priority_queue(优先级队列)
priority_queue
- 1. priority_queue的介绍及使用
-
- 1.1 priority_queue的介绍
- 1.2 priority_queue的使用
-
- 1.2.1 constructor(构造)
- 1.2.2 empty
- 1.2.3 size
- 1.2.4 top
- 1.2.5 emplace
- 1.2.6 push、pop、swap
- 1.3 数组中第K个大的元素
- 2.priority_queue的深度剖析及模拟实现
1. priority_queue的介绍及使用
1.1 priority_queue的介绍
在C++中,priority_queue是一个容器适配器,它提供了常数时间的最大元素查找。它通常实现为堆。堆是一种数据结构,其中最大(或最小)元素始终位于顶部。priority_queue是一个模板类,定义在头文件中。它有三个模板参数:元素类型、容器类型和比较函数类型(可选)。默认情况下,它使用std::vector作为其底层容器 。
1.2 priority_queue的使用
1.2.1 constructor(构造)
int main ()
{
int myints[]= {10,60,50,20};
priority_queue<int> q1;
priority_queue<int> q2(myints,myints+4);
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> q3(myints,myints+4);
return 0;
}
- q1为空。
- q2包含为 定义的四个整数,60(最高)位于其顶部。
- q3具有相同的四个整数,但由于它使用而不是默认值(即),因此它将 10 作为其顶部元素添加新元素。这个新元素是就地构造的,作为其构造函数的参数传递。
1.2.2 empty
在C++ STL中,empty()函数是一个预定义函数,用于检查集合是否为空。如果集合为空,则返回true(1),如果集合不为空,则返回false(0)。对于空的容器,empty()函数返回true,否则返回false 。
#include 1.2.3 size
C++ STL中的size()函数返回的是容器中元素的数量 。
1.2.4 top
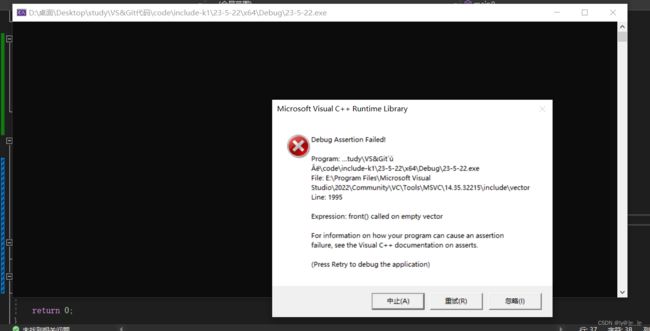
top() 函数是 C++ STL 中 priority_queue 类的一个成员函数,用于返回优先队列中的第一个元素的引用 。在使用 top() 函数时,需要注意优先队列是否为空,否则会出现未定义的行为 。
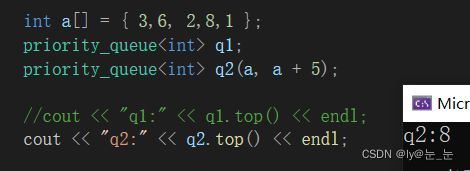
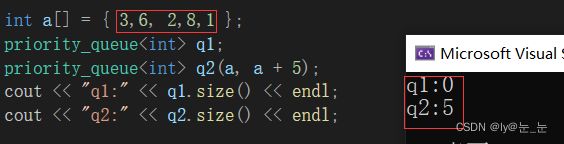
int main()
{
int a[] = { 3,6, 2,8,1 };
priority_queue<int> q1;
priority_queue<int> q2(a, a + 5);
cout << "q1:" << q1.top() << endl;//报错
cout << "q2:" << q2.top() << endl;//8
return 0;
}
1.2.5 emplace
构造和插入元素, 添加新元素。这个新元素是就地构造的,作为其构造函数的参数传递。
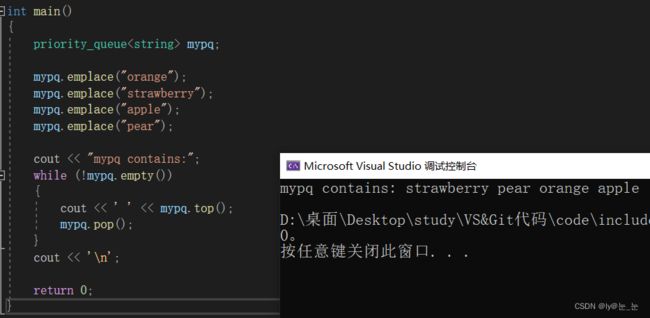
int main()
{
priority_queue<string> mypq;
mypq.emplace("orange");
mypq.emplace("strawberry");
mypq.emplace("apple");
mypq.emplace("pear");
cout << "mypq contains:";
while (!mypq.empty())
{
cout << ' ' << mypq.top();
mypq.pop();
}
cout << '\n';
return 0;
}
1.2.6 push、pop、swap
push() 函数用于将新元素插入到 priority_queue 中,并保持队列的有序性。
priority_queue 中的 pop() 函数用于删除队列中的第一个元素,即最大元素 。
swap() 函数用于交换两个 priority_queue 的元素。
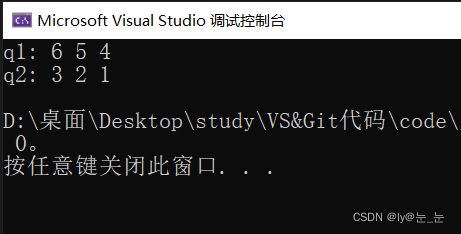
int main()
{
priority_queue<int> q1;
q1.push(1);
q1.push(2);
q1.push(3);
priority_queue<int> q2;
q2.push(4);
q2.push(5);
q2.push(6);
swap(q1, q2);
cout << "q1: ";
while (!q1.empty())
{
cout << q1.top() << ' ';
q1.pop();
}
cout << endl;
cout << "q2: ";
while (!q2.empty())
{
cout << q2.top() << ' ';
q2.pop();
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
1.3 数组中第K个大的元素
数组中第K个大的元素
第一种方法:对数组nums进行排序,然后找第k大个数。需要注意的是,算法中一般排序的时间复杂度都要比O(N)大,也就计数排序接近O(N)。

第二种方法:建立一个有N个元素的优先级队列,求第k个大的元素,则将优先级队列中前k-1个元素删除掉,最后队列的top就是所求元素
class Solution {
public:
int findKthLargest(vector<int>& nums, int k)
{
priority_queue<int> deq(nums.begin(), nums.end());
while(--k)
{
deq.pop();
}
return deq.top();
}
};
第三种方法:建立一个有K个元素的优先级队列(小堆),然后遍历nums,大的元素进队列,最后队列的top就是所求元素
class Solution {
public:
int findKthLargest(vector<int>& nums, int k)
{
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> deq(nums.begin(), nums.begin() + k);
for (size_t i = k; i < nums.size(); ++i)
{
if (nums[i] > deq.top())
{
deq.pop();
deq.push(nums[i]);
}
}
return deq.top();
}
};
2.priority_queue的深度剖析及模拟实现
priority_queue有三个模板参数:元素类型、容器类型和比较函数类型(可选)。默认情况下,它使用std::vector作为其底层容器 ,而且不需要迭代器,所以实现较为简单。
namespace k
{
template<class T, class Container = vector<T>>
class priority_deque
{
public:
size_t size()
{
return _con.size();
}
void push(const T& x)
{
_con.push_back(x);
adjust_up(_con.size() - 1);
}
void pop()
{
swap(_con[0], _con[_con.size() - 1]);
_con.pop_back();
adjust_down(0);
}
const T& top()
{
return _con[0];
}
bool empty()
{
return _con.empty();
}
protected:
void adjust_up(size_t child)
{
size_t parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
if (_con[parent] < _con[child])
{
swap(_con[child], _con[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void adjust_down(size_t parent)
{
size_t child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < _con.size())
{
if (child + 1 < _con.size() && _con[child] < _con[child + 1])
{
++child;
}
if (_con[parent] < _con[child])
{
swap(_con[child], _con[parent]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
private:
Container _con;
};
}
如上为priority_queue的实现,其中向上调整(adjust_up)、向下调整(asjust_down)调整的是大堆,是写死的,如过要小堆,则怎么弄?这就是模版的细节之处。只要定义一个比较方式,就可以解决。
namespace k
{
template<class T>
struct less
{
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x < y;
}
};
template<class T>
struct greater
{
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x > y;
}
};
template<class T, class Container = vector<T>, class Compare = less<T>>
class priority_deque
{
public:
size_t size()
{
return _con.size();
}
void push(const T& x)
{
_con.push_back(x);
adjust_up(_con.size() - 1);
}
void pop()
{
swap(_con[0], _con[_con.size() - 1]);
_con.pop_back();
adjust_down(0);
}
const T& top()
{
return _con[0];
}
bool empty()
{
return _con.empty();
}
protected:
void adjust_up(size_t child)
{
Compare com;
size_t parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
if (com(_con[parent], _con[child]))
{
swap(_con[child], _con[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void adjust_down(size_t parent)
{
size_t child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < _con.size())
{
Compare com;
if (child + 1 < _con.size() && com(_con[child], _con[child + 1]))
{
++child;
}
if (com(_con[parent], _con[child]))
{
swap(_con[child], _con[parent]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
private:
Container _con;
};
}
如上定义两个仿函数,然后模版引入就可以实现。