LinkedList源码
介绍
- 基于双向链表实现
- 线程不安全
- 插入删除效率较高,但不支持随机查找
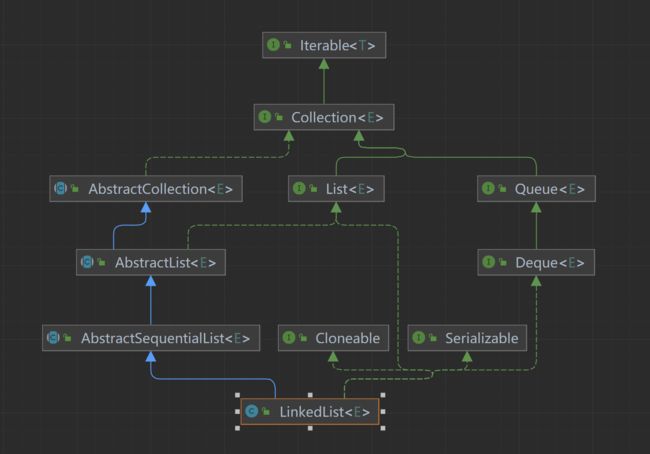
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
常量&变量
// 元素数量
transient int size = 0;
/**
* Pointer to first node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (first.prev == null && first.item != null)
* 头节点
*/
transient Node<E> first;
/**
* Pointer to last node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (last.next == null && last.item != null)
* 尾节点
*/
transient Node<E> last;
LinkedList 的底层数据结构为双向链表,每个节点包含两个引用,prev指向当前节点前一个节点,next指向当前节点后一个节点,可以从头结点遍历到尾结点,也可以从尾结点遍历到头结点。
构造方法
/**
* Constructs an empty list.
* 无参构造 创建一个空集合
*/
public LinkedList() {
}
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
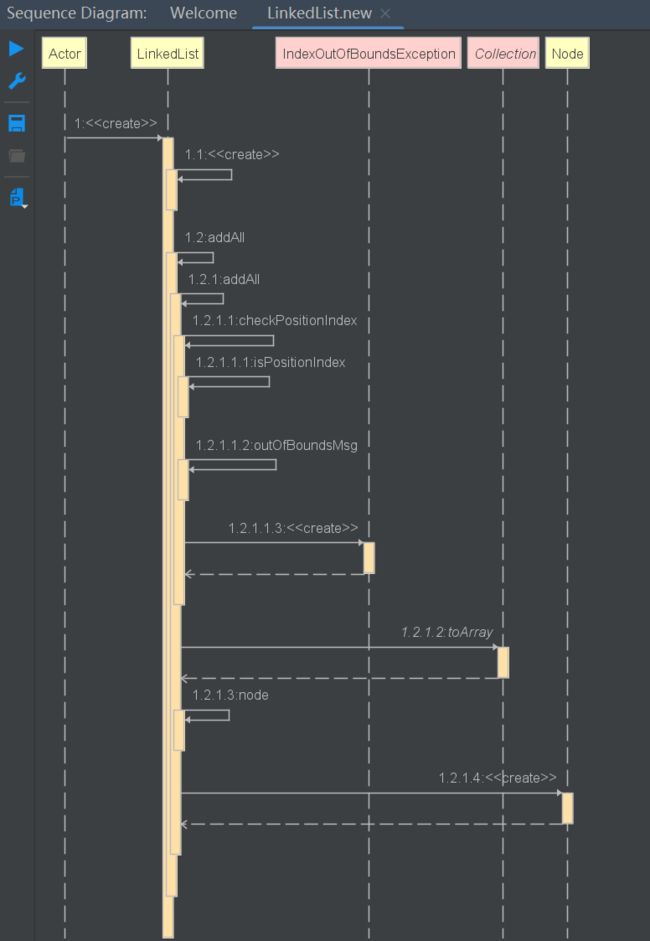
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
//调用无参,创建一个空集合
this();
addAll(c);
}
内部类
ListItr
ListItr类定义在LinkedList类的内部(作为普通内部类),它实现了ListIterator接口,具有迭代器的功能。
private class ListItr implements ListIterator<E> {
//上一次执行next()或previos()方法时的节点
private Node<E> lastReturned;
//下一次即将访问的元素(后继节点)
private Node<E> next;
//下一次要访问的元素的索引(后继节点的索引)
private int nextIndex;
//将修改次数modCount赋给expectedModCount 预期的修改次数 = 实际修改次数
private int expectedModCount = modCount;
ListItr(int index) {
// assert isPositionIndex(index);
//根据索引获得后继节点
next = (index == size) ? null : node(index);
//后继节点的索引
nextIndex = index;
}
//判断是否有下一个元素可访问
public boolean hasNext() {
//nextIndex小于size表示仍然还有后继结点,如果大于等于size那么表示要么是尾结点,要么索引越界了
return nextIndex < size;
}
//获取下一个访问的元素
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
//如果没有下一个元素
if (!hasNext())
//抛出NoSuchElementException异常
throw new NoSuchElementException();
//保存当前遍历的节点
lastReturned = next;
//下个节点
next = next.next;
//索引加1
nextIndex++;
//返回旧next节点的元素
return lastReturned.item;
}
//判断是否有上一个元素可访问
public boolean hasPrevious() {
//向前遍历,当索引大于0,表示前驱节点存在
return nextIndex > 0;
}
//获取上一个访问的元素
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
if (!hasPrevious())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
lastReturned = next = (next == null) ? last : next.prev;
nextIndex--;
return lastReturned.item;
}
//获取下一个访问的元素在线性表中的索引
public int nextIndex() {
return nextIndex;
}
//获取上一个访问元素在线性表中的索引
public int previousIndex() {
return nextIndex - 1;
}
/**
* 使用迭代器进行迭代的时候不能进行调用list.remove()或list.add()删除修改元素,否则会抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常
* 所以如果要增加或删除元素需要使用迭代器Iterator内部的remove()和add()方法
*/
//删除元素
public void remove() {
checkForComodification();
if (lastReturned == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
//后继节点
Node<E> lastNext = lastReturned.next;
//删除当前节点
unlink(lastReturned);
//next 和 上一次遍历的节点 是同一个对象 说明是向前遍历
if (next == lastReturned)
next = lastNext;
else
nextIndex--;
//置null 便于回收
lastReturned = null;
expectedModCount++;
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastReturned == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
lastReturned.item = e;
}
//添加
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
lastReturned = null;
if (next == null)
//当前节点是尾结点,直接在尾部添加
linkLast(e);
else
//插入到next节点前
linkBefore(e, next);
nextIndex++;
expectedModCount++;
}
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
while (modCount == expectedModCount && nextIndex < size) {
action.accept(next.item);
lastReturned = next;
next = next.next;
nextIndex++;
}
checkForComodification();
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
ListItr类不仅可以遍历元素,还可以遍历元素时添加、删除元素
ListItr类定义在LinkedList的内部,每个ListItr对象隐式持有LinkedList对象的引用,该迭代器在遍历时对ListItr对象添加、删除、修改元素,都会影响到LinkedList对象
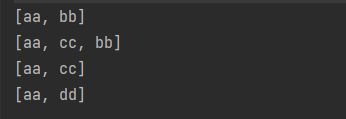
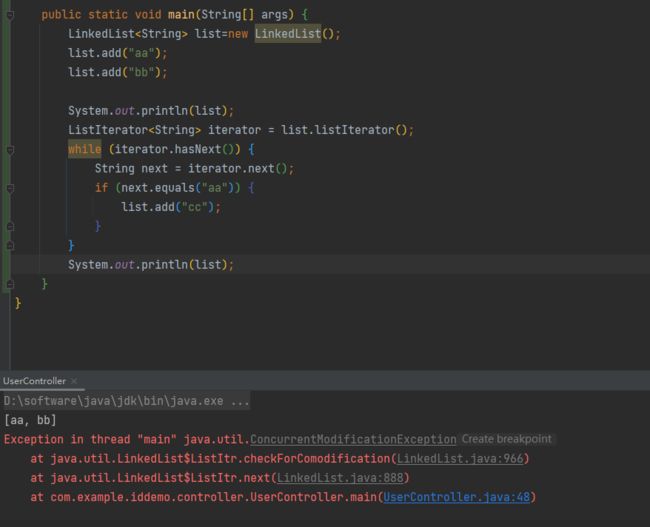
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<String> list=new LinkedList();
list.add("aa");
list.add("bb");
System.out.println(list);
ListIterator<String> iterator = list.listIterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
String next = iterator.next();
if (next.equals("aa")) {
iterator.add("cc");
}
}
System.out.println(list);
ListIterator<String> iterator2 = list.listIterator();
while (iterator2.hasNext()) {
String next = iterator2.next();
if (next.equals("bb")){
iterator2.remove();
}
}
System.out.println(list);
ListIterator<String> iterator3 = list.listIterator();
while (iterator3.hasNext()) {
String next = iterator3.next();
if (next.equals("cc")){
iterator3.set("dd");
}
}
System.out.println(list);
}
对集合使用迭代器遍历时,可以使用迭代器内部的remove()或add()方法对集合中元素进行增删操作
注:使用list的remove()或add()方法会报ConcurrentModificationException,list无set(E e)方法
Node
Node类就是LinkedList中元素的包装类,表示LinkedList中的一个一个元素
private static class Node<E> {
//元素
E item;
//后节点
Node<E> next;
//前节点
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
DescendingIterator
为listitter .previous提供降序迭代器的适配器,即从LinkedList的列表末尾开始,逆序遍历进而到达列表头部。
/**
* Adapter to provide descending iterators via ListItr.previous
*/
private class DescendingIterator implements Iterator<E> {
private final ListItr itr = new ListItr(size());
public boolean hasNext() {
return itr.hasPrevious();
}
public E next() {
return itr.previous();
}
public void remove() {
itr.remove();
}
}
LLSpliterator
用于并行流的可分割式迭代器
/** A customized variant of Spliterators.IteratorSpliterator */
static final class LLSpliterator<E> implements Spliterator<E> {
static final int BATCH_UNIT = 1 << 10; // batch array size increment
static final int MAX_BATCH = 1 << 25; // max batch array size;
final LinkedList<E> list; // null OK unless traversed
Node<E> current; // current node; null until initialized
int est; // size estimate; -1 until first needed
int expectedModCount; // initialized when est set
int batch; // batch size for splits
LLSpliterator(LinkedList<E> list, int est, int expectedModCount) {
this.list = list;
this.est = est;
this.expectedModCount = expectedModCount;
}
final int getEst() {
int s; // force initialization
final LinkedList<E> lst;
if ((s = est) < 0) {
if ((lst = list) == null)
s = est = 0;
else {
expectedModCount = lst.modCount;
current = lst.first;
s = est = lst.size;
}
}
return s;
}
public long estimateSize() { return (long) getEst(); }
public Spliterator<E> trySplit() {
Node<E> p;
int s = getEst();
if (s > 1 && (p = current) != null) {
int n = batch + BATCH_UNIT;
if (n > s)
n = s;
if (n > MAX_BATCH)
n = MAX_BATCH;
Object[] a = new Object[n];
int j = 0;
do { a[j++] = p.item; } while ((p = p.next) != null && j < n);
current = p;
batch = j;
est = s - j;
return Spliterators.spliterator(a, 0, j, Spliterator.ORDERED);
}
return null;
}
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Node<E> p; int n;
if (action == null) throw new NullPointerException();
if ((n = getEst()) > 0 && (p = current) != null) {
current = null;
est = 0;
do {
E e = p.item;
p = p.next;
action.accept(e);
} while (p != null && --n > 0);
}
if (list.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Node<E> p;
if (action == null) throw new NullPointerException();
if (getEst() > 0 && (p = current) != null) {
--est;
E e = p.item;
current = p.next;
action.accept(e);
if (list.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
return true;
}
return false;
}
public int characteristics() {
return Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.SUBSIZED;
}
}
常用方法
add
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
* 插入尾部,并返回true 与addLast方法等价
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and any
* subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
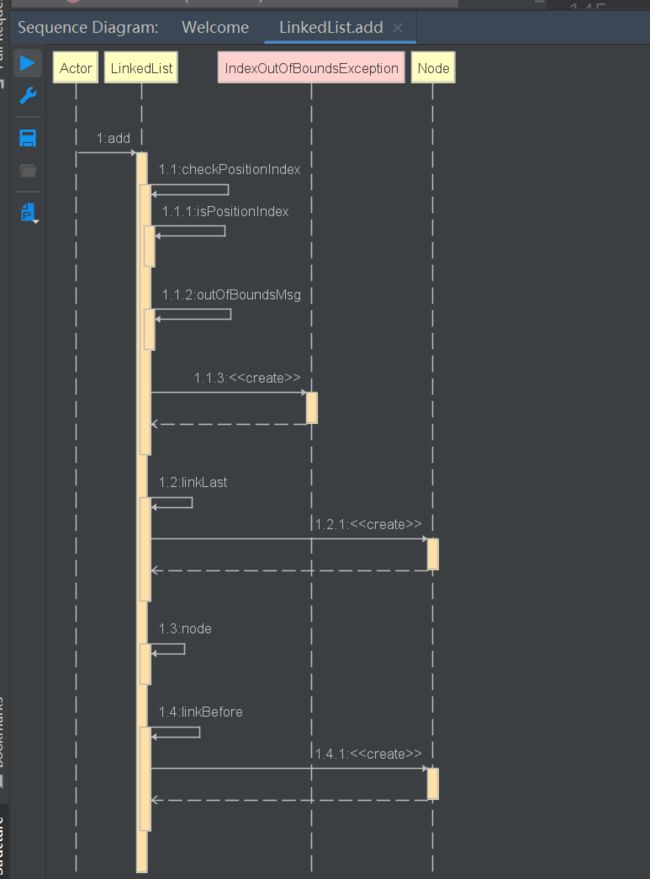
public void add(int index, E element) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
if (index == size)
//尾部添加
linkLast(element);
else
//在索引对应的节点前插入element
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}
checkPositionIndex
private void checkPositionIndex(int index) {
//不符合条件 报错
if (!isPositionIndex(index))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
/**
* Tells if the argument is the index of a valid position for an
* iterator or an add operation.
* 参数index是否符合条件
*/
private boolean isPositionIndex(int index) {
return index >= 0 && index <= size;
}
linkLast
在尾部添加元素
/**
* Links e as last element.
*/
void linkLast(E e) {
// 获取尾部元素
final Node<E> l = last;
// 实例化一个新的节点,前一个节点为l,当前节点为传入的添加节点,下一个节点为null
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
// 将尾部节点进行更新(添加上新加入的节点)
last = newNode;
// 当尾部节点为空时,头节点即为新添加的节点
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
// 否则,尾部节点的下一个为新添加的节点
else
l.next = newNode;
// 元素数量+1
size++;
// 修改次数+1
modCount++;
}
linkBefore
/**
* Inserts element e before non-null Node succ.
* 在非空节点succ前,插入元素 e
*/
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {
// assert succ != null;
//原index对应节点succ的前驱节点
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;
//创建新的节点 pred <-- e --> succ
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
//succ的前驱节点为newNode pred <-- e <--> succ
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)
// e <--> succ
first = newNode;
else
//pred的后继节点为newNode pred <--> e <--> succ
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
addAll
/**
* Appends all of the elements in the specified collection to the end of
* this list, in the order that they are returned by the specified
* collection's iterator. The behavior of this operation is undefined if
* the specified collection is modified while the operation is in
* progress. (Note that this will occur if the specified collection is
* this list, and it's nonempty.)
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
* 将指定集合中的所有元素追加到此列表的末尾。
*/
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
return addAll(size, c);
}
/**
* Inserts all of the elements in the specified collection into this
* list, starting at the specified position. Shifts the element
* currently at that position (if any) and any subsequent elements to
* the right (increases their indices). The new elements will appear
* in the list in the order that they are returned by the
* specified collection's iterator.
*
* @param index index at which to insert the first element
* from the specified collection
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
* 将指定集合(Collection c)中的所有元素插入到此列表中,从指定的位置(index)开始。
*/
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
//判断索引是否越界
checkPositionIndex(index);
//通过指定集合获得数组
Object[] a = c.toArray();
//数组的长度
int numNew = a.length;
//长度为空,直接返回失败
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
//节点的前驱节点、后继节点
Node<E> pred, succ;
//直接从尾部添加该集合
if (index == size) {
//后继节点为null,前驱节点为尾节点
succ = null;
pred = last;
} else {
//指定索引对应的节点为后继节点,节点的前节点为前驱节点
succ = node(index);
pred = succ.prev;
}
//遍历数组
for (Object o : a) {
//类型转换
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o;
//构造新节点 pred <-- e
Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null);
if (pred == null)
//新节点为头节点 e
first = newNode;
else
//前驱节点的下一个节点为新节点 pred <--> e
pred.next = newNode;
//为了下个循环,将新节点置为前驱节点
pred = newNode;
}
//如果后继节点为null(尾部插入的情况),前驱节点就是尾结点
if (succ == null) {
// pred <--> e
last = pred;
} else {
//前驱节点的后节点为后继节点 pred <--> e --> succ
pred.next = succ;
//后继节点的前节点为前驱节点 pred <--> e <--> succ
succ.prev = pred;
}
size += numNew;
modCount++;
return true;
}
remove(int index)
/**
* Removes the element at the specified position in this list. Shifts any
* subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their indices).
* Returns the element that was removed from the list.
*
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
* 删除指定下标的元素
*/
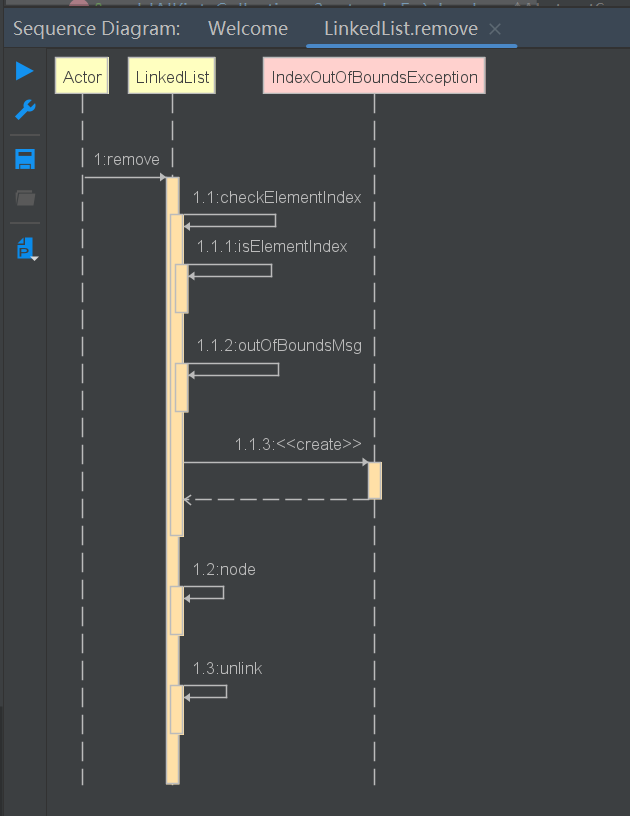
public E remove(int index) {
// 检测下标是否越界
checkElementIndex(index);
// 调用unlink删除元素
return unlink(node(index));
}
/**
* Unlinks non-null node x.
*/
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
// assert x != null;
// 获取当前元素
final E element = x.item;
// 获取下一个节点
final Node<E> next = x.next;
// 获取上一个节点
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
// 当上一个节点为null时,将当前节点的下一个节点设置为头节点
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
// 不为null时,将上一个节点的下一个节点设置为当前节点的下一个节点(跳过当前元素),然后将当前节点的前一个节点设置为null,断开连接
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
// 当下一个节点为null时,将尾节点设置为上一个节点
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
// 否则将下一个节点的前一个节点设置为前一个节点,并且将当前节点的下一个节点设置为null,断开连接
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
// 设置当前元素为null
x.item = null;
// 元素数量-1
size--;
// 修改次数+1
modCount++;
// 返回当前元素
return element;
}
remove()
/**
* Retrieves and removes the head (first element) of this list.
*
* @return the head of this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
* @since 1.5
* 删除头节点
*/
public E remove() {
// 直接调用removeFirst,删除头节点
return removeFirst();
}
/**
* Removes and returns the first element from this list.
*
* @return the first element from this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
*/
public E removeFirst() {
// 获取头节点
final Node<E> f = first;
// 头节点为null时直接抛出
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
// 调用删除头节点的方法
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
/**
* Unlinks non-null first node f.
*/
private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {
// assert f == first && f != null;
// 获取当前元素
final E element = f.item;
// 获取下一个节点
final Node<E> next = f.next;
// 将当前元素设置为null
f.item = null;
// 将下一个节点设置为null
f.next = null; // help GC
// 因为为删除头节点,所以将头节点设置为下一个节点(跳过当前头节点)
first = next;
// 当下一个节点为null时,尾节点设置为null
if (next == null)
last = null;
// 否则下一个节点的前一个节点设置为null,断开与之前头节点的连接
else
next.prev = null;
// 元素数量-1
size--;
// 操作次数+1
modCount++;
// 返回删除的元素
return element;
}
element
/**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the head (first element) of this list.
*
* @return the head of this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
* @since 1.5
* 获取头节点但不删除,链表为null抛出异常
*/
public E element() {
// 直接调用getFirst获取头节点返回
return getFirst();
}
/**
* Returns the first element in this list.
*
* @return the first element in this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
* 获取头节点
*/
public E getFirst() {
// 获取头节点
final Node<E> f = first;
// 当头节点为null时抛出异常
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
// 否则返回头节点的值
return f.item;
}
offer
/**
* Adds the specified element as the tail (last element) of this list.
*
* @param e the element to add
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Queue#offer})
* @since 1.5
* 尾部添加指定元素
*/
public boolean offer(E e) {
//直接调用add方法
return add(e);
}
poll
/**
* Retrieves and removes the head (first element) of this list.
*
* @return the head of this list, or {@code null} if this list is empty
* @since 1.5
* 获取头节点并删除
*/
public E poll() {
// 获取头节点
final Node<E> f = first;
// 当为null时直接返回null,否则调用unlinkFirst
return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f);
}
peek
/**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the head (first element) of this list.
*
* @return the head of this list, or {@code null} if this list is empty
* @since 1.5
* 获取头节点,但不删除,链表为null则返回null
*/
public E peek() {
// 获取头节点
final Node<E> f = first;
// 头节点为null直接返回null,否则返回元素
return (f == null) ? null : f.item;
}
push
/**
* Pushes an element onto the stack represented by this list. In other
* words, inserts the element at the front of this list.
*
* This method is equivalent to {@link #addFirst}.
*
* @param e the element to push
* @since 1.6
* 压入元素
*/
public void push(E e) {
// 直接调用addFirst方法,addFirst调用了linkFirst
addFirst(e);
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the beginning of this list.
*
* @param e the element to add
*/
public void addFirst(E e) {
linkFirst(e);
}
/**
* Links e as first element.
* 头部添加元素
*/
private void linkFirst(E e) {
// 获取头节点
final Node<E> f = first;
// 实例化一个新的节点,上一个节点为null,当前节点为传入元素,下个节点为头节点
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);
// 将新的节点赋值给头节点
first = newNode;
// 当头节点为空时,尾节点也直接设置为新节点
if (f == null)
last = newNode;
// 否则头节点的前一个节点为新节点
else
f.prev = newNode;
// 元素数量+1
size++;
// 修改次数+1
modCount++;
}
pop
/**
* Pops an element from the stack represented by this list. In other
* words, removes and returns the first element of this list.
*
* This method is equivalent to {@link #removeFirst()}.
*
* @return the element at the front of this list (which is the top
* of the stack represented by this list)
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
* @since 1.6
* 弹出元素
*/
public E pop() {
// 直接调用removeFirst方法,removeFirst进行判空,空抛出异常,然后调用unlinkFirst
return removeFirst();
}
/**
* Removes and returns the first element from this list.
*
* @return the first element from this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
*/
public E removeFirst() {
// 获取头节点
final Node<E> f = first;
// 头节点为null时直接抛出
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
// 调用删除头节点的方法
return unlinkFirst(f);
}