Spring6新特性来了!便捷替代Feign封装RPC接口
spring6的新特性笔者最近也有在研究,其中在HttpServiceProxyFactory服务代理工厂的使用方式体验上,笔者认为极其像是在用Feign编写RPC接口,使用服务代理工厂我们只要在全局配置单例的服务代里工厂bean再维护一个http interface接口就能统一的管理并根据需求去调用这些RPC服务了,不再像Feign服务调用以及dubbo服务注册与服务发现以及服务引入,soa服务暴露与引入,在进行远程调用前还要进行必要的配置。免去了相当一部分的繁琐操作。
尝鲜版demo
1、首先我们要拥有一台已经启动且正在等待我们远程调用的实例,并且你已经排除了潜在的远程调用问题(跨域,拦截器等可能导致远程调用请求失败的原因)
我这里准备了一个springboot实例,提供一个请求方法为get的接口:
@GetMapping("/getAllAirQualityIndex")
@ResponseBody
public ResponseMessage> getAllAirQualityIndex() {
List airQualityIndices = airQualityIndexService.selectAll();
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(airQualityIndices)) {
return ResponseMessage.success(null, "监测记录为空");
}
List result = new ArrayList<>(airQualityIndices.size());
airQualityIndices.forEach(airQualityIndex -> {
District district = districtService.selectEntityByPrimaryKey(airQualityIndex.getDistrictid());
if (Objects.isNull(district)) {
throw new RuntimeException("区域信息获取失败");
}
AirQualityIndexDTO airQualityIndexDTO = AirQualityIndexDTO.fillValue(airQualityIndex, district);
result.add(airQualityIndexDTO);
});
return ResponseMessage.success(result, "获取全部监测记录成功");
} 这里请读者牢记:接口URI为:
http://127.0.0.1:9000/getAllAirQualityIndex
后续编写接口会用到。
2、愉快的进行编写调用方实例,这里调用方直接拿被调用方的接口数据就行(不搭建三层了,嫌麻烦)
注意:
1、调用方项目的springboot版本为3.0.0或以上,需要引入下面的依赖;
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-webflux
io.projectreactor
reactor-test
test
2、JDK版本在17或以上;
3、不要轻易的相信@Resource注解去引入组件,因为import的包名可能不是javax嗷~~;
4、不要尝试在同一台实例内部进行远程调用(会报出连接被拒)
编写服务调用的接口
public interface Api {
@GetExchange(value = "/getRpcInfo")
RpcInfo getRpcInfo( );
@HttpExchange(value = "/getRpcInfo",method = "GET")
RpcInfo getRpc();
@GetExchange("/getAllAirQualityIndex")
Object getAirList();
}这里注意@GetExchange注解的使用和@GetMapping使用的方式几乎一毛一样,只不过你这里的value都必须要是远程调用的接口名(别配上了协议ip端口前缀)
配置全局单例服务代理bean组件
@SpringBootApplication
public class CloudHttpInterfaceApplication {
@Bean("HttpInterface")
@Scope(value = "singleton")
public HttpServiceProxyFactory getHttpFactory() {
return HttpServiceProxyFactory
.builder(WebClientAdapter
.forClient(WebClient.builder()
.baseUrl("http://localhost:9000/")
.build())).build();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(CloudHttpInterfaceApplication.class, args);
}
}这里不难发现我把url(http://localhost:9000/)配置在这个组件里了,如果调用的远程实例不止一台,我们可以维护一个map对象,key是实例名,value就是它的实例地址,编写一个适配器去根据你传回的参数适配你想调用的远程实例地址去构造组件,当然这样的话组件的作用域也就仅仅在请求上了。
编写简单的API适配器(没啥好处,维护map改进逻辑就还行)
@Configuration
@DependsOn({"HttpInterface"})
public class ServiceAdapter {
@Qualifier("HttpInterface")
@Autowired
HttpServiceProxyFactory httpServiceProxyFactory;
public T getServiceApi(Class serviceClazz){
return httpServiceProxyFactory.createClient(serviceClazz);
}
} 这里提一下注解@DependsOn的作用是实例化当前组件之前先实例化注解中的组件,当项目中的组件存在严格的依赖关系时,必须要先实例化底层组件再实例化上层组件。类似的注解还有@Order、@Conditional(在实例化当前组件时检查某类型的组件是否已经存在)及其衍生注解。
编写测试用例
@Autowired
ServiceAdapter serviceAdapter;
@Test
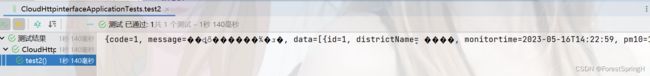
public void test2(){
Object airList = serviceAdapter.getServiceApi(Api.class).getAirList();
System.out.println(airList);
}测试结果
调用方控制台打印:
被调用方日志文件输出:
这里我们通过spring6提供的HTTP服务代理工厂的方式搭建了一个最基础的demo展示它的作用,只能说体验比Feign好!