Kubeadm方式搭建K8s集群【1.27.0版本】
文章目录
-
- 一、集群规划及架构
- 二、系统初始化准备(所有节点同步操作)
- 三、安装并配置cri-dockerd插件
- 四、安装kubeadm(所有节点同步操作)
- 五、初始化集群
- 六、Node节点添加到集群
- 七、安装网络组件Calico
- 八、测试CoreDNS解析可用性
一、集群规划及架构
官方文档:
二进制下载地址
环境规划:
- pod网段:10.244.0.0/16
- service网段:10.10.0.0/16
- 注意: pod和service网段不可冲突,如果冲突会导致K8S集群安装失败。
- 容器运行时本次使用containerd。
| 主机名 | IP地址 | 操作系统 |
|---|---|---|
| master-1 | 16.32.15.200 | CentOS7.8 |
| node-1 | 16.32.15.201 | CentOS7.8 |
| node-2 | 16.32.15.202 | CentOS7.8 |
二、系统初始化准备(所有节点同步操作)
1、关闭防火墙
systemctl disable firewalld --now
setenforce 0
sed -i -r 's/SELINUX=[ep].*/SELINUX=disabled/g' /etc/selinux/config
2、配置域名解析
cat >> /etc/hosts << EOF
16.32.15.200 master-1
16.32.15.201 node-1
16.32.15.202 node-2
EOF
在指定主机上面修改主机名
hostnamectl set-hostname master-1 && bash
hostnamectl set-hostname node-1 && bash
hostnamectl set-hostname node-2 && bash
3、配置服务器时间保持一致
yum -y install ntpdate
ntpdate ntp1.aliyun.com
添加定时同步 每天凌晨1点自动同步时间
echo "0 1 * * * ntpdate ntp1.aliyun.com" >> /var/spool/cron/root
crontab -l
4、禁用swap交换分区(kubernetes强制要求禁用)
swapoff --all
禁止开机自启动swap交换分区
sed -i -r '/swap/ s/^/#/' /etc/fstab
5、修改Linux内核参数,添加网桥过滤器和地址转发功能
cat >> /etc/sysctl.d/kubernetes.conf <<EOF
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
EOF
sysctl -p /etc/sysctl.d/kubernetes.conf
加载网桥过滤器模块
modprobe br_netfilter
lsmod | grep br_netfilter # 验证是否生效
6、配置ipvs功能
在kubernetes中Service有两种代理模型,一种是基于iptables的,一种是基于ipvs,两者对比ipvs的性能要高,如果想要使用ipvs模型,需要手动载入ipvs模块
yum -y install ipset ipvsadm
cat > /etc/sysconfig/modules/ipvs.modules <<EOF
modprobe -- ip_vs
modprobe -- ip_vs_rr
modprobe -- ip_vs_wrr
modprobe -- ip_vs_sh
modprobe -- nf_conntrack_ipv4
EOF
chmod +x /etc/sysconfig/modules/ipvs.modules
# 执行脚本
/etc/sysconfig/modules/ipvs.modules
# 验证ipvs模块
lsmod | grep -e ip_vs -e nf_conntrack_ipv4
7、安装Docker容器组件
curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo https://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo
wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-7.repo
yum makecache
# yum-utils软件用于提供yum-config-manager程序
yum install -y yum-utils
# 使用yum-config-manager创建docker阿里存储库
yum-config-manager --add-repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
yum install docker-ce-20.10.6 docker-ce-cli-20.10.6 -y
Docker配置加速源:
mkdir /etc/docker
cat <<EOF > /etc/docker/daemon.json
{
"registry-mirrors": ["https://aoewjvel.mirror.aliyuncs.com"],
"exec-opts": ["native.cgroupdriver=systemd"]
}
EOF
# 启动docker并设置开机自启
systemctl enable docker --now
systemctl status docker
8、重启服务器 可略过
reboot
三、安装并配置cri-dockerd插件
官网下载地址
三台服务器同时操作
1、安装cri-dockerd插件
wget https://github.com/Mirantis/cri-dockerd/releases/download/v0.3.1/cri-dockerd-0.3.1-3.el7.x86_64.rpm
rpm -ivh cri-dockerd-0.3.1-3.el7.x86_64.rpm
2、备份并更新cri-docker.service文件
mv /usr/lib/systemd/system/cri-docker.service{,.default}
vim /usr/lib/systemd/system/cri-docker.service
[Unit]
Description=CRI Interface for Docker Application Container Engine
Documentation=https://docs.mirantis.com
After=network-online.target firewalld.service docker.service
Wants=network-online.target
Requires=cri-docker.socket
[Service]
Type=notify
ExecStart=/usr/bin/cri-dockerd --network-plugin=cni --pod-infra-container-image=registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/pause:3.7
ExecReload=/bin/kill -s HUP $MAINPID
TimeoutSec=0
RestartSec=2
Restart=always
StartLimitBurst=3
StartLimitInterval=60s
LimitNOFILE=infinity
LimitNPROC=infinity
LimitCORE=infinity
TasksMax=infinity
Delegate=yes
KillMode=process
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
3、启动cir-dockerd
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl start cri-docker.service
systemctl enable cri-docker.service
四、安装kubeadm(所有节点同步操作)
1、配置国内yum源,一键安装 kubeadm、kubelet、kubectl
cat <<EOF > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo
[kubernetes]
name=Kubernetes
baseurl=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
EOF
yum install -y kubelet-1.27.0 kubeadm-1.27.0 kubectl-1.27.0
2、kubeadm将使用kubelet服务以容器方式部署kubernetes的主要服务,所以需要先启动kubelet服务
systemctl enable kubelet.service --now
五、初始化集群
在master-1主机上进行操作
1、生成初始化默认配置文件
kubeadm config print init-defaults > kubeadm.yaml
我们根据自己需求进行修改默认配置文件,我主要更改了一下配置如下:
- advertiseAddress:更改为master的IP地址
- criSocket:指定容器运行时
- imageRepository:配置国内加速源地址
- podSubnet:pod网段地址
- serviceSubnet:services网段地址
- 末尾添加了指定使用ipvs,开启systemd
- nodeRegistration.name:改为当前主机名称
最终初始化配置文件如下:
apiVersion: kubeadm.k8s.io/v1beta3
bootstrapTokens:
- groups:
- system:bootstrappers:kubeadm:default-node-token
token: abcdef.0123456789abcdef
ttl: 24h0m0s
usages:
- signing
- authentication
kind: InitConfiguration
localAPIEndpoint:
advertiseAddress: 16.32.15.200
bindPort: 6443
nodeRegistration:
criSocket: unix:///var/run/cri-dockerd.sock
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: master-1
taints: null
---
apiServer:
timeoutForControlPlane: 4m0s
apiVersion: kubeadm.k8s.io/v1beta3
certificatesDir: /etc/kubernetes/pki
clusterName: kubernetes
controllerManager: {}
dns: {}
etcd:
local:
dataDir: /var/lib/etcd
imageRepository: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers
kind: ClusterConfiguration
kubernetesVersion: 1.27.0
networking:
dnsDomain: cluster.local
podSubnet: 10.244.0.0/16
serviceSubnet: 10.96.0.0/12
scheduler: {}
---
apiVersion: kubeproxy.config.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: KubeProxyConfiguration
mode: ipvs
---
apiVersion: kubelet.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: KubeletConfiguration
cgroupDriver: systemd
2、进行初始化
kubeadm init --config=kubeadm.yaml --ignore-preflight-errors=SystemVerification
初始化成功后输出如下内容:
[init] Using Kubernetes version: v1.27.0
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks
[preflight] Pulling images required for setting up a Kubernetes cluster
[preflight] This might take a minute or two, depending on the speed of your internet connection
[preflight] You can also perform this action in beforehand using 'kubeadm config images pull'
W0504 22:24:16.508649 4725 images.go:80] could not find officially supported version of etcd for Kubernetes v1.27.0, falling back to the nearest etcd version (3.5.7-0)
[certs] Using certificateDir folder "/etc/kubernetes/pki"
[certs] Generating "ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "apiserver" certificate and key
[certs] apiserver serving cert is signed for DNS names [kubernetes kubernetes.default kubernetes.default.svc kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local master-1] and IPs [10.96.0.1 16.32.15.200]
[certs] Generating "apiserver-kubelet-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "front-proxy-ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "front-proxy-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "etcd/ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "etcd/server" certificate and key
[certs] etcd/server serving cert is signed for DNS names [localhost master-1] and IPs [16.32.15.200 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certs] Generating "etcd/peer" certificate and key
[certs] etcd/peer serving cert is signed for DNS names [localhost master-1] and IPs [16.32.15.200 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certs] Generating "etcd/healthcheck-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "apiserver-etcd-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "sa" key and public key
[kubeconfig] Using kubeconfig folder "/etc/kubernetes"
[kubeconfig] Writing "admin.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "kubelet.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "controller-manager.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "scheduler.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file "/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env"
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file "/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml"
[kubelet-start] Starting the kubelet
[control-plane] Using manifest folder "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-apiserver"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-controller-manager"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-scheduler"
[etcd] Creating static Pod manifest for local etcd in "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"
W0504 22:24:34.897353 4725 images.go:80] could not find officially supported version of etcd for Kubernetes v1.27.0, falling back to the nearest etcd version (3.5.7-0)
[wait-control-plane] Waiting for the kubelet to boot up the control plane as static Pods from directory "/etc/kubernetes/manifests". This can take up to 4m0s
[apiclient] All control plane components are healthy after 10.002479 seconds
[upload-config] Storing the configuration used in ConfigMap "kubeadm-config" in the "kube-system" Namespace
[kubelet] Creating a ConfigMap "kubelet-config" in namespace kube-system with the configuration for the kubelets in the cluster
[upload-certs] Skipping phase. Please see --upload-certs
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node master-1 as control-plane by adding the labels: [node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane node.kubernetes.io/exclude-from-external-load-balancers]
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node master-1 as control-plane by adding the taints [node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane:NoSchedule]
[bootstrap-token] Using token: abcdef.0123456789abcdef
[bootstrap-token] Configuring bootstrap tokens, cluster-info ConfigMap, RBAC Roles
[bootstrap-token] Configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to get nodes
[bootstrap-token] Configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to post CSRs in order for nodes to get long term certificate credentials
[bootstrap-token] Configured RBAC rules to allow the csrapprover controller automatically approve CSRs from a Node Bootstrap Token
[bootstrap-token] Configured RBAC rules to allow certificate rotation for all node client certificates in the cluster
[bootstrap-token] Creating the "cluster-info" ConfigMap in the "kube-public" namespace
[kubelet-finalize] Updating "/etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf" to point to a rotatable kubelet client certificate and key
[addons] Applied essential addon: CoreDNS
[addons] Applied essential addon: kube-proxy
Your Kubernetes control-plane has initialized successfully!
To start using your cluster, you need to run the following as a regular user:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
Alternatively, if you are the root user, you can run:
export KUBECONFIG=/etc/kubernetes/admin.conf
You should now deploy a pod network to the cluster.
Run "kubectl apply -f [podnetwork].yaml" with one of the options listed at:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/addons/
Then you can join any number of worker nodes by running the following on each as root:
kubeadm join 16.32.15.200:6443 --token abcdef.0123456789abcdef \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:afef55c724c1713edb7926d98f8c4063fbae928fc4eb11282589d6485029b9a6
3、配置kubectl的配置文件config,相当于对kubectl进行授权,这样kubectl命令可以使用这个证书对k8s集群进行管理
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
验证使用可以使用 kubectl 命令
kubectl get nodes
六、Node节点添加到集群
在两台node节点进行操
1、使用以下命令创建并查看token
kubeadm token create --print-join-command
2、在两台node节点执行,注意添加--cri-socket=指定cri-dockerd.sock。
kubeadm join 16.32.15.200:6443 --token abcdef.0123456789abcdef --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:d3d7853ba7691fad218fdfa1027390c7c68e8cf0d3c5033e37170ce00d09901c --cri-socket=unix:///var/run/cri-dockerd.sock
成功加入到集群如下图:
3、给两台node节点打上标签
master-1主机上执行
kubectl label nodes node-1 node-role.kubernetes.io/work=work
kubectl label nodes node-2 node-role.kubernetes.io/work=work
4、查看集群节点
kubectl get nodes
七、安装网络组件Calico
Calico在线文档地址:
Calico.yaml下载地址:
1、上传calico.yaml文件到服务器中,下面提供calico.yaml文件内容:
在master主机执行
kubectl apply -f calico.yaml
2、查看集群状态 && 查看自带Pod状态
kubectl get nodes
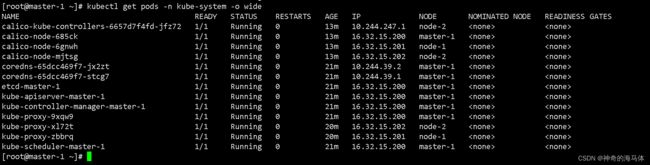
3、查看组件状态 是否为 Running状态 如下图:
kubectl get pods -n kube-system -o wide
八、测试CoreDNS解析可用性
1、下载busybox:1.28镜像
docker pull busybox:1.28
2、测试coredns
kubectl run busybox --image busybox:1.28 --restart=Never --rm -it busybox -- sh
If you don't see a command prompt, try pressing enter.
/ # nslookup kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local
Server: 10.96.0.10
Address 1: 10.96.0.10 kube-dns.kube-system.svc.cluster.local
Name: kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local
Address 1: 10.96.0.1 kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local
- 注意:busybox要用指定的1.28版本,不能用最新版本,最新版本,nslookup会解析不到dns和ip