MySQL高级查询
目录
1.聚合查询
1.1 COUNT 函数
1.2 SUM 函数
1.3 AVG 函数
1.4 MAX 函数
1.5 MIN 函数
1.6 ifnull 函数
2.分组查询 GROUP BY
2.1 分组条件查询 HAVING
2.2 SQL 查询关键字执行顺序
3.联合查询(多表查询)
3.1 前置知识—笛卡尔积
3.2 内连接
3.2.1 内连接语法
3.2.3 内连接查询的“问题”
3.3 外连接
3.3.1 语法连接
3.3.2 联表查询中on和where的区别
3.4 自连接
3.5 子查询(嵌套查询)
3.6 合并查询
3.6.1 union
3.6.2 union all
1.聚合查询
常⻅的统计总数、计算平局值等操作,可以使⽤聚合函数来实现,常⻅的聚合函数有:
| 函数 | 说明 |
| COUNT([DISTINCT] expr) | 返回查询到的数据的数量 |
| SUM([DISTINCT] expr) | 返回查询到的数据的总和,不是数字没有意义 |
| AVG([DISTINCT] expr) | 返回查询到的数据的平均值,不是数字没有意义 |
| MAX([DISTINCT] expr) | 返回查询到的数据的最⼤值,不是数字没有意义 |
| MIN([DISTINCT] expr) | 返回查询到的数据的最⼩值,不是数字没有意义 |
1.1 COUNT 函数
返回查询到的数据的条数。
-- 统计班级共有多少同学
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM student;
SELECT COUNT(0) FROM student;
-- 统计班级收集的 qq_mail 有多少个,qq_mail 为 NULL 的数据不会计⼊结果
SELECT COUNT(qq_mail) FROM student;1.2 SUM 函数
返回查询到的数据的总和,不是数字没有意义。
-- 统计数学成绩总分
SELECT SUM(math) FROM exam_result;
-- 不及格 (< 60) 的总分,没有结果,返回 NULL
SELECT SUM(math) FROM exam_result WHERE math < 60;1.3 AVG 函数
返回查询到的数据的平均值,不是数字没有意义。
-- 统计平均总分
SELECT AVG(chinese + math + english) 平均总分 FROM exam_result;1.4 MAX 函数
返回查询到的数据的最⼤值,不是数字没有意义。
-- 返回英语最⾼分
SELECT MAX(english) FROM exam_result;1.5 MIN 函数
返回查询到的数据的最⼩值,不是数字没有意义。
-- 返回 > 70 分以上的数学最低分
SELECT MIN(math) FROM exam_result WHERE math > 70;1.6 ifnull 函数
IFNULL 函数是 MySQL 控制流函数之⼀,它接受两个参数,如果不是 NULL,则返回第⼀个参数,否则 IFNULL 函数返回第⼆个参数。
ifnull 语法如下:
IFNULL(expression_1,expression_2);如果 expression_1 不为 NULL,则 IFNULL 函数返回 expression_1,否则返回 expression_2 的结果。
示例1:
SELECT IFNULL(1,0); -- returns 1IFNULL(1,0)返回1,因为1不为NULL。
示例2:
SELECT IFNULL('',1); -- returns ''IFNULL('',1)返回'',因为''字符串不为NULL。
示例3:
SELECT IFNULL(NULL,'Hello,Null'); -- returns Hello,NullIFNULL(NULL,'IFNULL function')返回IFNULL函数字符串,因为第⼀个参数为NULL。
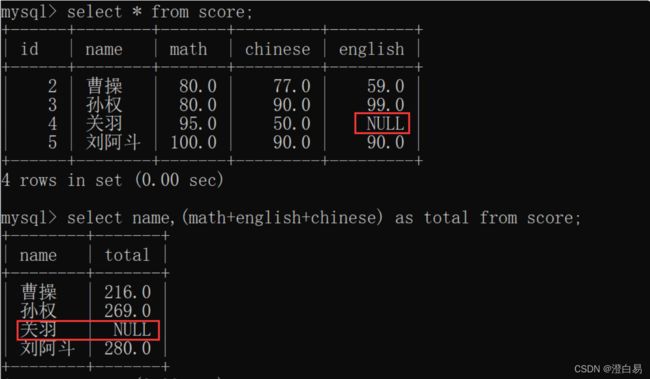
IFNULL函数的实例:
解决总成绩为null的问题:
使⽤ ifnull 函数来解决:
2.分组查询 GROUP BY
SELECT 中使⽤ GROUP BY ⼦句可以对指定列进⾏分组查询。需要满⾜:使⽤ GROUP BY 进⾏分组查询时,SELECT 指定的字段必须是“分组依据字段”,其他字段若想出现在 SELECT 中则必须包含在聚合函数中。
语法:
select column1, sum(column2), .. from table group by column1,column3;案例:
准备测试表及数据:职员表,有id(主键)、name(姓名)、role(⻆⾊)、salary(薪⽔)
create table emp(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20) not null,
role varchar(20) not null,
salary numeric(11,2)
);
insert into emp(name, role, salary) values
('⻢云','服务员', 1000.20),
('⻢化腾','游戏陪玩', 2000.99),
('孙悟空','游戏⻆⾊', 999.11),
('猪⽆能','游戏⻆⾊', 333.5),
('沙和尚','游戏⻆⾊', 700.33),
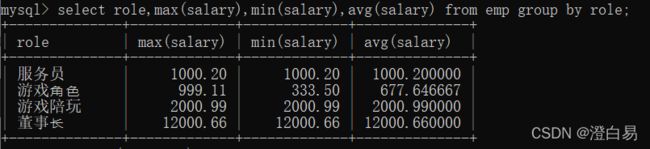
('隔壁⽼王','董事⻓', 12000.66);查询每个⻆⾊的最⾼⼯资、最低⼯资和平均⼯资:
select role,max(salary),min(salary),avg(salary) from emp group by role;2.1 分组条件查询 HAVING
GROUP BY ⼦句进⾏分组以后,需要对分组结果再进⾏条件过滤时,不能使⽤ WHERE 语句,⽽需要⽤ HAVING。
例如:
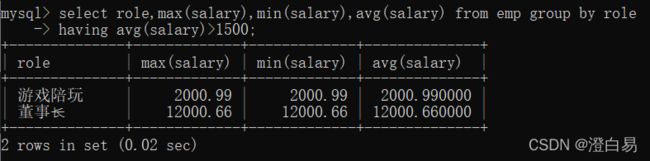
显示平均⼯资低于 1500 的⻆⾊和它的平均⼯资:
select role,max(salary),min(salary),avg(salary) from emp group by role
having avg(salary)>1500;2.2 SQL 查询关键字执行顺序
SQL 查询执⾏先后顺序: group by > having > order by > limit
3.联合查询(多表查询)
3.1 前置知识—笛卡尔积
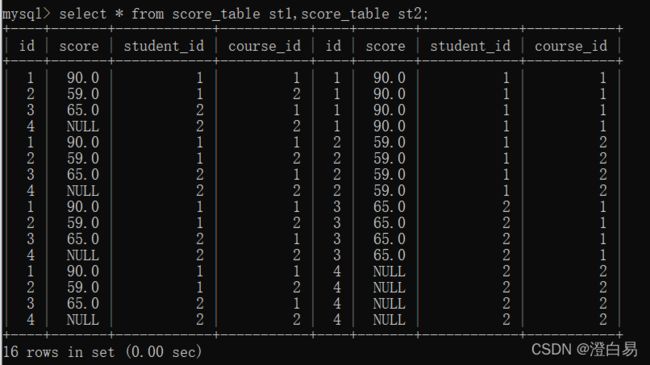
笛卡尔积⼜称直积,表示为 X*Y,⽐如 A 表中的数据为 m ⾏,B 表中的数据有 n ⾏,那么 A 和 B 做笛卡尔积,结果为 m*n ⾏。
⽐如以下表,它们的笛卡尔积就有 9 个:
创建数据库和测试数据
-- 创建班级表
drop table if exists class;
create table class(
id int primary key auto_increment comment '班级编号',
classname varchar(250) not null comment '班级名称'
);
-- 创建学⽣表
drop table if exists student;
create table student(
id int primary key auto_increment comment '学⽣编号',
sn varchar(50) comment '学号',
username varchar(250) not null comment '学⽣名称',
`mail` varchar(250) comment '邮箱',
class_id int,
foreign key (class_id) references class(id)
);
-- 创建课程表
drop table if exists course;
create table course(
id int primary key auto_increment comment '课程编号',
name varchar(250) not null
);
-- 成绩表
drop table if exists score_table;
create table score_table(
id int primary key auto_increment comment '成绩编号',
score decimal(4,1),
student_id int not null,
course_id int not null,
foreign key (student_id) references student(id),
foreign key (course_id) references course(id)
);添加测试数据:
-- 班级表添加数据
insert into class(id,classname) values(1,'Java班级'),(2,'C++班级');
-- 课程表添加数据
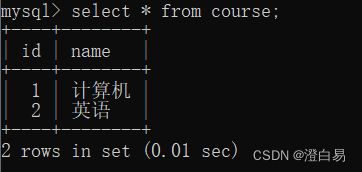
insert into course(id,name) values(1,'计算机'),(2,'英语');
-- 学生表添加数据
insert into student(id,sn,username,mail,class_id) values(1,'CN001','张三','[email protected]',1),(2,'CN002','李四','[email protected]',2),(3,'CN003','王五','[email protected]',1);
-- 成绩表添加数据
insert into score_table(id,score,student_id,course_id) values(1,90,1,1),(2,59,1,2),(3,65,2,1),(4,NULL,2,2);3.2 内连接
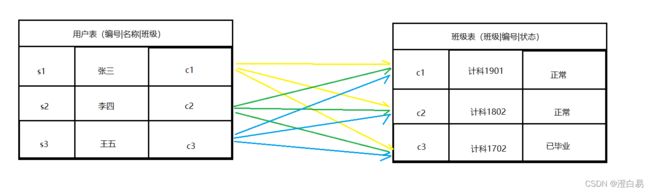
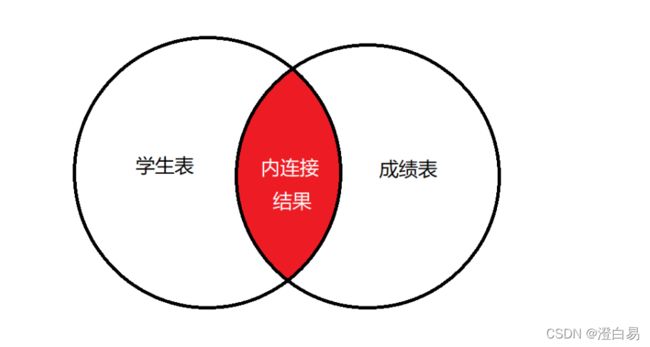
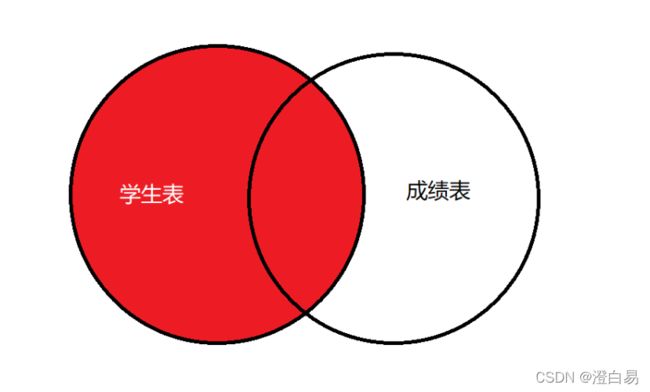
内连接侧重于两个表之间的共性,它的作⽤是使⽤连接,⽐较两个(或多个)表之间的共有数据,然后进⾏返回。
⽐如我要查询学⽣的成绩,涉及到两张表:学⽣表和成绩表,使⽤内连接查询的数据是下图的红⾊部分:
3.2.1 内连接语法
内连接的实现语法如下:
select * from t1 [inner|cross] join t2 [on 过滤条件] [where 过滤条件]内连接的写法有以下 4 种:
- select * from t1 join t2;
- select * from t1 inner join t2;
- select * from t1 cross join t2;
- select * from t1,t2;
主要掌握第1种和第4种就行。
实例:
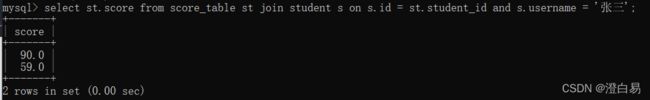
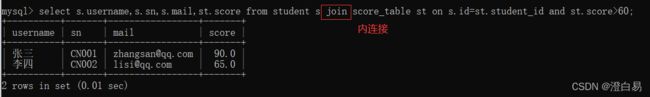
① 查询“张三”的成绩
select st.score from score_table st join student s on s.id=st.student_id
and s.username='张三';或者使⽤以下 3 种查询语句:
-
select st.score from score_table st inner join student s on s.id=st.student_id and s.username='张三'; -
select st.score from score_table st cross join student s on s.id=st.student_id and s.username='张三'; -
select st.score from score_table st,student s where st.student_id=s.id and s.username='张三';
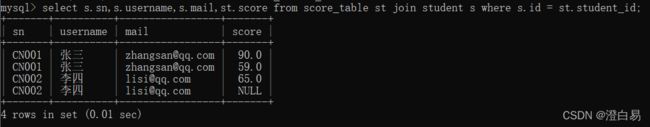
② 查询每个⼈的成绩和个⼈信息
select s.sn,s.username,s.mail,st.score
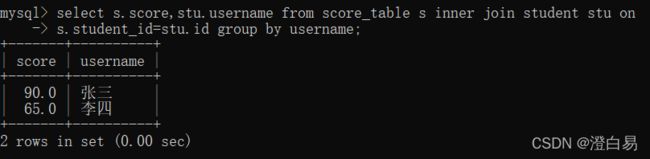
from student s,score_table st where s.id=st.student_id;③ 练习:查询每个⼈的总成绩和个⼈信息
select s.score,stu.username from score_table s inner join student stu on
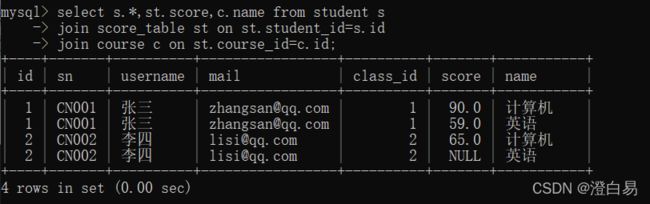
s.student_id=stu.id group by username;④ 查询每个⼈成绩+科⽬名+个⼈信息
这时需要查询三张表
select s.*,st.score,c.name from student s
join score_table st on st.student_id=s.id
join course c on st.course_id=c.id;3.2.3 内连接查询的“问题”
我们发现学⽣表有 3 个⽤户,然⽽使⽤内连接查询的时候,王五同学的数据⼀直没被查询到,王五同学可能是考完试转班过来的,所以只有学⽣表有数据,其他表没有数据。但即使这样,我们也不能漏⼀个⼈,如果其他表为空,成绩可以是 NULL 或者 0,但不能遗漏,这个时候就需要使⽤外连接了。
3.3 外连接
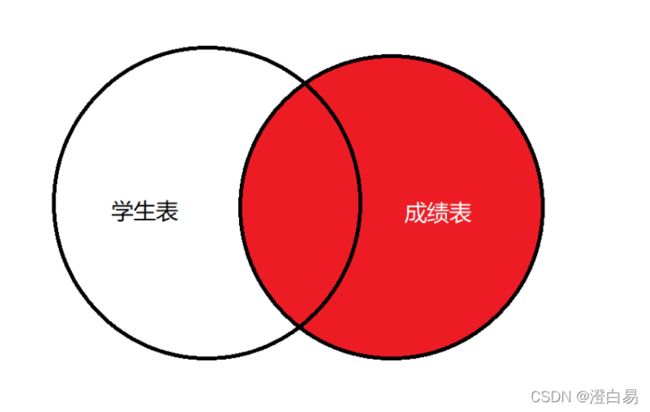
外连接包括内连接和其他⾄少⼀张表的所有满⾜条件的信息,外连接包括:
- 左(外)连接
- 右(外)连接
其中左连接查询的内容如下图红⾊部分:
右连接如下图红⾊部分:
3.3.1 语法连接
左连接语法如下:
select * from t1 left join t2 [on 连接条件];右连接语法如下:
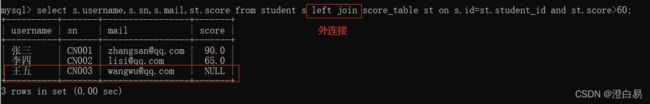
select * from t1 right join t2 [on 连接条件];查询所有⼈的成绩
使⽤左连接查询所有⼈的成绩:
select s.sn,s.username,s.mail,st.score from student s
left join score_table st on s.id=st.student_id;王五的数据也被查出来了。
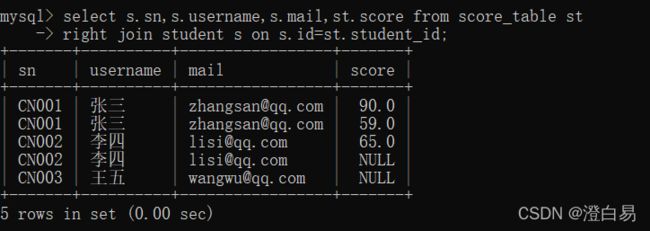
使⽤右连接查询所有⼈的成绩:
select s.sn,s.username,s.mail,st.score from score_table st
right join student s on s.id=st.student_id;3.3.2 联表查询中on和where的区别
区别:
- 内连接的on可以省略,外连接的on不可省略;
外连接不加on报错:
内连接可以不加on: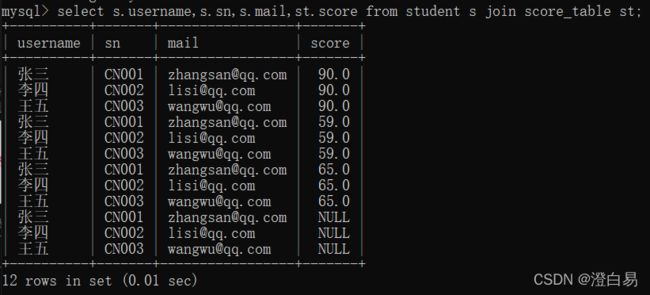
- on在内连接中的执行效果和在外连接中的执行效果是不一样的;
left join on不能过滤掉左表中的信息,而内连接on查询可以过滤掉全局数据。on查询不会对主表中的数据进行过滤。 - 在外连接中on和where是不一样的。
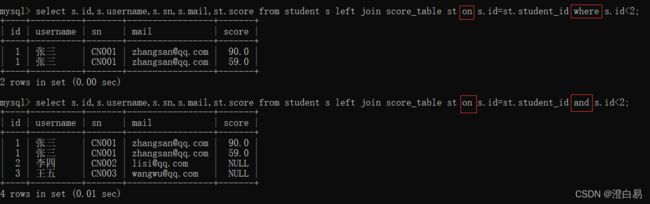
发现只用on查询结果不准确,所以在外连接查询中,要将查询条件的表达式全部写在where表达式中,而非on中。
3.4 自连接
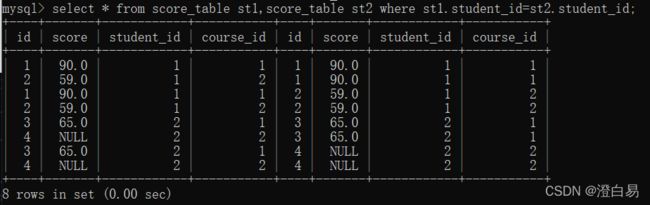
⾃连接是指在同⼀张表连接⾃身进⾏查询。语法与内连接语法一致,两张表都是自身。
语法:
select ... from 表1,表1 where 条件
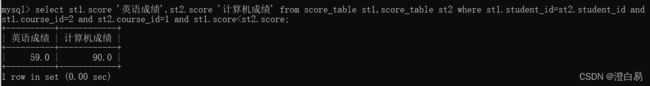
select ... from 表1 join 表1 on 条件举例:查询英语成绩<计算机成绩的数据
实现思路:
3.5 子查询(嵌套查询)
子查询是指嵌⼊在其他 sql 语句中的 select 语句,也叫嵌套查询。 将一个查询结果作为另一个查询的where选项。
语法:
-- 单⾏⼦查询
select ... from 表1 where 字段1 = (select ... from ...);
-- [NOT] IN
select ... from 表1 where 字段1 in (select ... from ...);
-- [NOT] EXISTS
select ... from 表1 where exists (select ... from ... where 条件);
-- 临时表:form⼦句中的⼦查询
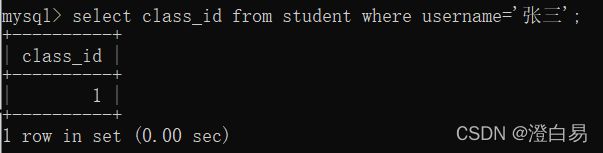
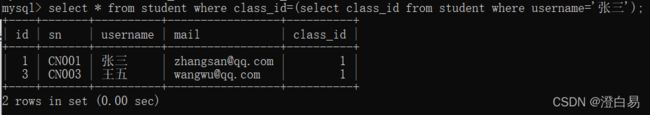
select ... from 表1, (select ... from ...) as tmp where 条件举例:查询张三的同班同学
实现步骤:
3.6 合并查询
合并查询⽤于合并结果集相同的两张(多张)表,它有两个关键字:
- union
- union all
语法:
-- UNION:去除重复数据
select ... from ... where 条件
union
select ... from ... where 条件
-- UNION ALL:不去重
select ... from ... where 条件
union all
select ... from ... where 条件使⽤UNION和UNION ALL时,前后查询的结果集中,字段需要⼀致。
3.6.1 union
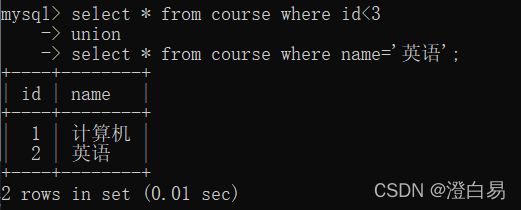
示例:查询 id 小于 3 和名字为“英语”的课程:
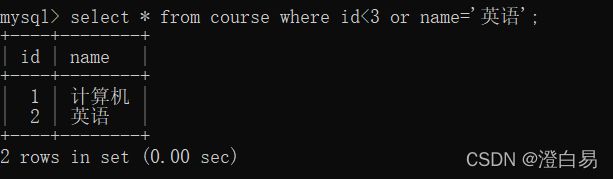
也可以用or来实现:
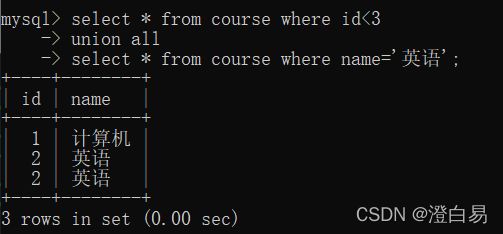
3.6.2 union all
示例:查询 id ⼩于 3,或者名字为“英语”的课程
可以看到结果集中重复出现的数据。