用于Alpha指令集处理器CModel裸机(不带操作系统)的CoreMark性能测试程序源码编译流程
CoreMark是一个综合基准,用于测量嵌入式系统中使用的中央处理器(CPU)的性能。它是在2009由eembc的shay gal-on开发的,并且试图将其发展成为工业标准,取代过时的dehrystone基准。代码用C编写,包含以下算法:列表处理(增删改查和排序)、矩阵操作(公共矩阵操作)、状态机(确定输入流是否包含有效数字)和CRC,都是在真实的嵌入式应用中很常见的操作,这也是CoreMark比其他测试标准更有实际价值的原因所在。用户可以自由的下载Coremark,并移植到自己的平台上运行,随后就可以看到分数。
CoreMark源码下载地址:https://github.com/eembc/coremark
├── barebones --移植到裸机环境下需要修改的目录
│ ├── core_portme.c --移植的目标平台配置信息
│ ├── core_portme.h --计时以及板级初始化实现
│ ├── core_portme.mak --该子目录的makefile
│ ├── cvt.c
│ └── ee_printf.c --打印函数串口发送实现
├── core_list_join.c --列表操作程序
├── core_main.c --主程序
├── coremark.h --项目配置与数据结构的定义头文件
├── coremark.md5
├── core_matrix.c --矩阵运算程序
├── core_state.c --状态机控制程序
├── core_util.c --CRC计算程序
├── cygwin --x86 cygwin和gcc 3.4(四核,双核和单核系统)的测试代码
│ ├── core_portme.c
│ ├── core_portme.h
│ └── core_portme.mak
├── freebsd --以下同理,是在不同操作系统下的测试代码
│ ├── ...
├── LICENSE.md
├── linux
│ ├── ...
├── linux64
│ ├── ...
├── macos
│ ├── ...
├── Makefile
├── README.md --自述文件,CoreMark项目的基本介绍
├── rtems
│ ├── ...
└── simple
├── ...
└──
Coremark的代码主要分为两部分,一部分是不能修改的程序主体,即项目根目录下的.c文件,另一部分是为了不同平台移植的代码,比如./barebones目录下的.c和.h文件。
为了能够兼容多平台,coremark项目工程组织比较复杂,为了简化,并符合CModel编译要求,重新组织工程目录如下:
├── core_list_join.c --列表操作程序 ├── core_main.c --主程序 ├── coremark.h --项目配置与数据结构的定义头文件 ├── core_matrix.c --矩阵运算程序 ├── core_state.c --状态机控制程序 ├── core_util.c --CRC计算程序 ├── Makefile --基于CModel特性编写的Makefile ├── core_portme.c --拷贝自./posix目录,做了相应修改 ├── core_portme.h --拷贝自./posix目录,做了相应修改 ├── core_portme_posix_overrides.h --拷贝自./posix目录,未做改动 ├── cmodel.lds --为CModel编写的链接脚本 ├── start.s --为CModle编写的程序装载代码
其中core_portme.h文件改动后如下:
/*
Copyright 2018 Embedded Microprocessor Benchmark Consortium (EEMBC)
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
Original Author: Shay Gal-on
*/
/* Topic: Description
This file contains configuration constants required to execute on
different platforms
*/
#ifndef CORE_PORTME_H
#define CORE_PORTME_H
#include "core_portme_posix_overrides.h"
#ifndef NULL
#define NULL 0
#endif
/************************/
/* Data types and settings */
/************************/
/* Configuration: HAS_FLOAT
Define to 1 if the platform supports floating point.
*/
#ifndef HAS_FLOAT
#define HAS_FLOAT 0 // 关闭float测试
#endif
/* Configuration : HAS_TIME_H
Define to 1 if platform has the time.h header file,
and implementation of functions thereof.
*/
#ifndef HAS_TIME_H
#define HAS_TIME_H 0 // 关闭time
#endif
/* Configuration : USE_CLOCK
Define to 1 if platform has the time.h header file,
and implementation of functions thereof.
*/
#ifndef USE_CLOCK
#define USE_CLOCK 0 // 关闭clock
#endif
/* Configuration : HAS_STDIO
Define to 1 if the platform has stdio.h.
*/
#ifndef HAS_STDIO
#define HAS_STDIO 0 // 没有输入输出
#endif
/* Configuration: HAS_PRINTF
Define to 1 if the platform has stdio.h and implements the printf
function.
*/
#ifndef HAS_PRINTF
#define HAS_PRINTF 0 // 没有printf
#endif
/* Configuration: CORE_TICKS
Define type of return from the timing functions.
*/
#if defined(_MSC_VER)
#include
typedef size_t CORE_TICKS;
#elif HAS_TIME_H
#include
typedef clock_t CORE_TICKS;
#else
typedef signed int CORE_TICKS;
#endif
/* Definitions: COMPILER_VERSION, COMPILER_FLAGS, MEM_LOCATION
Initialize these strings per platform
*/
#ifndef COMPILER_VERSION
#if defined(__clang__)
#define COMPILER_VERSION __VERSION__
#elif defined(__GNUC__)
#define COMPILER_VERSION "GCC"__VERSION__
#else
#define COMPILER_VERSION "Please put compiler version here (e.g. gcc 4.1)"
#endif
#endif
#ifndef COMPILER_FLAGS
#define COMPILER_FLAGS \
FLAGS_STR /* "Please put compiler flags here (e.g. -o3)" */
#endif
#ifndef MEM_LOCATION
#define MEM_LOCATION \
"Please put data memory location here\n\t\t\t(e.g. code in flash, data " \
"on heap etc)"
#define MEM_LOCATION_UNSPEC 1
#endif
#include
/* Data Types:
To avoid compiler issues, define the data types that need ot be used for
8b, 16b and 32b in .
*Imprtant*:
ee_ptr_int needs to be the data type used to hold pointers, otherwise
coremark may fail!!!
*/
typedef signed short ee_s16;
typedef unsigned short ee_u16;
typedef signed int ee_s32;
typedef double ee_f32;
typedef unsigned char ee_u8;
typedef unsigned int ee_u32;
typedef uintptr_t ee_ptr_int;
typedef unsigned int ee_size_t;
/* align an offset to point to a 32b value */
#define align_mem(x) (void *)(4 + (((ee_ptr_int)(x)-1) & ~3))
/* Configuration: SEED_METHOD
Defines method to get seed values that cannot be computed at compile
time.
Valid values:
SEED_ARG - from command line.
SEED_FUNC - from a system function.
SEED_VOLATILE - from volatile variables.
*/
#ifndef SEED_METHOD
#define SEED_METHOD SEED_VOLATILE
#endif
/* Configuration: MEM_METHOD
Defines method to get a block of memry.
Valid values:
MEM_MALLOC - for platforms that implement malloc and have malloc.h.
MEM_STATIC - to use a static memory array.
MEM_STACK - to allocate the data block on the stack (NYI).
*/
#ifndef MEM_METHOD
#define MEM_METHOD MEM_STACK // 没有malloc,从stack分配内存
#endif
/* Configuration: MULTITHREAD
Define for parallel execution
Valid values:
1 - only one context (default).
N>1 - will execute N copies in parallel.
Note:
If this flag is defined to more then 1, an implementation for launching
parallel contexts must be defined.
Two sample implementations are provided. Use or
to enable them.
It is valid to have a different implementation of
and in , to fit a particular architecture.
*/
#ifndef MULTITHREAD
#define MULTITHREAD 1 // 没有多线程,只开一个线程
#endif
/* Configuration: USE_PTHREAD
Sample implementation for launching parallel contexts
This implementation uses pthread_thread_create and pthread_join.
Valid values:
0 - Do not use pthreads API.
1 - Use pthreads API
Note:
This flag only matters if MULTITHREAD has been defined to a value
greater then 1.
*/
#ifndef USE_PTHREAD
#define USE_PTHREAD 0 // 不使用pthread多线程组件
#endif
/* Configuration: USE_FORK
Sample implementation for launching parallel contexts
This implementation uses fork, waitpid, shmget,shmat and shmdt.
Valid values:
0 - Do not use fork API.
1 - Use fork API
Note:
This flag only matters if MULTITHREAD has been defined to a value
greater then 1.
*/
#ifndef USE_FORK
#define USE_FORK 0
#endif
/* Configuration: USE_SOCKET
Sample implementation for launching parallel contexts
This implementation uses fork, socket, sendto and recvfrom
Valid values:
0 - Do not use fork and sockets API.
1 - Use fork and sockets API
Note:
This flag only matters if MULTITHREAD has been defined to a value
greater then 1.
*/
#ifndef USE_SOCKET
#define USE_SOCKET 0
#endif
/* Configuration: MAIN_HAS_NOARGC
Needed if platform does not support getting arguments to main.
Valid values:
0 - argc/argv to main is supported
1 - argc/argv to main is not supported
*/
#ifndef MAIN_HAS_NOARGC
#define MAIN_HAS_NOARGC 1 // main函数不支持参数输入
#endif
/* Configuration: MAIN_HAS_NORETURN
Needed if platform does not support returning a value from main.
Valid values:
0 - main returns an int, and return value will be 0.
1 - platform does not support returning a value from main
*/
#ifndef MAIN_HAS_NORETURN
#define MAIN_HAS_NORETURN 1 // main函数没有返回值
#endif
/* Variable: default_num_contexts
Number of contexts to spawn in multicore context.
Override this global value to change number of contexts used.
Note:
This value may not be set higher then the define.
To experiment, you can set the define to the highest value
expected, and use argc/argv in the to set this value from the
command line.
*/
extern ee_u32 default_num_contexts;
#if (MULTITHREAD > 1)
#if USE_PTHREAD
#include
#define PARALLEL_METHOD "PThreads"
#elif USE_FORK
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include /* for memcpy */
#define PARALLEL_METHOD "Fork"
#elif USE_SOCKET
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define PARALLEL_METHOD "Sockets"
#else
#define PARALLEL_METHOD "Proprietary"
#error \
"Please implement multicore functionality in core_portme.c to use multiple contexts."
#endif /* Method for multithreading */
#endif /* MULTITHREAD > 1 */
typedef struct CORE_PORTABLE_S
{
#if (MULTITHREAD > 1)
#if USE_PTHREAD
pthread_t thread;
#elif USE_FORK
pid_t pid;
int shmid;
void *shm;
#elif USE_SOCKET
pid_t pid;
int sock;
struct sockaddr_in sa;
#endif /* Method for multithreading */
#endif /* MULTITHREAD>1 */
ee_u8 portable_id;
} core_portable;
/* target specific init/fini */
void portable_init(core_portable *p, int *argc, char *argv[]);
void portable_fini(core_portable *p);
#if (SEED_METHOD == SEED_VOLATILE)
#if (VALIDATION_RUN || PERFORMANCE_RUN || PROFILE_RUN)
#define RUN_TYPE_FLAG 1
#else
#if (TOTAL_DATA_SIZE == 1200)
#define PROFILE_RUN 1
#else
#define PERFORMANCE_RUN 1
#endif
#endif
#endif /* SEED_METHOD==SEED_VOLATILE */
#endif /* CORE_PORTME_H */ core_portme.c文件修改后如下:
/*
Copyright 2018 Embedded Microprocessor Benchmark Consortium (EEMBC)
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
Original Author: Shay Gal-on
*/
#include
#include
#include "coremark.h"
#if CALLGRIND_RUN
#include
#endif
#if (MEM_METHOD == MEM_MALLOC)
/* Function: portable_malloc
Provide malloc() functionality in a platform specific way.
*/
void *
portable_malloc(size_t size)
{
return malloc(size);
}
/* Function: portable_free
Provide free() functionality in a platform specific way.
*/
void
portable_free(void *p)
{
free(p);
}
#else
void *
portable_malloc(ee_size_t size)
{
return NULL;
}
void
portable_free(void *p)
{
p = NULL;
}
#endif
#if (SEED_METHOD == SEED_VOLATILE)
#if VALIDATION_RUN
volatile ee_s32 seed1_volatile = 0x3415;
volatile ee_s32 seed2_volatile = 0x3415;
volatile ee_s32 seed3_volatile = 0x66;
#endif
#if PERFORMANCE_RUN
volatile ee_s32 seed1_volatile = 0x0;
volatile ee_s32 seed2_volatile = 0x0;
volatile ee_s32 seed3_volatile = 0x66;
#endif
#if PROFILE_RUN
volatile ee_s32 seed1_volatile = 0x8;
volatile ee_s32 seed2_volatile = 0x8;
volatile ee_s32 seed3_volatile = 0x8;
#endif
volatile ee_s32 seed4_volatile = ITERATIONS;
volatile ee_s32 seed5_volatile = 0;
#endif
/* Porting: Timing functions
How to capture time and convert to seconds must be ported to whatever is
supported by the platform. e.g. Read value from on board RTC, read value from
cpu clock cycles performance counter etc. Sample implementation for standard
time.h and windows.h definitions included.
*/
/* Define: TIMER_RES_DIVIDER
Divider to trade off timer resolution and total time that can be
measured.
Use lower values to increase resolution, but make sure that overflow
does not occur. If there are issues with the return value overflowing,
increase this value.
*/
#if USE_CLOCK
#define NSECS_PER_SEC CLOCKS_PER_SEC
#define EE_TIMER_TICKER_RATE 1000
#define CORETIMETYPE clock_t
#define GETMYTIME(_t) (*_t = clock())
#define MYTIMEDIFF(fin, ini) ((fin) - (ini))
#define TIMER_RES_DIVIDER 1
#define SAMPLE_TIME_IMPLEMENTATION 1
#elif defined(_MSC_VER)
#define NSECS_PER_SEC 10000000
#define EE_TIMER_TICKER_RATE 1000
#define CORETIMETYPE FILETIME
#define GETMYTIME(_t) GetSystemTimeAsFileTime(_t)
#define MYTIMEDIFF(fin, ini) \
(((*(__int64 *)&fin) - (*(__int64 *)&ini)) / (double)TIMER_RES_DIVIDER)
/* setting to millisces resolution by default with MSDEV */
#ifndef TIMER_RES_DIVIDER
#define TIMER_RES_DIVIDER 1000
#endif
#define SAMPLE_TIME_IMPLEMENTATION 1
#elif HAS_TIME_H
#define NSECS_PER_SEC 1000000000
#define EE_TIMER_TICKER_RATE 1000
#define CORETIMETYPE struct timespec
#define GETMYTIME(_t) clock_gettime(CLOCK_REALTIME, _t)
#define MYTIMEDIFF(fin, ini) \
((fin.tv_sec - ini.tv_sec) * (NSECS_PER_SEC / (double)TIMER_RES_DIVIDER) \
+ (fin.tv_nsec - ini.tv_nsec) / (double)TIMER_RES_DIVIDER)
/* setting to 1/1000 of a second resolution by default with linux */
#ifndef TIMER_RES_DIVIDER
#define TIMER_RES_DIVIDER 1000000
#endif
#define SAMPLE_TIME_IMPLEMENTATION 1
#else
#define SAMPLE_TIME_IMPLEMENTATION 0
#endif
#define EE_TICKS_PER_SEC (NSECS_PER_SEC / (double)TIMER_RES_DIVIDER)
#if SAMPLE_TIME_IMPLEMENTATION
/** Define Host specific (POSIX), or target specific global time variables. */
static CORETIMETYPE start_time_val, stop_time_val;
/* Function: start_time
This function will be called right before starting the timed portion of
the benchmark.
Implementation may be capturing a system timer (as implemented in the
example code) or zeroing some system parameters - e.g. setting the cpu clocks
cycles to 0.
*/
void
start_time(void)
{
GETMYTIME(&start_time_val);
#if CALLGRIND_RUN
CALLGRIND_START_INSTRUMENTATION
#endif
#if MICA
asm volatile("int3"); /*1 */
#endif
}
/* Function: stop_time
This function will be called right after ending the timed portion of the
benchmark.
Implementation may be capturing a system timer (as implemented in the
example code) or other system parameters - e.g. reading the current value of
cpu cycles counter.
*/
void
stop_time(void)
{
#if CALLGRIND_RUN
CALLGRIND_STOP_INSTRUMENTATION
#endif
#if MICA
asm volatile("int3"); /*1 */
#endif
GETMYTIME(&stop_time_val);
}
/* Function: get_time
Return an abstract "ticks" number that signifies time on the system.
Actual value returned may be cpu cycles, milliseconds or any other
value, as long as it can be converted to seconds by . This
methodology is taken to accommodate any hardware or simulated platform. The
sample implementation returns millisecs by default, and the resolution is
controlled by
*/
CORE_TICKS
get_time(void)
{
CORE_TICKS elapsed
= (CORE_TICKS)(MYTIMEDIFF(stop_time_val, start_time_val));
return elapsed;
}
/* Function: time_in_secs
Convert the value returned by get_time to seconds.
The type is used to accommodate systems with no support for
floating point. Default implementation implemented by the EE_TICKS_PER_SEC
macro above.
*/
secs_ret
time_in_secs(CORE_TICKS ticks)
{
secs_ret retval = (((float))ticks) / ((float))EE_TICKS_PER_SEC;
return retval;
}
#else
void
start_time(void)
{
}
/* Function: stop_time
This function will be called right after ending the timed portion of the
benchmark.
Implementation may be capturing a system timer (as implemented in the
example code) or other system parameters - e.g. reading the current value of
cpu cycles counter.
*/
void
stop_time(void)
{
}
/* Function: get_time
Return an abstract "ticks" number that signifies time on the system.
Actual value returned may be cpu cycles, milliseconds or any other
value, as long as it can be converted to seconds by . This
methodology is taken to accommodate any hardware or simulated platform. The
sample implementation returns millisecs by default, and the resolution is
controlled by
*/
CORE_TICKS
get_time(void)
{
return 0;
}
/* Function: time_in_secs
Convert the value returned by get_time to seconds.
The type is used to accommodate systems with no support for
floating point. Default implementation implemented by the EE_TICKS_PER_SEC
macro above.
*/
secs_ret
time_in_secs(CORE_TICKS ticks)
{
return 0;
}
#endif /* SAMPLE_TIME_IMPLEMENTATION */
ee_u32 default_num_contexts = MULTITHREAD;
/* Function: portable_init
Target specific initialization code
Test for some common mistakes.
*/
void
portable_init(core_portable *p, int *argc, char *argv[])
{
#if PRINT_ARGS
int i;
for (i = 0; i < *argc; i++)
{
ee_printf("Arg[%d]=%s\n", i, argv[i]);
}
#endif
(void)argc; // prevent unused warning
(void)argv; // prevent unused warning
if (sizeof(ee_ptr_int) != sizeof(ee_u8 *))
{
ee_printf(
"ERROR! Please define ee_ptr_int to a type that holds a "
"pointer!\n");
}
if (sizeof(ee_u32) != 4)
{
ee_printf("ERROR! Please define ee_u32 to a 32b unsigned type!\n");
}
#if (MAIN_HAS_NOARGC && (SEED_METHOD == SEED_ARG))
ee_printf(
"ERROR! Main has no argc, but SEED_METHOD defined to SEED_ARG!\n");
#endif
#if (MULTITHREAD > 1) && (SEED_METHOD == SEED_ARG)
int nargs = *argc, i;
if ((nargs > 1) && (*argv[1] == 'M'))
{
default_num_contexts = parseval(argv[1] + 1);
if (default_num_contexts > MULTITHREAD)
default_num_contexts = MULTITHREAD;
/* Shift args since first arg is directed to the portable part and not
* to coremark main */
--nargs;
for (i = 1; i < nargs; i++)
argv[i] = argv[i + 1];
*argc = nargs;
}
#endif /* sample of potential platform specific init via command line, reset \
the number of contexts being used if first argument is M*/
p->portable_id = 1;
}
/* Function: portable_fini
Target specific final code
*/
void
portable_fini(core_portable *p)
{
p->portable_id = 0;
}
#if (MULTITHREAD > 1)
/* Function: core_start_parallel
Start benchmarking in a parallel context.
Three implementations are provided, one using pthreads, one using fork
and shared mem, and one using fork and sockets. Other implementations using
MCAPI or other standards can easily be devised.
*/
/* Function: core_stop_parallel
Stop a parallel context execution of coremark, and gather the results.
Three implementations are provided, one using pthreads, one using fork
and shared mem, and one using fork and sockets. Other implementations using
MCAPI or other standards can easily be devised.
*/
#if USE_PTHREAD
ee_u8
core_start_parallel(core_results *res)
{
return (ee_u8)pthread_create(
&(res->port.thread), NULL, iterate, (void *)res);
}
ee_u8
core_stop_parallel(core_results *res)
{
void *retval;
return (ee_u8)pthread_join(res->port.thread, &retval);
}
#elif USE_FORK
static int key_id = 0;
ee_u8
core_start_parallel(core_results *res)
{
key_t key = 4321 + key_id;
key_id++;
res->port.pid = fork();
res->port.shmid = shmget(key, 8, IPC_CREAT | 0666);
if (res->port.shmid < 0)
{
ee_printf("ERROR in shmget!\n");
}
if (res->port.pid == 0)
{
iterate(res);
res->port.shm = shmat(res->port.shmid, NULL, 0);
/* copy the validation values to the shared memory area and quit*/
if (res->port.shm == (char *)-1)
{
ee_printf("ERROR in child shmat!\n");
}
else
{
memcpy(res->port.shm, &(res->crc), 8);
shmdt(res->port.shm);
}
exit(0);
}
return 1;
}
ee_u8
core_stop_parallel(core_results *res)
{
int status;
pid_t wpid = waitpid(res->port.pid, &status, WUNTRACED);
if (wpid != res->port.pid)
{
ee_printf("ERROR waiting for child.\n");
if (errno == ECHILD)
ee_printf("errno=No such child %d\n", res->port.pid);
if (errno == EINTR)
ee_printf("errno=Interrupted\n");
return 0;
}
/* after process is done, get the values from the shared memory area */
res->port.shm = shmat(res->port.shmid, NULL, 0);
if (res->port.shm == (char *)-1)
{
ee_printf("ERROR in parent shmat!\n");
return 0;
}
memcpy(&(res->crc), res->port.shm, 8);
shmdt(res->port.shm);
return 1;
}
#elif USE_SOCKET
static int key_id = 0;
ee_u8
core_start_parallel(core_results *res)
{
int bound, buffer_length = 8;
res->port.sa.sin_family = AF_INET;
res->port.sa.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(0x7F000001);
res->port.sa.sin_port = htons(7654 + key_id);
key_id++;
res->port.pid = fork();
if (res->port.pid == 0)
{ /* benchmark child */
iterate(res);
res->port.sock = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, IPPROTO_UDP);
if (-1 == res->port.sock) /* if socket failed to initialize, exit */
{
ee_printf("Error Creating Socket");
}
else
{
int bytes_sent = sendto(res->port.sock,
&(res->crc),
buffer_length,
0,
(struct sockaddr *)&(res->port.sa),
sizeof(struct sockaddr_in));
if (bytes_sent < 0)
ee_printf("Error sending packet: %s\n", strerror(errno));
close(res->port.sock); /* close the socket */
}
exit(0);
}
/* parent process, open the socket */
res->port.sock = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, IPPROTO_UDP);
bound = bind(res->port.sock,
(struct sockaddr *)&(res->port.sa),
sizeof(struct sockaddr));
if (bound < 0)
ee_printf("bind(): %s\n", strerror(errno));
return 1;
}
ee_u8
core_stop_parallel(core_results *res)
{
int status;
int fromlen = sizeof(struct sockaddr);
int recsize = recvfrom(res->port.sock,
&(res->crc),
8,
0,
(struct sockaddr *)&(res->port.sa),
&fromlen);
if (recsize < 0)
{
ee_printf("Error in receive: %s\n", strerror(errno));
return 0;
}
pid_t wpid = waitpid(res->port.pid, &status, WUNTRACED);
if (wpid != res->port.pid)
{
ee_printf("ERROR waiting for child.\n");
if (errno == ECHILD)
ee_printf("errno=No such child %d\n", res->port.pid);
if (errno == EINTR)
ee_printf("errno=Interrupted\n");
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
#else /* no standard multicore implementation */
#error \
"Please implement multicore functionality in core_portme.c to use multiple contexts."
#endif /* multithread implementations */
#endif
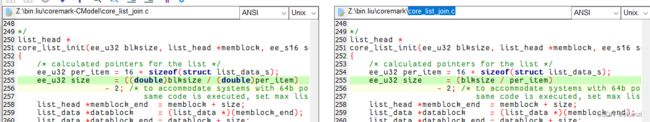
有几点需要注意,我目前用的CModel指令集不支持整数除法,所以对涉及到整数除法的地方做了双精度浮点转换。对应的./core_list_join.c文件也做了修改
./core_main.c文件修改后如下:
/*
Copyright 2018 Embedded Microprocessor Benchmark Consortium (EEMBC)
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
Original Author: Shay Gal-on
*/
/* File: core_main.c
This file contains the framework to acquire a block of memory, seed
initial parameters, tun t he benchmark and report the results.
*/
#include "coremark.h"
/* Function: iterate
Run the benchmark for a specified number of iterations.
Operation:
For each type of benchmarked algorithm:
a - Initialize the data block for the algorithm.
b - Execute the algorithm N times.
Returns:
NULL.
*/
static ee_u16 list_known_crc[] = { (ee_u16)0xd4b0,
(ee_u16)0x3340,
(ee_u16)0x6a79,
(ee_u16)0xe714,
(ee_u16)0xe3c1 };
static ee_u16 matrix_known_crc[] = { (ee_u16)0xbe52,
(ee_u16)0x1199,
(ee_u16)0x5608,
(ee_u16)0x1fd7,
(ee_u16)0x0747 };
static ee_u16 state_known_crc[] = { (ee_u16)0x5e47,
(ee_u16)0x39bf,
(ee_u16)0xe5a4,
(ee_u16)0x8e3a,
(ee_u16)0x8d84 };
void *
iterate(void *pres)
{
ee_u32 i;
ee_u16 crc;
core_results *res = (core_results *)pres;
ee_u32 iterations = res->iterations;
res->crc = 0;
res->crclist = 0;
res->crcmatrix = 0;
res->crcstate = 0;
for (i = 0; i < iterations; i++)
{
crc = core_bench_list(res, 1);
res->crc = crcu16(crc, res->crc);
crc = core_bench_list(res, -1);
res->crc = crcu16(crc, res->crc);
if (i == 0)
res->crclist = res->crc;
}
return NULL;
}
#if (SEED_METHOD == SEED_ARG)
ee_s32 get_seed_args(int i, int argc, char *argv[]);
#define get_seed(x) (ee_s16) get_seed_args(x, argc, argv)
#define get_seed_32(x) get_seed_args(x, argc, argv)
#else /* via function or volatile */
ee_s32 get_seed_32(int i);
#define get_seed(x) (ee_s16) get_seed_32(x)
#endif
#if (MEM_METHOD == MEM_STATIC)
ee_u8 static_memblk[TOTAL_DATA_SIZE];
#endif
char *mem_name[3] = { "Static", "Heap", "Stack" };
/* Function: main
Main entry routine for the benchmark.
This function is responsible for the following steps:
1 - Initialize input seeds from a source that cannot be determined at
compile time. 2 - Initialize memory block for use. 3 - Run and time the
benchmark. 4 - Report results, testing the validity of the output if the
seeds are known.
Arguments:
1 - first seed : Any value
2 - second seed : Must be identical to first for iterations to be
identical 3 - third seed : Any value, should be at least an order of
magnitude less then the input size, but bigger then 32. 4 - Iterations :
Special, if set to 0, iterations will be automatically determined such that
the benchmark will run between 10 to 100 secs
*/
#if MAIN_HAS_NOARGC
MAIN_RETURN_TYPE
main(void)
{
int argc = 0;
char *argv[1];
#else
MAIN_RETURN_TYPE
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
#endif
ee_u16 i, j = 0, num_algorithms = 0;
ee_s16 known_id = -1, total_errors = 0;
ee_u16 seedcrc = 0;
CORE_TICKS total_time;
core_results results[MULTITHREAD];
#if (MEM_METHOD == MEM_STACK)
ee_u8 stack_memblock[TOTAL_DATA_SIZE * MULTITHREAD];
#endif
/* first call any initializations needed */
portable_init(&(results[0].port), &argc, argv);
/* First some checks to make sure benchmark will run ok */
if (sizeof(struct list_head_s) > 128)
{
ee_printf("list_head structure too big for comparable data!\n");
return MAIN_RETURN_VAL;
}
results[0].seed1 = get_seed(1);
results[0].seed2 = get_seed(2);
results[0].seed3 = get_seed(3);
results[0].iterations = get_seed_32(4);
#if CORE_DEBUG
results[0].iterations = 1;
#endif
results[0].execs = get_seed_32(5);
if (results[0].execs == 0)
{ /* if not supplied, execute all algorithms */
results[0].execs = ALL_ALGORITHMS_MASK;
}
/* put in some default values based on one seed only for easy testing */
if ((results[0].seed1 == 0) && (results[0].seed2 == 0)
&& (results[0].seed3 == 0))
{ /* performance run */
results[0].seed1 = 0;
results[0].seed2 = 0;
results[0].seed3 = 0x66;
}
if ((results[0].seed1 == 1) && (results[0].seed2 == 0)
&& (results[0].seed3 == 0))
{ /* validation run */
results[0].seed1 = 0x3415;
results[0].seed2 = 0x3415;
results[0].seed3 = 0x66;
}
#if (MEM_METHOD == MEM_STATIC)
results[0].memblock[0] = (void *)static_memblk;
results[0].size = TOTAL_DATA_SIZE;
results[0].err = 0;
#if (MULTITHREAD > 1)
#error "Cannot use a static data area with multiple contexts!"
#endif
#elif (MEM_METHOD == MEM_MALLOC)
for (i = 0; i < MULTITHREAD; i++)
{
ee_s32 malloc_override = get_seed(7);
if (malloc_override != 0)
results[i].size = malloc_override;
else
results[i].size = TOTAL_DATA_SIZE;
results[i].memblock[0] = portable_malloc(results[i].size);
results[i].seed1 = results[0].seed1;
results[i].seed2 = results[0].seed2;
results[i].seed3 = results[0].seed3;
results[i].err = 0;
results[i].execs = results[0].execs;
}
#elif (MEM_METHOD == MEM_STACK)
for (i = 0; i < MULTITHREAD; i++)
{
results[i].memblock[0] = stack_memblock + i * TOTAL_DATA_SIZE;
results[i].size = TOTAL_DATA_SIZE;
results[i].seed1 = results[0].seed1;
results[i].seed2 = results[0].seed2;
results[i].seed3 = results[0].seed3;
results[i].err = 0;
results[i].execs = results[0].execs;
}
#else
#error "Please define a way to initialize a memory block."
#endif
/* Data init */
/* Find out how space much we have based on number of algorithms */
for (i = 0; i < NUM_ALGORITHMS; i++)
{
if ((1 << (ee_u32)i) & results[0].execs)
num_algorithms++;
}
for (i = 0; i < MULTITHREAD; i++)
results[i].size = (double)results[i].size / (double)num_algorithms;
/* Assign pointers */
for (i = 0; i < NUM_ALGORITHMS; i++)
{
ee_u32 ctx;
if ((1 << (ee_u32)i) & results[0].execs)
{
for (ctx = 0; ctx < MULTITHREAD; ctx++)
results[ctx].memblock[i + 1]
= (char *)(results[ctx].memblock[0]) + results[0].size * j;
j++;
}
}
/* call inits */
for (i = 0; i < MULTITHREAD; i++)
{
if (results[i].execs & ID_LIST)
{
results[i].list = core_list_init(
results[0].size, results[i].memblock[1], results[i].seed1);
}
if (results[i].execs & ID_MATRIX)
{
core_init_matrix(results[0].size,
results[i].memblock[2],
(ee_s32)results[i].seed1
| (((ee_s32)results[i].seed2) << 16),
&(results[i].mat));
}
if (results[i].execs & ID_STATE)
{
core_init_state(
results[0].size, results[i].seed1, results[i].memblock[3]);
}
}
/* automatically determine number of iterations if not set */
if (results[0].iterations == 0)
{
secs_ret secs_passed = 0;
ee_u32 divisor;
results[0].iterations = 1;
while (secs_passed < (secs_ret)1)
{
results[0].iterations *= 10;
start_time();
iterate(&results[0]);
stop_time();
secs_passed = time_in_secs(get_time());
}
/* now we know it executes for at least 1 sec, set actual run time at
* about 10 secs */
divisor = (ee_u32)secs_passed;
if (divisor == 0) /* some machines cast float to int as 0 since this
conversion is not defined by ANSI, but we know at
least one second passed */
divisor = 1;
results[0].iterations *= 1.0 + 10.0 / (double)divisor;
}
/* perform actual benchmark */
start_time();
#if (MULTITHREAD > 1)
if (default_num_contexts > MULTITHREAD)
{
default_num_contexts = MULTITHREAD;
}
for (i = 0; i < default_num_contexts; i++)
{
results[i].iterations = results[0].iterations;
results[i].execs = results[0].execs;
core_start_parallel(&results[i]);
}
for (i = 0; i < default_num_contexts; i++)
{
core_stop_parallel(&results[i]);
}
#else
iterate(&results[0]);
#endif
stop_time();
total_time = get_time();
/* get a function of the input to report */
seedcrc = crc16(results[0].seed1, seedcrc);
seedcrc = crc16(results[0].seed2, seedcrc);
seedcrc = crc16(results[0].seed3, seedcrc);
seedcrc = crc16(results[0].size, seedcrc);
switch (seedcrc)
{ /* test known output for common seeds */
case 0x8a02: /* seed1=0, seed2=0, seed3=0x66, size 2000 per algorithm */
known_id = 0;
ee_printf("6k performance run parameters for coremark.\n");
break;
case 0x7b05: /* seed1=0x3415, seed2=0x3415, seed3=0x66, size 2000 per
algorithm */
known_id = 1;
ee_printf("6k validation run parameters for coremark.\n");
break;
case 0x4eaf: /* seed1=0x8, seed2=0x8, seed3=0x8, size 400 per algorithm
*/
known_id = 2;
ee_printf("Profile generation run parameters for coremark.\n");
break;
case 0xe9f5: /* seed1=0, seed2=0, seed3=0x66, size 666 per algorithm */
known_id = 3;
ee_printf("2K performance run parameters for coremark.\n");
break;
case 0x18f2: /* seed1=0x3415, seed2=0x3415, seed3=0x66, size 666 per
algorithm */
known_id = 4;
ee_printf("2K validation run parameters for coremark.\n");
break;
default:
total_errors = -1;
break;
}
if (known_id >= 0)
{
for (i = 0; i < default_num_contexts; i++)
{
results[i].err = 0;
if ((results[i].execs & ID_LIST)
&& (results[i].crclist != list_known_crc[known_id]))
{
ee_printf("[%u]ERROR! list crc 0x%04x - should be 0x%04x\n",
i,
results[i].crclist,
list_known_crc[known_id]);
results[i].err++;
}
if ((results[i].execs & ID_MATRIX)
&& (results[i].crcmatrix != matrix_known_crc[known_id]))
{
ee_printf("[%u]ERROR! matrix crc 0x%04x - should be 0x%04x\n",
i,
results[i].crcmatrix,
matrix_known_crc[known_id]);
results[i].err++;
}
if ((results[i].execs & ID_STATE)
&& (results[i].crcstate != state_known_crc[known_id]))
{
ee_printf("[%u]ERROR! state crc 0x%04x - should be 0x%04x\n",
i,
results[i].crcstate,
state_known_crc[known_id]);
results[i].err++;
}
total_errors += results[i].err;
}
}
total_errors += check_data_types();
/* and report results */
ee_printf("CoreMark Size : %lu\n", (long unsigned)results[0].size);
ee_printf("Total ticks : %lu\n", (long unsigned)total_time);
#if HAS_FLOAT
ee_printf("Total time (secs): %f\n", time_in_secs(total_time));
if (time_in_secs(total_time) > 0)
ee_printf("Iterations/Sec : %f\n",
default_num_contexts * results[0].iterations
/ (double)time_in_secs(total_time));
#else
ee_printf("Total time (secs): %d\n", time_in_secs(total_time));
if (time_in_secs(total_time) > 0)
ee_printf("Iterations/Sec : %d\n",
default_num_contexts * results[0].iterations
/ (double)time_in_secs(total_time));
#endif
if (time_in_secs(total_time) < 10)
{
ee_printf(
"ERROR! Must execute for at least 10 secs for a valid result!\n");
total_errors++;
}
ee_printf("Iterations : %lu\n",
(long unsigned)default_num_contexts * results[0].iterations);
ee_printf("Compiler version : %s\n", COMPILER_VERSION);
ee_printf("Compiler flags : %s\n", COMPILER_FLAGS);
#if (MULTITHREAD > 1)
ee_printf("Parallel %s : %d\n", PARALLEL_METHOD, default_num_contexts);
#endif
ee_printf("Memory location : %s\n", MEM_LOCATION);
/* output for verification */
ee_printf("seedcrc : 0x%04x\n", seedcrc);
if (results[0].execs & ID_LIST)
for (i = 0; i < default_num_contexts; i++)
ee_printf("[%d]crclist : 0x%04x\n", i, results[i].crclist);
if (results[0].execs & ID_MATRIX)
for (i = 0; i < default_num_contexts; i++)
ee_printf("[%d]crcmatrix : 0x%04x\n", i, results[i].crcmatrix);
if (results[0].execs & ID_STATE)
for (i = 0; i < default_num_contexts; i++)
ee_printf("[%d]crcstate : 0x%04x\n", i, results[i].crcstate);
for (i = 0; i < default_num_contexts; i++)
ee_printf("[%d]crcfinal : 0x%04x\n", i, results[i].crc);
if (total_errors == 0)
{
ee_printf(
"Correct operation validated. See README.md for run and reporting "
"rules.\n");
#if HAS_FLOAT
if (known_id == 3)
{
ee_printf("CoreMark 1.0 : %f / %s %s",
default_num_contexts * results[0].iterations
/ (double)time_in_secs(total_time),
COMPILER_VERSION,
COMPILER_FLAGS);
#if defined(MEM_LOCATION) && !defined(MEM_LOCATION_UNSPEC)
ee_printf(" / %s", MEM_LOCATION);
#else
ee_printf(" / %s", mem_name[MEM_METHOD]);
#endif
#if (MULTITHREAD > 1)
ee_printf(" / %d:%s", default_num_contexts, PARALLEL_METHOD);
#endif
ee_printf("\n");
}
#endif
}
if (total_errors > 0)
ee_printf("Errors detected\n");
if (total_errors < 0)
ee_printf(
"Cannot validate operation for these seed values, please compare "
"with results on a known platform.\n");
#if (MEM_METHOD == MEM_MALLOC)
for (i = 0; i < MULTITHREAD; i++)
portable_free(results[i].memblock[0]);
#endif
/* And last call any target specific code for finalizing */
portable_fini(&(results[0].port));
return MAIN_RETURN_VAL;
}
void ee_printf(char *p, ...)
{
}在core_main.c文件末尾处加了ee_printf()函数定义,同时在coremark.h文件中添加了ee_printf()函数声明,如下:
/*
Copyright 2018 Embedded Microprocessor Benchmark Consortium (EEMBC)
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
Original Author: Shay Gal-on
*/
/* Topic: Description
This file contains declarations of the various benchmark functions.
*/
/* Configuration: TOTAL_DATA_SIZE
Define total size for data algorithms will operate on
*/
#ifndef TOTAL_DATA_SIZE
#define TOTAL_DATA_SIZE 2 * 1000
#endif
#define SEED_ARG 0
#define SEED_FUNC 1
#define SEED_VOLATILE 2
#define MEM_STATIC 0
#define MEM_MALLOC 1
#define MEM_STACK 2
#include "core_portme.h"
#if HAS_STDIO
#include
#endif
#if HAS_PRINTF
#define ee_printf printf
#else
void ee_printf(char *p, ...);
#endif
/* Actual benchmark execution in iterate */
void *iterate(void *pres);
/* Typedef: secs_ret
For machines that have floating point support, get number of seconds as
a double. Otherwise an unsigned int.
*/
#if HAS_FLOAT
typedef double secs_ret;
#else
typedef ee_u32 secs_ret;
#endif
#if MAIN_HAS_NORETURN
#define MAIN_RETURN_VAL
#define MAIN_RETURN_TYPE void
#else
#define MAIN_RETURN_VAL 0
#define MAIN_RETURN_TYPE int
#endif
void start_time(void);
void stop_time(void);
CORE_TICKS get_time(void);
secs_ret time_in_secs(CORE_TICKS ticks);
/* Misc useful functions */
ee_u16 crcu8(ee_u8 data, ee_u16 crc);
ee_u16 crc16(ee_s16 newval, ee_u16 crc);
ee_u16 crcu16(ee_u16 newval, ee_u16 crc);
ee_u16 crcu32(ee_u32 newval, ee_u16 crc);
ee_u8 check_data_types(void);
void * portable_malloc(ee_size_t size);
void portable_free(void *p);
ee_s32 parseval(char *valstring);
/* Algorithm IDS */
#define ID_LIST (1 << 0)
#define ID_MATRIX (1 << 1)
#define ID_STATE (1 << 2)
#define ALL_ALGORITHMS_MASK (ID_LIST | ID_MATRIX | ID_STATE)
#define NUM_ALGORITHMS 3
/* list data structures */
typedef struct list_data_s
{
ee_s16 data16;
ee_s16 idx;
} list_data;
typedef struct list_head_s
{
struct list_head_s *next;
struct list_data_s *info;
} list_head;
/*matrix benchmark related stuff */
#define MATDAT_INT 1
#if MATDAT_INT
typedef ee_s16 MATDAT;
typedef ee_s32 MATRES;
#else
typedef ee_f16 MATDAT;
typedef ee_f32 MATRES;
#endif
typedef struct MAT_PARAMS_S
{
int N;
MATDAT *A;
MATDAT *B;
MATRES *C;
} mat_params;
/* state machine related stuff */
/* List of all the possible states for the FSM */
typedef enum CORE_STATE
{
CORE_START = 0,
CORE_INVALID,
CORE_S1,
CORE_S2,
CORE_INT,
CORE_FLOAT,
CORE_EXPONENT,
CORE_SCIENTIFIC,
NUM_CORE_STATES
} core_state_e;
/* Helper structure to hold results */
typedef struct RESULTS_S
{
/* inputs */
ee_s16 seed1; /* Initializing seed */
ee_s16 seed2; /* Initializing seed */
ee_s16 seed3; /* Initializing seed */
void * memblock[4]; /* Pointer to safe memory location */
ee_u32 size; /* Size of the data */
ee_u32 iterations; /* Number of iterations to execute */
ee_u32 execs; /* Bitmask of operations to execute */
struct list_head_s *list;
mat_params mat;
/* outputs */
ee_u16 crc;
ee_u16 crclist;
ee_u16 crcmatrix;
ee_u16 crcstate;
ee_s16 err;
/* ultithread specific */
core_portable port;
} core_results;
/* Multicore execution handling */
#if (MULTITHREAD > 1)
ee_u8 core_start_parallel(core_results *res);
ee_u8 core_stop_parallel(core_results *res);
#endif
/* list benchmark functions */
list_head *core_list_init(ee_u32 blksize, list_head *memblock, ee_s16 seed);
ee_u16 core_bench_list(core_results *res, ee_s16 finder_idx);
/* state benchmark functions */
void core_init_state(ee_u32 size, ee_s16 seed, ee_u8 *p);
ee_u16 core_bench_state(ee_u32 blksize,
ee_u8 *memblock,
ee_s16 seed1,
ee_s16 seed2,
ee_s16 step,
ee_u16 crc);
/* matrix benchmark functions */
ee_u32 core_init_matrix(ee_u32 blksize,
void * memblk,
ee_s32 seed,
mat_params *p);
ee_u16 core_bench_matrix(mat_params *p, ee_s16 seed, ee_u16 crc);
为了使用alpha编译工具链编译裸机程序,需要编写链接脚本,避开C标准库链接流程,链接脚本如下:
ENTRY(_start) /*定义程序入口*/
SECTIONS /*定义程序各个段*/
{
PROVIDE(__START_ADDR = 0x0); /*定义程序起始内存地址*/
PROVIDE(__MAX_SIZE = 1024M); /*整个程序的内存空间限定在1G以内*/
PROVIDE(__HEAP_SIZE = 500M); /*堆内存空间大小*/
PROVIDE(__STACK_SIZE = 100M); /*栈内存空间大小*/
. = __START_ADDR; /*设置一个偏移地址,以便达到设置代码段开始地址的目的*/
.text : /*代码段设定,即配置众多object文件中哪些段内容要合并到目标程序的代码段*/
{
*(start2.o) /*指定 start.o 中的函数在最首部*/
*(.text)
}
.data : ALIGN(8) /*数据段定义,设置了地址8字节对齐*/
{
*(.data)
}
.bss (NOLOAD) : ALIGN(8) /*未初始化数据段定义*/
{
*(.bss)
}
.heap (NOLOAD) : ALIGN(16) /*堆内存空间定义,16字节对齐*/
{
. += __HEAP_SIZE;
}
.stack (NOLOAD) : ALIGN(16) /*栈内存空间定义,16字节对齐*/
{
. += __STACK_SIZE;
. = ALIGN(16);
}
/*检查程序内存使用是否超限*/
ASSERT(. < __START_ADDR + __MAX_SIZE, "Failed, out of memory!")
}
在连接脚本中,将程序路口内存地址设置为0位置 ,方便在CModel上进行调试
还需要编写程序加载和初始化汇编代码如下:
.set noreorder
.set volatile
.arch sw6b
.text
.globl _start
.align 4
_start:
br $27,$LNEXT # $27 <- absolute address of $LNEXT
$LNEXT:
ldih $29,0($27) !gpdisp!1
ldi $29,0($29) !gpdisp!1 # $29 <- gp
ldl $27,main($29) !literal # $27 <- &main
call $26,($27)
ldi $r16,0($r0) # $16 <- (exit code)
ldi $r0,405($r31) # $0 <- 405(exit func)
sys_call 0x83
$LDEAD:
br $LDEAD
初始化了gp寄存器值,这个很重要,是后续函数调用和全局变量调用的寻址基址寄存器
最后编写Makefile文件,如下:
CC := @gcc
AS := @as
LD := @ld
RM := @rm
ODP := @objdump
OCP := @objcopy -O binary
ECHO := @echo
O := -O0
G := -g
TG := coremark
sources := $(wildcard *.c)
objects := $(patsubst %.c, %.o, $(sources))
FLAGS_STR = "$(O)"
ifndef ITERATIONS
ITERATIONS=100
endif
CFLAGS += -DITERATIONS=$(ITERATIONS)
.PHONY : all
all : start.o $(objects)
$(LD) start.o $(objects) -T cmodel.lds -o $(TG)
$(ODP) -S $(TG) > $(TG).s
$(OCP) $(TG) $(TG).bin
$(ECHO) "Build success!"
start.o: start.s
$(AS) -c $< -o $@
%.o : %.c
$(CC) $(G) $(O) -c $(CFLAGS) $< -o $@ -DFLAGS_STR=\"$(FLAGS_STR)\"
.PHONY : clean
clean :
$(RM) $(wildcard *.o) $(wildcard *.bin) $(TG) $(TG).sw
$(ECHO) "Clean success!"
.PHONY : test
test :
./$(TG).swcoremark程序编译出来后,我们还使用objcopy工具,将coremark程序中的需要载入内存部分二进制内容拷贝到coremark.bin文件中,以便给CModel程序加载用。