SpringCloud源码探析(四)-OpenFeign使用及其原理
1.概述
在SpringCloud中,服务之间的调用方式可以通过ResTemplate进行调用,也可以通过Feign调用。ResTemplate的缺陷在于需要指定请求url,存在硬编码问题,导致代码难以复用和修改。而Feign调用就相对比较优雅,只需要配置服务名称即可。本文将介绍OpenFeign的使用及其原理。
2.OpenFeign使用及原理
2.1 SpringCloud集成OpenFeign
2.1.1 引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
<version>2.2.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
openfeign的版本与springcloud版本需要对应,我这里springcloud的版本是Hoxton.SR3。
2.1.2 编写Feign接口
@FeignClient(name = "userservice")
public interface FeignClientUser {
@GetMapping("/user/findOrderByUserId")
String getUserById();
}
2.1.3 启动类添加注解
@Slf4j
@EnableDiscoveryClient
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableFeignClients
public class OrderApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
log.info("这是新的OrderApplication");
SpringApplication.run(OrderApplication.class, args);
}
}
启动类上添加@EnableFeignClients接口,进行Feign接口扫描。
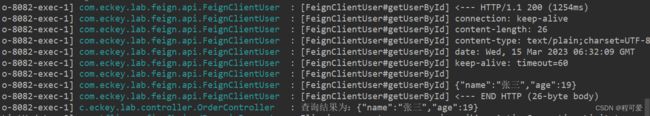
2.2 Feign日志配置
feign的日志配置主要有两种方式,一种是通过在配置文件配置的方式(这种方式通常是全局feign日志配置);另一种是通过注入Bean配置,可以实现不同类feign接口不同配置。
2.2.1 配置文件
配置文件添加如下配置:
feign.client.config.default.logger-level=FULL
2.2.2 注入Bean配置
//Feign配置,Bean注入到容器中
public class FeignClientConfiguration {
@Bean
public Logger.Level feignLogLevel() {
return Logger.Level.FULL;
}
}
//Feign接口上指定配置
@FeignClient(name = "userservice", configuration = FeignClientConfiguration.class)
public interface FeignClientUser {
@GetMapping("/user/findOrderByUserId")
String getUserById();
}
如果是引用外部Feign包,需要添加扫描包路径,如下:
@EnableFeignClients(basePackages = {"com.eckey.lab"})
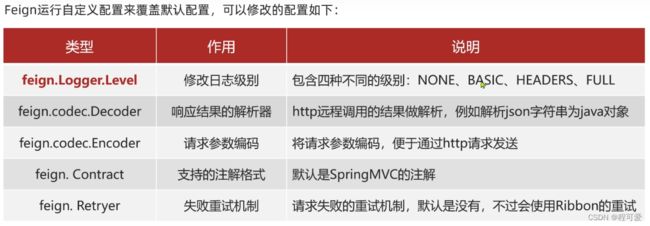
2.3 Feign自定义配置
2.4 OpenFeign使用原理
2.4.1 Feign调用流程图
1.开启Feign注解: 核心注解@FeignClient和@EnableFeignClients,开启Feign接口声明和Feign接口扫描;
2.服务器启动扫描注解,创建JDK注解: 服务启动时进行扫描,通过FeignInvocationHandler为每个远程接口创建JDK Proxy代理对象,并将这些对象注入Spring容器中;
3.找到MethodHandler方法处理器: FeignInvocationHandler根据要调用的方法找到对应的MethodHandler方法处理器;
4.构造Request对象并调用Encoder进行编码: MethodHandler方法处理器通过RequestTemplate构造参数和url,封装Request对象,并调用Encoder进行编码;
5.发送Request请求获取Response对象并进行解码: Client接口根据选择的Http框架,发送Request对象并接收返回的Response对象,进行判空和Decoder解码。
其实上述图变得好看一点就成了下面这张图(图片来源于知乎@黄青):

2.4.2 Feign源码分析
以上述代码为例来讲解,首先分析注解@EnableFeignClients和@FeignClient。@EnableFeignClients一般放于启动类接口上,@FeignClient放于Feign接口上。当程序开始运行时,@EnableFeignClients注解的作用是扫描所有@FeignClient注解修饰的接口,通过JDK底层的动态代理来创建接口,然后注入到容器中。@EnableFeignClients注解源码如下:
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Documented
@Import(FeignClientsRegistrar.class)
public @interface EnableFeignClients {
/**
* Alias for the {@link #basePackages()} attribute. Allows for more concise annotation
* declarations e.g.: {@code @ComponentScan("org.my.pkg")} instead of
* {@code @ComponentScan(basePackages="org.my.pkg")}.
* @return the array of 'basePackages'.
*/
String[] value() default {};
/**
* Base packages to scan for annotated components.
*
* {@link #value()} is an alias for (and mutually exclusive with) this attribute.
*
* Use {@link #basePackageClasses()} for a type-safe alternative to String-based
* package names.
*
* @return the array of 'basePackages'.
*/
String[] basePackages() default {};
/**
* Type-safe alternative to {@link #basePackages()} for specifying the packages to
* scan for annotated components. The package of each class specified will be scanned.
*
* Consider creating a special no-op marker class or interface in each package that
* serves no purpose other than being referenced by this attribute.
*
* @return the array of 'basePackageClasses'.
*/
Class<?>[] basePackageClasses() default {};
/**
* A custom @Configuration for all feign clients. Can contain override
* @Bean definition for the pieces that make up the client, for instance
* {@link feign.codec.Decoder}, {@link feign.codec.Encoder}, {@link feign.Contract}.
*
* @see FeignClientsConfiguration for the defaults
*/
Class<?>[] defaultConfiguration() default {};
/**
* List of classes annotated with @FeignClient. If not empty, disables classpath scanning.
* @return
*/
Class<?>[] clients() default {};
}
在上述源码中,引入了类FeignClientsRegistrar,该类在启动时会调用registerBeanDefinitions()方法,这个方法的内部只调用了registerDefaultConfiguration()和registerFeignClients()方法,registerDefaultConfiguration()方法主要检查是否有@EnableFeignClients注解,如果有的话,完成Feign框架的一些配置内容注册。registerBeanDefinitions方法代码如下:
class FeignClientsRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar,
ResourceLoaderAware, BeanClassLoaderAware, EnvironmentAware {
.......
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
registerDefaultConfiguration(metadata, registry);
registerFeignClients(metadata, registry);
}
private void registerDefaultConfiguration(AnnotationMetadata metadata,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
Map<String, Object> defaultAttrs = metadata
.getAnnotationAttributes(EnableFeignClients.class.getName(), true);
if (defaultAttrs != null && defaultAttrs.containsKey("defaultConfiguration")) {
String name;
if (metadata.hasEnclosingClass()) {
name = "default." + metadata.getEnclosingClassName();
}
else {
name = "default." + metadata.getClassName();
}
registerClientConfiguration(registry, name,
defaultAttrs.get("defaultConfiguration"));
}
}
......
}
这里还有一个重要的方法就是registerFeignClients(),这个方法主要扫描@FeignClient注解修饰的类,将类的内容解析为BeanDefinition,最终通过调用Spring框架的BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.resgisterBeanDefinition 将解析处理过的 FeignClientBeanDeifinition 添加到 spring 容器中。具体代码如下:
public void registerFeignClients(AnnotationMetadata metadata,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider scanner = getScanner();
scanner.setResourceLoader(this.resourceLoader);
Set<String> basePackages;
Map<String, Object> attrs = metadata
.getAnnotationAttributes(EnableFeignClients.class.getName());
AnnotationTypeFilter annotationTypeFilter = new AnnotationTypeFilter(
FeignClient.class);
final Class<?>[] clients = attrs == null ? null
: (Class<?>[]) attrs.get("clients");
if (clients == null || clients.length == 0) {
scanner.addIncludeFilter(annotationTypeFilter);
basePackages = getBasePackages(metadata);
}
else {
final Set<String> clientClasses = new HashSet<>();
basePackages = new HashSet<>();
for (Class<?> clazz : clients) {
basePackages.add(ClassUtils.getPackageName(clazz));
clientClasses.add(clazz.getCanonicalName());
}
AbstractClassTestingTypeFilter filter = new AbstractClassTestingTypeFilter() {
@Override
protected boolean match(ClassMetadata metadata) {
String cleaned = metadata.getClassName().replaceAll("\\$", ".");
return clientClasses.contains(cleaned);
}
};
scanner.addIncludeFilter(
new AllTypeFilter(Arrays.asList(filter, annotationTypeFilter)));
}
//遍历扫描配置上的包路径
for (String basePackage : basePackages) {
Set<BeanDefinition> candidateComponents = scanner
.findCandidateComponents(basePackage);
for (BeanDefinition candidateComponent : candidateComponents) {
if (candidateComponent instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
// verify annotated class is an interface
AnnotatedBeanDefinition beanDefinition = (AnnotatedBeanDefinition) candidateComponent;
AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata = beanDefinition.getMetadata();
Assert.isTrue(annotationMetadata.isInterface(),
"@FeignClient can only be specified on an interface");
Map<String, Object> attributes = annotationMetadata
.getAnnotationAttributes(
FeignClient.class.getCanonicalName());
String name = getClientName(attributes);
//每一个被@FeignClient注解修饰的接口就会被映射成一个BeanFactory
registerClientConfiguration(registry, name,
attributes.get("configuration"));
//注册Feign客户端
registerFeignClient(registry, annotationMetadata, attributes);
}
}
}
}
registerFeignClient方法源码如下,该方法内部组装BeanDefinition,然后注册到Spring IOC容器:
private void registerFeignClient(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry,
AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata, Map<String, Object> attributes) {
String className = annotationMetadata.getClassName();
BeanDefinitionBuilder definition = BeanDefinitionBuilder
.genericBeanDefinition(FeignClientFactoryBean.class);
validate(attributes);
definition.addPropertyValue("url", getUrl(attributes));
definition.addPropertyValue("path", getPath(attributes));
String name = getName(attributes);
definition.addPropertyValue("name", name);
String contextId = getContextId(attributes);
definition.addPropertyValue("contextId", contextId);
definition.addPropertyValue("type", className);
definition.addPropertyValue("decode404", attributes.get("decode404"));
definition.addPropertyValue("fallback", attributes.get("fallback"));
definition.addPropertyValue("fallbackFactory", attributes.get("fallbackFactory"));
definition.setAutowireMode(AbstractBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE);
String alias = contextId + "FeignClient";
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = definition.getBeanDefinition();
boolean primary = (Boolean) attributes.get("primary"); // has a default, won't be
// null
beanDefinition.setPrimary(primary);
String qualifier = getQualifier(attributes);
if (StringUtils.hasText(qualifier)) {
alias = qualifier;
}
//获取bean定义并进行注册
BeanDefinitionHolder holder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDefinition, className,
new String[] { alias });
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(holder, registry);
}
registerFeignClient()方法做了很多事情,它重新构造了一个类型是FeignClientFactoryBean的BeanDefinition,FeignClientFactoryBean类实现了FactoryBean接口,spring在生成bean时,如果发现BeanDefinition中的bean的class是由FactoryBean实现,就会调用实现类的getObject()方法来获取对象。至此,@EnableFeignClients的整个工作流程如下:
1.扫描指定路径(不指定就默认路径)下所有@FeignClient注解的类,然后每个类都生成一个BeanDefinition;
2.遍历每个BeanDefinition,取出每个@FeignClient注解的属性,构造新的BeanDefinition,传入FeignClientFactoryBean的class,然后注入到spring容器中。
当上述接口都被注入到容器之后,就要生成Feign客户端接口的动态代理。具体源码如下:
首先要分析的时feign在SpringCloud的核心配置类FeignAutoConfiguration,核心代码如下:
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(Feign.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties({FeignClientProperties.class, FeignHttpClientProperties.class})
public class FeignAutoConfiguration {
@Autowired(required = false)
private List<FeignClientSpecification> configurations = new ArrayList<>();
@Bean
public HasFeatures feignFeature() {
return HasFeatures.namedFeature("Feign", Feign.class);
}
@Bean
public FeignContext feignContext() {
FeignContext context = new FeignContext();
context.setConfigurations(this.configurations);
return context;
}
}
FeignClientSpecification是每个Feign客户端的配置类,上文registerClientConfiguration()方法中注入到spring容器中的就是这个内容,这些配置会被封装成FeignContext再注入到容器中。FeignContext 源码如下:
public class FeignContext extends NamedContextFactory<FeignClientSpecification> {
public FeignContext() {
super(FeignClientsConfiguration.class, "feign", "feign.client.name");
}
}
FeignContext 继承了NamedContextFactory,构造方法中传入了FeignClientsConfiguration,属性propertySourceName和propertyName。NamedContextFactory的作用主要是用来进行配置隔离的,它实现了ApplicationContextAware,定义了一个属性parent(springboot所使用的ApplicationContext类),源码如下:
public abstract class NamedContextFactory<C extends NamedContextFactory.Specification>
implements DisposableBean, ApplicationContextAware {
public interface Specification {
String getName();
Class<?>[] getConfiguration();
}
//一个Feign客户端对应一个AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
private Map<String, AnnotationConfigApplicationContext> contexts = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
//一个客户与其对应的配置类
private Map<String, C> configurations = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
//spring容器ApplicationContext
private ApplicationContext parent;
//默认的配置类
private Class<?> defaultConfigType;
private final String propertySourceName;
private final String propertyName;
public NamedContextFactory(Class<?> defaultConfigType, String propertySourceName,
String propertyName) {
this.defaultConfigType = defaultConfigType;
this.propertySourceName = propertySourceName;
this.propertyName = propertyName;
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext parent) throws BeansException {
this.parent = parent;
}
//根据客户端名称从context中获取AnnotationConfigApplicationContext,如果不存在,就向context中放入AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
protected AnnotationConfigApplicationContext getContext(String name) {
if (!this.contexts.containsKey(name)) {
synchronized (this.contexts) {
if (!this.contexts.containsKey(name)) {
this.contexts.put(name, createContext(name));
}
}
}
return this.contexts.get(name);
}
//创建了一个AnnotationConfigApplicationContext对象,遍历配置,将配置类放入,最后放入父容器parent,所有的客户端最终都有一个共同的父容器,这里为每一个客户端构建了一个AnnotationConfigApplicationContext,然后基于这个ApplicationContext来解析配置类,通过这种方式实现配置隔离
protected AnnotationConfigApplicationContext createContext(String name) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
if (this.configurations.containsKey(name)) {
for (Class<?> configuration : this.configurations.get(name)
.getConfiguration()) {
context.register(configuration);
}
}
for (Map.Entry<String, C> entry : this.configurations.entrySet()) {
if (entry.getKey().startsWith("default.")) {
for (Class<?> configuration : entry.getValue().getConfiguration()) {
context.register(configuration);
}
}
}
context.register(PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration.class,
this.defaultConfigType);
context.getEnvironment().getPropertySources().addFirst(new MapPropertySource(
this.propertySourceName,
Collections.<String, Object> singletonMap(this.propertyName, name)));
if (this.parent != null) {
// Uses Environment from parent as well as beans
context.setParent(this.parent);
}
context.refresh();
return context;
}
}
在动态代理过程中,主要是通过FeignClientFactoryBean的getObject方法来获取到代理对象,代码如下:
@Override
public Object getObject() throws Exception {
FeignContext context = applicationContext.getBean(FeignContext.class);
Feign.Builder builder = feign(context);
//判断是否指定url和url的具体位置,@FeignClient中指定的url属性,如果配置http://ip:port这种形式,就是直接访问,不经过注册中心
if (!StringUtils.hasText(this.url)) {
String url;
if (!this.name.startsWith("http")) {
url = "http://" + this.name;
}
else {
url = this.name;
}
url += cleanPath();
//走到这里是:http://+服务名,意味着是经过注册中心,然后通过loadBalance负载均衡方法获取一个Client
return loadBalance(builder, context, new HardCodedTarget<>(this.type,
this.name, url));
}
//指定了url且不是以http开头,则拼接http
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.url) && !this.url.startsWith("http")) {
this.url = "http://" + this.url;
}
String url = this.url + cleanPath();
Client client = getOptional(context, Client.class);
if (client != null) {
if (client instanceof LoadBalancerFeignClient) {
// not lod balancing because we have a url,
// but ribbon is on the classpath, so unwrap
client = ((LoadBalancerFeignClient)client).getDelegate();
}
builder.client(client);
}
Targeter targeter = get(context, Targeter.class);
return targeter.target(this, builder, context, new HardCodedTarget<>(
this.type, this.name, url));
}
它的流程主要是先从Spring容器中获取到FeignContext,FeignContext里面封装了每个Feign客户端的配置,然后通过FeignContext获取到一个Feign.Builder,Feign.Builder是用来构建动态代理类的,通过这个类的target方法,就能生成Feign动态代理。feign()方法源码如下:
protected Feign.Builder feign(FeignContext context) {
FeignLoggerFactory loggerFactory = get(context, FeignLoggerFactory.class);
Logger logger = loggerFactory.create(this.type);
// @formatter:off
Feign.Builder builder = get(context, Feign.Builder.class)
// required values
.logger(logger)
.encoder(get(context, Encoder.class))
.decoder(get(context, Decoder.class))
.contract(get(context, Contract.class));
// @formatter:on
configureFeign(context, builder);
return builder;
}
这个方法的主要作用就是从每个FeignClient对应的Spring容器中获取配置,填充到Feign.Builder中。
最后就是调用Feign.Builder的tartget方法:
public <T> T target(Target<T> target) {
return build().newInstance(target);
}
public Feign build() {
SynchronousMethodHandler.Factory synchronousMethodHandlerFactory =
new SynchronousMethodHandler.Factory(client, retryer, requestInterceptors, logger,
logLevel, decode404);
ParseHandlersByName handlersByName =
new ParseHandlersByName(contract, options, encoder, decoder,
errorDecoder, synchronousMethodHandlerFactory);
return new ReflectiveFeign(handlersByName, invocationHandlerFactory);
}
}
先调用build方法,这个方法就是将最开始填充到Feign.Builder给封装起来,构建了一个ReflectiveFeign,然后调用ReflectiveFeign的newInstance方法,传入HardCodedTarget。最后就到了newInstance()方法,通过target拿到接口类型,获取到所有方法并遍历处理,然后放入methodToHandler,通过InvocationHandlerFactory的create方法,传入methodToHandler和Target,获取到一个InvocationHandler,最后通过jdk动态代理,生成代理对象返回。
@Override
public <T> T newInstance(Target<T> target) {
Map<String, MethodHandler> nameToHandler = targetToHandlersByName.apply(target);
Map<Method, MethodHandler> methodToHandler = new LinkedHashMap<Method, MethodHandler>();
List<DefaultMethodHandler> defaultMethodHandlers = new LinkedList<DefaultMethodHandler>();
for (Method method : target.type().getMethods()) {
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {
continue;
} else if(Util.isDefault(method)) {
DefaultMethodHandler handler = new DefaultMethodHandler(method);
defaultMethodHandlers.add(handler);
methodToHandler.put(method, handler);
} else {
methodToHandler.put(method, nameToHandler.get(Feign.configKey(target.type(), method)));
}
}
InvocationHandler handler = factory.create(target, methodToHandler);
T proxy = (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.type().getClassLoader(), new Class<?>[]{target.type()}, handler);
for(DefaultMethodHandler defaultMethodHandler : defaultMethodHandlers) {
defaultMethodHandler.bindTo(proxy);
}
return proxy;
}
2.3 Feign优化
Feign底层默认使用URLConnection,不支持连接池,并发性能有限制。因此可以使用带连接池的Http客户端,例如Apache HttpClient、OKHttp。
3.小结
1.本文分析了openfeign的使用方式及原理,探索了openfeign的动态代理过程;
2.openfeign底层默认使用URLConnection,有一定的性能瓶颈;
3.openfeign严格意义上也是使用了一个RPC框架模型,它与dubbo的区别在于:dubbo通过TCP长连接的方式进行通信,适合数据量小、高并发和服务提供者远远少于消费者的场景;openfeign是通过REST API实现的远程调用,基于Http传输协议,服务提供者需要对外暴露Http接口供消费者调用,通过短连接的方式进行通信,不适合高并发的访问。
4.参考文献
1.https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1LQ4y127n4
2.https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV13a41137JF
3.https://www.zhihu.com/question/298707085
4.https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/78286377