Spring Security 的 RememberMe 详解 !!!!!
目录
目录
一、介绍
二、基本使用
2.1 开启记住我
三、原理分析
3.1 页面参数
3.2 RememberMeServices
3.3 TokenBasedRememberMeServices
3.4 认证流程
2. 自动登录的源码
3. 总结
四、安全性提升
五、自定义前后端分离 RememberMe
一、介绍
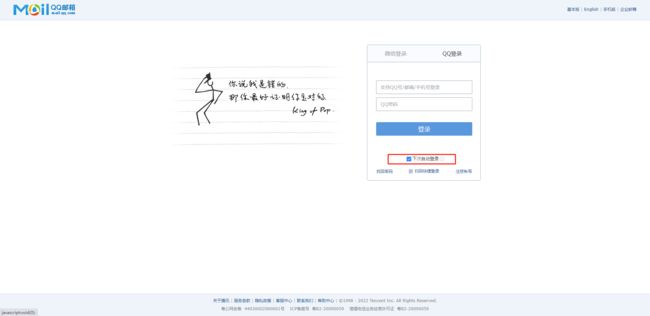
RememberMe 这个功能非常常见,下图就是 QQ 邮箱登录时的 "记住我" 选项。提到RememberMe ,一些初学者往往会有一些误解,认为RememberMe 功能就是把用户名/密码用 Cookie 保存在浏览器中,下次登录时不用再次输入用户名/密码。这个理解显然是不对的。我们这里所说的RememberMe 是一种服务器端的行为,传统的登录方式基于 Seesion 会话,一旦用户的会话超时过期,就要再次登录,这样太过于烦琐。如果能有一种机制,让用户会话过期之后,还能保持认证状态,就会方便很多,RemeberMe 就是为了解决这一需求而生的 。
具体的实现思路就是通过Cookie 来记录当前用户身份。当用户登录成功之后,会通过一定算法,将用户信息、时间戳等进行加密,加密完成后,通过响应头待会前端存储在cookie中,当浏览器会话过期之后,如果再次访问该网站,会自动将Cookie 中的信息发送给服务器,服务器对Cookie中的信息进行校验分析,进而确定出用户的身份,Cookie中所保存的用户信息也是有时效性的,例如三天、一周等。
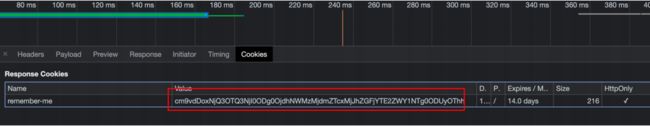
开启记住我之后,认证成功后会返回两个cookie ,一个是Jsession 一个是用户认证信息的加密后的信息。在下次发送请求是会携带这个两个cookie,会先找jseesionId 如果没有找到就会通过一定的算法将 加密的 cookie进行解密解密之后,拿着解密之后的信息进行认证,认证成功后会再次返回一个新的jseesionId。
使用JWT 之后不需要在用remeberMe 了 因为不使用Session了 ,
二、基本使用
2.1 开启记住我
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
/**
* 配置安全策略
* @param http
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/index").permitAll()
.anyRequest()
.authenticated()
.and()
.rememberMe() // 开启rememberMe 功能
// .alwaysRemember(true) // 总是记住我
.key(UUID.randomUUID().toString()) // 自定义 key 值
.and()
.formLogin()
.and()
.csrf()
.disable();
}
}可以看到⼀旦打开了记住我功能,登录⻚⾯中会多出⼀个 RememberMe 选项。
认证成功后返回Cookie
三、原理分析
3.1 页面参数
当在SecurityConfig配置中开启了"记住我"功能之后,在进⾏认证时如果勾选了"记住我"选项,通过前端页面和前端源代码分析可以得出开启 rememberMe 功能之后 ,前端页面会默认多按钮,会有一个参数 remember-me 参数 。
会携带参数到后台,由 RememberMeAuthenticationFilter 进行处理。
认证成功后后台也会多返回一个Cookie 叫 remeberme-me ,这个cookie 在以后的每次发送请求都会携带这个 cookie 到后台 ,如果Session过期了就会通过 remeberme-me 的信息进行解析去判断是否合法,如果合法就会返回一个新的 JSessionId 回来。
很显然,这个参数就是告诉服务器应该开启 RememberMe功能的。如果⾃ 定义登录⻚⾯开启 RememberMe 功能应该多加⼊⼀个⼀样的请求参数就可以啦。该请求会被 RememberMeAuthenticationFilter 进⾏拦截然后⾃动登录具体参⻅源码:
public class RememberMeAuthenticationFilter extends GenericFilterBean implements
ApplicationEventPublisherAware {
// ~ Instance fields
// ================================================================================================
private ApplicationEventPublisher eventPublisher;
private AuthenticationSuccessHandler successHandler;
private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
private RememberMeServices rememberMeServices;
public RememberMeAuthenticationFilter(AuthenticationManager authenticationManager,
RememberMeServices rememberMeServices) {
Assert.notNull(authenticationManager, "authenticationManager cannot be null");
Assert.notNull(rememberMeServices, "rememberMeServices cannot be null");
this.authenticationManager = authenticationManager;
this.rememberMeServices = rememberMeServices;
}
// ~ Methods
// ========================================================================================================
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
Assert.notNull(authenticationManager, "authenticationManager must be specified");
Assert.notNull(rememberMeServices, "rememberMeServices must be specified");
}
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
if (SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() == null) {
Authentication rememberMeAuth = rememberMeServices.autoLogin(request,
response);
if (rememberMeAuth != null) {
// Attempt authenticaton via AuthenticationManager
try {
rememberMeAuth = authenticationManager.authenticate(rememberMeAuth);
// Store to SecurityContextHolder
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(rememberMeAuth);
onSuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, rememberMeAuth);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("SecurityContextHolder populated with remember-me token: '"
+ SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication()
+ "'");
}
// Fire event
if (this.eventPublisher != null) {
eventPublisher
.publishEvent(new InteractiveAuthenticationSuccessEvent(
SecurityContextHolder.getContext()
.getAuthentication(), this.getClass()));
}
if (successHandler != null) {
successHandler.onAuthenticationSuccess(request, response,
rememberMeAuth);
return;
}
}
catch (AuthenticationException authenticationException) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(
"SecurityContextHolder not populated with remember-me token, as "
+ "AuthenticationManager rejected Authentication returned by RememberMeServices: '"
+ rememberMeAuth
+ "'; invalidating remember-me token",
authenticationException);
}
rememberMeServices.loginFail(request, response);
onUnsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response,
authenticationException);
}
}
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("SecurityContextHolder not populated with remember-me token, as it already contained: '"
+ SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() + "'");
}
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
}
/**
* Called if a remember-me token is presented and successfully authenticated by the
* {@code RememberMeServices} {@code autoLogin} method and the
* {@code AuthenticationManager}.
*/
protected void onSuccessfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authResult) {
}
/**
* Called if the {@code AuthenticationManager} rejects the authentication object
* returned from the {@code RememberMeServices} {@code autoLogin} method. This method
* will not be called when no remember-me token is present in the request and
* {@code autoLogin} reurns null.
*/
protected void onUnsuccessfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException failed) {
}
public RememberMeServices getRememberMeServices() {
return rememberMeServices;
}
public void setApplicationEventPublisher(ApplicationEventPublisher eventPublisher) {
this.eventPublisher = eventPublisher;
}
/**
* Allows control over the destination a remembered user is sent to when they are
* successfully authenticated. By default, the filter will just allow the current
* request to proceed, but if an {@code AuthenticationSuccessHandler} is set, it will
* be invoked and the {@code doFilter()} method will return immediately, thus allowing
* the application to redirect the user to a specific URL, regardless of whatthe
* original request was for.
*
* @param successHandler the strategy to invoke immediately before returning from
* {@code doFilter()}.
*/
public void setAuthenticationSuccessHandler(
AuthenticationSuccessHandler successHandler) {
Assert.notNull(successHandler, "successHandler cannot be null");
this.successHandler = successHandler;
}
}
通过以上源码得知 RememberMeAuthenticationFilter 会获取到容器中的RemeberMeService 。
- (1) 请求达到过滤器之后,首先判断 SecurityContextHolder 是否有值 , 没有值的话表示用户尚未登录,此时调用 autoLogin 方法进行自动登录。
- (2) 当自动登录成功后返回 rememberMeAuth 不为null 时 ,表示自动登录成功,此时调用 authenticate 方法对 key进行效验,并且将登录成功信息保存到 SecurityContextHolder 对象中,然后调用登录成功贵点,并发布登录成功事件。需要主要的是,登录成功的回调并不包含RememberMeMeService 中的loginSuccess 方法。
- (3) 如果自动登录失败,则调用 remeberMeService.loginFail 方法处理登录失败回调。onUnsuccessfulAuthentication 和 onSuccessfulAuthentication 都是该过滤器中定义的空方法,并没有任何实现这就是 RememberMeAuthenticationFilter 过滤器所做的事情,成功将RememberMeServices 的服务集成进来。
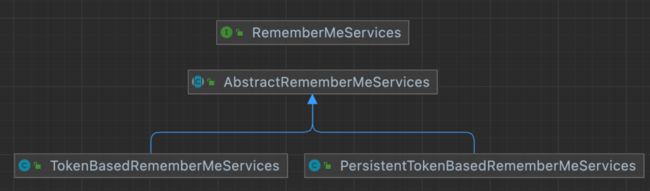
3.2 RememberMeServices
这里一共定义了三个方法:
- autoLogin 方法可以从请求中提取出需要的参数,完成自动登录功能。
- loginFail 方法是自动登录失败的回调。
- loginSuccess 方法是自动登录成功的回调。
3.3 TokenBasedRememberMeServices
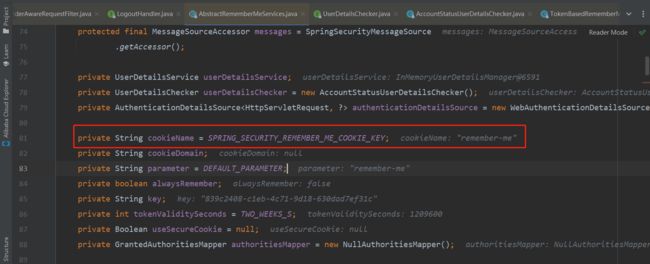
在开启记住我后如果没有加入额外配置默认实现就是由TokenBasedRememberMeServices进行的实现。查看这个类源码中proessAutoLoginCookie 方法实现:
processAutoLoginCookie 方法主要用来验证Cookie中的令牌信息是否合法:
- 首先判断cookieTokens 长度是否为3,如果不为3说明格式不对,则直接抛出异常。
- 从cookieTokens数组中取出第1项,也就是过期时间,判断令牌是否过期,如果已经过期,则抛出异常。
- 根据用户名(cookieTokens 数组的第1项)查询当前用户对象。
- 调用 makeTokenSignature 方法生成一个签名,签名的生成过程如下:首先将用户名、令牌过期时间、用户密码以及 key 组成一个字符串,中间用 " : " 割开,然后通过MD5消息摘要算法对该字符串进行加密,并将加密结果转为一个字符串返回。
- 判断第四步生成的签名和通过Cookie 传过来的签名是否相等(即cookieTokens数组的第二项),如果相等,表示令牌合法,则直接返回用户对象,否则抛出异常。
onLoginSuccess 方法 在 AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter 里调用 loginSuccess,loginSuccess 中调用的onLoginSuccess ,就是也在用户认证成功后,还么有生成 remeber-me 的cookie时,进行生成remember-me cookie ,并将cookie写回给前端。
- 在这个回调中,首先获取用户经和密码信息,如果用户密码在用户登录成功后successfulAuthentication 对象中擦除,则从数据库中重写加载出用户密码。
- 计算出令牌的过期时间,令牌的有效期是两周。
- 根据令牌的过期时间、用户名以及用户密码,计算出一个签名。
- 调用setCookie 方法设置Cookie ,第一个参数是一个数组,数组中一共包含三项。用户名、过期时间以及签名,在setCookie 方法中会将数组转为字符串,并进行Base64 编码后响应给前端。
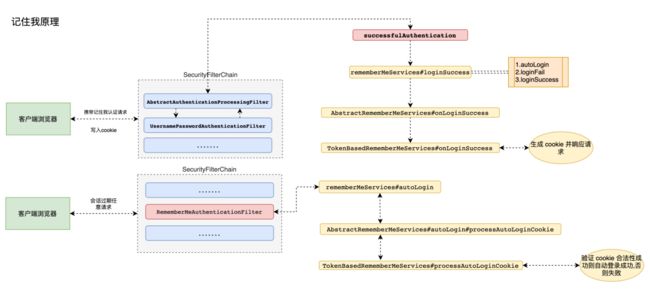
3.4 认证流程
1. 生成remeber-me cookie的流程源码
这个 remeber-me 的cookie生成的源代码的追溯要在 用户认证的filter 进行查看 调用的类是 AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter 在用户认证成功后调用了 RemeberMeServices 的 loginSuccess 方法进行生成 cookie 并返回给前端的 。
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
// 获取请求和响应对象
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
// 判断是否放行路径
if (!requiresAuthentication(request, response)) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Request is to process authentication");
}
Authentication authResult;
try {
// 调用子类认证方法获取用户登录信息
authResult = attemptAuthentication(request, response);
// 判断是否认证成功
if (authResult == null) {
// return immediately as subclass has indicated that it hasn't completed
// authentication
return;
}
// session信息处理
sessionStrategy.onAuthentication(authResult, request, response);
}
catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException failed) {
logger.error(
"An internal error occurred while trying to authenticate the user.",
failed);
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed);
return;
}
catch (AuthenticationException failed) {
// Authentication failed
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed);
return;
}
// Authentication success
if (continueChainBeforeSuccessfulAuthentication) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
// 调用认证成功处理方法
successfulAuthentication(request, response, chain, authResult);
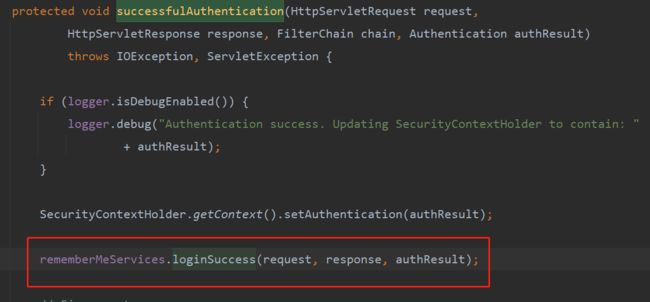
} protected void successfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain, Authentication authResult)
throws IOException, ServletException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Authentication success. Updating SecurityContextHolder to contain: "
+ authResult);
}
// 将用户认证信息设置到session中
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authResult);
// 调用remeberMeService 判断是否开启了此功能
rememberMeServices.loginSuccess(request, response, authResult);
// Fire event
if (this.eventPublisher != null) {
eventPublisher.publishEvent(new InteractiveAuthenticationSuccessEvent(
authResult, this.getClass()));
}
successHandler.onAuthenticationSuccess(request, response, authResult);
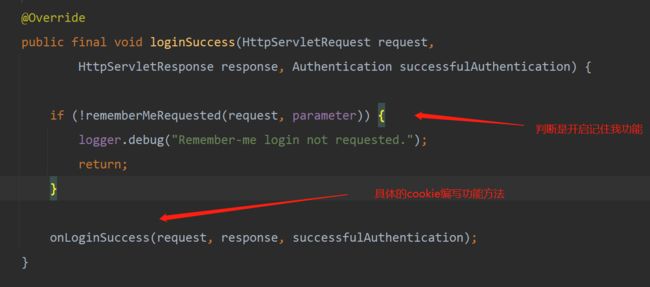
} public final void loginSuccess(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, Authentication successfulAuthentication) {
// 判断当前是否开启了记住我功能
if (!rememberMeRequested(request, parameter)) {
logger.debug("Remember-me login not requested.");
return;
}
// 表示开启记住我功能 进行cookie生成的回写操作
onLoginSuccess(request, response, successfulAuthentication);
}protected boolean rememberMeRequested(HttpServletRequest request, String parameter) {
// 判断是否开启了一直记住我
if (alwaysRemember) {
return true;
}
// 取出参数值
String paramValue = request.getParameter(parameter);
// 判断是否是这些值其中之一
if (paramValue != null) {
if (paramValue.equalsIgnoreCase("true") || paramValue.equalsIgnoreCase("on")
|| paramValue.equalsIgnoreCase("yes") || paramValue.equals("1")) {
return true;
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Did not send remember-me cookie (principal did not set parameter '"
+ parameter + "')");
}
return false;
}@Override
public void onLoginSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Authentication successfulAuthentication) {
// 获取认证用户信息
String username = retrieveUserName(successfulAuthentication);
String password = retrievePassword(successfulAuthentication);
// If unable to find a username and password, just abort as
// TokenBasedRememberMeServices is
// unable to construct a valid token in this case.
// 判断是否有值
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(username)) {
logger.debug("Unable to retrieve username");
return;
}
// 判断是否有值
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(password)) {
// 调用UserService 进行查询是该用户密码
UserDetails user = getUserDetailsService().loadUserByUsername(username);
password = user.getPassword();
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(password)) {
logger.debug("Unable to obtain password for user: " + username);
return;
}
}
// 生成 过期时间
int tokenLifetime = calculateLoginLifetime(request, successfulAuthentication);
long expiryTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// SEC-949
expiryTime += 1000L * (tokenLifetime < 0 ? TWO_WEEKS_S : tokenLifetime);
// 制作令牌
String signatureValue = makeTokenSignature(expiryTime, username, password);
// 将cookie写回
setCookie(new String[] { username, Long.toString(expiryTime), signatureValue },
tokenLifetime, request, response);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Added remember-me cookie for user '" + username
+ "', expiry: '" + new Date(expiryTime) + "'");
}
}
protected void setCookie(String[] tokens, int maxAge, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
String cookieValue = encodeCookie(tokens);
Cookie cookie = new Cookie(cookieName, cookieValue);
cookie.setMaxAge(maxAge);
cookie.setPath(getCookiePath(request));
if (cookieDomain != null) {
cookie.setDomain(cookieDomain);
}
if (maxAge < 1) {
cookie.setVersion(1);
}
if (useSecureCookie == null) {
cookie.setSecure(request.isSecure());
}
else {
cookie.setSecure(useSecureCookie);
}
cookie.setHttpOnly(true);
response.addCookie(cookie);
}- 用户信息认证进入到 AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter 中 首先判断当前请求是否放行请求,如果不是则会进行到 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 的 attemptAuthentication 进行用户信息认证 ,认证成功后进行session的处理,最后走到successfulAuthentication 进行Session的存储 和 调用 RemeberMeServices 的 loginSueccess 进行 cookie的封装和写入操作。
- AbstractRememberMeServices 的 loginSuccess 调用rememberMeRequested方法判断当前是否开启了记住我。
- onLoginSuccess 方法 父类没有实现,交于子类 TokenBasedRememberMeServices进行实现,这里进行获取用户认证成功后的信息,进行一些列的信息查询,生成存活时间,并进行MD5方式制作令牌。
- 最会调用 AbstractRememberMeServices的setCookie 将信息写入回去。
2. 自动登录的源码
所用的核心类是 RememberMeAuthenticationFilter
认证代码 :
// 验证方法
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
// 判断当前是否有认证信息 ,有则直接放行
if (SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() == null) {
// 通过 cookie 的信息判断是否符合自动登录
Authentication rememberMeAuth = rememberMeServices.autoLogin(request,
response);
// 判断用户是否为空
if (rememberMeAuth != null) {
// Attempt authenticaton via AuthenticationManager
try {
// 调用 认证方法
rememberMeAuth = authenticationManager.authenticate(rememberMeAuth);
// Store to SecurityContextHolder
// 放入Session
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(rememberMeAuth);
// 认证成功
onSuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, rememberMeAuth);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("SecurityContextHolder populated with remember-me token: '"
+ SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication()
+ "'");
}
// Fire event
if (this.eventPublisher != null) {
eventPublisher
.publishEvent(new InteractiveAuthenticationSuccessEvent(
SecurityContextHolder.getContext()
.getAuthentication(), this.getClass()));
}
if (successHandler != null) {
// 调用成功处理器进行页面或者内容返回
successHandler.onAuthenticationSuccess(request, response,
rememberMeAuth);
return;
}
}
catch (AuthenticationException authenticationException) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(
"SecurityContextHolder not populated with remember-me token, as "
+ "AuthenticationManager rejected Authentication returned by RememberMeServices: '"
+ rememberMeAuth
+ "'; invalidating remember-me token",
authenticationException);
}
rememberMeServices.loginFail(request, response);
onUnsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response,
authenticationException);
}
}
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("SecurityContextHolder not populated with remember-me token, as it already contained: '"
+ SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() + "'");
}
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
}核心方法就是 autoLogin 方法一下就是介绍
- 1.RememberMeServices 的 autoLogin 自动登录方法
- 调用的AbstractRememberMeServices 的 autoLogin 方法
-
/** @Param request 请求对象 @Param response 响应对象 */ @Override public final Authentication autoLogin(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) { // 获取到remeberme-me 的参数 String rememberMeCookie = extractRememberMeCookie(request); // 判断是否为空 如果为空表示没有开启自动登录 调转到登录页面 if (rememberMeCookie == null) { return null; } logger.debug("Remember-me cookie detected"); // 判断remeberme-me 的参数 长度 if (rememberMeCookie.length() == 0) { logger.debug("Cookie was empty"); cancelCookie(request, response); return null; } UserDetails user = null; try { // 解析出 remeberme-me 通过Base64 解析出 三个参数 // 用户名 、过期时间、签名 String[] cookieTokens = decodeCookie(rememberMeCookie); /// 校验 用户名 、过期时间、签名 的合法性 判断是否数据库中是否有。 user = processAutoLoginCookie(cookieTokens, request, response); // 检测用户的合法性 userDetailsChecker.check(user); logger.debug("Remember-me cookie accepted"); // 创建用户认证信息返回,并将新的JSessionId 返回用户 return createSuccessfulAuthentication(request, user); } catch (CookieTheftException cte) { cancelCookie(request, response); throw cte; } catch (UsernameNotFoundException noUser) { logger.debug("Remember-me login was valid but corresponding user not found.", noUser); } catch (InvalidCookieException invalidCookie) { logger.debug("Invalid remember-me cookie: " + invalidCookie.getMessage()); } catch (AccountStatusException statusInvalid) { logger.debug("Invalid UserDetails: " + statusInvalid.getMessage()); } catch (RememberMeAuthenticationException e) { logger.debug(e.getMessage()); } cancelCookie(request, response); return null; } - 调用 extractRememberMeCookie 验证是否有 remember-me 值
-
protected String extractRememberMeCookie(HttpServletRequest request) { // 获取所有的cookie Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies(); // 判断是否有cookie if ((cookies == null) || (cookies.length == 0)) { return null; } // 遍历所有cookie 看是否有 名称是 :rememeber-me 的 for (Cookie cookie : cookies) { if (cookieName.equals(cookie.getName())) { // 有则返回器值 return cookie.getValue(); } } // 没有返回空 return null; } - rememberMeCookie 不为空 则会去将他解码成对应数组 调用 decodeCookie 方法
-
// 将 enM6MTY2MjgwMjcxMzkzMzpkODZiMDFmYjUxZGM2ODExY2U5ODJjMzFkNDhiZWQ4Nw 解析 protected String[] decodeCookie(String cookieValue) throws InvalidCookieException { // 遍历 在最后加上了== // enM6MTY2MjgwMjcxMzkzMzpkODZiMDFmYjUxZGM2ODExY2U5ODJjMzFkNDhiZWQ4Nw== for (int j = 0; j < cookieValue.length() % 4; j++) { cookieValue = cookieValue + "="; } try { // 判断是否能进行 Base64 解码 Base64.getDecoder().decode(cookieValue.getBytes()); } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { throw new InvalidCookieException( "Cookie token was not Base64 encoded; value was '" + cookieValue + "'"); } // 真正的i将 value 进行Base64 解码操作 // 解码后的值 zs:1662802713933:d86b01fb51dc6811ce982c31d48bed87 // 用户界、 过期时间 、密钥 // 以:分隔 String cookieAsPlainText = new String(Base64.getDecoder().decode(cookieValue.getBytes())); // 将值以 : 进行拆分成 数组 String[] tokens = StringUtils.delimitedListToStringArray(cookieAsPlainText, DELIMITER); for (int i = 0; i < tokens.length; i++) { try { // 将每个数组进行 解码 tokens[i] = URLDecoder.decode(tokens[i], StandardCharsets.UTF_8.toString()); } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) { logger.error(e.getMessage(), e); } } // 将解码后的值返回 return tokens; }
-
- cookie 解码之后 会调用 AbstractRememberMeServices 的 processAutoLoginCookie,但是AbstractRememberMeServices 这个方法没有实现所有会调用子类 TokenBasedRememberMeServices 的 这个方法
- 这个方法里 完成对 解析的 cookie 内容进行校验和封装 UserDetails
-
/** 解析的 cookie 内容进行校验和封装 UserDetails */ @Override protected UserDetails processAutoLoginCookie(String[] cookieTokens, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) { // 判断长度是否为 3 if (cookieTokens.length != 3) { throw new InvalidCookieException("Cookie token did not contain 3" + " tokens, but contained '" + Arrays.asList(cookieTokens) + "'"); } // 过期时间 long tokenExpiryTime; try { // 获取到过期时间 tokenExpiryTime = new Long(cookieTokens[1]); } catch (NumberFormatException nfe) { throw new InvalidCookieException( "Cookie token[1] did not contain a valid number (contained '" + cookieTokens[1] + "')"); } //判断是否已经过期 if (isTokenExpired(tokenExpiryTime)) { throw new InvalidCookieException("Cookie token[1] has expired (expired on '" + new Date(tokenExpiryTime) + "'; current time is '" + new Date() + "')"); } // Check the user exists. // Defer lookup until after expiry time checked, to possibly avoid expensive // database call. // 用当前UserDetailsService 根据 用户名取查询 UserDetails userDetails = getUserDetailsService().loadUserByUsername( cookieTokens[0]); // 断言判断 如果没有查询到对应的用户信息则报错 Assert.notNull(userDetails, () -> "UserDetailsService " + getUserDetailsService() + " returned null for username " + cookieTokens[0] + ". " + "This is an interface contract violation"); // Check signature of token matches remaining details. // Must do this after user lookup, as we need the DAO-derived password. // If efficiency was a major issue, just add in a UserCache implementation, // but recall that this method is usually only called once per HttpSession - if // the token is valid, // it will cause SecurityContextHolder population, whilst if invalid, will cause // the cookie to be cancelled. // 生成令牌为后续验证使用 String expectedTokenSignature = makeTokenSignature(tokenExpiryTime, userDetails.getUsername(), userDetails.getPassword()); // 判断从cookie 中拿到的 令牌和 生成的令牌是否相同。 if (!equals(expectedTokenSignature, cookieTokens[2])) { throw new InvalidCookieException("Cookie token[2] contained signature '" + cookieTokens[2] + "' but expected '" + expectedTokenSignature + "'"); } return userDetails; } - processAutoLoginCookie 的方法中调用的 令牌生成
- 令牌是通过 用户 + 过期时间 +密码 + key 在通过 MD5 进行创建的类似于JWT
-
/** * Calculates the digital signature to be put in the cookie. Default value is MD5 * ("username:tokenExpiryTime:password:key") */ protected String makeTokenSignature(long tokenExpiryTime, String username, String password) { // 组合数据 String data = username + ":" + tokenExpiryTime + ":" + password + ":" + getKey(); MessageDigest digest; try { // 过去MD5类 digest = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5"); } catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) { throw new IllegalStateException("No MD5 algorithm available!"); } // 生成MD5的值 return new String(Hex.encode(digest.digest(data.getBytes()))); }
-
用户信息校验成功后会调用 AbstractRememberMeServices 的createSuccessfulAuthentication 方法将用户进行进行封装处理
-
protected Authentication createSuccessfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, UserDetails user) { RememberMeAuthenticationToken auth = new RememberMeAuthenticationToken(key, user, authoritiesMapper.mapAuthorities(user.getAuthorities())); auth.setDetails(authenticationDetailsSource.buildDetails(request)); return auth; } - 至此 autoLogin方法执行完成
-
-
-
.2.判断 autoLogin 的结果是否为 null
- 不为空 则进行认证 rememberMeAuth = authenticationManager.authenticate(rememberMeAuth);
- 设置到Session 中 发送成功消息 ....
3. 总结
当⽤户通过⽤户名/密码的形式登录成功后,系统会根据⽤户的⽤户名、密码以及令牌的过期时间计算出⼀个签名,这个签名使⽤ MD5 消息摘要算法⽣成,是不可逆的。然后再将⽤户名、令牌过期时间以及签名拼接成⼀个字符串,中间⽤“:” 隔开,对拼接好的字符串进⾏Base64 编码,然后将编码后的结果返回到前端,也就是我们在浏览器中看到的令牌。当会话过期之后,访问系统资源时会⾃动携带上Cookie中的令牌,服务端拿到 Cookie中的令牌后,先进⾏ Bae64解码,解码后分别提取出令牌中的三项数据:接着根据令牌中的数据判断令牌是否已经过期,如果没有过期,则根据令牌中的⽤户名查询出⽤户信息:接着再计算出⼀个签名和令牌中的签名进⾏对⽐,如果⼀致,表示会牌是合法令牌,⾃动登录成功,否则⾃动登录失败。
四、安全性提升
内容过多,请查看下一章
spring security rememberMe 提升安全性 讲解 !_weixin_52834606的博客-CSDN博客
五、自定义前后端分离 RememberMe
Spring Security 自定义记住我功能!_weixin_52834606的博客-CSDN博客