Hbase安装指南
Hbase简介
HBase是一个高可靠性、高性能、面向列、可伸缩的分布式存储系统,利用HBase技术可在廉价PC Server上搭建起大规模结构化存储集群。
HBase是Google Bigtable的开源实现,类似Google Bigtable利用GFS作为其文件存储系统,HBase利用Hadoop HDFS作为其文件存储系统;Google运行MapReduce来处理Bigtable中的海量数据,HBase同样利用Hadoop MapReduce来处理HBase中的海量数据;Google Bigtable利用 Chubby作为协同服务,HBase利用Zookeeper作为对应。
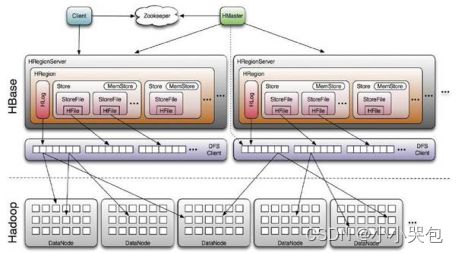
HBase系统架构如图所示
Client
HBase Client使用HBase的RPC机制与HMaster和HRegionServer进行通信,对于管理类操作,Client与HMaster进行RPC;对于数据读写类操作,Client与HRegionServer进行RPC
Zookeeper
Zookeeper Quorum中除了存储了-ROOT-表的地址和HMaster的地址,HRegionServer也会把自己以Ephemeral方式注册到Zookeeper中,使得HMaster可以随时感知到各个HRegionServer的健康状态。此外,Zookeeper也避免了HMaster的单点问题,见下文描述
HMaster
HMaster没有单点问题,HBase中可以启动多个HMaster,通过Zookeeper的Master Election机制保证总有一个Master运行,HMaster在功能上主要负责Table和Region的管理工作:
1. 管理用户对Table的增、删、改、查操作
2. 管理HRegionServer的负载均衡,调整Region分布
3. 在Region Split后,负责新Region的分配
4. 在HRegionServer停机后,负责失效HRegionServer 上的Regions迁移
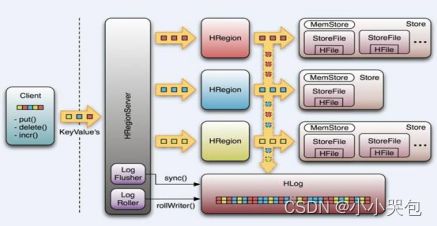
HRegionServer
HRegionServer主要负责响应用户I/O请求,向HDFS文件系统中读写数据,是HBase中最核心的模块。
HRegionServer内部管理了一系列HRegion对象,每个HRegion对应了Table中的一个Region,HRegion中由多个HStore组成。每个HStore对应了Table中的一个Column Family的存储,可以看出每个Column Family其实就是一个集中的存储单元,因此最好将具备共同IO特性的column放在一个Column Family中,这样最高效。
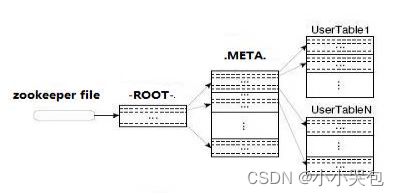
-ROOT- && .META. Table
HBase中有两张特殊的Table,-ROOT-和.META.
Ø .META.:记录了用户表的Region信息,.META.可以有多个regoin
Ø -ROOT-:记录了.META.表的Region信息,-ROOT-只有一个region
Ø Zookeeper中记录了-ROOT-表的location
Client访问用户数据之前需要首先访问zookeeper,然后访问-ROOT-表,接着访问.META.表,最后才能找到用户数据的位置去访问,中间需要多次网络操作,不过client端会做cache缓存。
Hbase的安装:
集群环境:
192.168.11.12 作为hbase主master
192.168.11.14 作为hbase备用master
192.168.11.16作为zookeeperNode/HRegionsever
192.168.11.18作为zookeeperNode/HRegionsever
192.168.11.20作为zookeeperNode/HRegionsever
192.168.11.12——192.168.11.20是hdfs的datanode
Hdfs的namenode为192.168.11.8 主机名为hadoopNN00
软件版本:
Hadoop-0.20.1-dev
Hbase-0.90.3
Hbase的安装是基于hdfs的,Hbase的配置主要涉及conf目录下的三个文件:hbase-env.sh,hbase-site.xml,regionserver。
Hbase-env.sh配置如下:
#必须配置的项目如下:
export JAVA_HOME=/root/jdk1.6.0_25
export HBASE_OPTS="-ea -XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC -XX:+CMSIncrementalMode"
export HBASE_MANAGES_ZK=true
export HBASE_CLASSPATH=/usr/local/hadoop-0.20.1-dev/conf调优配置项如下:
# Extra Java CLASSPATH elements. Optional.
# export HBASE_CLASSPATH=
# The maximum amount of heap to use, in MB. Default is 1000.
# export HBASE_HEAPSIZE=1000
# Extra Java runtime options.
# Below are what we set by default. May only work with SUN JVM.
# For more on why as well as other possible settings,
# see http://wiki.apache.org/hadoop/PerformanceTuning
export HBASE_OPTS="-ea -XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC -XX:+CMSIncrementalMode"
# Uncomment below to enable java garbage collection logging.
# export HBASE_OPTS="$HBASE_OPTS -verbose:gc -XX:+PrintGCDetails -XX:+PrintGCDateStamps -Xloggc:$HBASE_HOME/logs/gc-hbase.log"
# Uncomment and adjust to enable JMX exporting
# See jmxremote.password and jmxremote.access in $JRE_HOME/lib/management to configure remote password access.
# More details at: http://java.sun.com/javase/6/docs/technotes/guides/management/agent.html
#
# export HBASE_JMX_BASE="-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.ssl=false -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.authenticate=false"
# export HBASE_MASTER_OPTS="$HBASE_JMX_BASE -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.port=10101 -javaagent:lib/HelloWorldAgent.jar"
# export HBASE_REGIONSERVER_OPTS="$HBASE_JMX_BASE -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.port=10102"
# export HBASE_THRIFT_OPTS="$HBASE_JMX_BASE -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.port=10103"
# export HBASE_ZOOKEEPER_OPTS="$HBASE_JMX_BASE -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.port=10104"
# File naming hosts on which HRegionServers will run. $HBASE_HOME/conf/regionservers by default.
# export HBASE_REGIONSERVERS=${HBASE_HOME}/conf/regionservers
# Extra ssh options. Empty by default.
# export HBASE_SSH_OPTS="-o ConnectTimeout=1 -o SendEnv=HBASE_CONF_DIR"
# Where log files are stored. $HBASE_HOME/logs by default.
# export HBASE_LOG_DIR=${HBASE_HOME}/logs
# A string representing this instance of hbase. $USER by default.
# export HBASE_IDENT_STRING=$USER
# The scheduling priority for daemon processes. See 'man nice'.
# export HBASE_NICENESS=10
# The directory where pid files are stored. /tmp by default.
# export HBASE_PID_DIR=/var/hadoop/pids
# Seconds to sleep between slave commands. Unset by default. This
# can be useful in large clusters, where, e.g., slave rsyncs can
# otherwise arrive faster than the master can service them.
# export HBASE_SLAVE_SLEEP=0.1
# Tell HBase whether it should manage it's own instance of Zookeeper or not.
export HBASE_MANAGES_ZK=true
export HBASE_CLASSPATH=/usr/local/hadoop-0.20.1-dev/confhbase-site.xml配置如下:
hbase.rootdir
hdfs://hadoopNN00:9000/hbase
The directory shared by region servers.
hbase.master.port
60000
hbase.cluster.distributed
true
hbase.zookeeper.property.dataDir
/usr/local/hbase/zookeeper
hbase.zookeeper.property.clientPort
2181
hbase.zookeeper.quorum
192.168.11.16,192.168.11.18,192.168.11.20
其中,hbase.rootdir这一项的配置必须与hdfs的fs.name.default项一致,还要为hbase指定根目录/hbase
hbase.rootdir
hdfs://hadoopNN00:9000/hbase
The directory shared by region servers.
Regionserver的配置如下:
192.168.11.16
192.168.11.18
192.168.11.20
配置完毕后将hbase拷贝到各个机器中的相同目录下。
启动habse
在192.168.11.12上启动hbase集群:bin/start-hbase.sh,首先启动的是zookeeper,再是master,最后是HRegionserver