分布式事务框架(seata1.5.0)源码分析-AT模式
目录
AT一阶段
datasource代理
sql执行
commit逻辑-ConnectionProxy.commit
processGlobalTransactionCommit-全局事务下
processLocalCommitWithGlobalLocks-@GlobalLock注解
Rollback逻辑-ConnectionProxy.rollback
beforeImage和afterImage
INSERT
UPDATE
DELETE
SELECT_FOR_UPDATE
AT二阶段
Commit
Rollback
总结
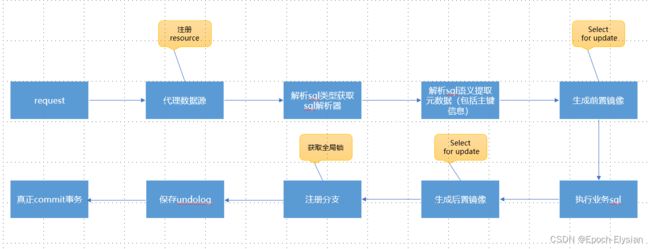
Seata的AT模式也是由两阶段提交协议演变而来,对业务无侵入,基于数据源代理自动生成回滚sql,基本流程如下:
一阶段:
- 解析 sql 并查询得到前镜像
- 执行业务 sql
- 查询执行后的数据作为后镜像
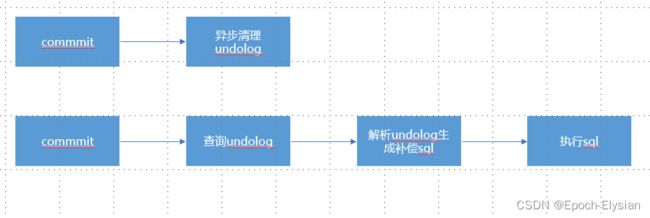
二阶段:
- commit:仅需把事务相关信息删除即可(异步删除,理论上不删除也没问题)
- rollback:通过一阶段的前镜像进行反向补偿
AT一阶段
datasource代理
在seata-spring-boot-starter包里找到SeataDataSourceAutoConfiguration,这个类就是代理数据源的配置类。
@ConditionalOnBean(DataSource.class)
@ConditionalOnExpression("${seata.enabled:true} && ${seata.enableAutoDataSourceProxy:true} && ${seata.enable-auto-data-source-proxy:true}")
@AutoConfigureAfter({SeataCoreAutoConfiguration.class})
public class SeataDataSourceAutoConfiguration {
/**
* The bean seataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator.
*/
@Bean(BEAN_NAME_SEATA_AUTO_DATA_SOURCE_PROXY_CREATOR)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(SeataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator.class)
public SeataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator seataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator(SeataProperties seataProperties) {
// 数据源代理模式默认AT
return new SeataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator(seataProperties.isUseJdkProxy(),
seataProperties.getExcludesForAutoProxying(), seataProperties.getDataSourceProxyMode());
}
}注入SeataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator(AOP切面代理类),代理数据源
public class SeataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator extends AbstractAutoProxyCreator {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SeataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator.class);
private final Set excludes;
private final String dataSourceProxyMode;
private final Object[] advisors;
public SeataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator(boolean useJdkProxy, String[] excludes, String dataSourceProxyMode) {
setProxyTargetClass(!useJdkProxy);
this.excludes = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(excludes));
this.dataSourceProxyMode = dataSourceProxyMode;
this.advisors = buildAdvisors(dataSourceProxyMode);
}
// 切面advisor
private Object[] buildAdvisors(String dataSourceProxyMode) {
//方法拦截增强
Advice advice = new SeataAutoDataSourceProxyAdvice(dataSourceProxyMode);
return new Object[]{new DefaultIntroductionAdvisor(advice)};
}
/**
* 添加 DefaultIntroductionAdvisor 增强器
* @param beanClass
* @param beanName
* @param customTargetSource
* @return
*/
@Override
protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(Class beanClass, String beanName, TargetSource customTargetSource) {
return advisors;
}
@Override
protected boolean shouldSkip(Class beanClass, String beanName) {
if (excludes.contains(beanClass.getName())) {
return true;
}
return SeataProxy.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass);
}
@Override
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
// we only care DataSource bean
if (!(bean instanceof DataSource)) {
return bean;
}
// when this bean is just a simple DataSource, not SeataDataSourceProxy
// 应用引入非SeataDataSourceProxy类型的数据源,如druid则进行代理
if (!(bean instanceof SeataDataSourceProxy)) {
//看下是否已经被代理了
Object enhancer = super.wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
// this mean this bean is either excluded by user or had been proxy before
if (bean == enhancer) {
return bean;
}
// else, build proxy, put to holder and return enhancer
DataSource origin = (DataSource) bean;
// 使用seata代理数据源包装原生数据源 AT模式下为DataSourceProxy
SeataDataSourceProxy proxy = buildProxy(origin, dataSourceProxyMode);
// 以原生数据源为key,包装后的数据源 为value,缓存到map中
DataSourceProxyHolder.put(origin, proxy);
return enhancer;
}
/*
* things get dangerous when you try to register SeataDataSourceProxy bean by yourself!
* if you insist on doing so, you must make sure your method return type is DataSource,
* because this processor will never return any subclass of SeataDataSourceProxy
*/
LOGGER.warn("Manually register SeataDataSourceProxy(or its subclass) bean is discouraged! bean name: {}", beanName);
// 走到这里说明是应用自定义了SeataDataSourceProxy类型的数据源,检查一下
SeataDataSourceProxy proxy = (SeataDataSourceProxy) bean;
DataSource origin = proxy.getTargetDataSource();
Object originEnhancer = super.wrapIfNecessary(origin, beanName, cacheKey);
// this mean origin is either excluded by user or had been proxy before
if (origin == originEnhancer) {
return origin;
}
// else, put to holder and return originEnhancer
DataSourceProxyHolder.put(origin, proxy);
return originEnhancer;
}
SeataDataSourceProxy buildProxy(DataSource origin, String proxyMode) {
if (BranchType.AT.name().equalsIgnoreCase(proxyMode)) {
return new DataSourceProxy(origin);
}
if (BranchType.XA.name().equalsIgnoreCase(proxyMode)) {
return new DataSourceProxyXA(origin);
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown dataSourceProxyMode: " + proxyMode);
}
} 也就是说seata使用DataSourceProxy对原生的数据源进行代理
public class DataSourceProxy extends AbstractDataSourceProxy implements Resource {
private static final String DEFAULT_RESOURCE_GROUP_ID = "DEFAULT";
private String resourceGroupId;
private String jdbcUrl;
private String resourceId;
private String dbType;
private String userName;
/**
* Instantiates a new Data source proxy.
*
* @param targetDataSource the target data source
*/
public DataSourceProxy(DataSource targetDataSource) {
this(targetDataSource, DEFAULT_RESOURCE_GROUP_ID);
}
/**
* Instantiates a new Data source proxy.
*
* @param targetDataSource the target data source
* @param resourceGroupId the resource group id
*/
public DataSourceProxy(DataSource targetDataSource, String resourceGroupId) {
if (targetDataSource instanceof SeataDataSourceProxy) {
LOGGER.info("Unwrap the target data source, because the type is: {}", targetDataSource.getClass().getName());
targetDataSource = ((SeataDataSourceProxy) targetDataSource).getTargetDataSource();
}
// 保证原始数据源
this.targetDataSource = targetDataSource;
// 这里的初始化
init(targetDataSource, resourceGroupId);
}
private void init(DataSource dataSource, String resourceGroupId) {
this.resourceGroupId = resourceGroupId;
// 初始化数据源
try (Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection()) {
jdbcUrl = connection.getMetaData().getURL();
// 数据库类型
dbType = JdbcUtils.getDbType(jdbcUrl);
if (JdbcConstants.ORACLE.equals(dbType)) {
userName = connection.getMetaData().getUserName();
} else if (JdbcConstants.MARIADB.equals(dbType)) {
dbType = JdbcConstants.MYSQL;
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("can not init dataSource", e);
}
// 根据数据库的jdbcUrl和数据库类型组装 resourceId
initResourceId();
// 1.以resourceId为key,当前DataSourceProxy代理对象为value缓存到map中
// 2.请求TC注册resource
DefaultResourceManager.get().registerResource(this);
if (ENABLE_TABLE_META_CHECKER_ENABLE) {
tableMetaExecutor.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
try (Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection()) {
TableMetaCacheFactory.getTableMetaCache(DataSourceProxy.this.getDbType())
.refresh(connection, DataSourceProxy.this.getResourceId());
} catch (Exception ignore) {
}
}, 0, TABLE_META_CHECKER_INTERVAL, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
//绑定上下文AT模式
//Set the default branch type to 'AT' in the RootContext.
RootContext.setDefaultBranchType(this.getBranchType());
}
/**
* Gets plain connection.
*
* @return the plain connection
* @throws SQLException the sql exception
*/
public Connection getPlainConnection() throws SQLException {
return targetDataSource.getConnection();
}
/**
* Gets db type.
*
* @return the db type
*/
public String getDbType() {
return dbType;
}
/**
* 使用ConnectionProxy代理Connection
* @return
* @throws SQLException
*/
@Override
public ConnectionProxy getConnection() throws SQLException {
Connection targetConnection = targetDataSource.getConnection();
return new ConnectionProxy(this, targetConnection);
}
/**
* 使用ConnectionProxy代理Connection
* @param username
* @param password
* @return
* @throws SQLException
*/
@Override
public ConnectionProxy getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
Connection targetConnection = targetDataSource.getConnection(username, password);
return new ConnectionProxy(this, targetConnection);
}
@Override
public String getResourceGroupId() {
return resourceGroupId;
}
@Override
public String getResourceId() {
if (resourceId == null) {
initResourceId();
}
return resourceId;
}
private void initResourceId() {
if (JdbcConstants.POSTGRESQL.equals(dbType)) {
initPGResourceId();
} else if (JdbcConstants.ORACLE.equals(dbType) && userName != null) {
initDefaultResourceId();
resourceId = resourceId + "/" + userName;
} else if (JdbcConstants.MYSQL.equals(dbType)) {
initMysqlResourceId();
} else {
initDefaultResourceId();
}
}
/**
* init the default resource id
*/
private void initDefaultResourceId() {
if (jdbcUrl.contains("?")) {
resourceId = jdbcUrl.substring(0, jdbcUrl.indexOf('?'));
} else {
resourceId = jdbcUrl;
}
}
/**
* prevent mysql url like
* jdbc:mysql:loadbalance://192.168.100.2:3306,192.168.100.1:3306/seata
* it will cause the problem like
* 1.rm client is not connected
*/
private void initMysqlResourceId() {
String startsWith = "jdbc:mysql:loadbalance://";
if (jdbcUrl.startsWith(startsWith)) {
String url;
if (jdbcUrl.contains("?")) {
url = jdbcUrl.substring(0, jdbcUrl.indexOf('?'));
} else {
url = jdbcUrl;
}
resourceId = url.replace(",", "|");
} else {
initDefaultResourceId();
}
}
/**
* prevent pg sql url like
* jdbc:postgresql://127.0.0.1:5432/seata?currentSchema=public
* jdbc:postgresql://127.0.0.1:5432/seata?currentSchema=seata
* cause the duplicated resourceId
* it will cause the problem like
* 1.get file lock fail
* 2.error table meta cache
*/
private void initPGResourceId() {
if (jdbcUrl.contains("?")) {
StringBuilder jdbcUrlBuilder = new StringBuilder();
jdbcUrlBuilder.append(jdbcUrl, 0, jdbcUrl.indexOf('?'));
StringBuilder paramsBuilder = new StringBuilder();
String paramUrl = jdbcUrl.substring(jdbcUrl.indexOf('?') + 1);
String[] urlParams = paramUrl.split("&");
for (String urlParam : urlParams) {
if (urlParam.contains("currentSchema")) {
if (urlParam.contains(Constants.DBKEYS_SPLIT_CHAR)) {
urlParam = urlParam.replace(Constants.DBKEYS_SPLIT_CHAR, "!");
}
paramsBuilder.append(urlParam);
break;
}
}
if (paramsBuilder.length() > 0) {
jdbcUrlBuilder.append("?");
jdbcUrlBuilder.append(paramsBuilder);
}
resourceId = jdbcUrlBuilder.toString();
} else {
resourceId = jdbcUrl;
}
}
@Override
public BranchType getBranchType() {
return BranchType.AT;
}
}创建DataSourceProxy对象的时候会向TC注册Resource,AT模式是一个数据源作为一个resource,对比TCC模式,是一个@tcc注解的方法作为一个resource。代理数据源的最终目的是为了代理数据连接,也就是Seata自己的ConnectionProxy。
分析到这里,我们再来看看一般执行数据库操作的基本过程(从数据源中取出connection >> commit/rollback)
- DataSource.getConnection获取连接
- connection.setAutoCommit(false)开启事务
- connection.prepareStatement(sql)创建PreparedStatement对象
- PreparedStatement.setXXX设置各种类型的参数值
- PreparedStatement.execute执行sql
- connection.commit/rollback提交或者回滚
sql执行
顺着数据库jdbc操作的流程来梳理seata代理的过程
首先seata通过DataSourceProxy代理数据源,应用程序通过DataSource.getConnection获取到连接代理对象ConnectionProxy
2)调用ConnectionProxy.prepareStatement(sql)创建PreparedStatement对象,代码在其父类AbstractConnectionProxy中,创建PreparedStatementProxy代理statement
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql) throws SQLException {
String dbType = getDbType();
// support oracle 10.2+
PreparedStatement targetPreparedStatement = null;
if (BranchType.AT == RootContext.getBranchType()) {
List sqlRecognizers = SQLVisitorFactory.get(sql, dbType);
if (sqlRecognizers != null && sqlRecognizers.size() == 1) {
SQLRecognizer sqlRecognizer = sqlRecognizers.get(0);
if (sqlRecognizer != null && sqlRecognizer.getSQLType() == SQLType.INSERT) {
TableMeta tableMeta = TableMetaCacheFactory.getTableMetaCache(dbType).getTableMeta(getTargetConnection(),
sqlRecognizer.getTableName(), getDataSourceProxy().getResourceId());
String[] pkNameArray = new String[tableMeta.getPrimaryKeyOnlyName().size()];
tableMeta.getPrimaryKeyOnlyName().toArray(pkNameArray);
targetPreparedStatement = getTargetConnection().prepareStatement(sql,pkNameArray);
}
}
}
if (targetPreparedStatement == null) {
targetPreparedStatement = getTargetConnection().prepareStatement(sql);
}
return new PreparedStatementProxy(this, targetPreparedStatement, sql);
} 3)PreparedStatementProxy.execute执行sql
public class PreparedStatementProxy extends AbstractPreparedStatementProxy
implements PreparedStatement, ParametersHolder { SQLException the sql exception
public PreparedStatementProxy(AbstractConnectionProxy connectionProxy, PreparedStatement targetStatement,
String targetSQL) throws SQLException {
super(connectionProxy, targetStatement, targetSQL);
}
@Override
public boolean execute() throws SQLException {
// 执行模板
return ExecuteTemplate.execute(this, (statement, args) -> statement.execute());
}
@Override
public ResultSet executeQuery() throws SQLException {
return ExecuteTemplate.execute(this, (statement, args) -> statement.executeQuery());
}
@Override
public int executeUpdate() throws SQLException {
return ExecuteTemplate.execute(this, (statement, args) -> statement.executeUpdate());
}
}这里使用了ExecuteTemplate执行模板
public class ExecuteTemplate {
public static T execute(StatementProxy statementProxy,
StatementCallback statementCallback,
Object... args) throws SQLException {
return execute(null, statementProxy, statementCallback, args);
}
public static T execute(List sqlRecognizers,
StatementProxy statementProxy,
StatementCallback statementCallback,
Object... args) throws SQLException {
// 未标注@GlobalLock注解 也 未处于AT模式,按普通操作执行
if (!RootContext.requireGlobalLock() && BranchType.AT != RootContext.getBranchType()) {
// Just work as original statement
return statementCallback.execute(statementProxy.getTargetStatement(), args);
}
// 数据库类型
String dbType = statementProxy.getConnectionProxy().getDbType();
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(sqlRecognizers)) {
// 解析sql,得到对应操作类型的 sql解析器(增删改查)
sqlRecognizers = SQLVisitorFactory.get(
statementProxy.getTargetSQL(),
dbType);
}
Executor executor;
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(sqlRecognizers)) {
//普通操作执行
executor = new PlainExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback);
} else {
if (sqlRecognizers.size() == 1) {
// 单挑sql
SQLRecognizer sqlRecognizer = sqlRecognizers.get(0);
switch (sqlRecognizer.getSQLType()) {
case INSERT:
executor = EnhancedServiceLoader.load(InsertExecutor.class, dbType,
new Class[]{StatementProxy.class, StatementCallback.class, SQLRecognizer.class},
new Object[]{statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer});
break;
case UPDATE:
executor = new UpdateExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);
break;
case DELETE:
executor = new DeleteExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);
break;
case SELECT_FOR_UPDATE:
executor = new SelectForUpdateExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);
break;
case INSERT_ON_DUPLICATE_UPDATE:
switch (dbType) {
case JdbcConstants.MYSQL:
case JdbcConstants.MARIADB:
executor =
new MySQLInsertOrUpdateExecutor(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);
break;
default:
throw new NotSupportYetException(dbType + " not support to INSERT_ON_DUPLICATE_UPDATE");
}
break;
default://像select sql按普通操作进行
executor = new PlainExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback);
break;
}
} else {
//批量多条sql
executor = new MultiExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizers);
}
}
T rs;
try {
//执行模板引擎
rs = executor.execute(args);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
if (!(ex instanceof SQLException)) {
// Turn other exception into SQLException
ex = new SQLException(ex);
}
throw (SQLException) ex;
}
return rs;
}
} 首先是要解析sql,得到对应操作类型的sql解析器后,再创建对应的Executor ,
来看下Executor的execute方法,在BaseTransactionalExecutor中
@Override
public T execute(Object... args) throws Throwable {
//全局事务id
String xid = RootContext.getXID();
if (xid != null) {
//xid绑定到connection中
statementProxy.getConnectionProxy().bind(xid);
}
// 设置GlobalLock标识,即是否有标注@GlobalLock注解
statementProxy.getConnectionProxy().setGlobalLockRequire(RootContext.requireGlobalLock());
// 模板方法
return doExecute(args);
}继续跟进doExecute至AbstractDMLBaseExecutor中
@Override
public T doExecute(Object... args) throws Throwable {
//连接代理对象
AbstractConnectionProxy connectionProxy = statementProxy.getConnectionProxy();
if (connectionProxy.getAutoCommit()) {
// 自动提交
return executeAutoCommitTrue(args);
} else {
// 非自动提交,我们开启事务后都是非自动提交的
return executeAutoCommitFalse(args);
}
}看下自动提交执行sql的逻辑
protected T executeAutoCommitTrue(Object[] args) throws Throwable {
ConnectionProxy connectionProxy = statementProxy.getConnectionProxy();
try {
//手工设置为非自动提交,开启事务,目的是保证undolog跟业务sql绑定在同一事务中
connectionProxy.changeAutoCommit();
//自旋获取全局锁成功后,再执行commmit
return new LockRetryPolicy(connectionProxy).execute(() -> {
// 走非自动提交的逻辑
T result = executeAutoCommitFalse(args);
// 提交事务
connectionProxy.commit();
return result;
});
} catch (Exception e) {
// when exception occur in finally,this exception will lost, so just print it here
LOGGER.error("execute executeAutoCommitTrue error:{}", e.getMessage(), e);
if (!LockRetryPolicy.isLockRetryPolicyBranchRollbackOnConflict()) {
//重试获取全局锁失败,执行rollback
connectionProxy.getTargetConnection().rollback();
}
throw e;
} finally {
connectionProxy.getContext().reset();
connectionProxy.setAutoCommit(true);
}
}
private static class LockRetryPolicy extends ConnectionProxy.LockRetryPolicy {
LockRetryPolicy(final ConnectionProxy connection) {
super(connection);
}
@Override
public T execute(Callable callable) throws Exception {
if (LOCK_RETRY_POLICY_BRANCH_ROLLBACK_ON_CONFLICT) {
//自旋重试执行Callable回调逻辑
return doRetryOnLockConflict(callable);
} else {
return callable.call();
}
}
} 如果是自动提交,seata会先设置为非自动提交,再自旋重试提交事务。也就是开启一个事务,以保证undolog跟业务sql绑定在同一事务中
非自动提交执行sql逻辑
protected T executeAutoCommitFalse(Object[] args) throws Exception {
if (!JdbcConstants.MYSQL.equalsIgnoreCase(getDbType()) && isMultiPk()) {
throw new NotSupportYetException("multi pk only support mysql!");
}
// 解析sql生成前置镜像
TableRecords beforeImage = beforeImage();
// 执行sql语句
T result = statementCallback.execute(statementProxy.getTargetStatement(), args);
int updateCount = statementProxy.getUpdateCount();
// 如果有影响行数
if (updateCount > 0) {
//解析sql生成后置镜像
TableRecords afterImage = afterImage(beforeImage);
//根据每一行的主键和前置/后置镜像构建UndoLog
prepareUndoLog(beforeImage, afterImage);
}
return result;
}commit逻辑-ConnectionProxy.commit
public class ConnectionProxy extends AbstractConnectionProxy {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ConnectionProxy.class);
private final ConnectionContext context = new ConnectionContext();
private final LockRetryPolicy lockRetryPolicy = new LockRetryPolicy(this);
private static final int REPORT_RETRY_COUNT = ConfigurationFactory.getInstance().getInt(
ConfigurationKeys.CLIENT_REPORT_RETRY_COUNT, DEFAULT_CLIENT_REPORT_RETRY_COUNT);
public static final boolean IS_REPORT_SUCCESS_ENABLE = ConfigurationFactory.getInstance().getBoolean(
ConfigurationKeys.CLIENT_REPORT_SUCCESS_ENABLE, DEFAULT_CLIENT_REPORT_SUCCESS_ENABLE);
/**
* Instantiates a new Connection proxy.
*
* @param dataSourceProxy the data source proxy
* @param targetConnection the target connection
*/
public ConnectionProxy(DataSourceProxy dataSourceProxy, Connection targetConnection) {
super(dataSourceProxy, targetConnection);
}
@Override
public void commit() throws SQLException {
//重写commit逻辑
try {
lockRetryPolicy.execute(() -> {
// 重点看这里
doCommit();
return null;
});
} catch (SQLException e) {
if (targetConnection != null && !getAutoCommit() && !getContext().isAutoCommitChanged()) {
//sql异常 非自动提交,才进行rollback
rollback();
}
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new SQLException(e);
}
}
private void doCommit() throws SQLException {
if (context.inGlobalTransaction()) {
// 全局事务下
processGlobalTransactionCommit();
} else if (context.isGlobalLockRequire()) {
// 本地事务下,但是标注了@GlobalLock注解来保证隔离性
processLocalCommitWithGlobalLocks();
} else {
// 直接提交
targetConnection.commit();
}
}
public static class LockRetryPolicy {
protected static final boolean LOCK_RETRY_POLICY_BRANCH_ROLLBACK_ON_CONFLICT = ConfigurationFactory
.getInstance().getBoolean(ConfigurationKeys.CLIENT_LOCK_RETRY_POLICY_BRANCH_ROLLBACK_ON_CONFLICT, DEFAULT_CLIENT_LOCK_RETRY_POLICY_BRANCH_ROLLBACK_ON_CONFLICT);
protected final ConnectionProxy connection;
public LockRetryPolicy(ConnectionProxy connection) {
this.connection = connection;
}
public T execute(Callable callable) throws Exception {
// the only case that not need to retry acquire lock hear is
// LOCK_RETRY_POLICY_BRANCH_ROLLBACK_ON_CONFLICT == true && connection#autoCommit == true
// because it has retry acquire lock when AbstractDMLBaseExecutor#executeAutoCommitTrue
// 只有autocommit为true才不需要重试获取锁,因为autocommit为true时,在这之前已经有重试逻辑了
if (LOCK_RETRY_POLICY_BRANCH_ROLLBACK_ON_CONFLICT && connection.getContext().isAutoCommitChanged()) {
return callable.call();
} else {
// LOCK_RETRY_POLICY_BRANCH_ROLLBACK_ON_CONFLICT == false
// or LOCK_RETRY_POLICY_BRANCH_ROLLBACK_ON_CONFLICT == true && autoCommit == false
return doRetryOnLockConflict(callable);
}
}
protected T doRetryOnLockConflict(Callable callable) throws Exception {
LockRetryController lockRetryController = new LockRetryController();
// 自旋,重试获取锁
while (true) {
try {
return callable.call();
} catch (LockConflictException lockConflict) {
onException(lockConflict);
// AbstractDMLBaseExecutor#executeAutoCommitTrue the local lock is released
if (connection.getContext().isAutoCommitChanged()
&& lockConflict.getCode() == TransactionExceptionCode.LockKeyConflictFailFast) {
lockConflict.setCode(TransactionExceptionCode.LockKeyConflict);
}
// 超出重试次数,抛出锁等待超时异常
lockRetryController.sleep(lockConflict);
} catch (Exception e) {
onException(e);
throw e;
}
}
}
/**
* Callback on exception in doLockRetryOnConflict.
*
* @param e invocation exception
* @throws Exception error
*/
protected void onException(Exception e) throws Exception {
}
}
} 不论是自动提交还是非自动提交,都是是自旋重试的过程,接着看doCommit中的processGlobalTransactionCommit和processLocalCommitWithGlobalLocks
processGlobalTransactionCommit-全局事务下
全局事务下在commit前,会先向TC注册事务分支,注册分支会以lockkeys尝试获取全局锁,lockkeys就是由每条记录的主键组成的string字符串,获取锁不成功进入自旋逻辑。注册分支成功后,再写入undolog,最后commit事务,向TC汇报分支执行状态。汇报状态也有一个自旋的过程,尽可能保证成功。
private void processGlobalTransactionCommit() throws SQLException {
try {
//注册分支,请求全局锁
register();
} catch (TransactionException e) {
//锁冲突,自旋重试
recognizeLockKeyConflictException(e, context.buildLockKeys());
}
try {
//写入undoLog,与业务事务绑定在一起
UndoLogManagerFactory.getUndoLogManager(this.getDbType()).flushUndoLogs(this);
targetConnection.commit();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
LOGGER.error("process connectionProxy commit error: {}", ex.getMessage(), ex);
//汇报失败状态
report(false);
throw new SQLException(ex);
}
if (IS_REPORT_SUCCESS_ENABLE) {
// 汇报成功状态
report(true);
}
context.reset();
}
private void register() throws TransactionException {
if (!context.hasUndoLog() || !context.hasLockKey()) {
return;
}
//向TC发起分支注册请求,这里AT模式的注册分支也会以LockKeys请求全局锁。
Long branchId = DefaultResourceManager.get().branchRegister(BranchType.AT, getDataSourceProxy().getResourceId(),
null, context.getXid(), context.getApplicationData(), context.buildLockKeys());
context.setBranchId(branchId);
}
private void report(boolean commitDone) throws SQLException {
if (context.getBranchId() == null) {
return;
}
int retry = REPORT_RETRY_COUNT;
//自旋重试,尽可能成功
while (retry > 0) {
try {
// 向TC汇报分支一阶段执行结果
DefaultResourceManager.get().branchReport(BranchType.AT, context.getXid(), context.getBranchId(),
commitDone ? BranchStatus.PhaseOne_Done : BranchStatus.PhaseOne_Failed, null);
return;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
LOGGER.error("Failed to report [" + context.getBranchId() + "/" + context.getXid() + "] commit done ["
+ commitDone + "] Retry Countdown: " + retry);
retry--;
if (retry == 0) {
throw new SQLException("Failed to report branch status " + commitDone, ex);
}
}
}
}processLocalCommitWithGlobalLocks-@GlobalLock注解
本地事务执行@GlobalLock注解逻辑的过程很简单,请求TC尝试获取全局锁,获取失败则进入自旋逻辑。获取到锁后,才能提交本地事务。以此来保证开了全局事务的交易 和本地事务下交易的隔离性。
/**
* 本地事务下,但是标注了@GlobalLock注解来保证隔离性
* @throws SQLException
*/
private void processLocalCommitWithGlobalLocks() throws SQLException {
// 本地事务下,标注了@GlobalLock注解,commit前以LockKeys先获取全局锁
checkLock(context.buildLockKeys());
try {
targetConnection.commit();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new SQLException(ex);
}
context.reset();
}
/**
* Check lock.
*
* @param lockKeys the lockKeys
* @throws SQLException the sql exception
*/
public void checkLock(String lockKeys) throws SQLException {
if (StringUtils.isBlank(lockKeys)) {
return;
}
// Just check lock without requiring lock by now.
try {
// 请求TC以lockkeys为键值获取全局锁
// lockkeys格式为 table:primarykey,假如说当前事务修改了多张表,TC检测到存在 有未完成的全局事务也修改了其中的某条记录,这个时候就会有锁冲突。
boolean lockable = DefaultResourceManager.get().lockQuery(BranchType.AT,
getDataSourceProxy().getResourceId(), context.getXid(), lockKeys);
if (!lockable) {
throw new LockConflictException(String.format("get lock failed, lockKey: %s",lockKeys));
}
} catch (TransactionException e) {
recognizeLockKeyConflictException(e, lockKeys);
}
}Rollback逻辑-ConnectionProxy.rollback
@Override
public void rollback() throws SQLException {
targetConnection.rollback();
if (context.inGlobalTransaction() && context.isBranchRegistered()) {
//全局事务下&&分支已注册,汇报分支执行失败
report(false);
}
context.reset();
}相比于commit,rollback的逻辑就简单多了,直接回滚事务,如果是处于全局事务下并且分支已注册的话,则向TC汇报分支事务执行失败。
我们看到代码中有不少处理@GlobalLock注解的代码,那么@GlobalLock注解是在什么解析的呢,答案其实就在GlobalTransactionScanner中
public class GlobalTransactionScanner extends AbstractAutoProxyCreator
implements ConfigurationChangeListener, InitializingBean, ApplicationContextAware, DisposableBean {
@Override
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
......
try {
synchronized (PROXYED_SET) {
......
if (TCCBeanParserUtils.isTccAutoProxy(bean, beanName, applicationContext)) {
......
} else {
// 非tcc模式bean
Class serviceInterface = SpringProxyUtils.findTargetClass(bean);
Class[] interfacesIfJdk = SpringProxyUtils.findInterfaces(bean);
// 查找类和方法上是否有全局事务@GlobalTransactional注解 或者@GlobalLock
if (!existsAnnotation(new Class[]{serviceInterface})
&& !existsAnnotation(interfacesIfJdk)) {
return bean;
}
if (globalTransactionalInterceptor == null) {
globalTransactionalInterceptor = new GlobalTransactionalInterceptor(failureHandlerHook);
ConfigurationCache.addConfigListener(
ConfigurationKeys.DISABLE_GLOBAL_TRANSACTION,
(ConfigurationChangeListener)globalTransactionalInterceptor);
}
interceptor = globalTransactionalInterceptor;
}
......
return bean;
}
} catch (Exception exx) {
throw new RuntimeException(exx);
}
}
private boolean existsAnnotation(Class[] classes) {
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(classes)) {
for (Class clazz : classes) {
if (clazz == null) {
continue;
}
//优先解析全局事务
GlobalTransactional trxAnno = clazz.getAnnotation(GlobalTransactional.class);
if (trxAnno != null) {
return true;
}
Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
trxAnno = method.getAnnotation(GlobalTransactional.class);
if (trxAnno != null) {
return true;
}
//本地事务,检测@GlobalLock注解
GlobalLock lockAnno = method.getAnnotation(GlobalLock.class);
if (lockAnno != null) {
return true;
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
就是说如果不处于全面事务,但是标注了@GlobalLock注解也是会添加GlobalTransactionalInterceptor拦截
public class GlobalTransactionalInterceptor implements ConfigurationChangeListener, MethodInterceptor, SeataInterceptor {
@Override
public Object invoke(final MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable {
Class targetClass =
methodInvocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(methodInvocation.getThis()) : null;
Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(methodInvocation.getMethod(), targetClass);
if (specificMethod != null && !specificMethod.getDeclaringClass().equals(Object.class)) {
final Method method = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(specificMethod);
// 查找类||方法上的全局事务注解
final GlobalTransactional globalTransactionalAnnotation =
getAnnotation(method, targetClass, GlobalTransactional.class);
// 代理方法增加@GlobalLock+@Transactional 或者 @GlobalTransaction 防止脏读
final GlobalLock globalLockAnnotation = getAnnotation(method, targetClass, GlobalLock.class);
boolean localDisable = disable || (degradeCheck && degradeNum >= degradeCheckAllowTimes);
if (!localDisable) {
if (globalTransactionalAnnotation != null || this.aspectTransactional != null) {
......
//执行全局事务处理逻辑
return handleGlobalTransaction(methodInvocation, transactional);
} else if (globalLockAnnotation != null) {
//本地事务下,@GlobalLock处理
return handleGlobalLock(methodInvocation, globalLockAnnotation);
}
}
}
return methodInvocation.proceed();
}
private Object handleGlobalLock(final MethodInvocation methodInvocation, final GlobalLock globalLockAnno) throws Throwable {
// 绑定@GlobalLock注解开启标识到RootContext中
return globalLockTemplate.execute(new GlobalLockExecutor() {
@Override
public Object execute() throws Throwable {
return methodInvocation.proceed();
}
@Override
public GlobalLockConfig getGlobalLockConfig() {
GlobalLockConfig config = new GlobalLockConfig();
config.setLockRetryInterval(globalLockAnno.lockRetryInterval());
config.setLockRetryTimes(globalLockAnno.lockRetryTimes());
return config;
}
});
}
}
从代码中可以看到@GlobalLock注解开启标识是绑定在上下文中,最终传递到connectionproxy中的
beforeImage和afterImage
我们以mysql为例分别看下INSERT、DELETE、UPDATE、SELECT_FOR_UPDATE这4种sql类型,对应的beforeImage、afterImage 生成的细节。具体代码就体现在各种类型对应的Executor中
INSERT
public abstract class BaseInsertExecutor extends AbstractDMLBaseExecutor implements InsertExecutor {
@Override
protected TableRecords beforeImage() throws SQLException {
//insert前自然是没有记录的
return TableRecords.empty(getTableMeta());
}
@Override
protected TableRecords afterImage(TableRecords beforeImage) throws SQLException {
// 解析sql,得到主键 列 >> 值 映射
// 主键id可能是自动生成的、也可能是insert sql里就已经有了的
Map> pkValues = getPkValues();
// 为保证读隔离,拼接select for update 查询后置镜像
TableRecords afterImage = buildTableRecords(pkValues);
if (afterImage == null) {
throw new SQLException("Failed to build after-image for insert");
}
return afterImage;
}
protected TableRecords buildTableRecords(Map> pkValuesMap) throws SQLException {
SQLInsertRecognizer recognizer = (SQLInsertRecognizer)sqlRecognizer;
List pkColumnNameList = getTableMeta().getPrimaryKeyOnlyName();
StringBuilder prefix = new StringBuilder("SELECT ");
StringBuilder suffix = new StringBuilder(" FROM ").append(getFromTableInSQL());
// build check sql
String firstKey = pkValuesMap.keySet().stream().findFirst().get();
int rowSize = pkValuesMap.get(firstKey).size();
suffix.append(WHERE).append(SqlGenerateUtils.buildWhereConditionByPKs(pkColumnNameList, rowSize, getDbType()));
StringJoiner selectSQLJoin = new StringJoiner(", ", prefix.toString(), suffix.toString());
List insertColumns = recognizer.getInsertColumns();
if (ONLY_CARE_UPDATE_COLUMNS && CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(insertColumns)) {
Set columns = new TreeSet<>(String.CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER);
columns.addAll(recognizer.getInsertColumns());
columns.addAll(pkColumnNameList);
for (String columnName : columns) {
selectSQLJoin.add(columnName);
}
} else {
selectSQLJoin.add(" * ");
}
ResultSet rs = null;
try (PreparedStatement ps = statementProxy.getConnection().prepareStatement(selectSQLJoin.toString())) {
int paramIndex = 1;
for (int r = 0; r < rowSize; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < pkColumnNameList.size(); c++) {
List UPDATE
public class UpdateExecutor extends AbstractDMLBaseExecutor {
@Override
protected TableRecords beforeImage() throws SQLException {
ArrayList> paramAppenderList = new ArrayList<>();
TableMeta tmeta = getTableMeta();
//解析sql,拼接select for update语句
String selectSQL = buildBeforeImageSQL(tmeta, paramAppenderList);
//执行select for update 获取前置镜像
return buildTableRecords(tmeta, selectSQL, paramAppenderList);
}
private String buildBeforeImageSQL(TableMeta tableMeta, ArrayList> paramAppenderList) {
SQLUpdateRecognizer recognizer = (SQLUpdateRecognizer) sqlRecognizer;
List updateColumns = recognizer.getUpdateColumns();
StringBuilder prefix = new StringBuilder("SELECT ");
StringBuilder suffix = new StringBuilder(" FROM ").append(getFromTableInSQL());
String whereCondition = buildWhereCondition(recognizer, paramAppenderList);
String orderByCondition = buildOrderCondition(recognizer, paramAppenderList);
String limitCondition = buildLimitCondition(recognizer, paramAppenderList);
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(whereCondition)) {
suffix.append(WHERE).append(whereCondition);
}
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(orderByCondition)) {
suffix.append(" ").append(orderByCondition);
}
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(limitCondition)) {
suffix.append(" ").append(limitCondition);
}
suffix.append(" FOR UPDATE");
StringJoiner selectSQLJoin = new StringJoiner(", ", prefix.toString(), suffix.toString());
if (ONLY_CARE_UPDATE_COLUMNS) {
if (!containsPK(updateColumns)) {
selectSQLJoin.add(getColumnNamesInSQL(tableMeta.getEscapePkNameList(getDbType())));
}
for (String columnName : updateColumns) {
selectSQLJoin.add(columnName);
}
// The on update xxx columns will be auto update by db, so it's also the actually updated columns
List onUpdateColumns = tableMeta.getOnUpdateColumnsOnlyName();
onUpdateColumns.removeAll(updateColumns);
for (String onUpdateColumn : onUpdateColumns) {
selectSQLJoin.add(ColumnUtils.addEscape(onUpdateColumn, getDbType()));
}
} else {
for (String columnName : tableMeta.getAllColumns().keySet()) {
selectSQLJoin.add(ColumnUtils.addEscape(columnName, getDbType()));
}
}
return selectSQLJoin.toString();
}
@Override
protected TableRecords afterImage(TableRecords beforeImage) throws SQLException {
TableMeta tmeta = getTableMeta();
if (beforeImage == null || beforeImage.size() == 0) {
//如果update没有更新到记录,后置镜像自然是空的
return TableRecords.empty(getTableMeta());
}
// 根据前置镜像,以主键信息构建select for update语句
String selectSQL = buildAfterImageSQL(tmeta, beforeImage);
ResultSet rs = null;
try (PreparedStatement pst = statementProxy.getConnection().prepareStatement(selectSQL)) {
SqlGenerateUtils.setParamForPk(beforeImage.pkRows(), getTableMeta().getPrimaryKeyOnlyName(), pst);
rs = pst.executeQuery();
// 执行select for update语句获取后置镜像
return TableRecords.buildRecords(tmeta, rs);
} finally {
IOUtil.close(rs);
}
}
private String buildAfterImageSQL(TableMeta tableMeta, TableRecords beforeImage) throws SQLException {
StringBuilder prefix = new StringBuilder("SELECT ");
//前置镜像执行完后,可以获得记录的主键信息,就可以按主键构建select for update 语句
String whereSql = SqlGenerateUtils.buildWhereConditionByPKs(tableMeta.getPrimaryKeyOnlyName(), beforeImage.pkRows().size(), getDbType());
String suffix = " FROM " + getFromTableInSQL() + " WHERE " + whereSql;
StringJoiner selectSQLJoiner = new StringJoiner(", ", prefix.toString(), suffix);
if (ONLY_CARE_UPDATE_COLUMNS) {
SQLUpdateRecognizer recognizer = (SQLUpdateRecognizer) sqlRecognizer;
List updateColumns = recognizer.getUpdateColumns();
if (!containsPK(updateColumns)) {
selectSQLJoiner.add(getColumnNamesInSQL(tableMeta.getEscapePkNameList(getDbType())));
}
for (String columnName : updateColumns) {
selectSQLJoiner.add(columnName);
}
// The on update xxx columns will be auto update by db, so it's also the actually updated columns
List onUpdateColumns = tableMeta.getOnUpdateColumnsOnlyName();
onUpdateColumns.removeAll(updateColumns);
for (String onUpdateColumn : onUpdateColumns) {
selectSQLJoiner.add(ColumnUtils.addEscape(onUpdateColumn, getDbType()));
}
} else {
for (String columnName : tableMeta.getAllColumns().keySet()) {
selectSQLJoiner.add(ColumnUtils.addEscape(columnName, getDbType()));
}
}
return selectSQLJoiner.toString();
}
} DELETE
public class DeleteExecutor extends AbstractDMLBaseExecutor {
@Override
protected TableRecords beforeImage() throws SQLException {
SQLDeleteRecognizer visitor = (SQLDeleteRecognizer) sqlRecognizer;
TableMeta tmeta = getTableMeta(visitor.getTableName());
ArrayList> paramAppenderList = new ArrayList<>();
//解析sql,构建select for update 语句
String selectSQL = buildBeforeImageSQL(visitor, tmeta, paramAppenderList);
//执行select for update 获取前置镜像
return buildTableRecords(tmeta, selectSQL, paramAppenderList);
}
private String buildBeforeImageSQL(SQLDeleteRecognizer visitor, TableMeta tableMeta, ArrayList> paramAppenderList) {
String whereCondition = buildWhereCondition(visitor, paramAppenderList);
String orderByCondition = buildOrderCondition(visitor, paramAppenderList);
String limitCondition = buildLimitCondition(visitor, paramAppenderList);
StringBuilder suffix = new StringBuilder(" FROM ").append(getFromTableInSQL());
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(whereCondition)) {
suffix.append(WHERE).append(whereCondition);
}
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(orderByCondition)) {
suffix.append(" ").append(orderByCondition);
}
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(limitCondition)) {
suffix.append(" ").append(limitCondition);
}
suffix.append(" FOR UPDATE");
StringJoiner selectSQLAppender = new StringJoiner(", ", "SELECT ", suffix.toString());
for (String column : tableMeta.getAllColumns().keySet()) {
selectSQLAppender.add(getColumnNameInSQL(ColumnUtils.addEscape(column, getDbType())));
}
return selectSQLAppender.toString();
}
@Override
protected TableRecords afterImage(TableRecords beforeImage) throws SQLException {
// delete 后置镜像为空
return TableRecords.empty(getTableMeta());
}
} SELECT_FOR_UPDATE
public class SelectForUpdateExecutor extends BaseTransactionalExecutor {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SelectForUpdateExecutor.class);
public SelectForUpdateExecutor(StatementProxy statementProxy, StatementCallback statementCallback,
SQLRecognizer sqlRecognizer) {
super(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);
}
/**
* 代理select for update 语句,请求获取全局锁
* 之所以代理select for update ,是为了满足某些特殊场景下,应用要求全局事务的隔离性为读提交。
* 对于全局事务而已,默认是读未提交(可能2阶段还未完成)
* 这个时候就可以使用@GlobalLock + select for update 或者 @GlobalTransactional + select for update保证全局的读提交
* @param args the args
* @return
* @throws Throwable
*/
@Override
public T doExecute(Object... args) throws Throwable {
Connection conn = statementProxy.getConnection();
DatabaseMetaData dbmd = conn.getMetaData();
T rs;
Savepoint sp = null;
boolean originalAutoCommit = conn.getAutoCommit();
try {
if (originalAutoCommit) {
/*
* In order to hold the local db lock during global lock checking
* set auto commit value to false first if original auto commit was true
*/
// 如果为自动提交,则设置为非自动提交,目的是可以
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
} else if (dbmd.supportsSavepoints()) {
/*
* In order to release the local db lock when global lock conflict
* create a save point if original auto commit was false, then use the save point here to release db
* lock during global lock checking if necessary
*/
// 回滚点
sp = conn.setSavepoint();
} else {
throw new SQLException("not support savepoint. please check your db version");
}
LockRetryController lockRetryController = new LockRetryController();
ArrayList> paramAppenderList = new ArrayList<>();
// 解析sql,构建select for update 查询主键信息的sql
// 因为原生的sql可能并不包含主键
String selectPKSQL = buildSelectSQL(paramAppenderList);
while (true) {
try {
// #870
// execute return Boolean
// executeQuery return ResultSet
rs = statementCallback.execute(statementProxy.getTargetStatement(), args);
// Try to get global lock of those rows selected
// 执行构建好sql,查询出的内容包含主键字段
TableRecords selectPKRows = buildTableRecords(getTableMeta(), selectPKSQL, paramAppenderList);
// 主键字符串
String lockKeys = buildLockKey(selectPKRows);
if (StringUtils.isNullOrEmpty(lockKeys)) {
break;
}
if (RootContext.inGlobalTransaction() || RootContext.requireGlobalLock()) {
// Do the same thing under either @GlobalTransactional or @GlobalLock,
// that only check the global lock here.
// 全局事务下,或者标注了@GlobalLock注解,请求TC获取全局锁
statementProxy.getConnectionProxy().checkLock(lockKeys);
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Unknown situation!");
}
break;
} catch (LockConflictException lce) {
//获取全局锁失败将继续重试
if (sp != null) {
conn.rollback(sp);
} else {
conn.rollback();
}
// trigger retry
lockRetryController.sleep(lce);
}
}
} finally {
if (sp != null) {
try {
if (!JdbcConstants.ORACLE.equalsIgnoreCase(getDbType())) {
conn.releaseSavepoint(sp);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
LOGGER.error("{} release save point error.", getDbType(), e);
}
}
if (originalAutoCommit) {
conn.setAutoCommit(true);
}
}
return rs;
}
private String buildSelectSQL(ArrayList> paramAppenderList) {
SQLSelectRecognizer recognizer = (SQLSelectRecognizer)sqlRecognizer;
StringBuilder selectSQLAppender = new StringBuilder("SELECT ");
selectSQLAppender.append(getColumnNamesInSQL(getTableMeta().getEscapePkNameList(getDbType())));
selectSQLAppender.append(" FROM ").append(getFromTableInSQL());
String whereCondition = buildWhereCondition(recognizer, paramAppenderList);
String orderByCondition = buildOrderCondition(recognizer, paramAppenderList);
String limitCondition = buildLimitCondition(recognizer, paramAppenderList);
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(whereCondition)) {
selectSQLAppender.append(" WHERE ").append(whereCondition);
}
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(orderByCondition)) {
selectSQLAppender.append(" ").append(orderByCondition);
}
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(limitCondition)) {
selectSQLAppender.append(" ").append(limitCondition);
}
selectSQLAppender.append(" FOR UPDATE");
return selectSQLAppender.toString();
}
} seata可以对select for update查询sql进行代理,请求全局锁,如果说为了满足某些特殊场景下,应用要求全局事务的隔离性为读提交。那么我们可以使用@GlobalLock + select for update 或者 @GlobalTransactional + select for update的组合。
分析到这里,AT模式的一阶段就结束了,接下来继续分析AT模式二阶段的处理
AT二阶段
public class DataSourceManager extends AbstractResourceManager {
@Override
public BranchStatus branchCommit(BranchType branchType, String xid, long branchId, String resourceId,
String applicationData) throws TransactionException {
// 2阶段commit,只是异步删除undolog表记录
return asyncWorker.branchCommit(xid, branchId, resourceId);
}
@Override
public BranchStatus branchRollback(BranchType branchType, String xid, long branchId, String resourceId,
String applicationData) throws TransactionException {
DataSourceProxy dataSourceProxy = get(resourceId);
if (dataSourceProxy == null) {
throw new ShouldNeverHappenException(String.format("resource: %s not found",resourceId));
}
try {
//2阶段回滚,使用undolog补偿修复数据
UndoLogManagerFactory.getUndoLogManager(dataSourceProxy.getDbType()).undo(dataSourceProxy, xid, branchId);
} catch (TransactionException te) {
StackTraceLogger.info(LOGGER, te,
"branchRollback failed. branchType:[{}], xid:[{}], branchId:[{}], resourceId:[{}], applicationData:[{}]. reason:[{}]",
new Object[]{branchType, xid, branchId, resourceId, applicationData, te.getMessage()});
if (te.getCode() == TransactionExceptionCode.BranchRollbackFailed_Unretriable) {
return BranchStatus.PhaseTwo_RollbackFailed_Unretryable;
} else {
return BranchStatus.PhaseTwo_RollbackFailed_Retryable;
}
}
return BranchStatus.PhaseTwo_Rollbacked;
}
}Commit
2阶段的commit处理异步删除undolog就好了,rollback则是使用undolog进行补偿
public abstract class AbstractUndoLogManager implements UndoLogManager {
/**
* Undo.
*
* @param dataSourceProxy the data source proxy
* @param xid the xid
* @param branchId the branch id
* @throws TransactionException the transaction exception
*/
@Override
public void undo(DataSourceProxy dataSourceProxy, String xid, long branchId) throws TransactionException {
Connection conn = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
PreparedStatement selectPST = null;
boolean originalAutoCommit = true;
for (; ; ) {
try {
// 获取原生数据库连接对象
conn = dataSourceProxy.getPlainConnection();
// The entire undo process should run in a local transaction.
// 设置非自动提交,确保下面的操作处于同一事务当中
if (originalAutoCommit = conn.getAutoCommit()) {
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
}
// Find UNDO LOG
// 查询事务分支对应的undolog记录
selectPST = conn.prepareStatement(SELECT_UNDO_LOG_SQL);
selectPST.setLong(1, branchId);
selectPST.setString(2, xid);
rs = selectPST.executeQuery();
boolean exists = false;
// undolog记录存在
while (rs.next()) {
exists = true;
// It is possible that the server repeatedly sends a rollback request to roll back
// the same branch transaction to multiple processes,
// ensuring that only the undo_log in the normal state is processed.
int state = rs.getInt(ClientTableColumnsName.UNDO_LOG_LOG_STATUS);
if (!canUndo(state)) {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("xid {} branch {}, ignore {} undo_log", xid, branchId, state);
}
return;
}
String contextString = rs.getString(ClientTableColumnsName.UNDO_LOG_CONTEXT);
Map context = parseContext(contextString);
byte[] rollbackInfo = getRollbackInfo(rs);
String serializer = context == null ? null : context.get(UndoLogConstants.SERIALIZER_KEY);
// 反序列化获取前置镜像、后置镜像等内容
UndoLogParser parser = serializer == null ? UndoLogParserFactory.getInstance()
: UndoLogParserFactory.getInstance(serializer);
BranchUndoLog branchUndoLog = parser.decode(rollbackInfo);
try {
// put serializer name to local
setCurrentSerializer(parser.getName());
List sqlUndoLogs = branchUndoLog.getSqlUndoLogs();
if (sqlUndoLogs.size() > 1) {
Collections.reverse(sqlUndoLogs);
}
for (SQLUndoLog sqlUndoLog : sqlUndoLogs) {
TableMeta tableMeta = TableMetaCacheFactory.getTableMetaCache(dataSourceProxy.getDbType()).getTableMeta(
conn, sqlUndoLog.getTableName(), dataSourceProxy.getResourceId());
sqlUndoLog.setTableMeta(tableMeta);
// 获取对应类型的undoExecutor
AbstractUndoExecutor undoExecutor = UndoExecutorFactory.getUndoExecutor(
dataSourceProxy.getDbType(), sqlUndoLog);
// 一阶段一个事务可能执行了多条更新类sql,遍历undolog进行补偿
undoExecutor.executeOn(conn);
}
} finally {
// remove serializer name
removeCurrentSerializer();
}
}
// If undo_log exists, it means that the branch transaction has completed the first phase,
// we can directly roll back and clean the undo_log
// Otherwise, it indicates that there is an exception in the branch transaction,
// causing undo_log not to be written to the database.
// For example, the business processing timeout, the global transaction is the initiator rolls back.
// To ensure data consistency, we can insert an undo_log with GlobalFinished state
// to prevent the local transaction of the first phase of other programs from being correctly submitted.
// See https://github.com/seata/seata/issues/489
// undolog存在,现在可以直接删除掉了
if (exists) {
deleteUndoLog(xid, branchId, conn);
conn.commit();
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("xid {} branch {}, undo_log deleted with {}", xid, branchId,
State.GlobalFinished.name());
}
} else {
// undolog不存在,说明分支事务一阶段异常了,可能是全局事务超时等导致的
// 这个时候insert一条记录代表此分支已经结束了
insertUndoLogWithGlobalFinished(xid, branchId, UndoLogParserFactory.getInstance(), conn);
conn.commit();
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("xid {} branch {}, undo_log added with {}", xid, branchId,
State.GlobalFinished.name());
}
}
return;
} catch (SQLIntegrityConstraintViolationException e) {
// Possible undo_log has been inserted into the database by other processes, retrying rollback undo_log
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("xid {} branch {}, undo_log inserted, retry rollback", xid, branchId);
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.rollback();
} catch (SQLException rollbackEx) {
LOGGER.warn("Failed to close JDBC resource while undo ... ", rollbackEx);
}
}
throw new BranchTransactionException(BranchRollbackFailed_Retriable, String
.format("Branch session rollback failed and try again later xid = %s branchId = %s %s", xid,
branchId, e.getMessage()), e);
} finally {
try {
if (rs != null) {
rs.close();
}
if (selectPST != null) {
selectPST.close();
}
if (conn != null) {
if (originalAutoCommit) {
conn.setAutoCommit(true);
}
conn.close();
}
} catch (SQLException closeEx) {
LOGGER.warn("Failed to close JDBC resource while undo ... ", closeEx);
}
}
}
}
}
Rollback
根据undolog的内容生成补偿sql,再执行补偿
public abstract class AbstractUndoExecutor {
public void executeOn(Connection conn) throws SQLException {
if (IS_UNDO_DATA_VALIDATION_ENABLE && !dataValidationAndGoOn(conn)) {
return;
}
PreparedStatement undoPST = null;
try {
// 根据不同的sql操作,根据后置镜像的内容,生成补偿sql
String undoSQL = buildUndoSQL();
undoPST = conn.prepareStatement(undoSQL);
TableRecords undoRows = getUndoRows();
for (Row undoRow : undoRows.getRows()) {
ArrayList undoValues = new ArrayList<>();
List pkValueList = getOrderedPkList(undoRows, undoRow, getDbType(conn));
for (Field field : undoRow.getFields()) {
if (field.getKeyType() != KeyType.PRIMARY_KEY) {
undoValues.add(field);
}
}
//准备参数
undoPrepare(undoPST, undoValues, pkValueList);
//执行补偿sql
undoPST.executeUpdate();
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
if (ex instanceof SQLException) {
throw (SQLException) ex;
} else {
throw new SQLException(ex);
}
}
finally {
//important for oracle
IOUtil.close(undoPST);
}
}
} 总结
分析源码的过程中我们发现,AT模式下,seata需要大量的sql解析、sql生成、select for update、全局锁等待操作,这些都是比较影响性能的,特别是如果业务中执行了大量的sql,sql解析与生成,select for update都将对程序的性能造成影响,全局锁的粒度也是比较大的。如果说程序对性能要求比较高,AT模式可能比较吃力。但是这个模式胜在对业务无侵入,开发简便、效率高。