python:图形用户界面GUI(模拟登录、计算器...)
文章目录
- 一、Tkinter简介
-
- 1、第一个tkinter窗口
- 2、在窗口内加入组件
-
- 2.1 思考题(问题与答案)
- 3、坐标管理器
- 二、Tkinter组件及其属性
-
- 1、Label组件和Entry组件
- 2、计算器代码
引言:我们以QQ为例,当我们点击QQ图标时候,它会 跳出一个登录界面,界面上面显示又两个 文本框,一个是账号,另一个是密码,如果 登录错误,会显示账号与密码错误; 登陆成功后, 进入了另一个界面,而登录界面就 消失了,上面有许多 列表框(联系人,消息等等),通过点击这些,可以实现想要达到的界面,之后就可以发信息等等(这个涉及到了通信等等技术,不讲),本章以实现界面为主,包括了从一个界面 跳转到另一个界面的功能。
一、Tkinter简介
上面所提到的功能,需要利用python中默认的GUI库——Tkinter,这个库在python安装好时候,就已经带有了,不需要利用pop工具手动下载。
主要会用到以上几种功能来实现。
1、第一个tkinter窗口
来看代码以及注释
import tkinter as tk #为tkinter来起一个别名
top=tk.Tk()
top.title("This is my first GUI.") #设置标题
top.mainloop() #进入主事件循环
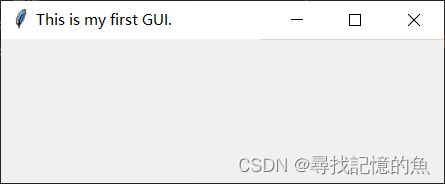
解释:
(1)先引入python中的tkinter库
(2)第二步调用TK()创建窗口对象,GUI可以有多个界面,但根窗口只能有一个。
2、在窗口内加入组件
我们通过之前的列子里面创建了一个简单的窗口,要想实现一些功能,巴西在窗口里面加上组件。
加入一个按钮(button)组件。
import tkinter as tk #为tkinter来起一个别名
top=tk.Tk()
top.title("This is my first GUI.")
btn=tk.Button(top,text="first button") #创建一个按钮对象
btn.pack() #设置按钮位置
top.mainloop()
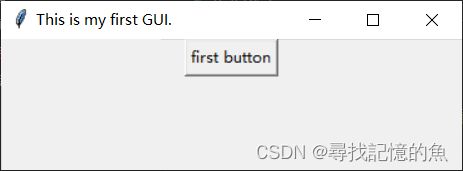
这里的窗口大小是我放大的,不是一开始就这样子的。
我来解释一下tk.button()里面的参数意义,第一个top是我们要将按钮所放在的窗口,而第二葛text是按钮内容。通过创建bnt按钮对象,来通过bnt.pack()来确定位置。
2.1 思考题(问题与答案)
思考:
(1)我们这个按钮里面可不可以加一个功能在里面呢,每当我们点击按钮时候,标题就会变成另一个提前设置好的标题内容。代码答案在图片下面 。
(提示:可以先定义一个函数,里面放入修改后的标题,并且在原来按钮位置,添加command=【函数名】)

答案:
import tkinter as tk #为tkinter来起一个别名
top=tk.Tk()
top.title("This is my first GUI.")
def button1():
top.title("This is my second GUI.")
btn=tk.Button(top,text="first button",command=button1) #创建一个按钮对象
btn.pack() #设置按钮位置
top.mainloop()
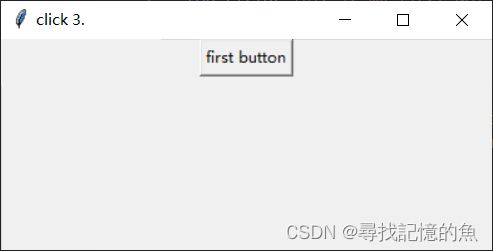
(2)我们在此基础上面,是否可以再加点难度,每次点击按钮时候,标题就会显示点击次数;

import tkinter as tk #为tkinter来起一个别名
top=tk.Tk()
top.title("This is my first GUI.")
count=0
def button1():
global count
count+=1
top.title("click {}.".format(count))
btn=tk.Button(top,text="first button",command=button1) #创建一个按钮对象
btn.pack() #设置按钮位置
top.mainloop()
3、坐标管理器
Tkinter库里面有三个坐标管理器:分别是包(packer)、Grid(网格)和Place(位置),其中packer和grid是最常用的。
(1)packer管理器是通过pack()来实现的,如果有多个组件来调用此方法,则会按照先后顺序来插入(来看代码)。
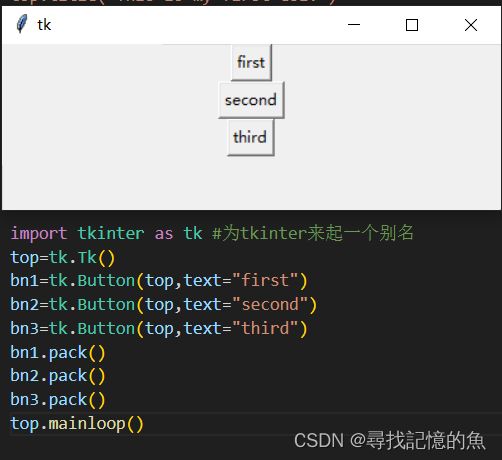
(2)Grid坐标管理器来通过grid(row= x,column=x)方法排版;
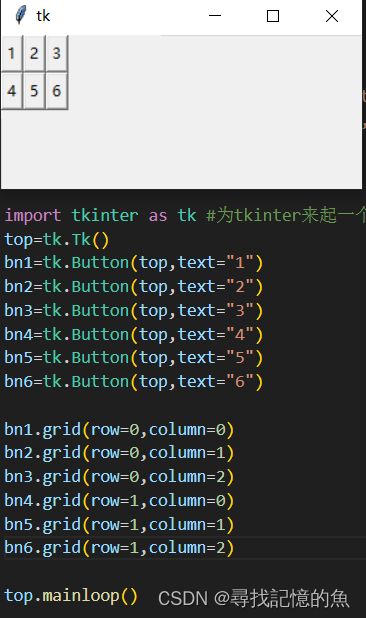
二、Tkinter组件及其属性
| 主要组件名 | 功能描述 |
|---|---|
| Button | 按钮组件,在程序中显示按钮 |
| Entry | 输入组件,用于显示简单的文本内容 |
| Label | 标签组件,用来显示文本和位图 |
| Listbox | 列表框组件,用来显示一个字符串列表给用户 |
| Text | 用于显示多行文本 |
各个组件都有自己的属性,比如label和button有text属性,而entry没有,属性可以在创建组件时候赋值。
下面给出Tkinter中公共属性:
| 属性名 | 属性描述 |
|---|---|
| Dimension | 组建的大小 |
| Color | 组建的颜色 |
| Font | 组建的字体 |
| Anchor | 组件包含的锚点 |
| Relief | 组建的样式 |
| Bitmap | 组件中的位图 |
1、Label组件和Entry组件
import tkinter as tk
top=tk.Tk()
top.title("login")
label1=tk.Label(top,text="请输入姓名:") #创建第一个标签
label2=tk.Label(top,text="请输入姓名:") #创建第二个标签
entry1=tk.Entry(top) #创建第一个文本框
entry2=tk.Entry(top) #创建第二个文本框
label1.pack() #这里我们之前讲过,按照顺序依次调用
entry1.pack()
label2.pack()
entry2.pack()
def button_clicked():
entry2.delete(0,tk.END) #先将2框清空
text=entry1.get() #获得1框内容
entry2.insert(0,text) #将1框内容插入2框
btn=tk.Button(top,text="copy",command=button_clicked) #动作
btn.pack()
top.mainloop() #显示
2、计算器代码
# *_* coding:utf8 *_*
import tkinter
from functools import partial
# 按钮输入调用
def get_input(entry, argu):
# 从entry窗口展示中获取输入的内容
input_data = entry.get()
# 出现连续+,则第二个+为无效输入,不做任何处理
if (input_data[-1:] == '+') and (argu == '+'):
return
# 出现连续+--,则第三个-为无效输入,不做任何处理
if (input_data[-2:] == '+-') and (argu == '-'):
return
# 窗口已经有--后面字符不能为+或-
if (input_data[-2:] == '--') and (argu in ['-', '+']):
return
# 窗口已经有 ** 后面字符不能为 * 或 /
if (input_data[-2:] == '**') and (argu in ['*', '/']):
return
# 输入合法将字符插入到entry窗口结尾
entry.insert("end", argu)
# 退格(撤销输入)
def backspace(entry):
input_len = len(entry.get())
# 删除entry窗口中最后的字符
entry.delete(input_len - 1)
# 清空entry内容(清空窗口)
def clear(entry):
entry.delete(0, "end")
# 计算
def calc(entry):
input_data = entry.get()
# 计算前判断输入内容是否为空;首字符不能为*/;*/不能连续出现3次;
if not input_data:
return
clear(entry)
try:
# eval() 函数用来执行一个字符串表达式,并返回表达式的值;并将执行结果转换为字符串
output_data = str(eval(input_data))
except Exception:
# 将提示信息输出到窗口
entry.insert("end", "Calculation error")
else:
# 将计算结果显示在窗口中
if len(output_data) > 20:
entry.insert("end", "Value overflow")
else:
entry.insert("end", output_data)
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = tkinter.Tk()
root.title("Yummy")
# 框体大小可调性,分别表示x,y方向的可变性;
root.resizable(0, 0)
button_bg = 'pink'
math_sign_bg = 'DarkTurquoise'
cal_output_bg = 'Yellow'
button_active_bg = 'gray'
entry = tkinter.Entry(root, justify="right", font=1)
entry.grid(row=0, column=0, columnspan=4, padx=10, pady=10)
def place_button(text, func, func_params, bg=button_bg, **place_params):
my_button = partial(tkinter.Button, root, bg=button_bg, padx=10, pady=3, activebackground=button_active_bg)
button = my_button(text=text, bg=bg, command=lambda: func(*func_params))
button.grid(**place_params)
# 文本输入类按钮
place_button('7', get_input, (entry, '7'), row=1, column=0, ipadx=5, pady=5)
place_button('8', get_input, (entry, '8'), row=1, column=1, ipadx=5, pady=5)
place_button('9', get_input, (entry, '9'), row=1, column=2, ipadx=5, pady=5)
place_button('4', get_input, (entry, '4'), row=2, column=0, ipadx=5, pady=5)
place_button('5', get_input, (entry, '5'), row=2, column=1, ipadx=5, pady=5)
place_button('6', get_input, (entry, '6'), row=2, column=2, ipadx=5, pady=5)
place_button('1', get_input, (entry, '1'), row=3, column=0, ipadx=5, pady=5)
place_button('2', get_input, (entry, '2'), row=3, column=1, ipadx=5, pady=5)
place_button('3', get_input, (entry, '3'), row=3, column=2, ipadx=5, pady=5)
place_button('0', get_input, (entry, '0'), row=4, column=0, padx=8, pady=5,
columnspan=2, sticky=tkinter.E + tkinter.W + tkinter.N + tkinter.S)
place_button('.', get_input, (entry, '.'), row=4, column=2, ipadx=7, padx=5, pady=5)
# 运算输入类按钮(只是背景色不同)
# 字符大小('+','-'宽度不一样,使用ipadx进行修正)
place_button('+', get_input, (entry, '+'), bg=math_sign_bg, row=1, column=3, ipadx=5, pady=5)
place_button('-', get_input, (entry, '-'), bg=math_sign_bg, row=2, column=3, ipadx=5, pady=5)
place_button('*', get_input, (entry, '*'), bg=math_sign_bg, row=3, column=3, ipadx=5, pady=5)
place_button('/', get_input, (entry, '/'), bg=math_sign_bg, row=4, column=3, ipadx=5, pady=5)
# 功能输入类按钮(背景色、触发功能不同)
place_button('<-', backspace, (entry,), row=5, column=0, ipadx=5, padx=5, pady=5)
place_button('C', clear, (entry,), row=5, column=1, pady=5, ipadx=5)
place_button('=', calc, (entry,), bg=cal_output_bg, row=5, column=2, ipadx=5, padx=5, pady=5,
columnspan=2, sticky=tkinter.E + tkinter.W + tkinter.N + tkinter.S)
root.mainloop()