【剑指offer】数据结构——链表
目录
- 数据结构——链表
-
- 直接解
-
- 【剑指offer】06. 从尾到头打印链表
-
- 牛客
- 力扣
- 【剑指offer】24. 反转链表
- 【剑指offer】25. 合并两个排序的链表
- 【剑指offer】35. 复杂链表的复制
- 【剑指offer】52. 两个链表的第一个公共结点
- 特殊解——双指针
-
- 【剑指offer】18. 删除链表的节点
- 【剑指offer】18.2 删除链表中重复的结点
- 【剑指offer】22. 链表中倒数第k个节点
数据结构——链表
直接解
【剑指offer】06. 从尾到头打印链表
题目描述
力扣
牛客
// 输入一个链表的头节点,从尾到头反过来返回每个节点
// 的值(用数组返回)。
题解
牛客
// 数组翻转法
// 时间复杂度:14ms
// 空间复杂度:9524KB
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) {
ArrayList array = new ArrayList<>();
while (listNode != null) {
array.add(listNode.val);
listNode = listNode.next;
}
Collections.reverse(array);
return array;
}
}
// 头插法
// 运行时间 12ms
// 占用内存 9692KB
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) {
ArrayList res = new ArrayList<>();
while (listNode != null) {
res.add(0, listNode.val);
listNode = listNode.next;
}
return res;
}
}
// 栈辅助
// 时间复杂度:13ms
// 空间复杂度:9528kB
public class Solution {
public ArrayList printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) {
ArrayList res = new ArrayList<>();
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
while (listNode != null) {
stack.push(listNode.val);
listNode = listNode.next;
}
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
res.add(stack.pop());
}
return res;
}
}
// 递归法
// 时间复杂度:12 ms
// 空间复杂度:9384 KB
public class Solution {
public ArrayList printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) {
ArrayList ret = new ArrayList<>();
if (listNode != null) {
ret.addAll(printListFromTailToHead(listNode.next));
ret.add(listNode.val);
}
return ret;
}
}
// 运行时间 13ms
// 占用内存 9656KB
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
private ArrayList res;
public ArrayList printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) {
this.res = new ArrayList<>();
recur(listNode);
return res;
}
private void recur(ListNode listNode) {
if (listNode == null) {
return;
}
recur(listNode.next);
res.add(listNode.val);
}
}
力扣
// 力扣与牛客网不同的是,它需要你返回int[],而不是ArrayList
// 所以其实是更难了
// 栈存法
// 时间复杂度:2 ms , 在所有 Java 提交中击败了 40.69% 的用户
// 空间复杂度:39 MB , 在所有 Java 提交中击败了 91.29% 的用户
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
Stack stack = new Stack();
ListNode temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
stack.push(temp.val);
temp = temp.next;
}
int size = stack.size();
int[] result = new int[size];
for (int i = 0; i <= result.length - 1; i++) {
result[i] = stack.pop();
}
return result;
}
}
// 递归法
// 时间复杂度:2 ms , 在所有 Java 提交中击败了 40.69% 的用户
// 空间复杂度:40.4 MB , 在所有 Java 提交中击败了 6.12% 的用户
import java.util.Arrays;
class Solution {
ArrayList tmp = new ArrayList();
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
recur(head);
int size = tmp.size();
int[] result = new int[size];
for (int i = 0; i <= size - 1; i++) {
result[i] = tmp.get(i);
}
return result;
}
void recur(ListNode head) {
if (head != null) {
recur(head.next);
tmp.add(head.val);
}
else {
return;
}
}
}
【剑指offer】24. 反转链表
题目描述
// 力扣
// 定义一个函数,输入一个链表的头节点,反转该链表并输出反转后链表的头节点。
// 牛客
// 输入一个链表,反转链表后,输出新链表的表头。
题解
// 方法应该有很多
直接法 //
// 笨办法,直接遍历所有元素,存起来,再倒叙提取出来放进新构造的链表中
// 牛客
// 运行时间:12ms
// 占用内存:9920k
import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null)
return head;
// 新建一个栈stack存储链表元素val,弹出的val正好是反转顺序
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
ListNode index = head; // 初始化链表索引,从头遍历链表
// while循环直到index到达链表尾后一位才停止,
// 所以循环结束后index会到达链表尾结点的下一个位置
// 我们将这个位置作为新链表的头结点,开始创建新链表
while (index != null) {
stack.push(index.val); // 每遍历个结点就将val压入栈存储
index = index.next; // 所以index右移
}
// index位置创建新结点,弹出一次stack存的val
index = new ListNode(stack.pop());
// 当前index位置作为新链表的头结点,创建一个指向记为result
ListNode result = index;
// index右移创建新结点,弹出stack存储的元素作为新结点的元素,
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
index.next = new ListNode(stack.pop()); // 创建新结点
index = index.next; // index右移
}
return result; // 返回刚刚新链表(片段)的头结点
}
}
// 力扣
// 执行用时:2 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了7.85%的用户
// 内存消耗:38.2 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了71.94%的用户
import java.util.Stack;
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null)
return head;
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
ListNode index = head;
while (index != null) {
stack.push(index.val);
index = index.next;
}
index = new ListNode(stack.pop());
ListNode result = index;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
index.next = new ListNode(stack.pop());
index = index.next;
}
return result;
}
}
头插法 /
// 这个方法画图就懂了,是比较推荐的方法
// 牛客
// 运行时间:10ms
// 占用内存:9780k
public class Solution {
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null)
return head;
ListNode newList = new ListNode(-1);
while (head != null) {
ListNode next = head.next;
head.next = newList.next;
newList.next = head;
head = next;
}
return newList.next;
}
}
// 力扣
// 执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
// 内存消耗:38 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了91.31%的用户
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null)
return head;
ListNode newList = new ListNode(-1);
while (head != null) {
ListNode next = head.next;
head.next = newList.next;
newList.next = head;
head = next;
}
return newList.next;
}
}
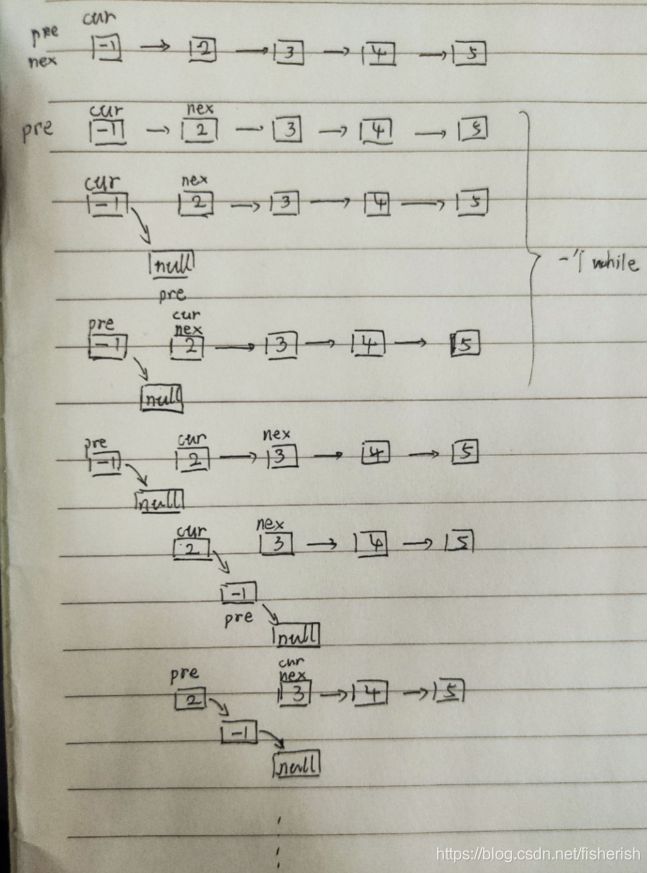
// 三指针法
// 也是比较推荐的方法,我画一个示意图方便理解
// 力扣
// 执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
// 内存消耗:38 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了92.77%的用户
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null)
return head;
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode nex = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
nex = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = nex;
}
return pre;
}
}
// 牛客
// 运行时间:11ms
// 占用内存:9876k
public class Solution {
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null)
return head;
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode nex = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
nex = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = nex;
}
return pre;
}
}
三指针法示意图:
/ 递归法 /
// 力扣
// 执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
// 内存消耗:38.5 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了32.42%的用户
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null)
return head;
ListNode next = head.next;
head.next = null;
ListNode newHead = reverseList(next);
next.next = head;
return newHead;
}
}
// 牛客
// 运行时间:12ms
// 占用内存:10048k
public class Solution {
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null)
return head;
ListNode next = head.next;
head.next = null;
ListNode newHead = ReverseList(next);
next.next = head;
return newHead;
}
}
【剑指offer】25. 合并两个排序的链表
题目描述
// 25. 合并两个排序的链表
// 输入两个递增排序的链表,合并这两个链表并使新链表中的
// 节点仍然是递增排序的。
// 输入两个单调递增的链表,输出两个链表合成后的链表,当然我
// 们需要合成后的链表满足单调不减规则。
题解
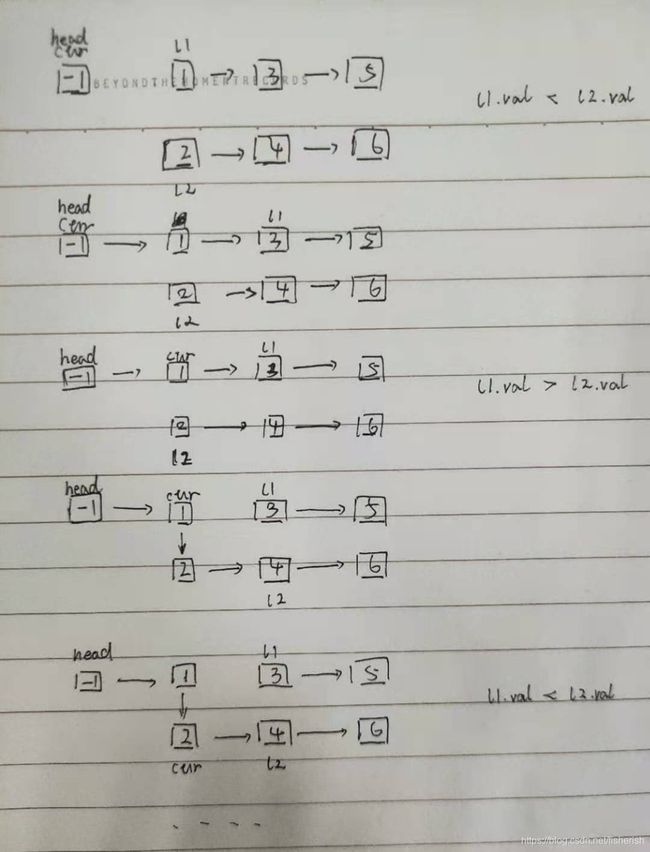
// 遍历法
// 力扣
// 执行用时:1 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了98.60%的用户
// 内存消耗:38.3 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了95.77%的用户
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null)
return l2;
if (l2 == null)
return l1;
ListNode head = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = head; // 单结点
// l1和l2这两个给定的指针作为遍历指针,在cur的前面遍历
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
// 谁小,cur.next会指向谁
if (l1.val <= l2.val) { // 如果l1值比l2值小
cur.next = l1; // cur.next指向l1
l1 = l1.next; // l1指针右移
}
else {
cur.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
// 上面的if else判据里,
// 如果l1值比l2值小,之前cur.next会指向l1,此时cur右移到之前l1位置
// 如果l2值比l1值小,之前cur.next会指向l2,此时cur右移到之前l2位置
cur = cur.next;
}
// 如果有链表没遍历完(该链表比另一个链表长)
// cur.next指向该链表当前指针,直接连上长链表未遍历的尾巴
if (l1 != null) {
cur.next = l1;
}
if (l2 != null) {
cur.next = l2;
}
return head.next; // 返回head.next
}
}
// 牛客
// 运行时间:16ms
// 占用内存:9948k
public class Solution {
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1,ListNode list2) {
if (list1 == null)
return list2;
if (list2 == null)
return list1;
ListNode head = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = head;
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {
if (list1.val <= list2.val) {
cur.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
}
else {
cur.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
if (list1 != null) {
cur.next = list1;
}
if (list2 != null) {
cur.next = list2;
}
return head.next;
}
}
// leetcode中的不同解法
// 运行时间:19ms 超过77.29%用Java提交的代码
// 占用内存:9916KB 超过70.27%用Java提交的代码
public class Solution {
public ListNode Merge(ListNode l1,ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null)
return l2;
else if (l2 == null)
return l1;
ListNode temp = new ListNode(0);
ListNode res;
if (l1.val <= l2.val) res = l1;
else res = l2;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val <= l2.val) {
while (l1.next != null && l1.next.val <= l2.val)
l1 = l1.next;
temp = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
temp.next = l2;
}
else { // l1.val > l2.val
while (l2.next != null && l1.val > l2.next.val)
l2 = l2.next;
temp = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
temp.next = l1;
}
}
return res;
}
}
遍历法图解(非leetcode中的解法)
/ 递归法
// 递归思路与遍历法是一样的,所以还是推荐遍历法,只是理解起来好看
// ,其资源消耗不可谓不小,因此该方法在牛客是无法通过的
// 力扣
// 执行用时:1 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了98.60%的用户
// 内存消耗:38.8 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了26.71%的用户
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null) {
return l2;
}
if (l2 == null) {
return l1;
}
ListNode head = new ListNode(-1);
if (l1.val <= l2.val) {
head = l1;
head.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2);
}
else {
head = l2;
head.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next);
}
return head;
}
}
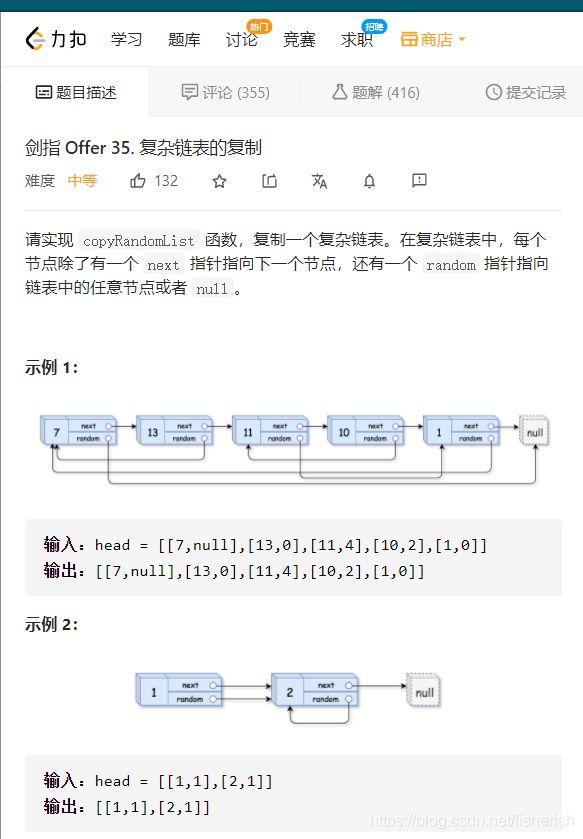
【剑指offer】35. 复杂链表的复制
题目描述
// 35. 复杂链表的复制
// 力扣
// 请实现 copyRandomList 函数,复制一个复杂链表。在复杂链表中
// ,每个节点除了有一个 next 指针指向下一个节点,还有一个 ran
// dom 指针指向链表中的任意节点或者 null。
// 牛客
// 输入一个复杂链表(每个节点中有节点值,以及两个指针,一个指向下
// 一个节点,另一个特殊指针random指向一个随机节点),请对此链表进
// 行深拷贝,并返回拷贝后的头结点。(注意,输出结果中请不要返回参
// 数中的节点引用,否则判题程序会直接返回空)
题解
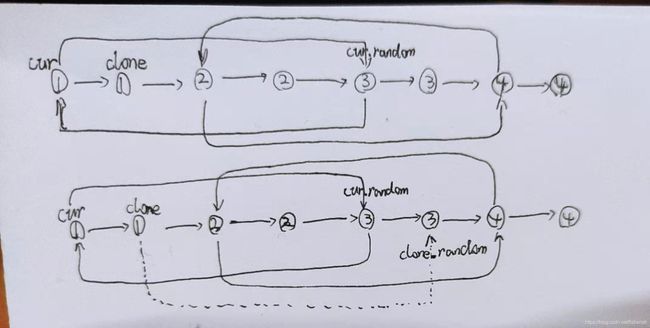
复制结点部分图解:
random指向图解:
// 力扣
// 执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
// 内存消耗:37.5 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了98.32%的用户
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if (head == null)
return null;
// 每一个结点之后插入其复制结点
Node cur = head; // 初始化遍历指针
while (cur != null) {
Node clone = new Node(cur.val); // 复制cur遍历的原链表结点,记为clone
clone.next = cur.next; // clone.next与cur.next一致
cur.next = clone; // 然后让cur.next指向clone本身
cur = clone.next; // 移动cur到下一个原链表结点
}
// 构建random指向
cur = head; // 重置cur回head
while (cur != null) { // 循环遍历链表
// 令clone结点为cur的下一个结点(clone结点即为cur的复制结点)
Node clone = cur.next;
if (cur.random != null) // 如果cur.random不为null
// 由于cur和clone的关系,clone是cur的下一个结点
// clone.random即为cur.random的下一个结点
clone.random = cur.random.next;
cur = clone.next; // cur移动至下一个原链表结点
}
// 两个链表拆分
cur = head; // 重置cur回head
Node cloneHead = head.next; // 设定复制链表的头结点
while (cur.next != null) { // 循环遍历,直到cur.next为空
// 令cur.next为next,到此我们有cur和next(cur.next)双指针
Node next = cur.next;
// 令cur的next直接指向next.next(cur.next.next)
// 原链表cur越过了cur的复制点,连上了原链表cur的下一个结点
cur.next = next.next;
cur = next; // cur右移
}
return cloneHead; // 拆分结束,最后返回复制链表头结点
}
}
// 牛客
// 运行时间:12ms
// 占用内存:9804k
public class Solution {
public RandomListNode Clone(RandomListNode pHead) {
if (pHead == null)
return null;
// 每个结点复制
RandomListNode cur = pHead;
while (cur != null) {
RandomListNode clone = new RandomListNode(cur.label);
clone.next = cur.next;
cur.next = clone;
cur = clone.next;
}
// random指向部署
cur = pHead;
while (cur != null) {
RandomListNode clone = cur.next;
if (cur.random != null)
clone.random = cur.random.next;
cur = clone.next;
}
// 分离
cur = pHead;
RandomListNode cloneHead = pHead.next;
while (cur.next != null) {
RandomListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = next.next;
cur = next;
}
return cloneHead;
}
}
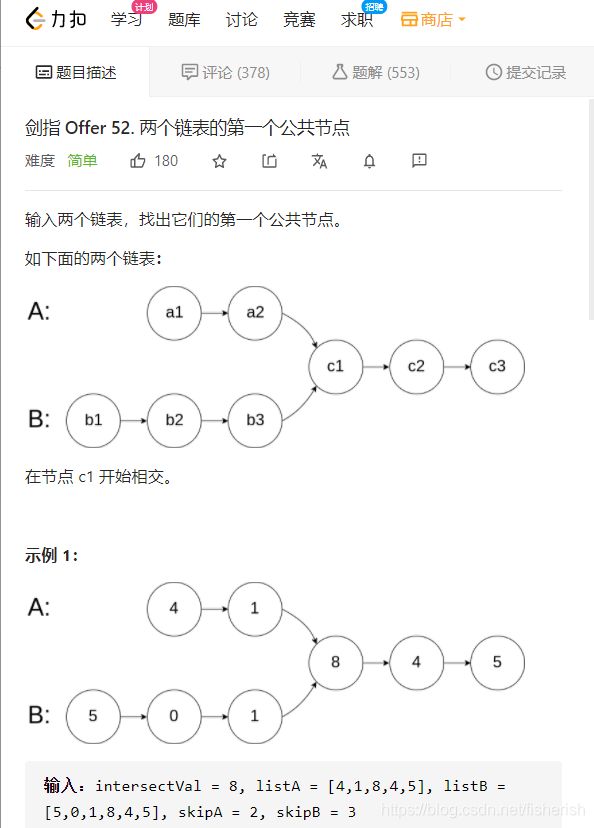
【剑指offer】52. 两个链表的第一个公共结点
// 52. 两个链表的第一个公共结点
// 力扣
// 输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共节点。
// 牛客
// 输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点。(注意因为传入数据是链表,
// 所以错误测试数据的提示是用其他方式显示的,保证传入数据是正确的)
题解
// HashSet法,
// 构建hashset用于存储遍历过的结点。
// 先让指针cur从headA移动,将遍历过的结点存入set。遍历完之后,
// 让cur回到headB,再遍历一次B链表,结点存入set,存不进的结点就是
// 相交的起点。
// 执行用时:10 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了10.60%的用户
// 内存消耗:41.9 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了10.07%的用户
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
Set set = new HashSet<>();
ListNode cur = headA;
while (cur != null) {
set.add(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = headB;
while (cur != null) {
if (!set.add(cur))
return cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}
}
// 牛客
// 双指针
// 假设俩链表A B,俩链表的公共长度是P,
// A链表的总长度是 A(私有链)+P(公共链)
// B链表的总长度是 B(私有链)+P(公共链),那么肯定有A+P+B = B+P+A。
// 我们让两个指针p1, p2分别从A B链表头出发,p1指针从A表头出发,
// 走A->P->B的路线,p2指针从B表头出发,走B->P->A的路线,最后两个指针
// 一定会在第一个公共结点相遇。
// 运行时间:12ms,超过95.24%用Java提交的代码
// 占用内存:9816KB,超过74.81%用Java提交的代码
public class Solution {
public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) {
ListNode p1 = pHead1;
ListNode p2 = pHead2;
while (p1 != p2) {
if (p1 != null)
p1 = p1.next;
else
p1 = pHead2;
if (p2 != null)
p2 = p2.next;
else
p2 = pHead1;
}
return p1;
}
}
// 牛客
// 运行时间:16ms,超过74.58%用Java提交的代码
// 占用内存:9988KB,超过73.19%用Java提交的代码
public class Solution {
public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) {
ListNode p1 = pHead1;
ListNode p2 = pHead2;
while (p1 != p2) {
p1 = (p1 == null) ? pHead2 : p1.next;
p2 = (p2 == null) ? pHead1 : p2.next;
}
return p1;
}
}
// 力扣
// 执行用时:1 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
// 内存消耗:41.1 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了82.68%的用户
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode p1 = headA, p2 = headB;
while (p1 != p2) {
p1 = (p1 == null) ? headB : p1.next;
p2 = (p2 == null) ? headA : p2.next;
}
return p1;
}
}
特殊解——双指针
【剑指offer】18. 删除链表的节点
题目描述
// 力扣
// 给定单向链表的头指针和一个要删除的节点的值,定义一个函数删除该节点。
// 返回删除后的链表的头节点。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
题解
// 双指针法 //
// 对数据结构有印象的就知道,删除一个链表结点,需要找待删除结点的前一个结点
// 令前一个结点直接指向待删除结点的next,这个待删除结点就从链表结构中被去除了。
// 执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
// 内存消耗:37.9 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了71.42%的用户
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteNode(ListNode head, int val) {
if (head == null)
return null;
// 假定val是一定找得到的,head.next不存在,那待删除结点是head本身,删除后返回null
if (head.next == null)
return null;
// 如果待删除节点是头结点,直接返回head.next
if (head.val == val && head.next != null)
return head.next;
// new一个链表引用pre,它的next指向head,即head前面多了一个节点
// 这个引用指针用来遍历待删除节点的前一个结点
ListNode pre = new ListNode(0); // pre.val初始化为0(无影响)
pre.next = head;
// 定义链表引用cur,它直接指向head,
// 这个引用指针用于遍历整个链表
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
// 非尾结点
// 若cur指针找到了val所在的结点
if (cur.val == val && cur.next != null) {
// 令pre.next直接越过待删除结点cur
// 直接指向cur的下一个结点cur.next
pre.next = cur.next;
cur = null; // 规范操作,令cur元素清空
break;
}
// 尾结点
if (cur.val == val && cur.next == null) {
pre.next = null; // 直接令pre.next指向null
break;
}
pre = pre.next; // 没找到val,右移一位
cur = cur.next; // 没找到val,右移一位
}
return head; // 题目要求返回删除后的链表,返回头引用即可
}
}
// 递归法 //
class Solution {
// 解题函数,也是递归函数
// 递归函数检查head.next是否为待删除结点
public ListNode deleteNode(ListNode head, int val) {
// 以下三个if语句跟双指针法是一样的,但是意义不一样
// 若head第一个结点就不存在,返回null
if (head == null)
return null;
// 1.当deleteNode还没被递归调用时:
// 此时head还指向头结点,如果head.next为null,说明整个链表就一个结点,删除之后为null
// 2.当deleteNode被递归调用后:
// 由于递归调用的语句是head.next = deleteNode(head.next, val);
// 因此字段head实际表示head.next,那字段head.next实际表示head.next.next,
// 若head.next.next为null,说明head.next是待删除尾结点,直接返回null,
// 这时候head.next会被指向这个返回的null,删除完成
// (注:如果这句if能触发,说明在head.next到达尾结点之前一直都没return过
// 说明尾结点必为待删除结点)
if (head.next == null)
return null;
// 1.当deleteNode还没被递归调用时:
// 如果待删除节点是头结点,直接返回head.next
// 2.当deleteNode被递归调用后:
// head实际表示head.next,所以如果head.next.val == val
// 说明head.next是待删除结点,返回head.next,也就是返回
// head.next.next,这时head.next会指向这个返回的head.next.next
// 原来的head.next从链表中被移除。
if (head.val == val && head.next != null)
return head.next;
// 将head.next指向deleteNode的返回值
// deleteNode将被递归调用,输入为head.next和val
head.next = deleteNode(head.next, val);
// 递归完成,返回删除好的链表头索引head
return head;
}
}
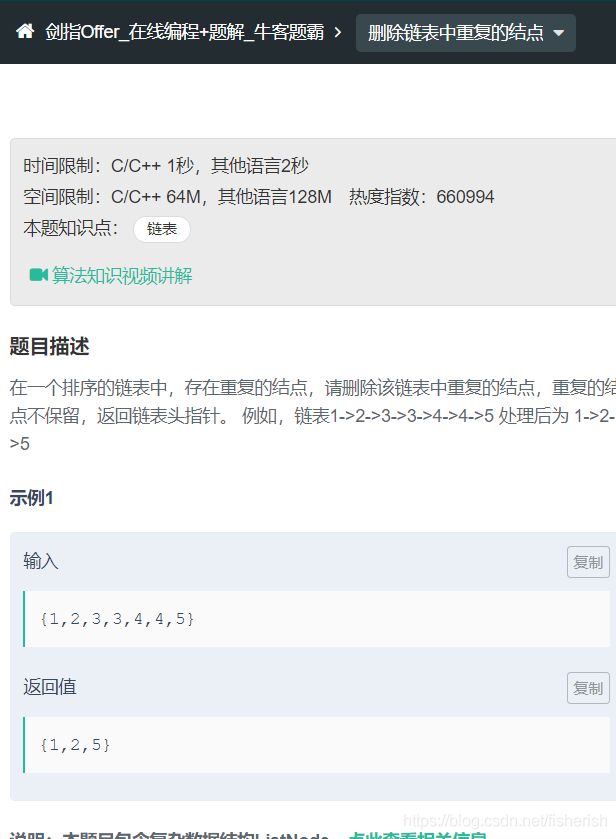
【剑指offer】18.2 删除链表中重复的结点
题目描述
// 18.2 删除链表中重复的结点
// 在一个排序的链表中,存在重复的结点,请删除该链表中重复的结点,
// 重复的结点不保留,返回链表头指针。例如,链表1->2->3->3->4->4->5
// 处理后为 1->2->5
题解
双指针
// 牛客
// 运行时间:14ms
// 占用内存:9916k
public class Solution{
public ListNode deleteDuplication(ListNode pHead) {
if (pHead == null || pHead.next == null)
return pHead;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = pHead;
ListNode pre = dummy;
ListNode cur = pHead;
cur = cur.next; // 先让cur右移一格,我们比较的是pre.next和cur
while (cur != null) {
// 如果发现重复结点
if (pre.next.val == cur.val) {
if (cur.next == null) { // 判断cur右移后是否到达链表尾
pre.next = null; // 到达链表尾,就直接让pre.next指向null
break; // 打断循环,返回结果
}
cur = cur.next; // cur继续右移(直到重复串的尾部)
// 如果右移后cur到达重复子串的尾部
if (pre.next.val != cur.val) {
pre.next = cur; // 直接令pre.next指向cur
cur = cur.next; // cur右移一格
}
}
// 未发现重复结点,一起右移
else {
pre = pre.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return dummy.next; // 不要返回pHead头节点了
}
}
// 简化版
// 运行时间:14ms
// 占用内存:9984k
public class Solution{
public ListNode deleteDuplication(ListNode pHead) {
if (pHead == null || pHead.next == null)
return pHead;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = pHead;
ListNode pre = dummy;
ListNode cur = pHead;
while (cur != null) {
// 如果发现重复结点
if (cur.next != null && cur.next.val == cur.val) {
while (cur.next != null && cur.next.val == cur.val) {
cur = cur.next; // cur继续右移(直到重复串的尾部)
}
// 再前进一格
cur = cur.next;
pre.next = cur;
}
// 未发现重复结点,一起右移
else {
pre = pre.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
/// 递归法 //
// 牛客
// 运行时间:11ms
// 占用内存:9948k
public class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplication(ListNode pHead) {
// 未开始递归时,pHead是头结点,开始递归后,pHead为遍历结点
if (pHead == null || pHead.next == null) {
return pHead;
}
// 1.未开始递归时,取头结点next记为next
// 2.开始递归后,pHead为遍历节点,且实际被pHead.next指向,
// next为pHead.next,所以实际被pHead.next.next指向
ListNode next = pHead.next;
// 1.未开始递归时,若头结点出现重复,则if成立,
// 直接开始while循环找重复子串尾结点
// 2.开始递归后,如果pHead和next的val相等
// 开始while循环找重复子串尾结点
if (pHead.val == next.val) {
// while循环继承了if的判断,同时保证next(pHead.next.next)不为null
while (next != null && pHead.val == next.val)
next = next.next; // next右移,直到遍历到重复子串的下一个结点
// 返回deleteDuplication递归调用
// 递归到底并返回之后,由于next被pHead.next指向,所以
// next循环右移就已经剔除了重复结点
return deleteDuplication(next);
}
// 若头结点未出现重复,else成立
else {
// 令pHead.next指向eleteDuplication的递归调用,输入pHead.next
// 假设链表一直没有重复节点,函数输入pHead实际是被上一个递归
// 的pHead.next指向,再递归取pHead.next,对于上一次递归
// 就是pHead.next.next,一直这样下去,实际就是遍历了整个
// 链表一次。
pHead.next = deleteDuplication(pHead.next);
return pHead;
}
}
}
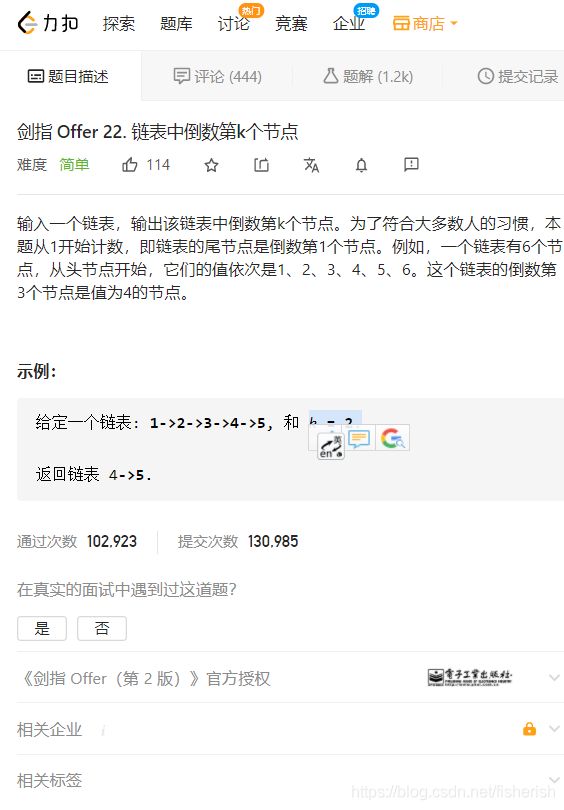
【剑指offer】22. 链表中倒数第k个节点
// 力扣
// 输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个节点。为了符合大多数人的习惯,
// 本题从1开始计数,即链表的尾节点是倒数第1个节点。例如,一个链表有
// 6个节点,从头节点开始,它们的值依次是1、2、3、4、5、6。这个链表的
// 倒数第3个节点是值为4的节点。
// 牛客
// 输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。
题解
双指针滑窗 //
// 由于需要返回以倒数第k个结点为头结点。第k结点往后的链表。
// 假如1->2->3->4->5,k = 2。我们需要返回的就是4->5。
// 那么我们就从链表头构建两个指针pre和end,end先右移扩大窗口,
// 直到pre到end的窗口的长度就等于第k结点往后的链表长度为止。
// 再以这个窗口滑动遍历链表,窗口右顶点到达链表尾即可返回。
// 力扣
// 力扣的版本比较简单,给定的k不会为0,也不会超过链表的长度,比较容易理解
class Solution {
public ListNode getKthFromEnd(ListNode head, int k) {
if (head == null) // 特殊情况判定
return head;
ListNode pre = head; // 滑窗前指针
ListNode end = head; // 滑窗后指针
int i = 1; //
// 将end右移,直到pre到end的窗口长度等于k到链表尾的长度
while (i < k) {
end = end.next;
i += 1;
}
while (end.next != null) { // 窗口右移,直到右顶点到达链表尾
end = end.next;
pre = pre.next;
}
return pre; // 此时的窗口左顶点位置即为倒数第k结点位置,直接返回
}
}
// 牛客
// 运行时间:14ms
// 占用内存:9976k
public class Solution {
public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head, int k) {
if (head == null)
return head;
if (k == 0) // 如果k是0,返回null
return null;
ListNode pre = head;
ListNode end = head;
int i = 1;
// 保证不要超过链表长度范围,把end指针向后,移动次数记为i
while (i != k && end.next != null) {
end = end.next;
i += 1; // end右移一次,i计数一次
}
// 如果k大于整个链表长度,i的大小是达不到k的,所以直接返回null
if (i < k)
return null;
// 如果k没有大于整个链表长度,滑窗
while (end.next != null) {
end = end.next;
pre = pre.next;
}
return pre;
}
}