利用决策树预测学生成绩等级
文章目录
-
- 1.数据准备
-
- 1.1 引入头文件
- 1.2 把student_1.csv数据拖入代码的同一文件夹下,同时读取文件中的数据。
- 1.3 特征选取
- 2.数据处理
-
- 2.1 对G1、G2、G3处理
- 2.2 同样对Pedu参数进行连续值处理。
- 2.3 由于数据集中每个参数差异比较大,所以这里把特征参数统一改为数字形式。
- 2.4 对于当前处理过的数据集,划分训练集和测试集,并设置好随机种子等其他参数。
- 3.训练得到的模型
-
- 3.1 决策树
- 3.1.1 开始对训练集中的数据进行训练。
- 3.1.2 利用已经训练好的模型来预测G3的值。
- 3.1.3 对模型中的参数进行优化,输出优化后最好的分数。
- 3.1.4 优化后的模型来绘制决策树。
- 3.2 集成学习
- 3.2.1 Decision Tree
- 3.2.2 Bagging算法
- 3.2.3 这里采用集成学习的Random Forest算法进行训练模型,对模型做出分数估测。
- 3.2.4 这里采用集成学习的AdaBoost算法进行训练模型,对模型做出分数估测。
- 3.2.5 这里采用集成学习的GBDT算法进行训练模型,对模型做出分数估测。
- 4.评价结果:
- 5.结论分析
使用决策树完成学生成绩等级预测,可选取部分或全部特征,分析参数对结果的影响,并进行调参优化,决策树可视化进行调参优化分析
1.数据准备
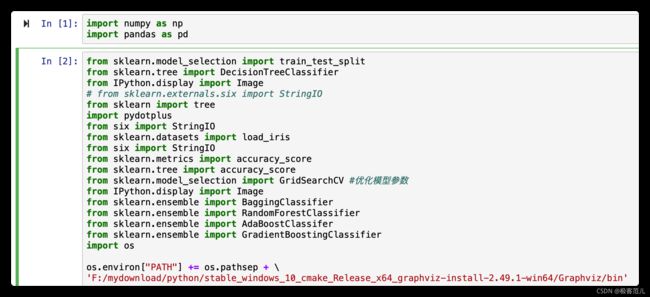
1.1 引入头文件
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from IPython.display import Image
# from sklearn.externals.six import StringIO
from sklearn import tree
import pydotplus
from six import StringIO
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from six import StringIO
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from sklearn.tree import accuracy_score
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV #优化模型参数
from IPython.display import Image
from sklearn.ensemble import BaggingClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifer
from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingClassifier
import os
os.environ["PATH"] += os.pathsep + \
'F:/mydownload/python/stable_windows_10_cmake_Release_x64_graphviz-install-2.49.1-win64/Graphviz/bin'
写入头文件之前,需要下载安装所必须的依赖包。有的无法使用pip安装的内容,使用手动导入依赖的方式.
1.2 把student_1.csv数据拖入代码的同一文件夹下,同时读取文件中的数据。
stu_grade = pd.read_csv('student_1.csv')
stu_grade.head() #只读取df中前五行数据,默认为五行
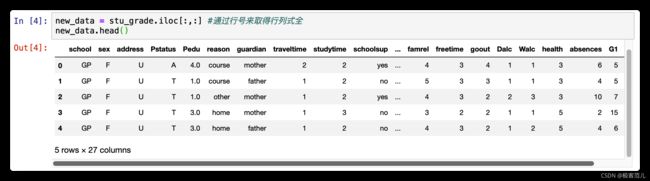
1.3 特征选取
课件中选取16个特征值,这里我采用了所有的特征值进行处理。
new_data = stu_grade.iloc[:,:] #通过行号来取得行列式全
new_data.head()
2.数据处理
2.1 对G1、G2、G3处理
对于离散值进行连续处理,同时设置lambda函数计算G1、G2、G3。
def choice_2(x): #将G1,G2,G3做连续值处理,转换成离散值,然后替换数据
x = int(x) #G1,G2为一阶段成绩和二阶段成绩
if x < 5: #G3为最终成绩
return 'bad'
elif x >= 5 and x < 10:
return 'medium'
elif x >= 10 and x < 15:
return 'good'
else:
return "excellent"
stu_data = new_data.copy()
stu_data['G1'] = pd.Series(map(lambda x:choice_2(x),stu_data['G1']))
stu_data['G2'] = pd.Series(map(lambda x:choice_2(x),stu_data['G2']))
stu_data['G3'] = pd.Series(map(lambda x:choice_2(x),stu_data['G3']))
stu_data.head()
2.2 同样对Pedu参数进行连续值处理。
def choice_3(x): #设置对Pedu的划分,做连续值处理,转化成离散值,然后替换数据
x = int(x)
if x > 3:
return "high"
elif x > 1.5:
return "medium"
else:
return "low"
stu_data["Pedu"] = pd.Series(map(lambda x:choice_3(x),stu_data["Pedu"]))
stu_data.head()
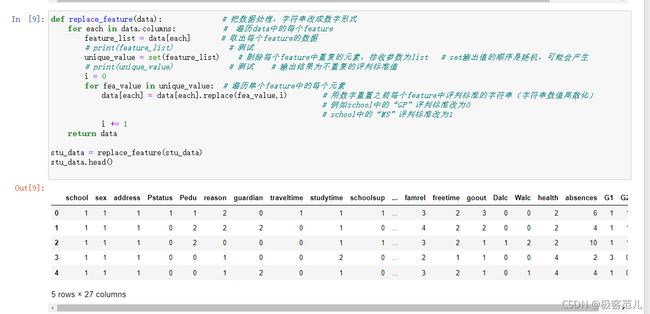
2.3 由于数据集中每个参数差异比较大,所以这里把特征参数统一改为数字形式。
def replace_feature(data): # 把数据处理,字符串改成数字形式
for each in data.colums: # 遍历data中的每个feature
unique_value = set(feature_list) #剔除每个feature中重复的元素,接受参数为list # set输出值的顺序是随机,可能会产生
i = 0
for fea_value in unique_value: #遍历单个feature中的每个元素
data[each] = data[each].replace(fea_value,i) # 用数字重置之前每个feature中评判标准的字符串(字符串数值离散化)
# 例如school中的“GP”评判标准改为0
# school中的"MS"判断标准改为1
i += 1
return data
stu_data = replace_feature(stu_data)
stu_data.head()
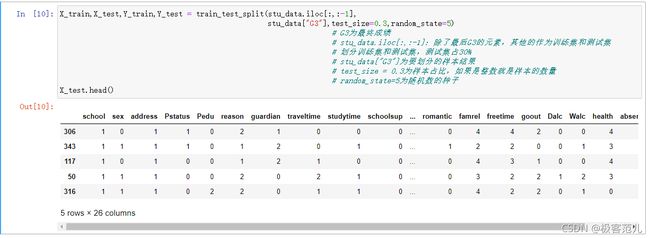
2.4 对于当前处理过的数据集,划分训练集和测试集,并设置好随机种子等其他参数。
X_train,X_test,Y_train,Y_test = train_test_split(stu_data.iloc[:,:-1],
stu_data['G3'],test_size=0.3,random_state=5)
3.训练得到的模型
3.1 决策树
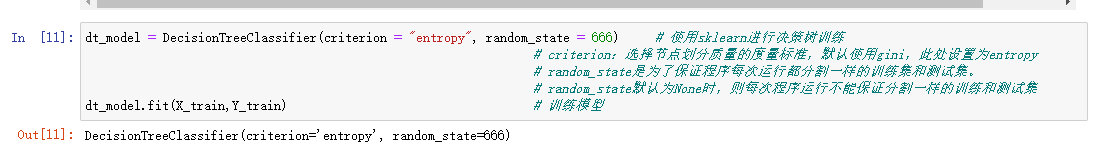
3.1.1 开始对训练集中的数据进行训练。
dt_model = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion = 'entropy',random_state = 666)
dt_model.fit(X_train,Y_train)
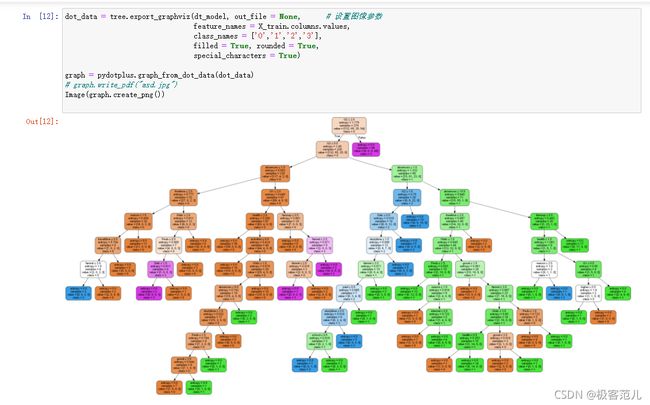
dot_data = tree.export_graphvis(dt_model,out_file = None,
feature_names = X_train,columns.values,
class_names = ['0','1','2','3'],
filled = True, round = True,
special_characters = True)
graph = pydotplus.graph_from_dot_data(dot_data)
# graph.write_pdf("asd.jpg")
Image(graph.create_png())
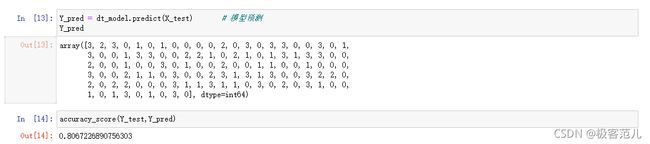
3.1.2 利用已经训练好的模型来预测G3的值。
Y_pred = dt_model.predict(X_test)
Y_pred
accuracy_score(Y_test,Y_pred)
对训练好的模型进行打分。
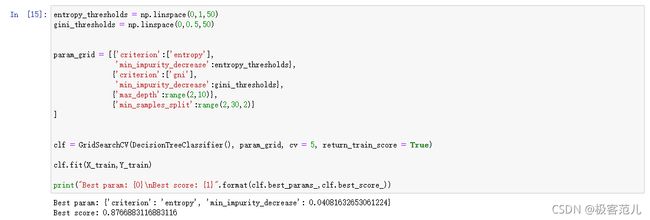
entropy_thresholds = np.linspace(0,1,50)
gini_thresholds = np.linspace(0,0.5,50)
param_grid = [{'criterion:entropy'],'min_impurity_decrease':entropy_thresholds},{'criterion':['gni'],'min_impurity_decrease':gini_thresholds},{'max_depth':range(2,10)},{'min_samples_split':range(2,30,2)}
]
clf = GridSearchCV(DecisionTreeClassifier(),param_grid,cv = 5,return_train_score = True)
clf.fit(X_train,Y_train)
print("Best param: {0}\nBest score: {1}".format(clf.best_params_,clf.best_score_))
3.1.3 对模型中的参数进行优化,输出优化后最好的分数。
clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion = 'entropy',min_impurity_decrease = 0.04081632653061224)
clf.fit(X_train,Y_train)
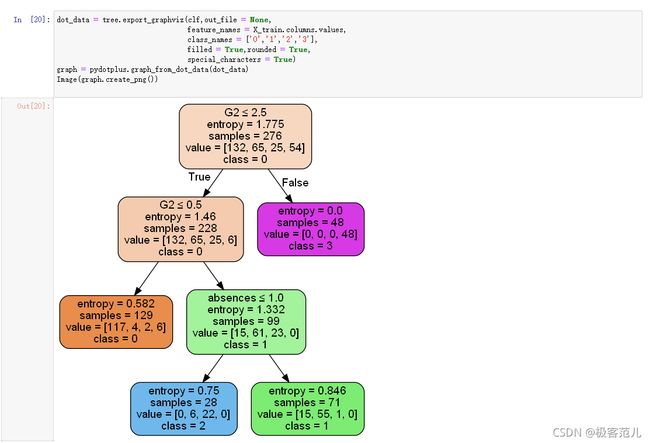
3.1.4 优化后的模型来绘制决策树。
dot_data = tree.export_graphviz(clf,out_file = None,feature_names = X_train.colums.values,class_names = ['0','1','2','3'],
filled = True,rounded = True,
special_characters = True)
graph = pydotplus.graph_from_dot_data(dot_data)
Image(graph.create_png())
输出优化后的分数。
Y_pred1 = clf.predict(X_test)
Y_pred1
accuracy_score(Y_test,Y_pred1)
3.2 集成学习
重新划分数据集用于训练模型。
X_train,X_test,Y_train,Y_test = train_test_split(stu_data,iloc[:,:-1],
stu_data['G3'],test_size=0.3,random_state=35)
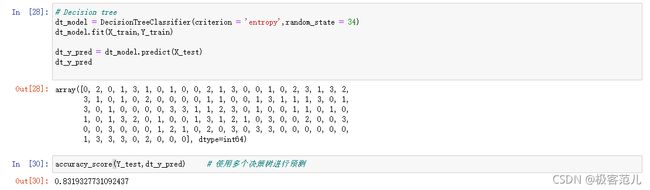
3.2.1 Decision Tree
这里采用集成学习的多个决策树方式进行训练模型,以及模型的评估。
# Decision tree
dt_model = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion = 'entropy',random_state = 34)
dt_model.fit(X_train,Y_train)
dt_y_pred = dt_model.predict(X_test)
dt_y_pred
accuracy_score(Y_test,dt_y_pred) # 使用多个决策树进行预测
3.2.2 Bagging算法
这里采用集成学习的Bagging算法进行训练模型,对模型做出分数估测。
# Bagging
tree = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion = 'entropy',random_state = 34)
bt_model = BaggingClassifier(tree,n_estimators = 100,
max_samples = 1.0,random_state = 34)
# tree是使用的若分类决策树
# n_estimators是若若分类器的个数默认为10
# max_samples是从抽取数据中选择训练样本的数量
# random_state是随机种子数
bt_model.fit(X_train,Y_train)
bt_y_pred = bt_model.predict(X_test)
bt_y_pred
accuracy_score(Y_test,bt_y_pred)
3.2.3 这里采用集成学习的Random Forest算法进行训练模型,对模型做出分数估测。
# Random Forest
rf_model = RandomFrorestClassifier(n_estimators = 100,max_features = None,criterion = 'entropy')
# N_estimators表示为决策树的个数
# max_features表示随机选择特征的个数,默认是特征数的根号
# criterion:随机森林划分特征的方法
rf_model.fit(X_train,Y_train)
rf_y_pred = rf_model.predict(X_test)
rf_y_pred
accuracy_score(Y_test,rf_y_pred)
3.2.4 这里采用集成学习的AdaBoost算法进行训练模型,对模型做出分数估测。
# AdaBoost
ad_model = AdaBoostClassifier(n_estimators = 100,random_state =33) #CART gini
# n_estimators:基分类器提升(循环)次数,默认是50次,这个值过大,模型容易过拟合;值过小,模型容易欠拟合。
ad_model.fit(X_train,Y_train)
ad_y_pred = ad_model.predict(X_test)
ad_y_pred
accuracy_score
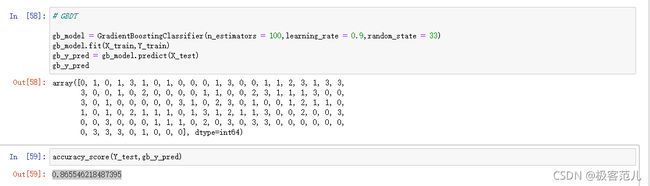
3.2.5 这里采用集成学习的GBDT算法进行训练模型,对模型做出分数估测。
# GBDT
gb_model = GradientBoostingClsaaifier(n_estimators = 100,learning_rate = 0.9,random_state = 33)
gb_model.fit(X_train,Y_train)
gb_y_pred = gb_model.predict(X_test)
gb_y_pred
accuracy_score(Y_test,gb_y_pred)
4.评价结果:
| 模型 | 得分 |
|---|---|
| 决策树(优化前) | 0.806 |
| 决策树(优化后) | 0.848 |
| 多个决策树 | 0.831 |
| Bagging | 0.890 |
| Random Forest | 0.882 |
| AdaBoost | 0.806 |
| GBDT | 0.865 |
5.结论分析
根据决策树和集成学习两大类的训练模型可以看出:两种方式实现各有千秋,同样由优缺点。决策树在优化参数前后预测结果有了较明显的提升,并且有可视化的图片便于观察。集成学习中的Bagging算法对于预测结果是最好的,随之的得分情况也是最高。但是AdaBoost算法的表现就相对不够。