Java基础之字节流
文章目录
-
- 一、字节输入流
-
- 1.1 字节输入流读取单个字节
- 1.2 字节输入流一个字节一个字节读取数据
- 1.3 字节输入流一个字节数组一个字节数组读取数据
- 二、字节输入流读出数据乱码问题
- 三、字节输出流
-
- 3.1 一次向指定文本写入一个字节数据
- 3.2 一次向指定文本写入一个字节数组数据
- 3.3 一次向指定文本写入写一个字节数组的部分数据
- 3.4 追加数据而不覆盖
- 四、通过字节流拷贝数据
-
- 4.1 将utf-8编码格式的txt文件数据拷贝至ascii编码格式的txt文件中
- 4.2 将ascii编码格式的txt文件数据拷贝至UTF-8编码格式的txt文件中
- 4.3 将txt文件数据拷贝至docx文件中
字节流分为字节输入流FileInputStream和字节输出流FileOutputStream,其中输入与输出是相对于内存而言的;输入即从文件中读出数据输入至内存;输出即从内存向文件中输出数据。
一、字节输入流
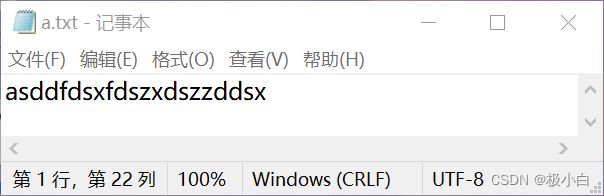
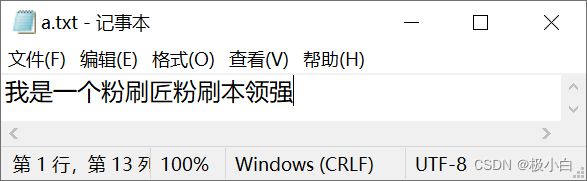
1.1 字节输入流读取单个字节
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建字节输入流对象,并指明从a.txt读取数据(注意:此路径必须正确且文件必须存在)
FileInputStream fileInputStream=new FileInputStream("D:\\Code\\ideaCode\\FileTest\\aa\\a.txt");
//读取一个字节(读出的数据为ASCII码值)
int read = fileInputStream.read();
//将数据转换为char类型
char data=(char)read;
//打印输出
System.out.println("使用字节输入流读取了一个数据:"+data);
//关闭资源
fileInputStream.close();
}
a.txt文件内容:
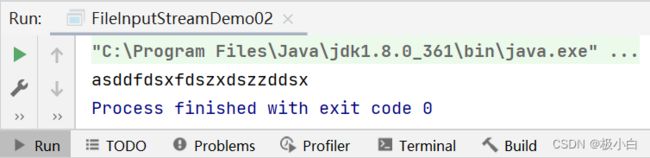
1.2 字节输入流一个字节一个字节读取数据
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建字节输入流对象,并指明从a.txt读取数据(注意:此路径必须正确且文件必须存在)
FileInputStream fileInputStream=new FileInputStream("D:\\Code\\ideaCode\\FileTest\\aa\\a.txt");
//设置有效字节,初始值为0
int read=0;
//一个字节一个字节读取数据,当读取至文件数据末尾空值时,fileInputStream.read()返回值为-1
while((read=fileInputStream.read())!=-1){
//打印输出
System.out.print((char)read);
}
//关闭资源
fileInputStream.close();
}
a.txt文件内容:
1.3 字节输入流一个字节数组一个字节数组读取数据
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建字节输入流对象,并指明从a.txt读取数据(注意:此路径必须正确且文件必须存在)
FileInputStream fileInputStream=new FileInputStream("D:\\Code\\ideaCode\\FileTest\\aa\\a.txt");
//定义一个字节数组,设置其初始长度为128
byte[] bytes=new byte[128];
//定义有效字节长度,初始值为0
int length=0;
//一个字节数组一个字节数组读取数据
while((length=fileInputStream.read(bytes))!=-1){
//将字节数组打印输出,输出其有效数据
System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,length));
}
//关闭资源
fileInputStream.close();
}
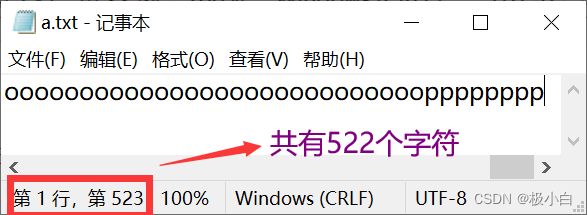
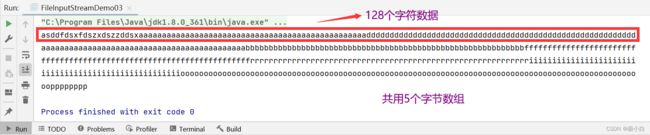
a.txt文件内容:
运行结果解析:
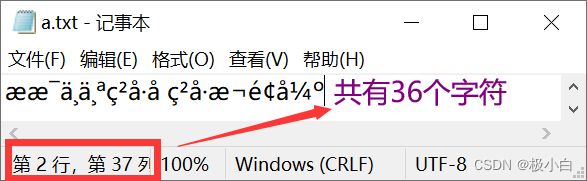
我们在a.txt中写入了522个字符,而我们通过一个长度为128的字节数组方式进行读取数据,128\*4=512<522,因此我们将会分5次打印输出,当读满一个字节数组,我们就会打印此字节数组,若读至文本数据末尾,我们也会打印字节数组,并结束循环。
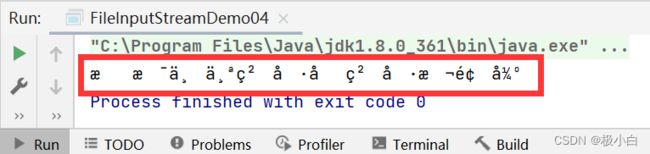
二、字节输入流读出数据乱码问题
当我们在文本文件中写入中文,再通过字节输入流读取数据到控制台,会出现乱码现象。
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建字节输入流对象,并指明从a.txt读取数据(注意:此路径必须正确且文件必须存在)
FileInputStream fileInputStream=new FileInputStream("D:\\Code\\ideaCode\\FileTest\\aa\\a.txt");
//设置有效字节,初始值为0
int read=0;
//一个字节一个字节读取数据,当读取至文件数据末尾空值时,fileInputStream.read()返回值为-1
while((read=fileInputStream.read())!=-1){
//打印输出
System.out.print((char)read);
}
//关闭资源
fileInputStream.close();
}
原因:
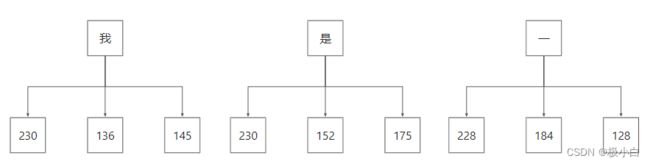
由于我们的记事本的编码格式为UTF-8,而在UTF-8中,一个中文字符占3个字节,当我们通过字节输入流读取数据并打印至控制台时,由于字节输入流无法指定编码格式,控制台会默认使用ASCII编码,一个字节一个字节的读取数据,导致一个中文字符被拆分为3个字符被读取出来,从而导致乱码。
三、字节输出流
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| void write(int b) | 一次向指定文本写入一个字节数据 |
| void write(byte[] b) | 一次向指定文本写入一个字节数组数据 |
| void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) | 一次向指定文本写入写一个字节数组的部分数据 |
3.1 一次向指定文本写入一个字节数据
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建字节输出流对象,并指明数据要写入的文件(此文件可以不存在,代码运行时可自行创建)
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream=new FileOutputStream("D:\\Code\\ideaCode\\FileTest\\aa\\b.txt");
//一次向指定文本写入一个字节数据(97=>a)
fileOutputStream.write(97);
//关闭资源
fileOutputStream.close();
}
3.2 一次向指定文本写入一个字节数组数据
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建字节输出流对象,并指明数据要写入的文件(此文件可以不存在,代码运行时可自行创建)
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream=new FileOutputStream("D:\\Code\\ideaCode\\FileTest\\aa\\b.txt");
//一次向指定文本写入一个字节数组数据(b,c,d,e,f,g,h)
byte[] bytes={98,99,100,101,102,103,104};
fileOutputStream.write(bytes);
//关闭资源
fileOutputStream.close();
}
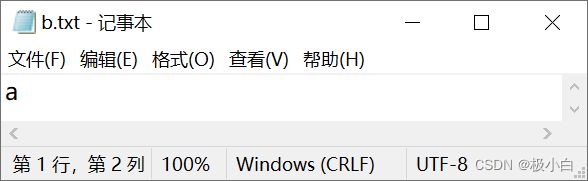
b.txt文件内容:(我们发现我们新写入的数据覆盖了之前写入的数据)
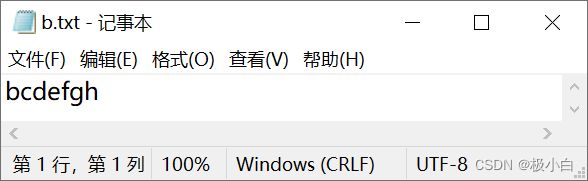
3.3 一次向指定文本写入写一个字节数组的部分数据
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建字节输出流对象,并指明数据要写入的文件(此文件可以不存在,代码运行时可自行创建)
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream=new FileOutputStream("D:\\Code\\ideaCode\\FileTest\\aa\\b.txt");
//一次向指定文本写入写一个字节数组的部分数据(b,c,d,e,f,g,h,i)
byte[] bytes={98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105};
//写入efgh数据,e的索引为3,efgh长度为4
fileOutputStream.write(bytes,3,4);
//关闭资源
fileOutputStream.close();
}
b.txt文件内容:(我们发现我们新写入的数据覆盖了之前写入的数据)
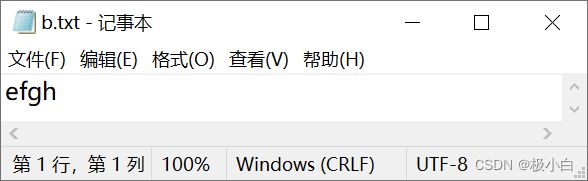
3.4 追加数据而不覆盖
若我们不想每次写入数据都覆盖之前的数据,字节输出流也为我们提供了追加数据的方式。
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建字节输出流对象,并指明数据要写入的文件(此文件可以不存在,代码运行时可自行创建),并设置其为追加方式写入数据
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream=new FileOutputStream("D:\\Code\\ideaCode\\FileTest\\aa\\b.txt",true);
//一次向指定文本写入一个字节数组数据(a,a,a,a,a,a,a,a)
byte[] bytes={97,97,97,97,97,97,97,97};
fileOutputStream.write(bytes);
//关闭资源
fileOutputStream.close();
}
b.txt文件内容:(我们看到新写入的数据追加到了之前数据之后,并未覆盖之前数据)
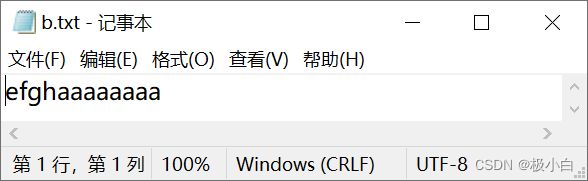
四、通过字节流拷贝数据
通过字节流将一个文本文件的数据拷贝至另一个相同类型的文本中,数据不会发生乱码,因为相同类型的文件在进行拷贝时会将数据编码一起拷贝至新文本中。
注意:我们不能将两个不同文件类型的数据进行拷贝,例如将txt数据拷贝至docx中。
4.1 将utf-8编码格式的txt文件数据拷贝至ascii编码格式的txt文件中
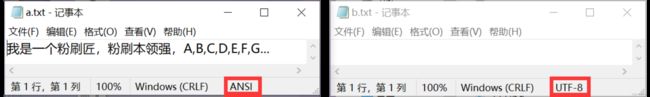
utf-8编码格式的a.txt文本与ascii编码格式的b.txt文本
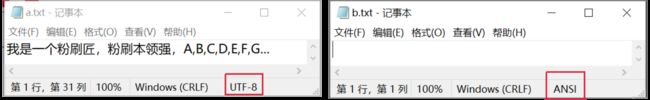
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建一个字节输入流,并指明数据要从a.txt文件中读取(注意:此路径必须正确且文件必须存在)
FileInputStream fileInputStream=new FileInputStream("D:\\Code\\ideaCode\\FileTest\\aa\\a.txt");
//创建字节输出流对象,并指明数据要写入b.txt(此文件可以不存在,代码运行时可自行创建)
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream=new FileOutputStream("D:\\Code\\ideaCode\\FileTest\\aa\\b.txt");
//拷贝数据
//定义一个字节数组,设置其初始长度为1024
byte[] bytes=new byte[1024];
//定义有效字节长度,初始值为0
int len=0;
//一个字节数组一个字节数组读取数据
while((len=fileInputStream.read(bytes))!=-1){
//向b.txt写入数据
fileOutputStream.write(bytes,0,len);
}
//关闭资源
fileInputStream.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
}
代码运行完成后的b.txt:(无乱码,并且b.txt的编码格式被改为UTF-8)
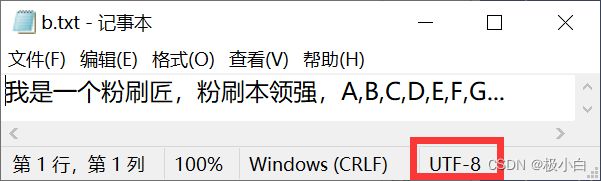
4.2 将ascii编码格式的txt文件数据拷贝至UTF-8编码格式的txt文件中
ascii编码格式的txt文本与UTF-8编码格式的txt文本
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建一个字节输入流,并指明数据要从a.txt文件中读取(注意:此路径必须正确且文件必须存在)
FileInputStream fileInputStream=new FileInputStream("D:\\Code\\ideaCode\\FileTest\\aa\\a.txt");
//创建字节输出流对象,并指明数据要写入b.txt(此文件可以不存在,代码运行时可自行创建)
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream=new FileOutputStream("D:\\Code\\ideaCode\\FileTest\\aa\\b.txt");
//拷贝数据
//定义一个字节数组,设置其初始长度为1024
byte[] bytes=new byte[1024];
//定义有效字节长度,初始值为0
int len=0;
//一个字节数组一个字节数组读取数据
while((len=fileInputStream.read(bytes))!=-1){
//向b.txt写入数据
fileOutputStream.write(bytes,0,len);
}
//关闭资源
fileInputStream.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
}
代码运行完成后的b.txt:(无乱码,并且b.txt的编码格式被改为ascii)

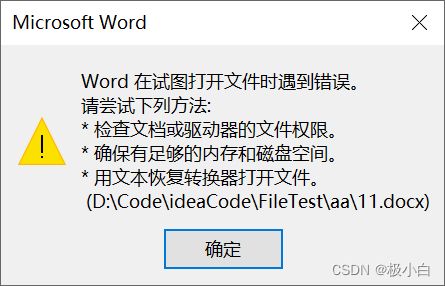
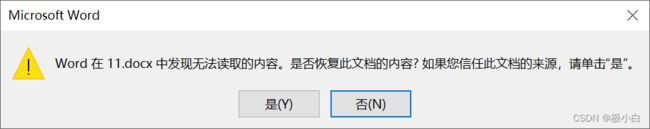
4.3 将txt文件数据拷贝至docx文件中
其中我们将a.txt设置为UTF-8编码,并且将11.docx设置为UTF-8编码。
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建一个字节输入流,并指明数据要从a.txt文件中读取(注意:此路径必须正确且文件必须存在)
FileInputStream fileInputStream=new FileInputStream("D:\\Code\\ideaCode\\FileTest\\aa\\a.txt");
//创建字节输出流对象,并指明数据要写入11.docx(此文件可以不存在,代码运行时可自行创建)
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream=new FileOutputStream("D:\\Code\\ideaCode\\FileTest\\aa\\11.docx");
//拷贝数据
//定义一个字节数组,设置其初始长度为1024
byte[] bytes=new byte[1024];
//定义有效字节长度,初始值为0
int len=0;
//一个字节数组一个字节数组读取数据
while((len=fileInputStream.read(bytes))!=-1){
//向b.txt写入数据
fileOutputStream.write(bytes,0,len);
}
//关闭资源
fileInputStream.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
}
代码运行完成后的11.docx:(出现问题,并且无法展示数据)
OK!字节流介绍完毕!!!