mybatis之动态SQL常见标签的使用
引入where标签的原因:
在上篇文章使用if语句的查询中,我们在SQL语句后面都写入了where 1=1,以保证每次都能够查询出结果,但这种方法并不是最合理的,假设我们现在将where后面的1=1去掉:
如下所示:
<select id="queryBlogIF" resultType="Blog">
SELECT * FROM BLOG where
<if test="title != null">
title like #{title}
</if>
<if test="author != null">
AND author like #{author}
</if>
</select>
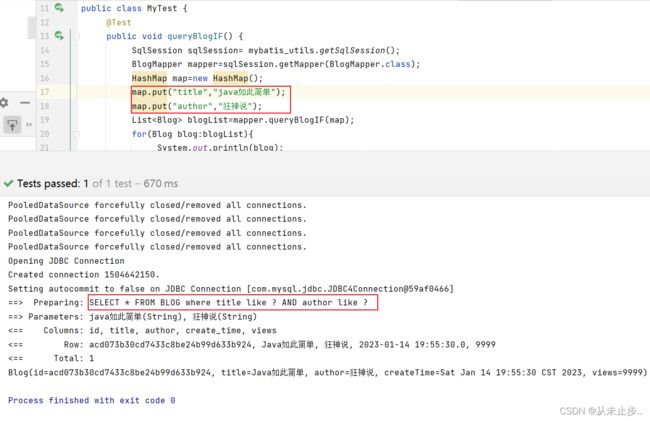
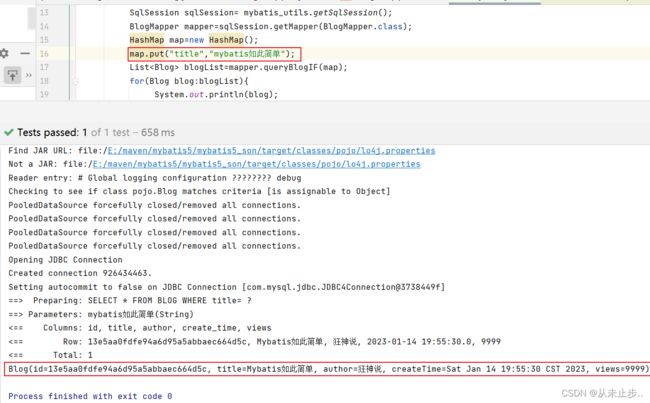
我们传入单独的title,查询结果:
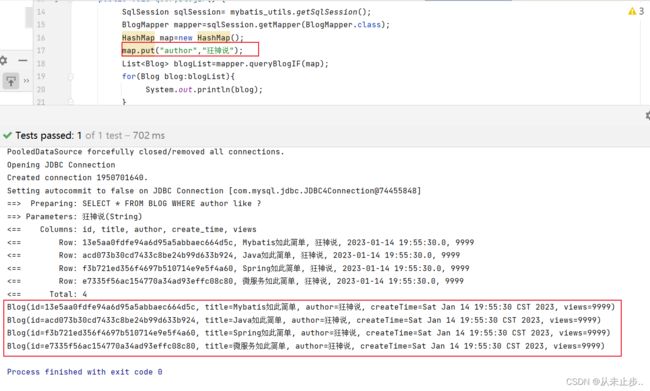
我们传入单独的author,查询结果:
查看报错原因,我们会发现,是由于拼接后的SQL语句出现问题
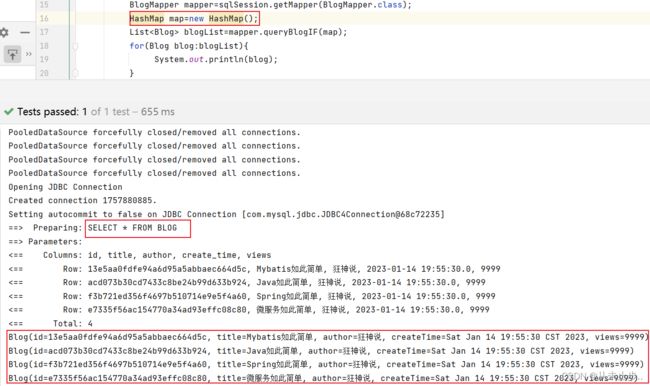
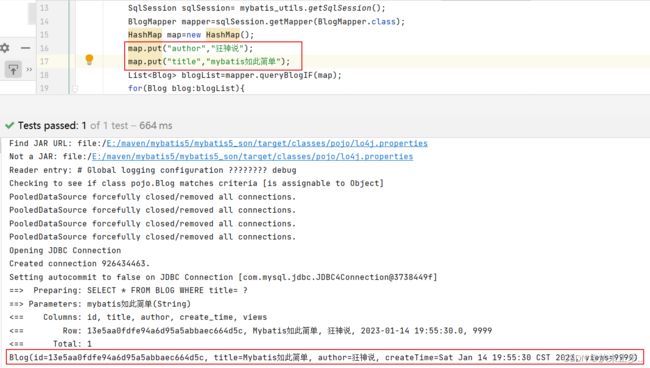
我们传入title和author,查询结果:
综合分析上述三种结果,我们可以得出这样一个结论,"and"关键字并不能在我们单独使用某个条件的时候自动的被去除,由此才会发生SQL语句拼接导致的语法错误
针对上述这种情况,我们由此引入where标签!
where标签的使用:
修改SQL语句如下所示:
<select id="queryBlogIF" resultType="Blog">
SELECT * FROM BLOG
<where>
<if test="title != null">
and title like #{title}
</if>
<if test="author != null">
AND author like #{author}
</if>
</where>
</select>
测试1:
测试2:
引入where标签后,并不会出现拼接错误的SQL语句,而是智能的将多余的and去掉,以保证SQL语句可以正确执行
where 元素只会在子元素返回任何内容的情况下才插入 “WHERE” 子句,若子句的开头为 “AND” 或 “OR”,where 元素也会将它们去除
举例:
当author和title都没有传入的时候,where会自动被去除,相当于查询所有的数据
choose/when/otherwise:
但有时候,我们不想使用所有的条件,而只是想从多个条件中选择一个使用
针对这种情况,MyBatis 提供了 choose 元素,它有点像 Java 中的 switch 语句,还是上面的例子,但是思路变为:传入了 “title” 就按 “title” 查找,传入了 “author” 就按 “author” 查找的情形。若两者都没有传入,就返回标记为 views 的 BLOG
<select id="queryBlogIF" resultType="Blog">
SELECT * FROM BLOG
<where>
<choose>
<when test="title != null">
title= #{title}
</when>
<when test="author != null">
author = #{author}
</when>
<otherwise>
views=#{views}
</otherwise>
</choose>
</where>
</select>
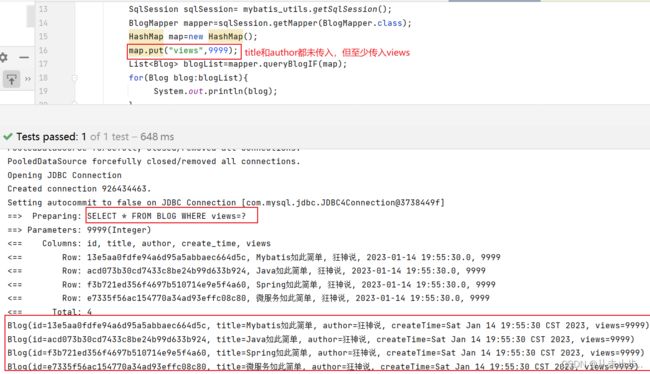
当title和author都未传入时,至少保证要传入views[也就是otherwise标签中的元素,否则查询结果为null]:
当只传入title的值时,查询结果只输出title为我们传入的值的数据:
当author和title同时传入时:
SQL执行过程分析如下:
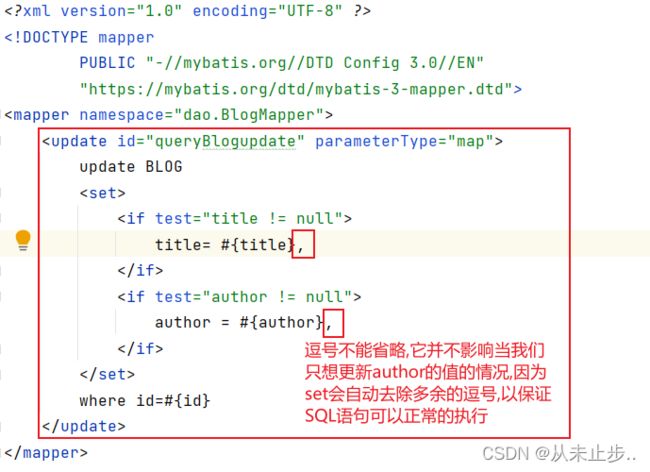
动态更新语句:
第一步:接口中编写方法
//更新博客
int queryBlogupdate(Map map);
第二步:.xml文件中编写SQL语句
<update id="queryBlogupdate" parameterType="map">
update BLOG
<set>
<if test="title != null">
title= #{title},
</if>
<if test="author != null">
author = #{author},
</if>
</set>
where id=#{id}
</update>
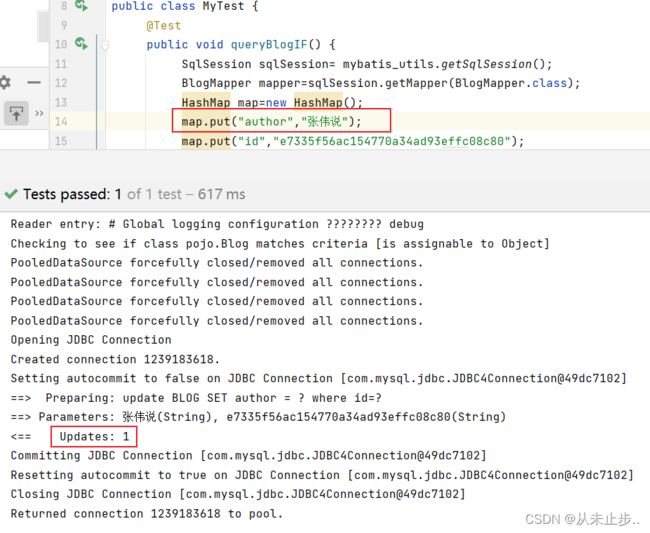
第三步:测试类中进行测试
@Test
public void queryBlogIF() {
SqlSession sqlSession= mybatis_utils.getSqlSession();
BlogMapper mapper=sqlSession.getMapper(BlogMapper.class);
HashMap map=new HashMap();
//传入要更新的字段
map.put("author","张三说");
map.put("title","数据结构如此简单");
map.put("id","e7335f56ac154770a34ad93effc08c80");
mapper.queryBlogupdate(map);
sqlSession.close();
}
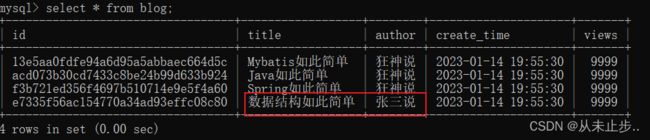
部分输出结果如下:
数据库中查询:
set 元素会动态地在行首插入 SET 关键字,并会删掉额外的逗号(这些逗号是在使用条件语句给列赋值时引入的)
举例:
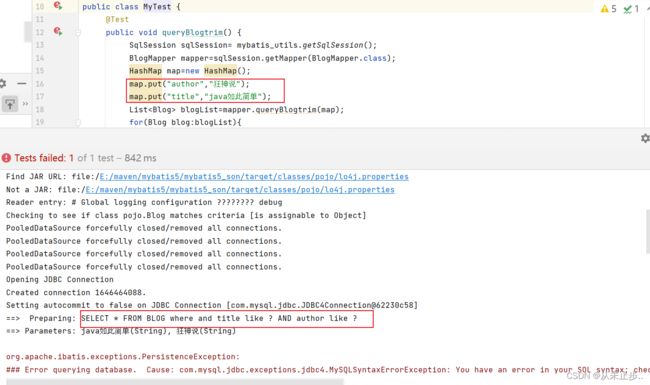
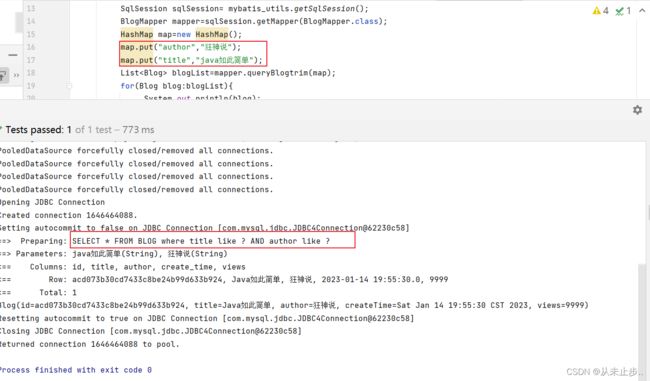
上述的SQL语句不变,这次我们只更新author:
细心的小伙伴会发现在更新数据的SQL语句中,每个参数后面都有“逗号”,那么为什么上述例子中,我们更新了SQL语句第二个参数的数据,还成功了呢?难道逗号不会对此有影响吗?
原因如下:
set 元素可以用于动态包含需要更新的列,忽略其它不更新的列
trim标签:
trim标签的作用:
1:在自己包含的内容前加上某些前缀,例如prefix="where",也可以在其后加上某写后缀,例如:suffix="set"
2:把包含内容的首部某些内容覆盖,即忽略,例如:prefixOverrides="and|or",也可以把尾部的某些内容覆盖,例如:suffixOverrides=","
使用方法1:
<trim prefix="WHERE" prefixOverrides="AND |OR ">
...
</trim>
prefix=“where”:等价于加where标签的效果
prefixOverrides=“AND |OR”:表示去除首部多余的and或者or
举例:
未加trim标签的效果:
SQL语句:
<select id="queryBlogtrim" resultType="Blog">
SELECT * FROM BLOG
<if test="title != null">
and title like #{title}
</if>
<if test="author != null">
AND author like #{author}
</if>
</select>
添加trim标签并添加prefix=“WHERE” 属性的效果:
SQL语句:
<select id="queryBlogtrim" resultType="Blog">
SELECT * FROM BLOG
<trim prefix="where">
<if test="title != null">
and title like #{title}
</if>
<if test="author != null">
AND author like #{author}
</if>
</trim>
</select>
与上述未添加的效果不同之处在于,这次多了个where
添加trim标签并添加prefix=“WHERE” 和prefixOverrides="AND |OR 属性的效果:
完整的正确用法如下:
<select id="queryBlogtrim" resultType="Blog">
SELECT * FROM BLOG
<trim prefix="where" prefixOverrides="and|or">
<if test="title != null">
and title like #{title}
</if>
<if test="author != null">
AND author like #{author}
</if>
</trim>
</select>
此时与最初的对比,不仅有了where,而且,对于的and也会被自动的去除
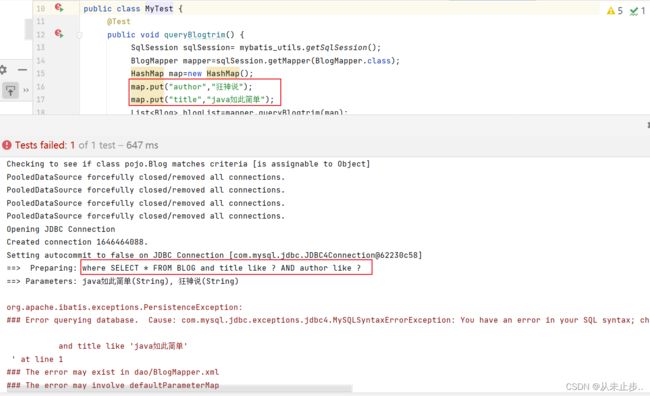
注意:
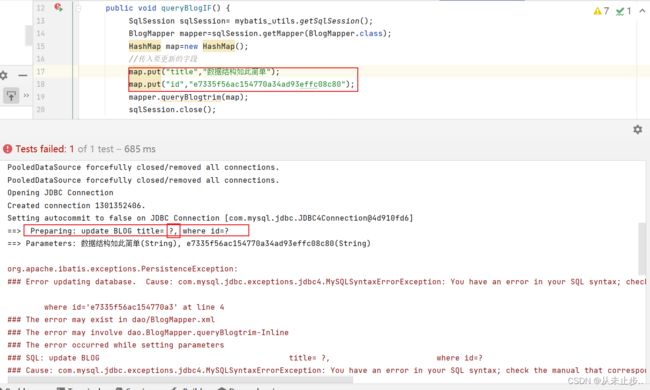
如果有小伙伴报下述这种错误,请去检查是不是把trim标签的位置放错了,trim标签应该放在SQL语句下面一行
使用方法2:
<trim prefix="SET" suffixOverrides=",">
...
</trim>
prefix=“set”:等价于加set标签的效果
suffixOverrides=“,”,表示去除尾部多余的逗号
举例;
未加trim标签的效果:
SQL语句:
<update id="queryBlogtrim" parameterType="map">
update BLOG
<if test="author != null">
author = #{author},
</if>
<if test="title != null">
title= #{title},
</if>
where id=#{id}
</update>
添加trim标签并添加prefix="SET"属性的效果:
SQL语句:
<update id="queryBlogtrim" parameterType="map">
update BLOG
<trim prefix="set">
<if test="author != null">
author = #{author},
</if>
<if test="title != null">
title= #{title},
</if>
</trim>
where id=#{id}
</update>
与上述未添加的效果不同之处在于,这次多了个set
添加trim标签并添加 prefix=“SET” suffixOverrides=","属性的效果:
完整的正确用法如下:
<update id="queryBlogtrim" parameterType="map">
update BLOG
<trim prefix="SET" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="author != null">
author = #{author},
</if>
<if test="title != null">
title= #{title},
</if>
</trim>
where id=#{id}
</update>
此时与最初的对比,不仅有了set,而且,对于的多余的“,”也会被自动的去除
注:prefix/suffix,前者表示在SQL语句增加前缀,而后者表示在SQL语句中增加后缀,在开头我们只是举例prefix=“where”,当然它也可以prefix=“set”,它并不是谁唯一的,具体的前/后缀值,我们可以根据实际的SQL语句所需进行设定
与
以查询为例:
未使用
<select id="selectBlog" parameterType="map" resultType="Blog">
select * from blog
<where>
<if test="title!=null">
title =#{title}
</if>
<if test="author!=null">
and author=#{author}
</if>
</where>
</select>
使用
SQL标签的作用:将公共的代码单拎出来,提高公共代码的复用
第一步:使用SQL标签抽取公共的部分:
<sql id="if-title-author">
<if test="title!=null">
title =#{title}
</if>
<if test="author!=null">
and author=#{author}
</if>
</sql>
第二步:在需要使用的地方,通过
<select id="selectBlog" parameterType="map" resultType="Blog">
select * from blog
<where>
<include refid="if-title-author"></include>
</where>
</select>
而使用SQL标签与未使用SQL标签的区别仅仅就体现在是否将公共的代码块提取出来,方便复用,其它并无任何的差别
注意事项:
1:最好基于单表来定义SQL片段-----复杂的事情重复率低
2:不要存在where标签