SDN实验(五)——Mininet多数据中心流量带宽实验
SDN实验(五)——Mininet多数据中心流量带宽实验
-
- (一)实验目的
- (二)数据中心网络拓扑
- (三)流量模拟
- (四)自定义命令实现
- (五)网络测试
(一)实验目的
- 通过Mininet迷你搭建基于不同数据中心的网络拓扑;
- 掌握多数据中心网络拓扑的构建;
- 熟悉网络性能测试工具iperf,根据实验测试SDN网络的性能;
- 通过程序生成模拟流量。
(二)数据中心网络拓扑
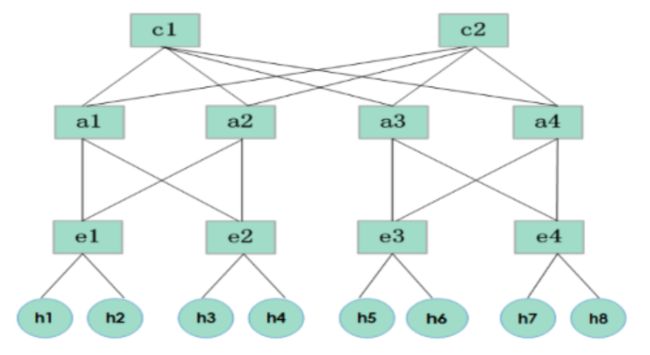
数据中心拓扑也叫胖树拓扑
2. 数据中心网络拓扑代码实现
也可以用miniedit来实现拓扑,但是会比较复杂一点,如果对python的语法比较熟悉,可以使用循环来实现拓扑(有比较多的冗余结构)。
from mininet.topo import Topo
from mininet.net import Mininet
from mininet.node import RemoteController
from mininet.link import TCLink
from mininet.util import dumpNodeConnections
class MyTopo(Topo):
def __init__(self):
super(MyTopo,self).__init__()
#Marking the number of switch for per level
L1 = 2;
L2 = L1*2
L3 = L2
#Starting create the switch
c = [] #core switch
a = [] #aggregate switch
e = [] #edge switch
#notice: switch label is a special data structure
for i in range(L1):
c_sw = self.addSwitch('c{}'.format(i+1)) #label from 1 to n,not start with 0
c.append(c_sw)
for i in range(L2):
a_sw = self.addSwitch('a{}'.format(L1+i+1))
a.append(a_sw)
for i in range(L3):
e_sw = self.addSwitch('e{}'.format(L1+L2+i+1))
e.append(e_sw)
#Starting create the link between switchs
#first the first level and second level link
for i in range(L1):
c_sw = c[i]
for j in range(L2):
self.addLink(c_sw,a[j])
#second the second level and third level link
for i in range(L2):
self.addLink(a[i],e[i])
if not i%2:
self.addLink(a[i],e[i+1])
else:
self.addLink(a[i],e[i-1])
#Starting create the host and create link between switchs and hosts
for i in range(L3):
for j in range(2):
hs = self.addHost('h{}'.format(i*2+j+1))
self.addLink(e[i],hs)
topos = {"mytopo":(lambda:MyTopo())}
- Mininet测试
sudo mn --custom ./data_center_topo.py --topo=mytopo --controller=remote
(三)流量模拟
-
为什么进行流量模拟
网络性能评估中一个巨大的挑战就是如何生成真实的网络流量,可以通过程序来创造人工的网络流量,通过建立测试化境来模拟真是的状况。 -
流量随机模型再Mininet的应用
流量随机模型:主机向在网络中的另一任意主机以等概率发送数据包。
使用mininet中的iperf工具在网络中生成UDP流量,iperf客户端传送数据流到iperf的服务端,由服务端接收并记录相关信息。我们需要实现的是将批处理流的自定义命令添加到mininet中,在mininet中使用此自定义命令,实现上述功能。
(四)自定义命令实现
在Mininet中拓展自定义命令主要又4个步骤:
- 修改/mininet/net.py
- 修改/mininet/cli.py
- 修改/bin/mn
- 重新编译mininet核心文件:~/mininet/util/install.sh -n
- 修改net.py
添加到iperf方法后面
其中,iperf_single方法主要实现了两个主机之间的UDP带宽测试,并将测试的结果存储在"/home/ryan/temp_log/"目录下。iperfMulti则从Host1开始,随机选取UDP数据流的发送对象。持续测试period时长,默认是60秒。
def iperf_single( self, hosts=None, udpBw='10M', period=60, port=5001):
""" Run iperf between two hosts using UDP and record communications.
hosts: list of hosts; if None, uses opposite hosts
returns: results two-element array of server and client speeds
"""
if not hosts:
return
else:
assert len( hosts ) == 2
client, server = hosts
filename = client.name[1:]+'.out'
output( '*** Iperf: testing bandwidth between ' )
output( "%s and %s\n" % ( client.name, server.name ) )
iperfArgs = 'iperf -u '
bwArgs = '-b ' + udpBw + ' '
print( "***start server***" )
server.cmd( iperfArgs + '-s -i 1' + ' > /home/ryan/temp_log/' + filename + '&')
print( "***start client***" )
client.cmd( iperfArgs + '-t ' + str(period) + ' -c ' +server.IP() + ' ' + bwArgs +\
'> /home/ryan/temp_log/' + 'client' + filename + '&')
def iperfMulti( self, bw, period=60 ):
base_port = 5001
server_list = []
host_list = [h for h in self.hosts]
_len = len(host_list)
for i in xrange(0, _len):
client = host_list[i]
server = client
while( server == client ):
server = random.choice(host_list)
server_list.append(server)
self.iperf_single(hosts=[client,server],udpBw=bw,period=period,port=base_port)
sleep(.05)
base_port += 1
sleep(period)
print("test has done")
- 修改cli.py
添加到do_iperfudp方法后面
def do_iperfmulti( self, line ):
"""
Multi iperf UDP test between nodes
"""
args = line.split()
if len(args) == 1:
udpBw = args[0]
self.mn.iperfMulti(udpBw)
elif len(args) == 2:
udpBw = args[0]
period = args[1]
self.mn.iperfMulti(udpBw,float(period))
else:
error( 'invalid number of args: iperfMulti udpBw period\n '+
'udpBw examples:1M 120\n' )
- 修改mn
将iperfmulti加入TEST和ALTSPELLING列表中。(mn中已经存在了TEST和ALTSPLLING,我们要做的是把自定义的命令添加进去)
# TESTS dict can contain functions and/or Mininet() method names
# XXX: it would be nice if we could specify a default test, but
# this may be tricky
TESTS = { name: True
for name in ( 'pingall', 'pingpair', 'iperf', 'iperfudp', 'iperfmulti' ) }
# Map to alternate spellings of Mininet() methods
ALTSPELLING = { 'pingall': 'pingAll', 'pingpair': 'pingPair',
'iperfudp': 'iperfUdp', 'iperfmulti': 'iperfMulti' }
- 重新编译
~/mininet/util/install.sh -n
(五)网络测试
- 运行数据中心拓扑
sudo mn --custom ./data_center_topo.py --topo=mytopo --controller=remote
- 开启Ryu控制器,注意要使用带生成树协议的版本,否则会因为环路形成广播风暴
ryu-manager simple_switch_stp_13.py
- 用iperfmulti测试流量
iperfmulti 25M 10
- 查看流量日志
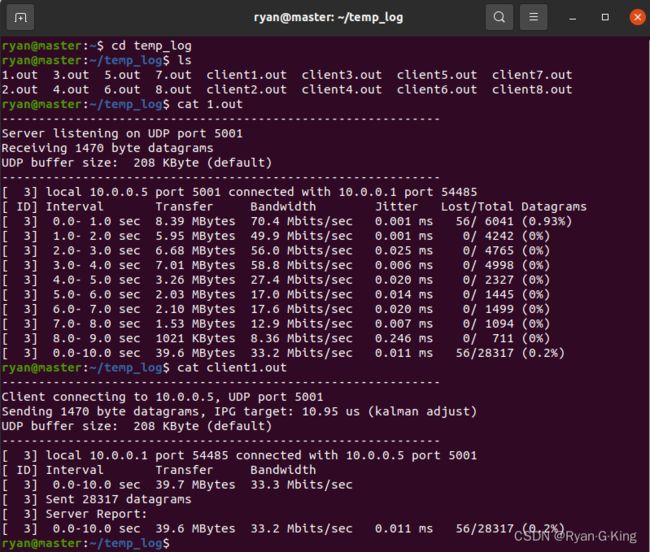
为什么会有16个文件呢?因为8个主机分别当了一次服务器和客户端,所以会产生16个文件。
图中记录了Server 10.0.0.1 (Host1) 侦听端口5001的记录,即与10.0.0.1 (Host1)的测试记录。一共测试了10秒,每隔1秒记录一次,记录内容有转发包的大小,带宽,延时抖动和丢包率等。还记录了Client 10.0.0.1 (Host1)的测试记录。
参考:
[1] 山上有风景:https://www.cnblogs.com/ssyfj/
[2] Ryubook:http://osrg.github.io/ryu-book/en/html/
[3] Ryu官方文档:https://ryu.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
[4] 未来网络学院:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1ft4y1a7ip/?spm_id_from=333.337.search-card.all.click&vd_source=f8206d9b2ac93039311dbe9fdd0bcc87