spdk记录
spdk记录
- hello_bdev
-
- 命令行参数
- 示例函数
- 文档摘录
往期文章:
spdk环境搭建
hello_bdev
代码路径:examples/bdev/hello_world/hello_bdev.c
可执行文件路径:build/examples/hello_bdev
刚开始直接执行hello_bdev显示找不到Malloc0
./build/examples/hello_bdev
[2023-05-30 20:27:02.389489] Starting SPDK v23.05-pre git sha1 ee06693c3 / DPDK 22.11.1 initialization...
[2023-05-30 20:27:02.390910] [ DPDK EAL parameters: hello_bdev --no-shconf -c 0x1 --huge-unlink --log-level=lib.eal:6 --log-level=lib.cryptodev:5 --log-level=user1:6 --iova-mode=pa --base-virtaddr=0x200000000000 --match-allocations --file-prefix=spdk_pid11584 ]
TELEMETRY: No legacy callbacks, legacy socket not created
[2023-05-30 20:27:02.511380] app.c: 738:spdk_app_start: *NOTICE*: Total cores available: 1
[2023-05-30 20:27:02.561201] reactor.c: 937:reactor_run: *NOTICE*: Reactor started on core 0
[2023-05-30 20:27:02.600284] accel_sw.c: 601:sw_accel_module_init: *NOTICE*: Accel framework software module initialized.
[2023-05-30 20:27:02.621229] hello_bdev.c: 222:hello_start: *NOTICE*: Successfully started the application
[2023-05-30 20:27:02.621612] hello_bdev.c: 231:hello_start: *NOTICE*: Opening the bdev Malloc0
[2023-05-30 20:27:02.621691] bdev.c:7681:spdk_bdev_open_ext: *NOTICE*: Currently unable to find bdev with name: Malloc0
[2023-05-30 20:27:02.621761] hello_bdev.c: 235:hello_start: *ERROR*: Could not open bdev: Malloc0
[2023-05-30 20:27:02.621852] app.c: 844:spdk_app_stop: *WARNING*: spdk_app_stop'd on non-zero
[2023-05-30 20:27:02.691191] hello_bdev.c: 308:main: *ERROR*: ERROR starting application
在网上找到了相应issue,https://github.com/spdk/spdk/issues/1550

正确的执行方式为:
./build/examples/hello_bdev -c ./examples/bdev/hello_world/bdev.json -b Malloc0
[2023-05-30 20:25:59.131197] Starting SPDK v23.05-pre git sha1 ee06693c3 / DPDK 22.11.1 initialization...
[2023-05-30 20:25:59.132037] [ DPDK EAL parameters: hello_bdev --no-shconf -c 0x1 --huge-unlink --log-level=lib.eal:6 --log-level=lib.cryptodev:5 --log-level=user1:6 --iova-mode=pa --base-virtaddr=0x200000000000 --match-allocations --file-prefix=spdk_pid11462 ]
TELEMETRY: No legacy callbacks, legacy socket not created
[2023-05-30 20:25:59.252268] app.c: 738:spdk_app_start: *NOTICE*: Total cores available: 1
[2023-05-30 20:25:59.303646] reactor.c: 937:reactor_run: *NOTICE*: Reactor started on core 0
[2023-05-30 20:25:59.359161] accel_sw.c: 601:sw_accel_module_init: *NOTICE*: Accel framework software module initialized.
[2023-05-30 20:25:59.387635] hello_bdev.c: 222:hello_start: *NOTICE*: Successfully started the application
[2023-05-30 20:25:59.388053] hello_bdev.c: 231:hello_start: *NOTICE*: Opening the bdev Malloc0
[2023-05-30 20:25:59.388153] hello_bdev.c: 244:hello_start: *NOTICE*: Opening io channel
[2023-05-30 20:25:59.388529] hello_bdev.c: 138:hello_write: *NOTICE*: Writing to the bdev
[2023-05-30 20:25:59.388757] hello_bdev.c: 117:write_complete: *NOTICE*: bdev io write completed successfully
[2023-05-30 20:25:59.388931] hello_bdev.c: 84:hello_read: *NOTICE*: Reading io
[2023-05-30 20:25:59.389019] hello_bdev.c: 65:read_complete: *NOTICE*: Read string from bdev : Hello World!
[2023-05-30 20:25:59.389128] hello_bdev.c: 74:read_complete: *NOTICE*: Stopping app
命令行参数
-b参数
static char *g_bdev_name = "Malloc0";
/*
* Usage function for printing parameters that are specific to this application
*/
static void
hello_bdev_usage(void)
{
printf(" -b name of the bdev to use\n" );
}
/*
* This function is called to parse the parameters that are specific to this application
*/
static int
hello_bdev_parse_arg(int ch, char *arg)
{
switch (ch) {
case 'b':
g_bdev_name = arg;
break;
default:
return -EINVAL;
}
return 0;
}
spdk_app_parse_args(argc, argv, &opts, "b:", NULL, hello_bdev_parse_arg, hello_bdev_usage)
hello_context.bdev_name = g_bdev_name;
可以看出,g_bdev_name本来就是Malloc0,-b Malloc0没啥用
-c参数
static void
usage(void (*app_usage)(void))
{
printf("%s [options]\n", g_executable_name);
printf("options:\n");
printf(" -c, --config JSON config file (default %s)\n" ,
g_default_opts.json_config_file != NULL ? g_default_opts.json_config_file : "none");
-c后加json配置文件名,bdev.json文件内容如下:
{
"subsystems": [
{
"subsystem": "bdev",
"config": [
{
"method": "bdev_malloc_create",
"params": {
"name": "Malloc0",
"num_blocks": 32768,
"block_size": 512
}
}
]
}
]
}
简要看json的解析过程,全局查询json_config_file,找到spdk_subsystem_init_from_json_config函数
void
spdk_subsystem_init_from_json_config(const char *json_config_file, const char *rpc_addr,
spdk_subsystem_init_fn cb_fn, void *cb_arg,
bool stop_on_error)
{
struct load_json_config_ctx *ctx = calloc(1, sizeof(*ctx));
int rc;
assert(cb_fn);
if (!ctx) {
cb_fn(-ENOMEM, cb_arg);
return;
}
ctx->cb_fn = cb_fn;
ctx->cb_arg = cb_arg;
ctx->stop_on_error = stop_on_error;
ctx->thread = spdk_get_thread();
rc = app_json_config_read(json_config_file, ctx);
if (rc) {
goto fail;
}
/* Capture subsystems array */
rc = spdk_json_find_array(ctx->values, "subsystems", NULL, &ctx->subsystems);
switch (rc) {
case 0:
/* Get first subsystem */
ctx->subsystems_it = spdk_json_array_first(ctx->subsystems);
if (ctx->subsystems_it == NULL) {
SPDK_NOTICELOG("'subsystems' configuration is empty\n");
}
break;
case -EPROTOTYPE:
SPDK_ERRLOG("Invalid JSON configuration: not enclosed in {}.\n");
goto fail;
case -ENOENT:
SPDK_WARNLOG("No 'subsystems' key JSON configuration file.\n");
break;
case -EDOM:
SPDK_ERRLOG("Invalid JSON configuration: 'subsystems' should be an array.\n");
goto fail;
default:
SPDK_ERRLOG("Failed to parse JSON configuration.\n");
goto fail;
}
/* If rpc_addr is not an Unix socket use default address as prefix. */
if (rpc_addr == NULL || rpc_addr[0] != '/') {
rpc_addr = SPDK_DEFAULT_RPC_ADDR;
}
/* FIXME: rpc client should use socketpair() instead of this temporary socket nonsense */
rc = snprintf(ctx->rpc_socket_path_temp, sizeof(ctx->rpc_socket_path_temp), "%s.%d_config",
rpc_addr, getpid());
if (rc >= (int)sizeof(ctx->rpc_socket_path_temp)) {
SPDK_ERRLOG("Socket name create failed\n");
goto fail;
}
rc = spdk_rpc_initialize(ctx->rpc_socket_path_temp);
if (rc) {
goto fail;
}
ctx->client_conn = spdk_jsonrpc_client_connect(ctx->rpc_socket_path_temp, AF_UNIX);
if (ctx->client_conn == NULL) {
SPDK_ERRLOG("Failed to connect to '%s'\n", ctx->rpc_socket_path_temp);
goto fail;
}
rpc_client_set_timeout(ctx, RPC_CLIENT_CONNECT_TIMEOUT_US);
ctx->client_conn_poller = SPDK_POLLER_REGISTER(rpc_client_connect_poller, ctx, 100);
return;
fail:
app_json_config_load_done(ctx, -EINVAL);
}
全局查询bdev_malloc_create,找到rpc_bdev_malloc_create函数
static void
rpc_bdev_malloc_create(struct spdk_jsonrpc_request *request,
const struct spdk_json_val *params)
{
struct malloc_bdev_opts req = {NULL};
struct spdk_json_write_ctx *w;
struct spdk_bdev *bdev;
int rc = 0;
if (spdk_json_decode_object(params, rpc_construct_malloc_decoders,
SPDK_COUNTOF(rpc_construct_malloc_decoders),
&req)) {
SPDK_DEBUGLOG(bdev_malloc, "spdk_json_decode_object failed\n");
spdk_jsonrpc_send_error_response(request, SPDK_JSONRPC_ERROR_INTERNAL_ERROR,
"spdk_json_decode_object failed");
goto cleanup;
}
rc = create_malloc_disk(&bdev, &req);
if (rc) {
spdk_jsonrpc_send_error_response(request, rc, spdk_strerror(-rc));
goto cleanup;
}
free_rpc_construct_malloc(&req);
w = spdk_jsonrpc_begin_result(request);
spdk_json_write_string(w, spdk_bdev_get_name(bdev));
spdk_jsonrpc_end_result(request, w);
return;
cleanup:
free_rpc_construct_malloc(&req);
}
SPDK_RPC_REGISTER("bdev_malloc_create", rpc_bdev_malloc_create, SPDK_RPC_RUNTIME)
运行到该函数的回溯栈为
(gdb) bt
#0 rpc_bdev_malloc_create (request=0xcac1f474c379e400, params=0x555555cc9570) at bdev_malloc_rpc.c:49
#1 0x00005555556b0a53 in jsonrpc_handler (request=0x555555cc04e0, method=0x555555c648e0, params=0x555555c64900) at rpc.c:124
#2 0x00005555556b2c5e in jsonrpc_server_handle_request (request=0x555555cc04e0, method=0x555555c648e0, params=0x555555c64900) at jsonrpc_server_tcp.c:222
#3 0x00005555556b1665 in parse_single_request (request=0x555555cc04e0, values=0x555555c64880) at jsonrpc_server.c:75
#4 0x00005555556b1c68 in jsonrpc_parse_request (conn=0x7ffff5f7e040, json=0x7ffff5f7e058, size=172) at jsonrpc_server.c:205
#5 0x00005555556b2eaa in jsonrpc_server_conn_recv (conn=0x7ffff5f7e040) at jsonrpc_server_tcp.c:284
#6 0x00005555556b3297 in spdk_jsonrpc_server_poll (server=0x7ffff5f7e010) at jsonrpc_server_tcp.c:402
#7 0x00005555556b0d59 in spdk_rpc_accept () at rpc.c:213
#8 0x00005555556a13c4 in rpc_subsystem_poll (arg=0x0) at rpc.c:21
#9 0x00005555556a82fd in thread_execute_timed_poller (thread=0x555555c9ec00, poller=0x555555cbf2c0, now=41542509569737) at thread.c:970
#10 0x00005555556a8613 in thread_poll (thread=0x555555c9ec00, max_msgs=0, now=41542509569737) at thread.c:1060
#11 0x00005555556a8837 in spdk_thread_poll (thread=0x555555c9ec00, max_msgs=0, now=41542509569737) at thread.c:1119
#12 0x000055555566d309 in _reactor_run (reactor=0x555555c7b780) at reactor.c:914
#13 0x000055555566d3fb in reactor_run (arg=0x555555c7b780) at reactor.c:952
#14 0x000055555566d887 in spdk_reactors_start () at reactor.c:1068
#15 0x0000555555669c5d in spdk_app_start (opts_user=0x7fffffffdea0, start_fn=0x55555556e1fb <hello_start>, arg1=0x7fffffffde40) at app.c:779
#16 0x000055555556e5d9 in main (argc=5, argv=0x7fffffffe078) at hello_bdev.c:306
p req
$19 = {name = 0x555555cc9580 "Malloc0", uuid = {u = {raw = '\000' <repeats 15 times>}}, num_blocks = 32768, block_size = 512, physical_block_size = 0, optimal_io_boundary = 0, md_size = 0,
md_interleave = false, dif_type = SPDK_DIF_DISABLE, dif_is_head_of_md = false}
猜测rpc_bdev_malloc_create函数与spdk_subsystem_init_from_json_config中的
SPDK_POLLER_REGISTER(rpc_client_connect_poller, ctx, 100);有关。
有兴趣的可以继续研究rpc_bdev_malloc_create函数中的create_malloc_disk函数
示例函数
hello_bdev.c中的代码逻辑比较简单,执行顺序为
spdk_app_start
hello_start
hello_write
write_complete
hello_read
read_complete
与spdk/examples/nvme/hello_world/hello_world.c中做的事情类似
hello_start函数首先通过spdk_bdev_open_ext得到文件描述符,而后获取bdev设备,IO通道,申请缓冲区,写入"Hello World!\n",调用spdk_bdev_write将缓冲区数据写入Malloc0设备,偏移量为0,写完成后重置缓冲区数据,调用spdk_bdev_read读取相同位置数据,读完成后打印返回数据,释放之前申请的IO通道,块设备描述符。
简要分析hello_write的调用过程
// 函数调用栈
(gdb) bt
#0 _sw_accel_copy_iovs (dst_iovs=0x555555cca0b8, dst_iovcnt=1, src_iovs=0x555555cca0a8, src_iovcnt=1) at accel_sw.c:115
#1 0x0000555555696577 in sw_accel_submit_tasks (ch=0x555555dadfd0, accel_task=0x555555cc9fb0) at accel_sw.c:455
#2 0x000055555568e5a2 in accel_submit_task (accel_ch=0x555555e51190, task=0x555555cc9fb0) at accel.c:305
#3 0x000055555568e723 in spdk_accel_submit_copy (ch=0x555555e51130, dst=0x200016600000, src=0x2000162efd00, nbytes=512, flags=0, cb_fn=0x55555556e83f <malloc_done>, cb_arg=0x200010aa2ae0) at accel.c:340
#4 0x000055555556eec4 in bdev_malloc_writev (mdisk=0x555555cc95c0, ch=0x555555e51130, task=0x200010aa2ae0, iov=0x200010aa2710, iovcnt=1, len=512, offset=0, md_buf=0x0, md_len=0, md_offset=0) at bdev_malloc.c:277
#5 0x000055555556f43b in _bdev_malloc_submit_request (mch=0x555555e50e60, bdev_io=0x200010aa2700) at bdev_malloc.c:382
#6 0x000055555556f69c in bdev_malloc_submit_request (ch=0x555555e50e00, bdev_io=0x200010aa2700) at bdev_malloc.c:457
#7 0x0000555555674c66 in bdev_submit_request (bdev=0x555555cc95c0, ioch=0x555555e50e00, bdev_io=0x200010aa2700) at bdev.c:1297
#8 0x000055555567784d in bdev_io_do_submit (bdev_ch=0x555555e50d50, bdev_io=0x200010aa2700) at bdev.c:2477
#9 0x000055555567947a in _bdev_io_submit (ctx=0x200010aa2700) at bdev.c:3173
#10 0x0000555555679a48 in bdev_io_submit (bdev_io=0x200010aa2700) at bdev.c:3293
#11 0x000055555567e0f7 in bdev_write_blocks_with_md (desc=0x555555e50b60, ch=0x555555e50cf0, buf=0x2000162efd00, md_buf=0x0, offset_blocks=0, num_blocks=1, cb=0x55555556dd5e <write_complete>, cb_arg=0x7fffffffde40) at bdev.c:5195
#12 0x000055555567e1df in spdk_bdev_write_blocks (desc=0x555555e50b60, ch=0x555555e50cf0, buf=0x2000162efd00, offset_blocks=0, num_blocks=1, cb=0x55555556dd5e <write_complete>, cb_arg=0x7fffffffde40) at bdev.c:5219
#13 0x000055555567e188 in spdk_bdev_write (desc=0x555555e50b60, ch=0x555555e50cf0, buf=0x2000162efd00, offset=0, nbytes=512, cb=0x55555556dd5e <write_complete>, cb_arg=0x7fffffffde40) at bdev.c:5211
#14 0x000055555556decc in hello_write (arg=0x7fffffffde40) at hello_bdev.c:139
#15 0x000055555556e4d3 in hello_start (arg1=0x7fffffffde40) at hello_bdev.c:276
#16 0x00005555556683f7 in app_start_application () at app.c:264
#17 0x0000555555668478 in app_start_rpc (rc=0, arg1=0x0) at app.c:285
#18 0x000055555569f259 in app_json_config_load_done (ctx=0x555555c9f000, rc=0) at json_config.c:111
#19 0x000055555569ffa6 in app_json_config_load_subsystem (_ctx=0x555555c9f000) at json_config.c:473
#20 0x00005555556a7bd0 in msg_queue_run_batch (thread=0x555555c9ec00, max_msgs=8) at thread.c:804
#21 0x00005555556a8528 in thread_poll (thread=0x555555c9ec00, max_msgs=0, now=121496004745246) at thread.c:1026
#22 0x00005555556a8837 in spdk_thread_poll (thread=0x555555c9ec00, max_msgs=0, now=121496004745246) at thread.c:1119
#23 0x000055555566d309 in _reactor_run (reactor=0x555555c7b780) at reactor.c:914
#24 0x000055555566d3fb in reactor_run (arg=0x555555c7b780) at reactor.c:952
#25 0x000055555566d887 in spdk_reactors_start () at reactor.c:1068
#26 0x0000555555669c5d in spdk_app_start (opts_user=0x7fffffffdea0, start_fn=0x55555556e1fb <hello_start>, arg1=0x7fffffffde40) at app.c:779
#27 0x000055555556e5d9 in main (argc=5, argv=0x7fffffffe078) at hello_bdev.c:306
追溯到最后,就是使用memcpy拷贝数据,那么src与dst分别是什么呢
static void
_sw_accel_copy_iovs(struct iovec *dst_iovs, uint32_t dst_iovcnt,
struct iovec *src_iovs, uint32_t src_iovcnt)
{
struct spdk_ioviter iter;
void *src, *dst;
size_t len;
for (len = spdk_ioviter_first(&iter, src_iovs, src_iovcnt,
dst_iovs, dst_iovcnt, &src, &dst);
len != 0;
len = spdk_ioviter_next(&iter, &src, &dst)) {
memcpy(dst, src, len);
}
}
src为hello_context->buff,dst为mdisk->malloc_buf + offset,故在Malloc bdev中写入数据只是简单地将数据拷贝到bdev相应的缓冲区,没看到sq cq之类的操作。
(gdb) p src
$11 = (void *) 0x2000162efd00
(gdb) p dst
$12 = (void *) 0x200016600000
(gdb) p len
$13 = 512
(gdb) f 4
#4 0x000055555556eec4 in bdev_malloc_writev (mdisk=0x555555cc95c0, ch=0x555555e51130, task=0x200010aa2ae0, iov=0x200010aa2710, iovcnt=1, len=512, offset=0, md_buf=0x0, md_len=0, md_offset=0) at bdev_malloc.c:277
277 res = spdk_accel_submit_copy(ch, dst, iov[i].iov_base,
(gdb) p mdisk->malloc_buf + offset
$14 = (void *) 0x200016600000
(gdb) f 13
#13 0x000055555567e188 in spdk_bdev_write (desc=0x555555e50b60, ch=0x555555e50cf0, buf=0x2000162efd00, offset=0, nbytes=512, cb=0x55555556dd5e <write_complete>, cb_arg=0x7fffffffde40) at bdev.c:5211
5211 return spdk_bdev_write_blocks(desc, ch, buf, offset_blocks, num_blocks, cb, cb_arg);
(gdb) p buf
$15 = (void *) 0x2000162efd00
在调用栈需要特别关注的就是bdev_write_blocks_with_md函数,在这个函数中创建了spdk_bdev_io结构体,当一个IO请求完成,都会调用spdk_bdev_free_io释放对应空间
static int
bdev_write_blocks_with_md(struct spdk_bdev_desc *desc, struct spdk_io_channel *ch,
void *buf, void *md_buf, uint64_t offset_blocks, uint64_t num_blocks,
spdk_bdev_io_completion_cb cb, void *cb_arg)
{
struct spdk_bdev *bdev = spdk_bdev_desc_get_bdev(desc);
struct spdk_bdev_io *bdev_io;
struct spdk_bdev_channel *channel = __io_ch_to_bdev_ch(ch);
if (!desc->write) {
return -EBADF;
}
if (!bdev_io_valid_blocks(bdev, offset_blocks, num_blocks)) {
return -EINVAL;
}
bdev_io = bdev_channel_get_io(channel);
if (!bdev_io) {
return -ENOMEM;
}
// 设置IO请求信息
bdev_io->internal.ch = channel;
bdev_io->internal.desc = desc;
bdev_io->type = SPDK_BDEV_IO_TYPE_WRITE;
bdev_io->u.bdev.iovs = &bdev_io->iov;
bdev_io->u.bdev.iovs[0].iov_base = buf;
bdev_io->u.bdev.iovs[0].iov_len = num_blocks * bdev->blocklen;
bdev_io->u.bdev.iovcnt = 1;
bdev_io->u.bdev.md_buf = md_buf;
bdev_io->u.bdev.num_blocks = num_blocks;
bdev_io->u.bdev.offset_blocks = offset_blocks;
bdev_io->u.bdev.memory_domain = NULL;
bdev_io->u.bdev.memory_domain_ctx = NULL;
bdev_io->u.bdev.accel_sequence = NULL;
bdev_io_init(bdev_io, bdev, cb_arg, cb); // 设置回调函数
bdev_io_submit(bdev_io);
return 0;
}
函数调用中有几次都通过函数指针跳转,最关键的即为bdev_submit_request->bdev_malloc_submit_reques
static inline void
bdev_submit_request(struct spdk_bdev *bdev, struct spdk_io_channel *ioch,
struct spdk_bdev_io *bdev_io)
{
/* After a request is submitted to a bdev module, the ownership of an accel sequence
* associated with that bdev_io is transferred to the bdev module. So, clear the internal
* sequence pointer to make sure we won't touch it anymore. */
if ((bdev_io->type == SPDK_BDEV_IO_TYPE_WRITE ||
bdev_io->type == SPDK_BDEV_IO_TYPE_READ) && bdev_io->u.bdev.accel_sequence != NULL) {
assert(!bdev_io_needs_sequence_exec(bdev_io->internal.desc, bdev_io));
bdev_io->internal.accel_sequence = NULL;
}
bdev->fn_table->submit_request(ioch, bdev_io);
}
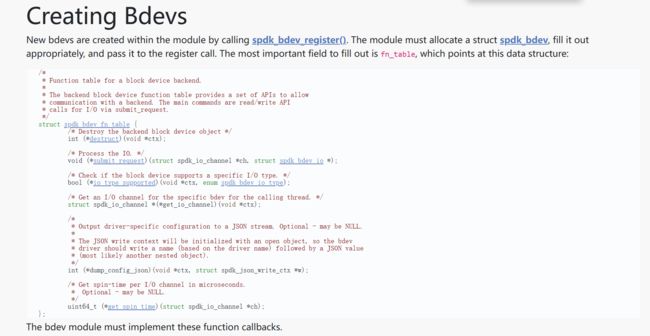
其中spdk_bdev_fn_table结构体定义为
/**
* Function table for a block device backend.
*
* The backend block device function table provides a set of APIs to allow
* communication with a backend. The main commands are read/write API
* calls for I/O via submit_request.
*/
struct spdk_bdev_fn_table {
/** Destroy the backend block device object */
int (*destruct)(void *ctx);
/** Process the IO. */
void (*submit_request)(struct spdk_io_channel *ch, struct spdk_bdev_io *);
/** Check if the block device supports a specific I/O type. */
bool (*io_type_supported)(void *ctx, enum spdk_bdev_io_type);
/** Get an I/O channel for the specific bdev for the calling thread. */
struct spdk_io_channel *(*get_io_channel)(void *ctx);
/**
* Output driver-specific information to a JSON stream. Optional - may be NULL.
*
* The JSON write context will be initialized with an open object, so the bdev
* driver should write a name (based on the driver name) followed by a JSON value
* (most likely another nested object).
*/
int (*dump_info_json)(void *ctx, struct spdk_json_write_ctx *w);
/**
* Output bdev-specific RPC configuration to a JSON stream. Optional - may be NULL.
*
* This function should only be implemented for bdevs which can be configured
* independently of other bdevs. For example, RPCs to create a bdev for an NVMe
* namespace may not be generated by this function, since enumerating an NVMe
* namespace requires attaching to an NVMe controller, and that controller may
* contain multiple namespaces. The spdk_bdev_module's config_json function should
* be used instead for these cases.
*
* The JSON write context will be initialized with an open object, so the bdev
* driver should write all data necessary to recreate this bdev by invoking
* constructor method. No other data should be written.
*/
void (*write_config_json)(struct spdk_bdev *bdev, struct spdk_json_write_ctx *w);
/** Get spin-time per I/O channel in microseconds.
* Optional - may be NULL.
*/
uint64_t (*get_spin_time)(struct spdk_io_channel *ch);
/** Get bdev module context. */
void *(*get_module_ctx)(void *ctx);
/** Get memory domains used by bdev. Optional - may be NULL.
* Vbdev module implementation should call \ref spdk_bdev_get_memory_domains for underlying bdev.
* Vbdev module must inspect types of memory domains returned by base bdev and report only those
* memory domains that it can work with. */
int (*get_memory_domains)(void *ctx, struct spdk_memory_domain **domains, int array_size);
/**
* Reset I/O statistics specific for this bdev context.
*/
void (*reset_device_stat)(void *ctx);
/**
* Dump I/O statistics specific for this bdev context.
*/
void (*dump_device_stat_json)(void *ctx, struct spdk_json_write_ctx *w);
/** Check if bdev can handle spdk_accel_sequence to handle I/O of specific type. */
bool (*accel_sequence_supported)(void *ctx, enum spdk_bdev_io_type type);
};
在命令行参数解析时的rpc_bdev_malloc_create函数中调用了create_malloc_disk,在该函数中设置了相关信息
struct malloc_disk {
struct spdk_bdev disk;
void *malloc_buf;
void *malloc_md_buf;
TAILQ_ENTRY(malloc_disk) link;
};
static const struct spdk_bdev_fn_table malloc_fn_table = {
.destruct = bdev_malloc_destruct,
.submit_request = bdev_malloc_submit_request,
.io_type_supported = bdev_malloc_io_type_supported,
.get_io_channel = bdev_malloc_get_io_channel,
.write_config_json = bdev_malloc_write_json_config,
};
static struct spdk_bdev_module malloc_if = {
.name = "malloc",
.module_init = bdev_malloc_initialize,
.module_fini = bdev_malloc_deinitialize,
.get_ctx_size = bdev_malloc_get_ctx_size,
};
int
create_malloc_disk(struct spdk_bdev **bdev, const struct malloc_bdev_opts *opts)
/*
* Allocate the large backend memory buffer from pinned memory.
*
* TODO: need to pass a hint so we know which socket to allocate
* from on multi-socket systems.
*/
mdisk->malloc_buf = spdk_zmalloc(opts->num_blocks * block_size, 2 * 1024 * 1024, NULL,
SPDK_ENV_LCORE_ID_ANY, SPDK_MALLOC_DMA);
mdisk->disk.max_copy = 0;
mdisk->disk.ctxt = mdisk;
mdisk->disk.fn_table = &malloc_fn_table;
mdisk->disk.module = &malloc_if;
rc = spdk_bdev_register(&mdisk->disk);
TAILQ_INSERT_TAIL(&g_malloc_disks, mdisk, link);
}
spdk文档中有关于自定义块设备的介绍 Writing a Custom Block Device Module
spdk bdev的用户指南:Block Device User Guide


malloc bdev设备申请的malloc_buf没看见有持久化操作,故malloc bdev数据只存在于内存之中
文档摘录
spdk采用轮询而不是中断的原因:
1)大部分硬件设计不支持用户空间中断机制
2)中断会引发上下文切换,产生比较大的开销,轮询由于只需通过主机内存而不是MMIO查看相应位是否发生翻转,一些技术例如intel的DDIO可以保证这部分主机内存在于CPU缓存中
// 4.19版本nvme 驱动
152 /*
153 * An NVM Express queue. Each device has at least two (one for admin
154 * commands and one for I/O commands).
155 */
156 struct nvme_queue {
157 struct device *q_dmadev;
158 struct nvme_dev *dev;
159 spinlock_t sq_lock;
160 struct nvme_command *sq_cmds; // SQ内存地址
161 struct nvme_command __iomem *sq_cmds_io; // 使用CMB的SQ IO地址
162 spinlock_t cq_lock ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;
163 volatile struct nvme_completion *cqes; // CQ内存地址
164 struct blk_mq_tags **tags;
165 dma_addr_t sq_dma_addr; // SQ总线地址
166 dma_addr_t cq_dma_addr; // CQ总线地址
167 u32 __iomem *q_db; // DB寄存器 IO地址
168 u16 q_depth;
169 s16 cq_vector;
170 u16 sq_tail; // 主机能写的两个DB寄存器的值
171 u16 cq_head;
172 u16 last_cq_head;
173 u16 qid;
174 u8 cq_phase;
175 u32 *dbbuf_sq_db;
176 u32 *dbbuf_cq_db;
177 u32 *dbbuf_sq_ei;
178 u32 *dbbuf_cq_ei;
179 };
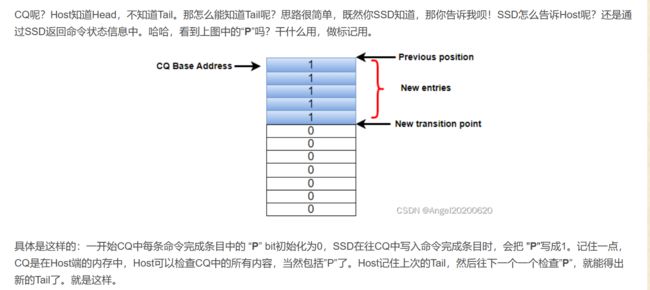
// spdk相关的CQ轮询代码
int32_t
nvme_pcie_qpair_process_completions(struct spdk_nvme_qpair *qpair, uint32_t max_completions)
{
while (1) {
cpl = &pqpair->cpl[pqpair->cq_head];
if (!next_is_valid && cpl->status.p != pqpair->flags.phase) {
break;
}
if (spdk_likely(pqpair->cq_head + 1 != pqpair->num_entries)) {
next_cq_head = pqpair->cq_head + 1;
next_phase = pqpair->flags.phase;
} else {
next_cq_head = 0;
next_phase = !pqpair->flags.phase;
}
next_cpl = &pqpair->cpl[next_cq_head];
next_is_valid = (next_cpl->status.p == next_phase);
if (next_is_valid) {
__builtin_prefetch(&pqpair->tr[next_cpl->cid]);
}
tr = &pqpair->tr[cpl->cid];
pqpair->sq_head = cpl->sqhd;
__builtin_prefetch(&tr->req->stailq);
nvme_pcie_qpair_complete_tracker(qpair, tr, cpl, true);
if (++num_completions == max_completions) {
break;
}
}
}
SPDK 驱动程序选择将硬件队列直接暴露给应用程序,并要求一次只能从一个线程访问硬件队列。实际上,应用程序为每个线程分配一个硬件队列(而不是内核驱动程序中每个核心一个硬件队列)。这保证了线程可以提交请求,而不必与系统中的其他线程执行任何类型的协调(即锁定)。
SPDK(存储性能开发套件)官方文档中文版