> lst) { int total = 0; for (int value : lst) { total += value; } return total; } int main() { int a = makeSum({1, 2, 3}); int b = makeSum({10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60}); cout << a << endl; cout << b << endl; return 0; }
2. 深入研究 C++
2.1 C++ 中的字符串
- 在 C++ 中使用字符串有三种方法
- 一种是 C 风格,将字符看成字符数组
- 一种是 C++ 风格,将字符串封装到一种易于使用的 string 类型中
- 还有一种是非标准的普通类(第 2 章介绍)
#includestring myString = "Hello, World"; cout << "The value of myString is " << myString << endl; cout << "The second letter is " << myString[1] << endl;
2.2 指针和动态内存
- 动态内存允许所创建的程序具有在编译时大小可变的数据,大多数复杂程序都会以某种方式使用动态内存
2.2.1 堆栈和堆
C++ 程序中的内存分为两个部分:堆栈和堆
-
堆栈(和栈是一个意思)
- 堆栈就像一副扑克牌,当前顶部的牌代表程序当前的作用域,通常是当前正在执行的函数。当前函数中声明的所有变量将占用顶部堆栈帧 (也就是最上面的那张牌) 的内存。如果当前函数 foo() 调用了另一个函数 bar(),就会翻开一张新牌,这样 bar() 就会拥有自己的堆栈帧供其运行
- 任何从 foo() 传递给 bar() 的参数都会从 foo() 堆栈帧复制到 bar 堆栈帧
- 堆栈帧为每个函数提供了独立的内存空间。如果在 foo() 堆栈中声明了一个变量,那么除非专门要求,否则调用 bar() 函数不会更改该变量
- foo() 函数执行完毕时,堆栈就会消失,该函数中声明的所有变量都不会再占用内存
- 在堆栈上分配内存的变量不需要程序员手动释放内存(删除),这个过程是自动完成的
-
堆栈帧
- 堆栈帧指的是在堆栈中为当前正在运行的函数分配的区域(或空间)。传入的参数、返回地址(当这个函数结束后必须跳转到该返回地址)以及函数所用的内存单元(即函数存储在堆栈上的局部变量)都在堆栈帧中
- 堆栈帧通常是在新的函数调用的时候创建,并在函数返回的时候销毁。说白了,堆栈由堆栈帧组成. 当调用函数时堆栈帧被压入栈中, 当函数返回时堆栈帧被从栈中弹出
-
堆
- 堆是与当前函数或堆栈帧完全没有关系的内存区域。如果想在函数调用结束之后仍然保存其中声明的变量,可以将变量放到堆中
- 堆的结构不如堆栈复杂,可以将堆当作一堆位,程序可在任何时候向堆中添加新位或修改堆中已有的位
- 必须确保释放 (删除) 在堆上分配的任何内存,这个过程不会自动完成,除非使用了智能指针
2.2.2 使用指针
- 明确地分配内存,就可在堆上放置任何内容。例如,要在堆上放置一个整数,需要给它分配内存,但首先需要声明一个指针
- 指针只是指向一个整数值的地址。为访问这个值,需要对指针解除引用
- 可将解除引用看成沿着指针箭头的方向寻找堆中实际的值
- 在解除引用之前指针必须有效。对 null 或未初始化的指针解除引用会导致不可确定的行为
// 应避免使用未初始化的变量/指针 int *myIntegerPointer = new int; // 使用 new 操作符分配内存 int *myIntegerPointer = nullptr; // 如果不希望立即分配内存,可以把它们初始化为空指针 - 给堆中新分配的整数赋值
*myIntegerPointer = 8; // 没改变指针,只是改变指针指向的内存 - 使用完动态分配的内存后,需要使用 delete 操作符释放内存。为防止在释放指针指向的内存后再使用指针,建议把指针设置为 nullptr
delete myIntegerPointer; myIntegerPointer = nullptr; - 指针并非总是指向堆内存,可声明一个指向堆栈中变量甚至指向其他指针的指针
- 为让指针指向某个变量,需要使用 “取址” 运算符 &
int i = 8; int *myIntegerPointer = &i; - 如果指针指向某个结构,可以首先用 * 对指针解除引用,然后使用普通的 . 语法访问结构中的字段
Employee *anEmployee = getEmployee(); cout << (*anEmployee).salary << endl; // 同下等价 cout << anEmployee->salary << endl; // -> 运算符允许同时对指针解除引用并访问字段
2.2.3 动态分配的数组
- 堆也可以用于动态分配数组。使用 new[] 操作符可给数组分配内存
- 从下图看出:指针变量仍在堆栈中,但动态创建的数组在堆中
int arraySize = 8; int *myVariableSizedArray = new int[arraySize];
- 现在已经分配了内存,可将 myVariableSizedArray 当作基于堆栈的普通数组使用
myVariableSizedArray[3] = 2; // 使用完这个数组后,应该将其从堆中删除,这样其他变量就可以使用这块内存 delete[] myVariableSizedArray; myVariableSizedArray = nullptr;
避免使用 C 中的 malloc() 和 free(),而使用 new 和 delete,或者使用 new[] 和 delete[]
2.2.4 空指针变量
void func(char* str) {cout << "char* version" << endl;}
void func(int i) {cout <<"int version" << endl;}
int main() {
func(NULL); // NULL 不是指针,而等价于 0,所以调用整数版本
func(nullptr); // 真正的空指针常量 nullptr,调用 char* 版本
return 0;
}
2.2.5 智能指针
-
智能指针对象在超出作用域时,例如在函数执行完毕后,会自动释放内存。C++ 中有两种最重要的智能指针
-
std::unique_ptr
- 类似于普通指针,但在超出作用域或被删除时,会自动释放内存或资源
- unique_ptr 只属于它指向的对象
- 优点:内存和资源始终被释放(即使执行返回语句或抛出异常时)
- 创建 unique_ptr
/* unique_ptr 是一个通用的智能指针,它可以指向任意类型的内存 所以它是一个模板,而模板需要用尖括号指定模板参数 在尖括号中必须指定 unique_ptr 要指向的内存类型 make_unique 为 C++14 引入 */ auto anEmployee = make_unique<Employee>(); // 不再需要调用 delete,因为会自动完成 unique_ptr<Employee> anEmployee(new Employee); // C++11 标准- unique_ptr 也可用于存储 C 风格的数组
auto employees = make_unique<Employee[]>(10); cout << "Salary: " << employees[0].salary << endl; -
std::shared_ptr
- shared ptr 允许数据的分布式 “所有权”:每次指定 shared ptr 时,都递增一个引用计数,指出数据又多了位 “拥有者”。shared ptr 超出作用域时,就递减引用计数。当引用计数为 0 时,就表示数据不再有任何拥有者,于是释放指针引用的对象
- 创建 shared_ptr
auto anEmployee = make_shared<Employee>(); if (anEmployee) { cout << "Salary: " << anEmployee->salary << endl; }- 从 C++17 开始,也可将数组存储在 shared_ptr 中
shared_ptr<Employee[]> employees(new Employee[10]); cout << "Salary: " << employees[0].salary << endl;
2.3 const 的多种用法
2.3.1 使用 const 定义常量
- 使用 const 取代 #define 定义常量
const int versionNumberMajor = 2; const int versionNumberMinor = 1; const std::string productName = "Super Hyper Net Modulator";
2.3.2 使用 const 保护参数
void mysteryFunction(const std::string *someString) {
*someString ="Test"; // 不允许修改
}
int main() {
std::string myString = "The string";
mysteryFunction(&myString);
return 0;
}
2.4 引用
- 给类型附加一个& ,则指示相应的变量是引用。在幕后它实际上是一个指向原始变量的指针。变量 x 和引用变量 xReference 指向同一个值。如果通过其中一个更改值,则也可在另个中看到更改
int x = 42; int &xReference = x;
2.4.1 按引用传递
- 通常,给函数传递变量时,传递的是值。如果函数接收整型参数,实际上传入的是整数的一个副本,因此不会修改原始变量的值。C 中通常使用栈变量中的指针,以允许函数修改另一个堆栈帧中的变量
- 在 C++ 中,不是给函数传递指针,而是按引用传递参数
// 不会影响传递给它的变量,因为变量是按照值传递的 // 因此函数接收的是传递给它的值的一个副本 void addOne(int i) { i++; } // 使用了引用,因此可以改变原始变量的值 void addOne(int &i) { i++; }
2.4.2 按 const 引用传递
- 当向函数传递值时,会制作一个完整副本。当传递引用时,实际上只是传递一个指向原始数据的指针,这样就不需要制作副本。通过传递 const 引用,可做到二者兼顾:不需要副本,原始变量也不会修改
void printString(const std::string &myString) { std::cout << myString << std::endl; } int main() { std::string someString = "Hello world!"; printString(someString); printString("Hello World!"); return 0; }
2.5 异常
#include 2.6 类型推断
2.6.1 关键字 auto
- auto 可用于告诉编译器,在编译时自动推断变量的类型
- 但使用 auto 去除了引用和 const 限定符
#include 2.6.2 decltype
- 关键字 decltype 把表达式作为实参,计算出该表达式的类型
// 编译器推断出 y 的类型是 int,因为这是 x 的类型 int x = 123; decltype(x) y = 456; - auto 与 decltype 的区别在于
- decltype 不会去除引用和 const 限定符
- 按如下方式使用 decltype 定义f2,导致 f2 的类型为 const string&,从而不生成副本
decltype(foo()) f2 = foo();
3. 作为面向对象语言的 C++
3.1 定义类
- 在 C++ 中,类通常在头文件(.h)中声明,在对应的源文件(.cpp)中定义其非内联方法和静态数据成员
// AirlineTicket.h
#pragma once
#include - 这个定义首先声明一个类名,在大括号内声明了类的数据成员(属性)以及方法(行为)
- 每个数据成员及方法都有特定的访问级别:public、protected 或 private。这些标记可按任意顺序出现,也可重复使用
- public 成员可在类的外部访问
- private 成员不能在类的外部访问(推荐把所有的数据成员都声明为 private,在需要时,可通过 public 读取器和设置器来访问它们)
3.1.1 构造函数初始化
- 方法一:构造函数初始化器
AirlineTicket::AirlineTicket() : mPassengerName("Unknown Passenger"), mNumberOfMiles(0), mHasEliteSuperRewardsStatus(false) {} - 方法二:将初始化任务放在构造函数体中
AirlineTicket::AirlineTicket() { mPassengerName = "Unknown Passenger"; mNumberOfMiles = 0; mHasEliteSuperRewardsStatus = false; } - 如果构造函数只是初始化数据成员,实际上就没必要使用构造函数,因为可在类定义中直接初始化数据成员。如果类还需要执行其他一些初始化类型,如打开文件、分配内存等,则需要编写构造函数进行处理
private: std::string mPassengerName = "Unknown Passenger"; int mNumberOfMiles = 0; bool mHasEliteSuperRewardsStatus = false;
3.1.2 部分 AirlineTicket 类方法的定义
// AirlineTicket.cpp
#include "AirlineTicket.h"
using namespace std;
AirlineTicket::AirlineTicket() : mPassengerName("Unknown Passenger"),
mNumberOfMiles(0),
mHasEliteSuperRewardsStatus(false) {}
AirlineTicket::~AirlineTicket() {}
double AirlineTicket::calculatePriceInDollars() const {
if (hasEliteSuperRewardsStatus()) {
// Elite Super Rewards customers fly for free!
return 0;
}
return getNumberOfMiles() * 0.1;
}
const string &AirlineTicket::getPassengerName() const {
return mPassengerName;
}
...
3.2 使用类
// AirlineTicketTest.cpp
#include 4. 统一初始化
struct CircleStruct {
int x, y;
double radius;
};
class CircleClass {
public:
CircleClass(int x, int y, double radius)
: mX(x), mY(y), mRadius(radius) {}
private:
int mX, mY;
double mRadius;
};
- C++11 之前,对于结构和类的初始化方式是不同的
CircleStruct myCirclel = {10,10,2.5}; CircleClass myCircle2(10,10,2.5); - C++11 之后,允许一律使用 {…} 语法初始化类型
// 其中 = 号是可选的 CircleStruct myCirclel = {10,10,2.5}; CircleClass myCircle2 = {10,10,2.5}; - 统一初始化还可用来初始化动态分配的数组
int *pArray = new int[4]{0,1,2,3};
- 统一初始化还可在构造函数初始化器中初始化类成员数组
class MyClass {
public:
MyClass() : mArray{0,1,2,3} {}
private:
int mArray[4];
};
- 直接列表初始化与复制列表初始化
- 复制列表初始化:T obj = {arg1, arg2, …};
- 对于复制列表初始化,放在大括号中的初始化器的所有元素都必须使用相同的类型
- 直接列表初始化:T obj {arg1, arg2, …};
- 复制列表初始化:T obj = {arg1, arg2, …};
5. 第一个有用的 C++ 程序
- 建立一个雇员数据库
5.1 雇员记录系统
-
管理公司雇员记录的程序应该灵活并具有有效的功能,这个程序包含的功能有
- 添加雇员
- 解雇雇员
- 雇员晋升
- 查看所有雇员,包括过去以及现在的雇员
- 查看所有当前雇员
- 查看所有以前雇员
-
程序的代码分为三个部分
- Employee 类封装了单个雇员的信息
- Database 类管理公司的所有雇员
- 单独的用户界面提供程序的接口
5.2 Employee 类
- Employee.h
#pragma once // 防止文件被包含多次
#include - Employee.cpp
#include 5.3 Database 类
- Database.h
#pragma
#include - Database.cpp
#include 5.4 用户界面
- UserInterface.cpp
#include