Golang | Web开发之Gin框架快速入门基础实践
欢迎关注「全栈工程师修炼指南」公众号
点击 下方卡片 即可关注我哟!
设为「星标⭐」每天带你 基础入门 到 进阶实践 再到 放弃学习!
专注 企业运维实践、网络安全、系统运维、应用开发、物联网实战、全栈文章 等知识分享
“ 花开堪折直须折,莫待无花空折枝。 ”
作者主页:[ https://www.weiyigeek.top ]
博客:[ https://blog.weiyigeek.top ]
作者<开发安全运维>学习交流群,回复【学习交流群】即可加入
文章目录:
0x00 前言简述
描述: 通过上一阶段的Go语言的基础学习,相信各位看友有一定的Go语言开发的基础,今天将给大家引入Go语言的Web框架,但是在介绍此之前,我们先了解前面我们学习的后端语言通常都有相依赖的Web框架, 例如 PHP 的 Laravel、THinkPHP、Yii等框架 ,Java 的 Spring Boot 、Quarkus、Micronaut、Jakarta EEVert.x 等框架,作为一名Google推出的Go语言来说也拥有众多的Web框架,例如今天讲解的Gin框架,以及 Aero、Beego 、Iris、Echo、Revel、Martini 等众多优秀的Web框架, 其各有各的特点。
总之,选择正确的Go Web Framework对于交付高质量和高效率的网络应用程序至关重要。
1.什么是Gin?
描述: Gin 是一个用 Go (Golang) 编写的 web 框架, 它提供类似Martini的API,但性能更佳,速度提升高达40倍, 号称是Go语言最快的全功能Web框架,所以如果你是性能和高效的追求者,你会爱上 Gin.
官网地址: https://gin-gonic.com/
帮助文档: https://gin-gonic.com/zh-cn/docs/
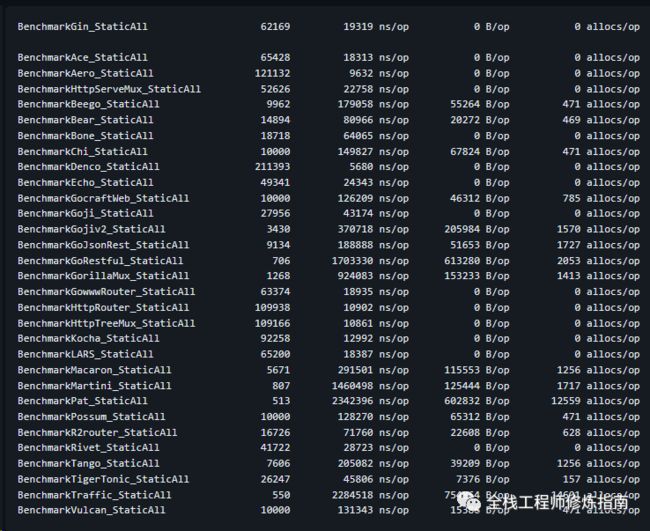
Go Web框架基准测试: https://github.com/gin-gonic/gin/blob/master/BENCHMARKS.md
2.有啥特点Gin?
描述: 其主要特点可以归纳终结为一下所述。
快速 : 基于 Radix 树的路由,小内存占用、没有反射、可预测的 API 性能。
路由组 : 帮助您更好地组织您的路由,例如,按照需要授权和不需要授权和不同API版本进行分组,此外路由分组可以无限嵌套而不降低性能。
内置渲染: 其为 JSON,XML 和 HTML 渲染提供了易于使用的 API。
JSON 解析: 解析并验证请求的 JSON,例如检查所需值的存在。
中间件 处理 : 传入的 HTTP 请求可以由一系列中间件和最终操作来处理, 例如:Logger,Authorization,GZIP,最终操作 DB。
Crash 处理 : 可以 catch 一个发生在 HTTP 请求中的 panic 并 recover 它。这样你的服务器将始终可用例如,你可以向 Sentry 报告这个 panic!
Error 处理: 支持收集 HTTP 请求期间发生的所有错误。最终,中间件可以将它们写入日志文件,数据库并通过网络发送。
可扩展性: 新建一个中间件非常简单,去查看示例代码吧
3.如何下载安装Gin?
描述: 由于Gin是基于Golang开发的所以必须得先安装Go环境,如果你还没安装此环境可以参考博主此系列教程文章【1.Go编程快速入门学习】( https://blog.weiyigeek.top/2020/4-23-283.html#0x01-Go语言开发环境搭建),下述操作都是假设你已经安装配置好Go语言相关环境情况下进行的。
温馨提示: Gin 必须是在Go 1.13 及以上版本上运行,当然我相信大家用的不会这么老的版本的。
在 Windows 操作系统开发
# 启用模块以及配置模块拉取镜像
PS C:\Users\WeiyiGeek> $env:GO111MODULE = "on"
PS C:\Users\WeiyiGeek> $env:GOPROXY = "https://goproxy.cn,direct"
# 拉取最新的gin模块包
PS C:\Users\WeiyiGeek> go get -u -v github.com/gin-gonic/gin在 Linux 操作系统开发
# 启用模块以及配置模块拉取镜像
$ GO111MODULE = "on"
$ GOPROXY = "https://goproxy.cn,direct"
# 拉取最新的gin模块包
$ go get -u -v github.com/gin-gonic/gin0x01 快速上手
描述: 作者为了方便看友们快速上手,此处将其常规使用方法函数进行示例演示,为加深学习印象与成果。
1.Hello-World 示例
描述: 下载安装 Gin 软件包后创建一个 hello-gin 项目文件夹以及main.go文件,此处作者以一个简单的hello woirld示例来讲解。
创建文件夹: $ mkdir -p $GOPATH/src/github.com/weiyigeek/hello-gin && cd "$_"
// hello-gin/main.go
// 声明当前文件属于哪个包,如果是主文件则写成main
package main
// 导入gin包
import "github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
func main() {
// 生成了一个实例,这个实例即 WSGI 应用程序
r := gin.Default()
// 声明了一个GET方法路由 / 及对应的处理函数
r.GET("/", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.String(200, "Hello, Go Gin Web!")
})
// 返回以JSON格式的字符串
r.GET("/test", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.JSON(200, gin.H{
"msg": "Test, Go Gin Web!",
})
})
// 除了GET方法以外,GIN还支持的其他HTTP方法如下;
r.POST("/somePost", func(c *gin.Context) { c.JSON(200, gin.H{ "msg": "posting",}) })
r.PUT("/somePut", func(c *gin.Context) { c.JSON(200, gin.H{ "msg": "putting",}) })
r.DELETE("/someDelete", func(c *gin.Context) { c.JSON(200, gin.H{ "msg": "deleting",}) })
r.PATCH("/somePatch", func(c *gin.Context) { c.JSON(200, gin.H{ "msg": "patching",}) })
r.HEAD("/someHead", func(c *gin.Context) { c.JSON(200, gin.H{ "msg": "head",}) })
r.OPTIONS("/someOptions", func(c *gin.Context) { c.JSON(200, gin.H{ "msg": "options",}) })
// 特殊的 Any 函数即响应所有HTTP方法
r.Any("/testing", func(c *gin.Context) { c.JSON(200, gin.H{ "msg": "Any registers a route that matches all the HTTP methods. EX: GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, HEAD, OPTIONS, DELETE, CONNECT, TRACE.",}) })
// 让应用运行在本地服务器上,默认监听端口是 8090
g.Run(":8080") // listen and serve on 0.0.0.0:8080
}初始化及编写和执行 Go 代码
# 初始化
go mod init hello-gin
go mod tidy # 英 / 'taɪdi'
# 运行
$ go run main.go2.JSON/XML/YAML/ProtoBuf格式渲染示例
描述: 本小节演示了AsciiJSON、JSON、purejson以及JSONP与SecureJSON示例以及XML/YAML/ProtoBuf渲染显示。
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
// 开辟一块内存空间
var data = make(map[string]interface{})
func setupRouter() *gin.Engine {
// Disable Console Color
gin.DisableConsoleColor()
// Default返回一个Engine实例,该实例已连接Logger和Recovery中间件。
r := gin.Default()
// 示例1.AsciiJSON 生成具有转义的非 ASCII 字符的 ASCII-only JSON。
r.GET("/AsciiJSON", func(c *gin.Context) {
data = map[string]interface{}{
"lang": "GO语言",
"tag": "
",
}
// 针对中文以及特殊符号进行的是Unicode编码
// 输出 : {"lang":"GO\u8bed\u8a00","tag":"\u003cbr\u003e"}
c.AsciiJSON(http.StatusOK, data)
})
// 示例2.通常,JSON 使用 unicode 替换特殊 HTML 字符,例如 < 变为 \ u003c。如果要按字面对这些字符进行编码,则可以使用 PureJSON。
// 提供 unicode 实体
r.GET("/json", func(c *gin.Context) {
// 温馨提示: gin.H 是 map[string]interface{} 的一种快捷方式
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"html": "Hello, world! Go-Gin 框架",
})
})
// 提供字面字符(即原始数据未经过编码处理)
r.GET("/purejson", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.PureJSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"html": "Hello, world! Go-Gin 框架",
})
})
// 示例3.使用 JSONP 向不同域的服务器请求数据,如果查询参数存在回调,则将回调添加到响应体中。
r.GET("/JSONP", func(ctx *gin.Context) {
data = map[string]interface{}{
"name": "WeiyiGeek",
"site": "weiyigeek.top",
}
// /JSONP?callback=u 其默认参数是callback
// 将输出:u({\"name\":\"WeiyiGeek\",\"site\":\"weiyigeek.top\"})
ctx.JSONP(http.StatusOK, data)
})
// 示例4.使用 SecureJSON 防止 json 劫持,如果给定的结构是数组值,则默认预置 "while(1)," 到响应体。
r.GET("/SecureJSON", func(c *gin.Context) {
// 你也可以使用自己的 SecureJSON 前缀,据说Google采用的是while的方法,facebook采用的是for的方法。
r.SecureJsonPrefix(")]}',\n")
names := []string{"Go", "Java", "PHP"}
// 若不设置SecureJsonPrefix,默认输出:for(;;);["Go", "Java", "PHP"]
c.SecureJSON(http.StatusOK, names)
})
return r
}
func main() {
r := setupRouter()
// Listen and Server in 0.0.0.0:8080
r.Run(":8080")
}补充说明: Gin请求响应XML/JSON/YAML/ProtoBuf格式输出示例片段
// 方式1.JSON 格式方法1, 温馨提示 gin.H 是 map[string]interface{} 的一种快捷方式
r.GET("/someJSON", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"message": "hey", "status": http.StatusOK})
})
// 方式2.JSON 格式方法2,
r.GET("/AsciiJSON", func(c *gin.Context) {
data = map[string]interface{}{
"lang": "Golang",
"tag": "gin",
}
c.AsciiJSON(http.StatusOK, data)
})
// 方式3.JSON 格式方法3
r.GET("/moreJSON", func(c *gin.Context) {
// 你也可以使用一个结构体
var msg struct {
Name string `json:"user"`
Message string
Number int
}
msg.Name = "Lena"
msg.Message = "hey"
msg.Number = 123
// 注意 msg.Name 在 JSON 中变成了 "user"
// 将输出:{"user": "Lena", "Message": "hey", "Number": 123}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, msg)
})
// XML 格式输出
r.GET("/someXML", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.XML(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"message": "hey", "status": http.StatusOK})
})
// YAML 格式输出
r.GET("/someYAML", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.YAML(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"message": "hey", "status": http.StatusOK})
})
// ProtoBuf 格式输出
r.GET("/someProtoBuf", func(c *gin.Context) {
reps := []int64{int64(1), int64(2)}
label := "test"
// protobuf 的具体定义写在 testdata/protoexample 文件中。
data := &protoexample.Test{
Label: &label,
Reps: reps,
}
// 请注意,数据在响应中变为二进制数据
// 将输出被 protoexample.Test protobuf 序列化了的数据
c.ProtoBuf(http.StatusOK, data)
})3.Basic-Auth 方法示例
代码示例:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
var db = make(map[string]string)
// 或者模拟一些私人数据
var secrets = gin.H{
"foo": gin.H{"email": "[email protected]", "phone": "123433"},
"weiyigeek": gin.H{"email": "[email protected]", "phone": "666"},
}
func setupRouter() *gin.Engine {
// Disable Console Color
// gin.DisableConsoleColor()
r := gin.Default()
// 1.Query 和 POST form 请求示例
// Ping test
r.GET("/ping", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.String(http.StatusOK, "pong")
})
// 方式1.Get user value, example : /user/weiyigeek
r.GET("/user/:name", func(c *gin.Context) {
user := c.Params.ByName("name")
value, ok := db[user]
fmt.Println(user)
if ok {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"user": user, "value": value})
} else {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"user": user, "status": "no value"})
}
})
// 方式2.Get user value, example : /username?id=1&user=weiyigeek&page=1
r.GET("/username", func(c *gin.Context) {
id := c.Query("id")
user := c.Query("user")
page := c.DefaultQuery("page", "0")
if id != "" && user != "" || page != "" {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"code": "200", "data": gin.H{"id": id, "user": user, "page": page}})
} else {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"code": "0", "status": "err"})
}
})
// 方式3.POST user value, example :
// POST /username
// id=1&user=weiyigeek&page=10
r.POST("/username", func(c *gin.Context) {
id := c.PostForm("id")
user := c.PostForm("user") // 表单数据
page := c.DefaultPostForm("page", "10") // 默认值
if secret, ok := secrets[user]; ok {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"id": id, "user": user, "page": page, "secret": secret})
} else {
c.JSON(http.StatusForbidden, gin.H{"user": user, "secret": "NO SECRET :("})
}
})
// 路由组使用 gin.BasicAuth() 中间件设置 Auth 认证访问
// gin.Accounts 是 map[string]string 的一种快捷方式
// 方式1
// authorized := r.Group("/create")
// authorized.Use(gin.BasicAuth(gin.Credentials{
// "foo": "bar",
// "weiyieek": "123456",
//}))
// 方式2
authorized := r.Group("/admin", gin.BasicAuth(gin.Accounts{
"foo": "bar", // user:foo password:bar
"weiyigeek": "123456", // user:manu password:123
}))
// admin/secrets 端点 触发 "localhost:8080/admin/secrets
/* example curl for /admin with basicauth header
Zm9vOmJhcg== is base64("weiyieek:123456")
JS -> btoa("weiyigeek:123456") => 'd2VpeWlnZWVrOjEyMzQ1Ng=='
curl -X POST http://localhost:8080/admin/secrets \
-H 'authorization: Basic d2VpeWlnZWVrOjEyMzQ1Ng==' \
-H 'content-type: application/json' \
-d '{"value":"weiyigeek.top"}'
*/
authorized.POST("secrets", func(c *gin.Context) {
// 获取用户,它是由 BasicAuth 中间件设置的
user := c.MustGet(gin.AuthUserKey).(string)
// 解析提交的JSON数据(Parse JSON)
var json struct {
Value string `json:"value" binding:"required"`
}
// 将提交的数据与对应用户绑定
if c.Bind(&json) == nil {
db[user] = json.Value
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"status": "ok", "code": "200"})
} else {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"status": "err", "code": "0"})
}
})
// authorized POST username value
authorized.POST("/user", func(c *gin.Context) {
// 获取用户,它是由 BasicAuth 中间件设置的
user := c.MustGet(gin.AuthUserKey).(string)
// 根据authorization头,获取自定义数据
if secret, ok := secrets[user]; ok {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"user": user, "secret": secret})
} else {
c.JSON(http.StatusForbidden, gin.H{"user": user, "secret": "NO SECRET :("})
}
})
return r
}
func main() {
r := setupRouter()
// Listen and Server in 0.0.0.0:8080
r.Run(":8080")
}执行结果:
# 正式环境设置环境变量与代码
[GIN-debug] [WARNING] Running in "debug" mode. Switch to "release" mode in production.
- using env: export GIN_MODE=release
- using code: gin.SetMode(gin.ReleaseMode)
[GIN-debug] GET /ping --> main.setupRouter.func1 (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] GET /user/:name --> main.setupRouter.func2 (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] GET /username --> main.setupRouter.func3 (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] POST /username --> main.setupRouter.func4 (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] POST /admin/secrets --> main.setupRouter.func5 (4 handlers)
[GIN-debug] POST /admin/user --> main.setupRouter.func6 (4 handlers)
[GIN-debug] Listening and serving HTTP on :8080
# 1.在终端中运行curl进行POST请求写入值到auth用户中
$ curl --location 'http://127.0.0.1:8080/admin/secrets' \
--header 'authorization: Basic d2VpeWlnZWVrOjEyMzQ1Ng==' \
--header 'content-type: application/json' \
--data '{"value":"weiyigeek.top"}'
# {"code":"200","status":"ok"}
# 2.GET请求通过url方法Params获取用户字段信息并返回该auth用户写入信息。
curl --location 'http://127.0.0.1:8080/user/weiyigeek'
# {"user": "weiyigeek", "value": "weiyigeek.top" }
# 3.GET请求通过url参数获取用户字段并返回其kv。
curl --location 'http://127.0.0.1:8080/username?id=1&user=weiyigeek&page=10' \
--header 'authorization: Basic Zm9vOmJhcg=='
# {"code":"200","data":{"id":"1","page":"10","user":"weiyigeek"}}
# 4.POST请求通过获取发送的表单数据获取用户字段并模拟一些私人数据。
curl --location 'http://127.0.0.1:8080/username' \
--header 'authorization: Basic Zm9vOmJhcg==' \
--form 'id="1"' \
--form 'user="weiyigeek"' \
--form 'page="10"'
# {"id":"1","page":"10","secret":{"email":"[email protected]","phone":"666"},"user":"weiyigeek"}
# 5.通过POST请求通过认证auth后获取用户字段并模拟一些私人数据
curl --location --request POST 'http://127.0.0.1:8080/admin/user' \
--header 'authorization: Basic d2VpeWlnZWVrOjEyMzQ1Ng=='
# {"secret":{"email":"[email protected]","phone":"666"},"user":"weiyigeek"}4.路由、表单参数绑定示例
描述: 在网页中往往需要从URL 路由参数、URL 请求参数、表单中提交数据到后端进行处理,例如最常见的就是登录时需要传递用户名与密码以及验证码,所以作为Gin这么优秀的Web框架也是支持处理表单数据的。
请求参数获取总结:
Param("参数名") 方法: 获取路由参数
Query("参数名") 方法:获取URL参数
DefaultQuery("参数名","默认值") 方法:获取URL参数值,当不存在该参数时自动填充默认值
QueryMap("参数名") 方法:映射URL查询字符串
PostForm("参数名") 方法: 获取 POST 提交表单参数值
DefaultPostForm("参数名","默认值") 方法:获取 POST 提交表单参数值,当不存在该参数时自动填充默认值
PostFormMap("参数名") 方法:映射表单参数
ShouldBind(&结构体实例化对象) 方法:针对提交的GET请求或者POST请求参数自动进行绑定。
// 如果是
GET请求,只使用Form绑定引擎(query)。
// 如果是POST请求,首先检查content-type是否为JSON或XML,然后再使用Form或(form-data)。
// 查看更多:https://github.com/gin-gonic/gin/blob/master/binding/binding.go#L88
代码示例:
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
func setupRouter() *gin.Engine {
// Disable Console Color
gin.DisableConsoleColor()
// Default返回一个Engine实例,该实例已连接Logger和Recovery中间件。
r := gin.Default()
// 示例1. 使用现有的基础请求对象解析查询字符串参数。
// 示例 URL:/param_get?firstname=Weiyi&lastname=Geek
r.GET("/param_get", func(c *gin.Context) {
firstname := c.DefaultQuery("firstname", "Guest")
lastname := c.Query("lastname") // 注意: c.Request.URL.Query().Get("lastname") 的一种快捷方式
c.String(http.StatusOK, "Hello %s %s, Welcome To Study Go Gin!", firstname, lastname)
})
// 示例2.提交常规类型的数据表单并解析POST请求数据字符串参数。
// Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
r.POST("/form_post", func(c *gin.Context) {
name := c.PostForm("name")
msg := c.DefaultPostForm("message", "empty")
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"code": 200, "data": gin.H{"name": name, "message": msg}})
})
// 示例3.使用QueryMap、PostFormMap 函数映射查询字符串或表单参数
// Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
r.POST("/form_getpostmap", func(c *gin.Context) {
post_id := c.QueryMap("id")
post_info := c.PostFormMap("user")
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"code": 200, "id": post_id, "post": post_info})
})
// 示例4.获取URL路由中的参数
// 此 handler 将匹配 /router_get/john (但不会匹配 /router_get/ 或者 /router_get)
r.GET("/router_get/:name", func(c *gin.Context) {
name := c.Param("name")
c.String(http.StatusOK, "Hello %s", name)
})
// 此 handler 将匹配 /router_get/john/ 和 /router_get/john/send (若如果没有其他路由匹配 /router_get/john,它将重定向到 /router_get/john/)
r.GET("/router_get/:name/*action", func(c *gin.Context) {
name := c.Param("name")
action := c.Param("action")
message := name + " is " + action
c.String(http.StatusOK, message)
})
// 示例6.c.ShouldBind 函数:针对提交URL参数进行自动选择合适的绑定。
//GET /router_get/login?user=weiyigeek&password=123456
r.GET("/router_get/login", func(c *gin.Context) {
// 你可以使用显式绑定声明绑定 Query Param:
// c.ShouldBindWith(&form, binding.Query)
// 或者简单地使用 ShouldBind 方法自动绑定:
// POST请求:登录表单的结构体
type LoginForm struct {
User string `form:"user" binding:"required"`
Password string `form:"password" binding:"required"`
}
var login LoginForm
// 在这种情况下,将自动选择合适的绑定 (值得学习。)
if c.ShouldBind(&login) == nil {
if login.User == "user" && login.Password == "password" {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"code": 200, "message": "you are logged in"})
} else {
c.JSON(http.StatusUnauthorized, gin.H{"code": 401, "stmessageatus": "unauthorized"})
}
}
})
// 示例6.c.ShouldBind 函数:针对提交数据表单进行自动选择合适的绑定。
// POST /router_get/login
// ......
// user=weiyigeek&password=123456
r.POST("/login", func(c *gin.Context) {
// 简单地使用 ShouldBind 方法自动绑定:
// POST请求:登录表单的结构体
type LoginForm struct {
User string `form:"user" binding:"required"`
Password string `form:"password" binding:"required"`
}
var login LoginForm
// 在这种情况下,将自动选择合适的绑定 (值得学习。)
if c.ShouldBind(&login) == nil {
if login.User == "weiyigeek" && login.Password == "123456" {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"code": 200, "message": "you are logged in"})
} else {
c.JSON(http.StatusUnauthorized, gin.H{"code": 401, "stmessageatus": "unauthorized"})
}
}
})
// 示例7.c.ShouldBind 函数绑定 HTML 复选框表单数据
//
r.POST("/mutil_color", func(c *gin.Context) {
// 绑定 HTML 复选框
type myForm struct {
Colors []string `form:"colors[]"`
}
var fakeForm myForm
// 解析 form 表单
if c.ShouldBind(&fakeForm) == nil {
// 输出结果: {"code": 200,"color":["red","green","blue"]}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"code": 200, "color": fakeForm.Colors})
}
})
return r
}
func main() {
r := setupRouter()
// Listen and Server in 0.0.0.0:8080
r.Run(":8080")
}运行结果:
[GIN-debug] GET /param_get --> main.setupRouter.func1 (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] POST /form_post --> main.setupRouter.func2 (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] POST /form_getpostmap --> main.setupRouter.func3 (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] GET /router_get/:name --> main.setupRouter.func4 (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] GET /router_get/:name/*action --> main.setupRouter.func5 (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] GET /router_get/login --> main.setupRouter.func6 (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] POST /login --> main.setupRouter.func7 (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] POST /mutil_color --> main.setupRouter.func8 (3 handlers)执行结果
# 示例1
curl --location 'http://127.0.0.1:8080/param_get?firstname=Weiyi&lastname=Geek'
# Hello Weiyi Geek, Welcome To Study Go Gin!
# 示例2
curl --location 'http://127.0.0.1:8080/form_post' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \
--data-urlencode 'name=WeiyiGeek' \
--data-urlencode 'message=一个想成为全栈的男人'
# {"code":200,"data":{"message":"一个想成为全栈的男人","name":"WeiyiGeek"}}
# 示例3
curl --location --globoff 'http://127.0.0.1:8080/form_getpostmap?id[name]=weiyigeek&id[site]=www.weiyigeel.top' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \
--data 'user[name]=weiyigeek&user[message]=一个想成为全栈的男人'
# {"code":200,"id":{"name":"weiyigeek","site":"www.weiyigeel.top"},"post":{"message":"一个想成为全栈的男人","name":"weiyigeek"}}
# 示例4
curl --location 'http://127.0.0.1:8080/router_get/weiyigeek'
# Hello weiyigeek
# 示例5
curl --location 'http://127.0.0.1:8080/router_get/weiyigeek/devops'
# weiyigeek is /devops
# 示例6 & 示例7
curl --location 'http://127.0.0.1:8080/router_get/login?user=user&password=password'
curl --location 'http://127.0.0.1:8080/login' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \
--data 'user=user&password=password'
# {"code":200,"message":"you are logged in"}5.Cookie、Header 获取和设置
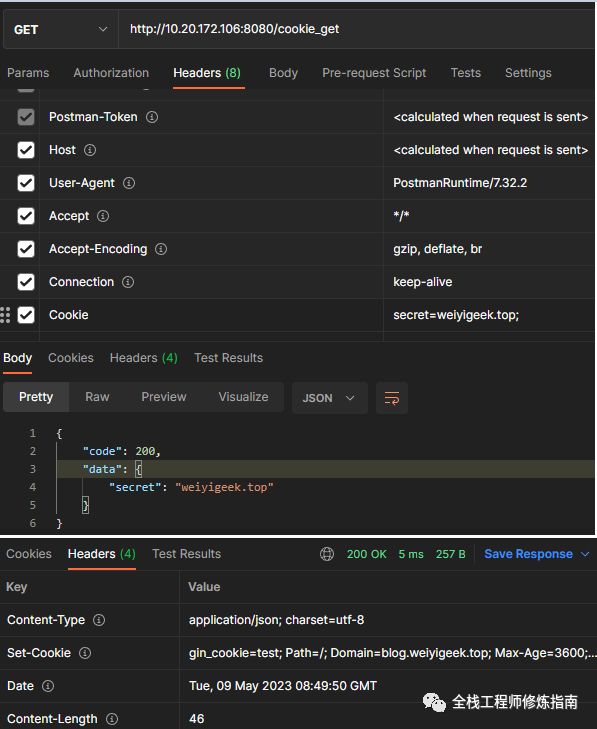
描述: 在 Gin 中我们可以使用 c.Cookie 和 c.SetCookie方法 以及 c.GetHeader 和 c.Header 方法快速的获取设置 Cookie与Header值。
代码示例:
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
// 示例1.设置与获取 Cookie Handler
func getCookieHandler(c *gin.Context) {
// 获取 cookies 中 secret 字段信息
secret, err := c.Cookie("secret")
// 判断 获取cookies 是否有误
if err == nil {
// 设置 Cookies:SetCookie(name string, value string, maxAge int, path string, domain string, secure bool, httpOnly bool)
c.SetCookie("gin_cookie", "test", 3600, "/", "blog.weiyigeek.top", false, true)
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"code": 200,
"data": gin.H{
"secret": secret,
},
})
} else {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{
"code": 0,
"message": "请求参数有误!",
})
}
}
// 示例2.设置与获取 header Handler
func getHeaderHandler(c *gin.Context) {
// 获取 header 中 secret 字段信息
secret := c.GetHeader("secret")
// 判断 获取 header 是否为空
if secret != "" {
// 设置 header (key string, value string)
c.Header("gin_header", "blog.weiyigeek.top")
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"code": 200,
"data": gin.H{
"secret": secret,
},
})
} else {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{
"code": 0,
"message": "请求参数有误!",
})
}
}
func main() {
// Default返回一个Engine实例,该实例已连接Logger和Recovery中间件。
r := gin.Default()
// 示例1.设置与获取 Cookie
r.GET("/cookie_get", getCookieHandler)
// 示例2.设置与获取 Header
r.GET("/header_get", getHeaderHandler)
// Listen and Server in 0.0.0.0:8080
r.Run(":8080")
}执行结果:
# Cookie 获取与设置
curl --location 'http://10.20.172.106:8080/cookie_get' \
--header 'Cookie: secret=weiyigeek.top;'
# Header 获取与设置
curl --location 'http://10.20.172.106:8080/header_get' \
--header 'secret: weiyigeek.top'偷偷的告诉你哟?【极客全栈修炼】微信小程序已经上线了,
可直接在微信里面直接浏览博主博客了哟,后续将上线更多有趣的小工具。
6.路由组及模型绑定和验证
描述: 在Gin中若要将请求体绑定到结构体中可使用模型绑定,其目前支持JSON、XML、YAML和标准表单值的绑定(foo=bar&boo=baz),但是使用时,必须要在要绑定的所有字段上,设置相应的tag。
例如,使用 JSON 绑定时,设置字段标签为 json:"参数名称",如果一个字段的 tag 加上了 binding:"required",但绑定时是空值, Gin 会报错。
Gin提供了两类绑定方法, 在使用 Bind 方法时,Gin 会尝试根据 Content-Type 推断如何绑定。
Must bind
Methods - Bind, BindJSON, BindXML, BindQuery, BindYAML
说明: 上述方法属于MustBindWith的具体调用,如果发生绑定错误则请求终止,并触发 c.AbortWithError(400, err).SetType(ErrorTypeBind)。
Should bind
Methods - ShouldBind, ShouldBindJSON, ShouldBindXML, ShouldBindQuery, ShouldBindYAML
说明: Behavior - 这些方法属于ShouldBindWith的具体调用,如果发生绑定错误,Gin 会返回错误并由开发者处理错误和请求。
代码示例
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin/binding"
)
// 绑定 FORM / JSON / XML
type Login struct {
User string `form:"user" json:"user" xml:"user" binding:"required"`
Password string `form:"password" json:"password" xml:"password" binding:"required"`
// Birthday time.Time `form:"birthday" json:"birthday" xml:"birthday" time_format:"2006-01-02" time_utc:"1"`
}
// 你可以使用显式绑定声明绑定 Uri:
// c.ShouldBindWith(&uri, binding.Uri)
// 使用 ShouldBindUri 函数绑定 Uri 路由参数
func bindUri(c *gin.Context) {
// 自定义结构体进行数据绑定
type Person struct {
ID string `uri:"uuid" binding:"required"`
Name string `uri:"name" binding:"required"`
}
var person Person
// 绑定路由参数
if err := c.ShouldBindUri(&person); err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"msg": err.Error()})
return
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"name": person.Name, "uuid": person.ID})
}
// 使用 ShouldBindQuery 函数只绑定 url 查询参数而忽略 post 数据
func bindQuery(c *gin.Context) {
// GET请求:url 查询参数的结构体
type BlogUrl struct {
Name string `form:"name" binding:"required"`
Blog string `form:"blog" binding:"required"`
}
var site BlogUrl
// 绑定 URL 请求参数
if c.ShouldBindQuery(&site) == nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"code": 200, "data": gin.H{"name": site.Name, "blog": site.Blog}})
} else {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"code": 0, "message": "Query Param Error!"})
}
}
// 使用 ShouldBindJSON 绑定 JSON 数据
func bindJson(c *gin.Context) {
var json Login
if err := c.ShouldBindJSON(&json); err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
if json.User != "weiyigeek" || json.Password != "123456" {
c.JSON(http.StatusUnauthorized, gin.H{"code": 0, "status": "unauthorized"})
return
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"code": 200, "status": "you are logged in"})
}
// 使用 ShouldBindXML 绑定 xml 数据
func bindXml(c *gin.Context) {
var xml Login
if err := c.ShouldBindXML(&xml); err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
if xml.User != "weiyigeek" || xml.Password != "123456" {
c.JSON(http.StatusUnauthorized, gin.H{"code": 0, "status": "unauthorized"})
return
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"code": 200, "status": "you are logged in"})
}
// 使用 ShouldBindForm 绑定 表单 数据
func bindForm(c *gin.Context) {
var form Login
if err := c.ShouldBindWith(&form, binding.Form); err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
if form.User != "weiyigeek" || form.Password != "123456" {
c.JSON(http.StatusUnauthorized, gin.H{"code": 0, "status": "unauthorized"})
return
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"code": 200, "status": "you are logged in"})
}
// 绑定表单数据至自定义结构体
type StructA struct {
Name string `form:"name" json:"name" xml:"name" text:"name"`
}
type StructB struct {
// 方式1
NestedStruct StructA
// 方式2
// NestedStructPointer *StructA
// 方式3
// NestedAnonyStruct struct {
// FieldX string `form:"field_x"`
// }
Blog string `form:"blog" json:"blog" xml:"blog" text:"name"`
}
func bindCustom(c *gin.Context) {
var person StructB
if c.Bind(&person) == nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"person": person.NestedStruct,
"blog": person.Blog,
})
} else {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{
"message": "BadRequest",
})
}
}
func main() {
// Default返回一个Engine实例,该实例已连接Logger和Recovery中间件。
r := gin.Default()
// 简单的路由组: v1
v1 := r.Group("/v1")
{
// 示例1.使用 ShouldBindUri 函数绑定 Uri 路由参数
v1.GET("/person/:name/:uuid", bindUri)
// 示例2.使用 ShouldBindQuery 函数只绑定 url 查询参数而忽略 post 数据
v1.Any("/site", bindQuery)
}
// 简单的路由组: v2
v2 := r.Group("/v2")
{
// 示例3.使用 ShouldBindJSON 绑定 JSON 数据
v2.POST("/loginJSON", bindJson)
// 示例4.使用 ShouldBindXML 绑定 xml 数据
v2.POST("/loginXML", bindXml)
// 示例5.使用 ShouldBindForm 绑定 表单 数据
v2.POST("/loginFORM", bindForm)
}
// 简单的路由组: v3
v3 := r.Group("/v3")
{
v3.POST("/person", bindCustom)
}
// Listen and Server in 0.0.0.0:8080
r.Run(":8080")
}运行结果:
[GIN-debug] GET /v1/person/:name/:uuid --> main.bindUri (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] GET /v1/site --> main.bindQuery (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] POST /v1/site --> main.bindQuery (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] PUT /v1/site --> main.bindQuery (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] PATCH /v1/site --> main.bindQuery (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] HEAD /v1/site --> main.bindQuery (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] OPTIONS /v1/site --> main.bindQuery (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] DELETE /v1/site --> main.bindQuery (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] CONNECT /v1/site --> main.bindQuery (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] TRACE /v1/site --> main.bindQuery (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] POST /v2/loginJSON --> main.bindJson (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] POST /v2/loginXML --> main.bindXml (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] POST /v2/loginFORM --> main.bindForm (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] POST /v3/person --> main.bindCustom (3 handlers)访问结果:
# 示例1
http://10.20.172.106:8080/v1/person/weiyigeek/d932949f-6653-419b-977f-57e1ec1ec52d
# {"name":"weiyigeek","uuid":"d932949f-6653-419b-977f-57e1ec1ec52d"}
# 示例2
http://10.20.172.106:8080/v1/site?name=weiyigeek&blog=blog.weiyigeek.top
curl --location --request POST 'http://10.20.172.106:8080/v1/site?name=weiyigeek&blog=blog.weiyigeek.top' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded'
# {"code":200,"data":{"blog":"blog.weiyigeek.top","name":"weiyigeek"}}
# 示例3.Content-Type: application/json
curl --location 'http://10.20.172.106:8080/v2/loginJSON' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{"user":"weiyigeek","password":"123456"}'
# 示例4.Content-Type: application/xml
curl --location 'http://10.20.172.106:8080/v2/loginXML' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/xml' \
--data '
weiyigeek
123
'
# 示例5.application/x-www-form-urlencoded
curl --location 'http://10.20.172.106:8080/v2/loginFORM' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \
--data-urlencode 'user=weiyigeek' \
--data-urlencode 'password=123456'
# 示例6.
curl --location 'http://10.20.172.106:8080/v3/person' \
--form 'name="WeiyiGeek"' \
--form 'blog="blog.weiyigeek.top"'
# {"blog":"blog.weiyigeek.top","person":{"name":"WeiyiGeek"}}补充示例: 将 request body 绑定到不同的结构体中, 此处需要注意使用 c.ShouldBindBodyWith 会在绑定之前将 body 存储到上下文中, 其对性能造成轻微影响,如果调用一次就能完成绑定的话,建议不要用这个方法而是使用c.ShouldBind方法。
type formA struct {
Foo string `json:"foo" xml:"foo" binding:"required"`
}
type formB struct {
Bar string `json:"bar" xml:"bar" binding:"required"`
}
func SomeHandler(c *gin.Context) {
objA := formA{}
objB := formB{}
// 读取 c.Request.Body 并将结果存入上下文。
if errA := c.ShouldBindBodyWith(&objA, binding.JSON); errA == nil {
c.String(http.StatusOK, `the body should be formA`)
// 这时, 复用存储在上下文中的 body。
} else if errB := c.ShouldBindBodyWith(&objB, binding.JSON); errB == nil {
c.String(http.StatusOK, `the body should be formB JSON`)
// 可以接受其他格式
} else if errB2 := c.ShouldBindBodyWith(&objB, binding.XML); errB2 == nil {
c.String(http.StatusOK, `the body should be formB XML`)
} else {
...
}
}7.HTTP重定向的几种方式
描述: 在Gin中要实现重定向是很容易内部、外部重定向均支持,通常情况下有三种重定向,一种是 301 重定向,另一种是 302 重定向,最后一种是路由重定向(即访问的路由地址不会发生改变,请求内部其路由返回数据的,有点反代的感觉)
代码示例:
package main
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"log"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
gin.SetMode(gin.DebugMode)
g := gin.Default()
// HTTP 重定向很容易
// 通过 GET 方法进行 HTTP 301 重定向
g.GET("/redirect-test-1", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.Redirect(http.StatusMovedPermanently, "http://www.weiyigeek.top/")
})
// GET 方法进行 HTTP 302 重定向
g.POST("/redirect-test-2", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.Redirect(http.StatusFound, "/test2")
})
// 通过使用 HandleContext 进行路由重定向
g.GET("/test1", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.Request.URL.Path = "/test2"
g.HandleContext(c) // 返回的是 /test2 路由的数据
})
g.GET("/test2", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.JSON(200, gin.H{"hello": "world"})
})
// 默认监听并在 0.0.0.0:8080 上启动服务
g.Run()
}执行效果:
curl -i http://10.20.172.106:8080/redirect-test-1
curl -X POST -i http://10.20.172.106:8080/redirect-test-2
curl -i http://10.20.172.106:8080/test1亲,文章就要看完了,不关注一下【全栈工程师修炼指南】吗?
8.外部请求转发及数据验证
描述: 我们可以通过DataFromReader方法将指定的读取器写入主体流并更新HTTP代码,并返回给客户端,其次在提交数据时可以针对数据类型进行验证。
示例代码:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"time"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin/binding"
"github.com/go-playground/validator"
)
// 示例1.SomeDataFromReader 将外部URL请求响应给指定用户
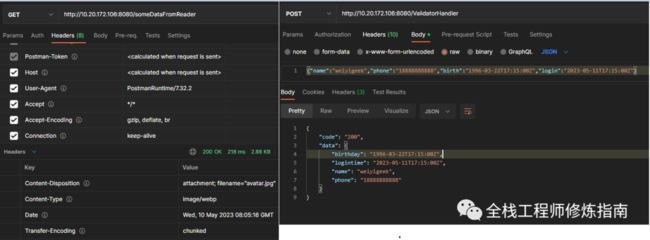
func getSomeDataFromReader(c *gin.Context) {
// GET 请求外部地址
response, err := http.Get("https://blog.weiyigeek.top/img/avatar.jpg")
if err != nil || response.StatusCode != http.StatusOK {
c.Status(http.StatusServiceUnavailable)
return
}
// 外部地址请求响应结果
reader := response.Body
contentLength := response.ContentLength
contentType := response.Header.Get("Content-Type")
extraHeaders := map[string]string{
"Content-Disposition": `attachment; filename="avatar.jpg"`,
}
// DataFromReader 将指定的读取器写入主体流并更新HTTP代码,并返回给客户端
// DataFromReader(code int, contentLength int64, contentType string, reader io.Reader, extraHeaders map[string]string)
c.DataFromReader(http.StatusOK, contentLength, contentType, reader, extraHeaders)
}
// 示例2. Validator Handler 自定义验证器
// User 结构体包含绑定和验证的数据。
type User struct {
Name string `json:"name"`
Phone string `json:"phone"`
Birth time.Time `json:"birth" binding:"required" time_format:"2006-01-02"`
Login time.Time `json:"login" binding:"required" time_format:"2006-01-02"`
}
// 验证用户输入基础信息是否为空
func UserStructLevelValidation(sl validator.StructLevel) {
user := sl.Current().Interface().(User)
if len(user.Name) == 0 && len(user.Phone) == 0 {
sl.ReportError(user.Name, "Name", "name", "fnameorlname", "")
sl.ReportError(user.Phone, "Phone", "phone", "fnameorlphone", "")
}
}
// 验证用户输入日期是否有误
var userDateValida validator.Func = func(fl validator.FieldLevel) bool {
// 使用了反射机制
date, ok := fl.Field().Interface().(time.Time)
fmt.Println(date)
if ok {
// 判断输入的时间是否在当前时间之后
today := time.Now()
if today.After(date) {
return false
}
}
return true
}
func postValidatorHandler(c *gin.Context) {
// 实例化结构体对象,解析并绑定对应数据
var user User
if err := c.ShouldBindWith(&user, binding.JSON); err == nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"code": "200", "data": gin.H{"name": user.Name, "phone": user.Phone, "birthday": user.Birth, "logintime": user.Login}})
} else {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"code": "0", "message": err.Error()})
}
}
func main() {
// Default返回一个Engine实例,该实例已连接Logger和Recovery中间件。
r := gin.Default()
// 示例1.SomeDataFromReader 将外部URL请求响应给指定用户
r.GET("/someDataFromReader", getSomeDataFromReader)
if v, ok := binding.Validator.Engine().(*validator.Validate); ok {
v.RegisterStructValidation(UserStructLevelValidation, User{})
//v.RegisterValidation("datevalida", userDateValida)
}
// 示例2.Validator Handler 自定义验证器 Header
r.POST("/ValidatorHandler", postValidatorHandler)
// Listen and Server in 0.0.0.0:8080
r.Run(":8080")
}执行结果:
0x0n 入坑出坑
错误1.在VScode中无法安装Go插件中相关依赖模块
解决办法:
Tools environment: GOPATH=D:\Study\Go\package
Installing 7 tools at D:\Study\Go\package\bin in module mode.
gotests
gomodifytags
impl
goplay
dlv
staticcheck
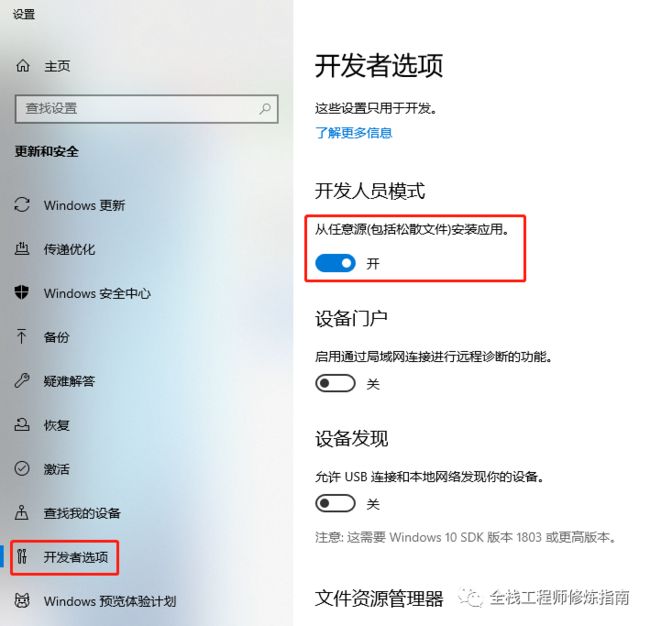
gopls错误2.在Windows10中使用rotatelogs模块时创建软连接报A required privilege is not held by the client.错误。
错误信息: failed to rotate: failed to create new symlink: symlink \system.log.20230214.log s/system.log.20230214.log_symlink: A required privilege is not held by the client.
问题原因: 命令行终端问题或者未开启Windows10系统开发人员选项。
解决办法:
# 1.提升执行程序命令终端权限
- 在Windows10桌面,右键点击桌面左下角的开始按钮 ,在弹出的菜单中选择CMD “命令提示符 (管理员)”一项
- 在PowerShell中执行 `Start-Process -verb runas "C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe" 命令
# 2.开启Windows10系统开发人员选项
- 点击【开始】-> 搜索开发者模式 -> 打开开发人员模式本文至此完毕,更多技术文章,尽情等待下篇好文!
原文地址: https://blog.weiyigeek.top/2020/4-23-602.html
如果此篇文章对你有帮助,请你将它分享给更多的人!
![]()
![]() 学习书籍推荐 往期发布文章
学习书籍推荐 往期发布文章 ![]()
公众号回复【0008】获取【Ubuntu22.04安装与加固脚本】
公众号回复【10001】获取【WinServer安全加固脚本】
公众号回复【10002】获取【KylinOS银河麒麟安全加固脚本】
公众号回复【0011】获取【k8S二进制安装部署教程】
公众号回复【0014】获取【Nginx学习之路汇总】
公众号回复【0015】获取【Jenkins学习之路汇总】
公众号回复【10005】获取【adb工具刷抖音赚米】
热文推荐
容灾恢复 | 记一次K8S集群中etcd数据快照的备份恢复实践
欢迎长按(扫描)二维码 ,获取更多渠道哟!
欢迎关注 【全栈工程师修炼指南】(^U^)ノ~YO
添加作者微信【weiyigeeker 】 一起学习交流吧!
关注回复【学习交流群】即可加入【安全运维沟通交流小群】
温馨提示: 由于作者水平有限,本章错漏缺点在所难免,希望读者批评指正,若有问题或建议请在文章末尾留下您宝贵的经验知识,或联系邮箱地址
[email protected] 或 关注公众号 [全栈工程师修炼指南] 留言。
点个【赞 + 在看】吧!
点击【"阅读原文"】获取更多有趣的知识!